The Difference Between Router Mode and Bridge Mode
In network configuration, router mode and bridge mode are two common and important concepts. They play a crucial role in home, business, and even industrial networks. Understanding the difference between these two modes can help optimize network device configurations, enhancing both performance and stability.
1. What is Router Mode?
Router mode is the default operating mode of a router. In this mode, the router automatically assigns IP addresses to each device connected to the network and uses Network Address Translation (NAT) to connect devices in the local area network (LAN) to the wide area network (WAN), such as the internet. The router acts as a gateway, managing all the data traffic entering and leaving the LAN.

Key functions of router mode:
- IP Address Allocation: The router uses DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) to assign unique IP addresses to each device in the network.
- NAT Functionality: NAT translates private IP addresses to public IP addresses, allowing internal devices to access external networks.
- Network Isolation: In router mode, the internal network is isolated from the external network (e.g., the internet), enhancing security.
- Firewall Functionality: Routers typically include built-in firewalls that prevent external threats from accessing the internal network.
2. What is Bridge Mode?
Bridge mode is a configuration that disables certain functions of a router, allowing it to act as a network extender, either wirelessly or via a wired connection. In this mode, the router no longer assigns IP addresses or performs NAT; instead, it lets all connected devices communicate directly with the primary router or upstream network device, effectively extending the network coverage.
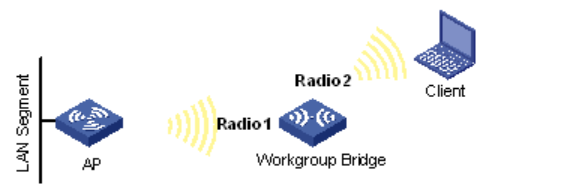
Key functions of bridge mode:
- Extend Network Coverage: Bridge mode effectively expands the Wi-Fi or wired network coverage, making it ideal for large spaces like factories, warehouses, or hotels.
- Reduce Network Latency: Since bridge mode bypasses NAT, the data transmission path is shorter, potentially reducing network latency.
- Multi-Router Connectivity: Bridge mode allows multiple routers to be connected, creating a unified network that is easier to manage and use.
3. Differences Between Router Mode and Bridge Mode
IP Address Allocation:
- Router Mode: The router assigns IP addresses to each connected device, typically using DHCP.
- Bridge Mode: The router does not assign IP addresses; this task is handled by the primary router.
Network Address Translation (NAT):
- Router Mode: NAT is used to enable internal devices to access the internet.
- Bridge Mode: No NAT is performed; all devices communicate directly with the upstream network.
Network Security:
- Router Mode: Provides security features such as a firewall and NAT, offering higher security.
- Bridge Mode: Lacks firewall and NAT features, relying on the upstream device for security.
Network Coverage:
- Router Mode: Primarily used to create a new LAN.
- Bridge Mode: Used to extend the coverage of an existing network.
Use Cases:
- Router Mode: Suitable for standalone networks in homes, offices, factories, or other environments requiring an independent network.
- Bridge Mode: Ideal for expanding Wi-Fi coverage or using multiple routers within the same network.
4. How to Choose?
Choosing between these modes depends on your specific needs:
- If you need to create an independent LAN and want to manage and monitor network traffic, router mode is the best choice.
- If you already have a primary router and need to extend the existing network’s coverage, bridge mode is the way to go.
5. Conclusion
Both router mode and bridge mode have their advantages and are suited to different scenarios. Understanding their differences and applications can help you configure your network devices more effectively, leading to optimal performance and security. Whether you are setting up a home network, an office environment, or an industrial application, mastering these modes is key to building a stable and reliable network.

For more advanced networking solutions and custom support, Wallys provides professional-grade Wi-Fi equipment tailored to meet industrial needs. Wallys specializes in the development and production of industrial-grade Wi-Fi devices, offering custom hardware and software support to help you build efficient and stable wireless networks.
Wallys Industrial DR9574 WIFI7 ROUTER

Email:sales1@wallystech.com
