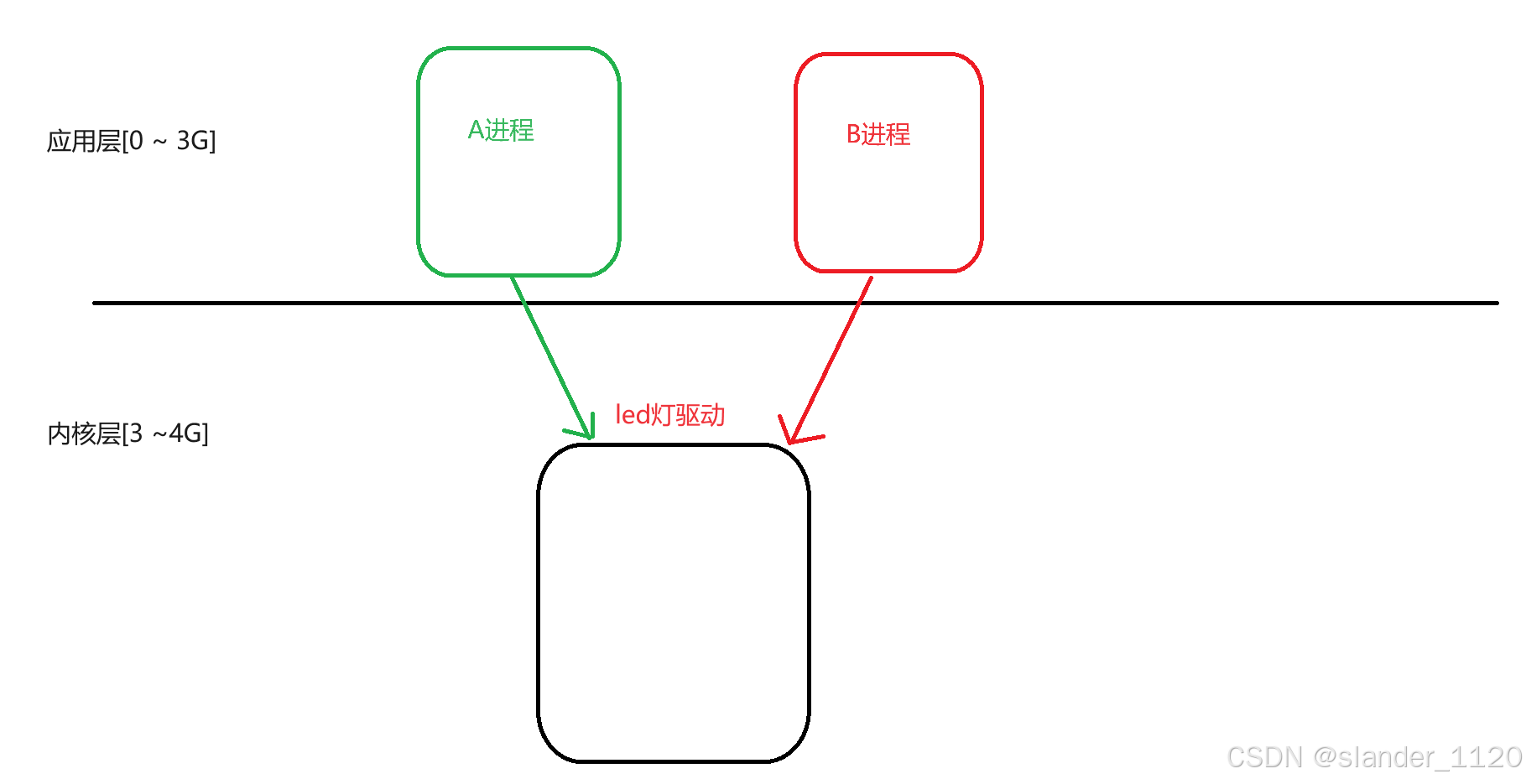
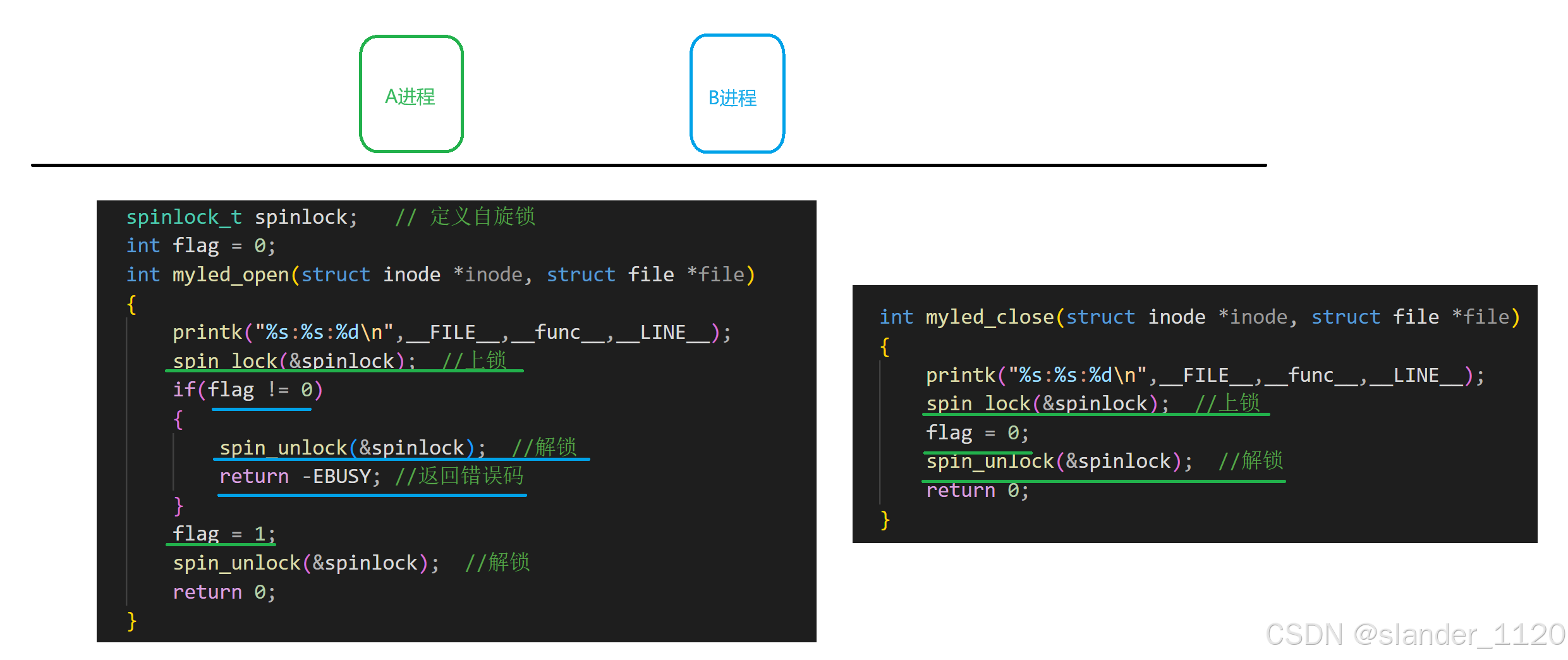
一、内核中并发和竟态相关概念
一、什么时候产生竟态
1.同一个驱动程序,同时被多个应用层程序进行访问
2.访问同一个临界资源,驱动产生竟态
二、竟态产生根本原因
1.在单核cpu中,如果内核支持抢占,就会产生竟态
2.在多核cpu中,核与核之间就会产生竟态
3.中断和进程之间也会产生竟态
4.中断和中断之间也会产生竟态(前提中断需要支持嵌套,A核GIC控制器不支持中断嵌套,M核NVIC控制器支持中断嵌套)
三、解决竟态
1.顺序执行
2.互斥执行
二、解决竟态方法
一、中断屏蔽
1.只针对单核cpu使用,顾名思义当中断到来时,将中断进行屏蔽
2.但是中断屏蔽时间不能过长
3.如果时间过长就会导致用户数据丢失,或者操作系统崩溃
API接口:
local_irq_disable();//中断屏蔽 临界资源 local_irq_enable(); //中断开启
二、自旋锁
工作原理:
1.当一个进程获取到自旋锁之后,另一个进程也想获取自旋锁,此时后一个进程进入自旋状态(原地打转)
特点:
1.自旋锁针对于多核cpu设计
2.自旋锁需要消耗cpu资源,并且自旋状态处于运行状态
3.自旋锁保护的临界资源比较小,在临界资源中不可以出现copy_to_user和copy_from_user使用
4.自旋锁会产生死锁
5.自旋锁上锁会关闭抢占
6.自旋锁工作于中断上下文,也可以工作于进程上下文
API接口
- spinlock_t spinlock; // 定义自旋锁 - void spin_lock_init(spinlock_t *lock); //初始化锁 - void spin_lock(spinlock_t *lock); //上锁 - void spin_unlock(spinlock_t *lock); //解锁使用:
1.当A进程获取自旋锁成功,B进程获取自旋锁失败,返回错误码,只有当A进程解锁之后,B进程获取自旋锁成功
代码:
demo.c
#include <linux/init.h> #include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/cdev.h> #include <linux/device.h> #include <linux/slab.h> #include <linux/fs.h> #define CNAME "myled" struct cdev *cdev; char kbuf[128] = {}; #if 0 unsigned int major = 500; //静态指定设备号 #else unsigned int major = 0; //动态分配设备号 #endif unsigned int count = 3; unsigned int minor = 0; struct class* cls; struct device* device; spinlock_t spinlock; // 定义自旋锁 int flag = 0; int myled_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) { printk("%s:%s:%d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__); spin_lock(&spinlock); //上锁 if(flag != 0) { spin_unlock(&spinlock); //解锁 return -EBUSY; //返回错误码 } flag = 1; spin_unlock(&spinlock); //解锁 return 0; } ssize_t myled_read(struct file *file, char __user *ubuf, size_t size, loff_t *loff) { int ret; printk("%s:%s:%d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__); //如果用户空间想读的大小256个字节,大于内核空间的大小128个字节,需要更正用户空间读的大小 if(size > sizeof(kbuf)) size = sizeof(kbuf); ret = copy_to_user(ubuf,kbuf,size); //将内核空间的数据,写入到用户空间 if(ret){ printk("copy to user is error\n"); return -EIO; } return size; } ssize_t myled_write(struct file *file, const char __user *ubuf, size_t size, loff_t *loff) { int ret; printk("%s:%s:%d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__); //如果用户空间想写的大小256个字节,大于内核空间的大小128个字节,需要更正用户空间写的大小 if(size > sizeof(kbuf)) size = sizeof(kbuf); ret = copy_from_user(kbuf,ubuf,size); //将用户空间的数据,写入到内核空间 if(ret){ printk("copy from user is error\n"); return -EIO; } printk("kernel kbuf=%s\n",kbuf); return size; } int myled_close(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) { printk("%s:%s:%d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__); spin_lock(&spinlock); //上锁 flag = 0; spin_unlock(&spinlock); //解锁 return 0; } //操作方法结构体 const struct file_operations fops = { .open = myled_open, .read = myled_read, .write = myled_write, .release = myled_close, }; //入口 static int __init demo_init(void) { int ret; dev_t devno; int i = 0; //分配对象 cdev = cdev_alloc(); if(cdev == NULL){ printk("cdev alloc is error\n"); ret = -EIO; goto ERR1; } //对象初始化 cdev_init(cdev,&fops); if(major > 0) { //静态指定设备号 ret = register_chrdev_region(MKDEV(major,minor), count, CNAME); if(ret){ printk("register chrdev region is error\n"); ret = -EIO; goto ERR2; } }else{ //动态指定设备号 ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&devno, 0, count,CNAME); if(ret){ printk("alloc chrdev region is error\n"); ret = -EIO; goto ERR2; } major = MAJOR(devno);//根据设备号,获取主设备号的值 minor = MINOR(devno);//根据设备号,获取次设备号的值 } //对象注册 ret = cdev_add(cdev,MKDEV(major,minor),count); if(ret){ printk("dev add is error\n"); ret = -EIO; goto ERR3; } //三盏灯,自动创建三个设备节点 /dev/myled0 /dev/myled1 /dev/myled2 cls = class_create(THIS_MODULE, CNAME); //向上层提交目录信息 if(IS_ERR(cls)) { printk("class create is error\n"); ret = EIO; goto ERR4; } for(i=0;i<count;i++) //向上层提交设备节点信息 { device = device_create(cls, NULL, MKDEV(major,i),NULL, "myled%d", i); if(IS_ERR(device)) { printk("device create is error\n"); ret = EIO; goto ERR5; } } spin_lock_init(&spinlock); //初始化自旋锁锁 return 0; //!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!一定不能省略!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ERR5: //如果第一个设备节点和第二个设备节点创建成功,第三个设备节点创建失败,取消向上层提交第一个和第二个设备节点信息 for(--i;i>=0;i--) { device_destroy(cls, MKDEV(major,i)); //取消向上层提交设备节点信息 } class_destroy(cls); //取消向上层提交目录信息 ERR4: cdev_del(cdev); //对象注销 ERR3: unregister_chrdev_region(MKDEV(major,minor), count); //注销设备号 ERR2: kfree(cdev); //释放结构体指针 ERR1: return ret; } //出口 static void __exit demo_exit(void) { int i = 0; for(i=0;i<count;i++) { device_destroy(cls, MKDEV(major,i)); //取消向上层提交设备节点信息 } class_destroy(cls); //取消向上层提交目录信息 cdev_del(cdev); //对象注销 unregister_chrdev_region(MKDEV(major,minor), count); //注销设备号 kfree(cdev); //释放结构体指针 } module_init(demo_init); //指定入口地址 module_exit(demo_exit); //指定出口地址 MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");//许可证
三、信号量
工作原理:
1.当一个进程获取到信号量之后。另外一个进程也想获取信号量,此时后一个进程就会处于休眠状态
特点:
1.信号量针对多核cpu设计
2.信号量不消耗cpu资源
3.信号量保护的临界资源比较大,在临界区可以出现延时,耗时,甚至休眠的操作
4.在临界资源中可以出现copy_to_user和copy_from_user
5.信号量不会产生死锁
6.信号量上锁不会关闭抢占
7.信号量工作于进程上下文
API接口:
- struct semaphore sema; // 定义信号量 - void sema_init(struct semaphore *sem, int val); //初始化信号量 - sem:定义信号量 - 写1:表示互斥执行 - 写0:表示同步执行 - void down(struct semaphore *sem); //上锁 - void up(struct semaphore *sem); //解锁 - int down_trylock(struct semaphore *sem); //尝试获取锁 - 尝试获取锁成功返回0 - 尝试获取锁失败返回1使用:
当A进程获取到信号量成功,B进程想要获取信号量,需要等待A进程解锁之后才能获取成功
编译代码:
#include <linux/init.h> #include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/cdev.h> #include <linux/device.h> #include <linux/slab.h> #include <linux/fs.h> #define CNAME "myled" struct cdev *cdev; char kbuf[128] = {}; #if 0 unsigned int major = 500; //静态指定设备号 #else unsigned int major = 0; //动态分配设备号 #endif unsigned int count = 3; unsigned int minor = 0; struct class* cls; struct device* device; struct semaphore sema; // 定义信号量 int myled_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) { printk("%s:%s:%d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__); //成功返回0 失败返回1 if((down_trylock(&sema))) { return -EBUSY; //返回错误码 } return 0; } ssize_t myled_read(struct file *file, char __user *ubuf, size_t size, loff_t *loff) { int ret; printk("%s:%s:%d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__); //如果用户空间想读的大小256个字节,大于内核空间的大小128个字节,需要更正用户空间读的大小 if(size > sizeof(kbuf)) size = sizeof(kbuf); ret = copy_to_user(ubuf,kbuf,size); //将内核空间的数据,写入到用户空间 if(ret){ printk("copy to user is error\n"); return -EIO; } return size; } ssize_t myled_write(struct file *file, const char __user *ubuf, size_t size, loff_t *loff) { int ret; printk("%s:%s:%d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__); //如果用户空间想写的大小256个字节,大于内核空间的大小128个字节,需要更正用户空间写的大小 if(size > sizeof(kbuf)) size = sizeof(kbuf); ret = copy_from_user(kbuf,ubuf,size); //将用户空间的数据,写入到内核空间 if(ret){ printk("copy from user is error\n"); return -EIO; } printk("kernel kbuf=%s\n",kbuf); return size; } int myled_close(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) { printk("%s:%s:%d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__); up(&sema); return 0; } //操作方法结构体 const struct file_operations fops = { .open = myled_open, .read = myled_read, .write = myled_write, .release = myled_close, }; //入口 static int __init demo_init(void) { int ret; dev_t devno; int i = 0; //分配对象 cdev = cdev_alloc(); if(cdev == NULL){ printk("cdev alloc is error\n"); ret = -EIO; goto ERR1; } //对象初始化 cdev_init(cdev,&fops); if(major > 0) { //静态指定设备号 ret = register_chrdev_region(MKDEV(major,minor), count, CNAME); if(ret){ printk("register chrdev region is error\n"); ret = -EIO; goto ERR2; } }else{ //动态指定设备号 ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&devno, 0, count,CNAME); if(ret){ printk("alloc chrdev region is error\n"); ret = -EIO; goto ERR2; } major = MAJOR(devno);//根据设备号,获取主设备号的值 minor = MINOR(devno);//根据设备号,获取次设备号的值 } //对象注册 ret = cdev_add(cdev,MKDEV(major,minor),count); if(ret){ printk("dev add is error\n"); ret = -EIO; goto ERR3; } //三盏灯,自动创建三个设备节点 /dev/myled0 /dev/myled1 /dev/myled2 cls = class_create(THIS_MODULE, CNAME); //向上层提交目录信息 if(IS_ERR(cls)) { printk("class create is error\n"); ret = EIO; goto ERR4; } for(i=0;i<count;i++) //向上层提交设备节点信息 { device = device_create(cls, NULL, MKDEV(major,i),NULL, "myled%d", i); if(IS_ERR(device)) { printk("device create is error\n"); ret = EIO; goto ERR5; } } sema_init(&sema, 1); //初始化信号量 return 0; //!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!一定不能省略!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ERR5: //如果第一个设备节点和第二个设备节点创建成功,第三个设备节点创建失败,取消向上层提交第一个和第二个设备节点信息 for(--i;i>=0;i--) { device_destroy(cls, MKDEV(major,i)); //取消向上层提交设备节点信息 } class_destroy(cls); //取消向上层提交目录信息 ERR4: cdev_del(cdev); //对象注销 ERR3: unregister_chrdev_region(MKDEV(major,minor), count); //注销设备号 ERR2: kfree(cdev); //释放结构体指针 ERR1: return ret; } //出口 static void __exit demo_exit(void) { int i = 0; for(i=0;i<count;i++) { device_destroy(cls, MKDEV(major,i)); //取消向上层提交设备节点信息 } class_destroy(cls); //取消向上层提交目录信息 cdev_del(cdev); //对象注销 unregister_chrdev_region(MKDEV(major,minor), count); //注销设备号 kfree(cdev); //释放结构体指针 } module_init(demo_init); //指定入口地址 module_exit(demo_exit); //指定出口地址 MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");//许可证
四、互斥体
工作原理:
当一个进程获取到互斥体之后,另外一个进程也想要获取,后一个进程如果获取不到,会稍微一会进入休眠状态,所以对于保护临界资源比较小的时候,互斥体的效率高于信号量
特点:
1.互斥体针对多核cpu设计
2.互斥体不消耗cpu资源
3.互斥体保护临界资源比较大,所以在临界区可以出现延时,耗时,甚至休眠
4.在临界区可以使用copy_to_user和copy_from_user
5.互斥体不会产生死锁
6.互斥体不会关闭抢占
7.互斥体工作于进程上下文
API接口:
- struct mutex mutex; // 定义互斥体 - mutex_init(&mutex); //初始化互斥体 - void mutex_lock(struct mutex *lock); //上锁 - void mutex_unlock(struct mutex *lock); //解锁 - int mutex_trylock(struct mutex *lock);; //尝试获取互斥体 - 尝试获取锁成功返回1 - 尝试获取锁失败返回0使用:
当A进程获取到互斥锁成功后,B进程获取互斥锁,。只有等A进程解锁,B进程才能获取成功
编译代码:
#include <linux/init.h> #include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/cdev.h> #include <linux/device.h> #include <linux/slab.h> #include <linux/fs.h> #define CNAME "myled" struct cdev *cdev; char kbuf[128] = {}; #if 0 unsigned int major = 500; //静态指定设备号 #else unsigned int major = 0; //动态分配设备号 #endif unsigned int count = 3; unsigned int minor = 0; struct class* cls; struct device* device; struct mutex mutex; // 定义互斥体 int myled_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) { printk("%s:%s:%d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__); //成功返回1 失败返回0 if(!(mutex_trylock(&mutex))) { return -EBUSY; //返回错误码 } return 0; } ssize_t myled_read(struct file *file, char __user *ubuf, size_t size, loff_t *loff) { int ret; printk("%s:%s:%d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__); //如果用户空间想读的大小256个字节,大于内核空间的大小128个字节,需要更正用户空间读的大小 if(size > sizeof(kbuf)) size = sizeof(kbuf); ret = copy_to_user(ubuf,kbuf,size); //将内核空间的数据,写入到用户空间 if(ret){ printk("copy to user is error\n"); return -EIO; } return size; } ssize_t myled_write(struct file *file, const char __user *ubuf, size_t size, loff_t *loff) { int ret; printk("%s:%s:%d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__); //如果用户空间想写的大小256个字节,大于内核空间的大小128个字节,需要更正用户空间写的大小 if(size > sizeof(kbuf)) size = sizeof(kbuf); ret = copy_from_user(kbuf,ubuf,size); //将用户空间的数据,写入到内核空间 if(ret){ printk("copy from user is error\n"); return -EIO; } printk("kernel kbuf=%s\n",kbuf); return size; } int myled_close(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) { printk("%s:%s:%d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__); mutex_unlock(&mutex); //解锁 return 0; } //操作方法结构体 const struct file_operations fops = { .open = myled_open, .read = myled_read, .write = myled_write, .release = myled_close, }; //入口 static int __init demo_init(void) { int ret; dev_t devno; int i = 0; //分配对象 cdev = cdev_alloc(); if(cdev == NULL){ printk("cdev alloc is error\n"); ret = -EIO; goto ERR1; } //对象初始化 cdev_init(cdev,&fops); if(major > 0) { //静态指定设备号 ret = register_chrdev_region(MKDEV(major,minor), count, CNAME); if(ret){ printk("register chrdev region is error\n"); ret = -EIO; goto ERR2; } }else{ //动态指定设备号 ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&devno, 0, count,CNAME); if(ret){ printk("alloc chrdev region is error\n"); ret = -EIO; goto ERR2; } major = MAJOR(devno);//根据设备号,获取主设备号的值 minor = MINOR(devno);//根据设备号,获取次设备号的值 } //对象注册 ret = cdev_add(cdev,MKDEV(major,minor),count); if(ret){ printk("dev add is error\n"); ret = -EIO; goto ERR3; } //三盏灯,自动创建三个设备节点 /dev/myled0 /dev/myled1 /dev/myled2 cls = class_create(THIS_MODULE, CNAME); //向上层提交目录信息 if(IS_ERR(cls)) { printk("class create is error\n"); ret = EIO; goto ERR4; } for(i=0;i<count;i++) //向上层提交设备节点信息 { device = device_create(cls, NULL, MKDEV(major,i),NULL, "myled%d", i); if(IS_ERR(device)) { printk("device create is error\n"); ret = EIO; goto ERR5; } } mutex_init(&mutex); //初始化互斥体 return 0; //!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!一定不能省略!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ERR5: //如果第一个设备节点和第二个设备节点创建成功,第三个设备节点创建失败,取消向上层提交第一个和第二个设备节点信息 for(--i;i>=0;i--) { device_destroy(cls, MKDEV(major,i)); //取消向上层提交设备节点信息 } class_destroy(cls); //取消向上层提交目录信息 ERR4: cdev_del(cdev); //对象注销 ERR3: unregister_chrdev_region(MKDEV(major,minor), count); //注销设备号 ERR2: kfree(cdev); //释放结构体指针 ERR1: return ret; } //出口 static void __exit demo_exit(void) { int i = 0; for(i=0;i<count;i++) { device_destroy(cls, MKDEV(major,i)); //取消向上层提交设备节点信息 } class_destroy(cls); //取消向上层提交目录信息 cdev_del(cdev); //对象注销 unregister_chrdev_region(MKDEV(major,minor), count); //注销设备号 kfree(cdev); //释放结构体指针 } module_init(demo_init); //指定入口地址 module_exit(demo_exit); //指定出口地址 MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");//许可证
五、原子变量
工作原理:
原子变量本身就是一个变量,没有自选或者休眠状态,获取到原子变量就成功,获取不到就失败,原子变量在内核中通过内联汇编实现,省区中间环节
定义原子变量:
typedef struct { int counter; } atomic_t;API接口:
- atomic_t atomic = ATOMIC_INIT(1); //定义并且初始化原子变量 - bool atomic_dec_and_test(atomic_t *v); //上锁 -1 - 减1之后和0值进行比较,是否相等 - 减1之后和0值相等,返回1 - 减1之后和0值不相等,返回0 - void atomic_inc(atomic_t *v); //解锁 +1 ======================================================== - atomic_t atomic = ATOMIC_INIT(-1); //定义并且初始化原子变量 - bool atomic_inc_and_test(atomic_t *v); //上锁 +1 - 加1之后和0值进行比较,是否相等 - 加1之后和0值相等,返回1 - 加1之后和0值不相等,返回0 - void atomic_dec(atomic_t *v); //解锁 -1编译代码:
#include <linux/init.h> #include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/cdev.h> #include <linux/device.h> #include <linux/slab.h> #include <linux/fs.h> #define CNAME "myled" struct cdev *cdev; char kbuf[128] = {}; #if 0 unsigned int major = 500; //静态指定设备号 #else unsigned int major = 0; //动态分配设备号 #endif unsigned int count = 3; unsigned int minor = 0; struct class* cls; struct device* device; atomic_t atomic = ATOMIC_INIT(1); //定义并且初始化原子变量 int myled_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) { printk("%s:%s:%d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__); //成功返回1 失败返回0 if(!(atomic_dec_and_test(&atomic))) //上锁 -1 { atomic_inc(&atomic); //解锁 +1 return -EBUSY; //返回错误码 } return 0; } ssize_t myled_read(struct file *file, char __user *ubuf, size_t size, loff_t *loff) { int ret; printk("%s:%s:%d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__); //如果用户空间想读的大小256个字节,大于内核空间的大小128个字节,需要更正用户空间读的大小 if(size > sizeof(kbuf)) size = sizeof(kbuf); ret = copy_to_user(ubuf,kbuf,size); //将内核空间的数据,写入到用户空间 if(ret){ printk("copy to user is error\n"); return -EIO; } return size; } ssize_t myled_write(struct file *file, const char __user *ubuf, size_t size, loff_t *loff) { int ret; printk("%s:%s:%d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__); //如果用户空间想写的大小256个字节,大于内核空间的大小128个字节,需要更正用户空间写的大小 if(size > sizeof(kbuf)) size = sizeof(kbuf); ret = copy_from_user(kbuf,ubuf,size); //将用户空间的数据,写入到内核空间 if(ret){ printk("copy from user is error\n"); return -EIO; } printk("kernel kbuf=%s\n",kbuf); return size; } int myled_close(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) { printk("%s:%s:%d\n",__FILE__,__func__,__LINE__); atomic_inc(&atomic); //解锁 +1 return 0; } //操作方法结构体 const struct file_operations fops = { .open = myled_open, .read = myled_read, .write = myled_write, .release = myled_close, }; //入口 static int __init demo_init(void) { int ret; dev_t devno; int i = 0; //分配对象 cdev = cdev_alloc(); if(cdev == NULL){ printk("cdev alloc is error\n"); ret = -EIO; goto ERR1; } //对象初始化 cdev_init(cdev,&fops); if(major > 0) { //静态指定设备号 ret = register_chrdev_region(MKDEV(major,minor), count, CNAME); if(ret){ printk("register chrdev region is error\n"); ret = -EIO; goto ERR2; } }else{ //动态指定设备号 ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&devno, 0, count,CNAME); if(ret){ printk("alloc chrdev region is error\n"); ret = -EIO; goto ERR2; } major = MAJOR(devno);//根据设备号,获取主设备号的值 minor = MINOR(devno);//根据设备号,获取次设备号的值 } //对象注册 ret = cdev_add(cdev,MKDEV(major,minor),count); if(ret){ printk("dev add is error\n"); ret = -EIO; goto ERR3; } //三盏灯,自动创建三个设备节点 /dev/myled0 /dev/myled1 /dev/myled2 cls = class_create(THIS_MODULE, CNAME); //向上层提交目录信息 if(IS_ERR(cls)) { printk("class create is error\n"); ret = EIO; goto ERR4; } for(i=0;i<count;i++) //向上层提交设备节点信息 { device = device_create(cls, NULL, MKDEV(major,i),NULL, "myled%d", i); if(IS_ERR(device)) { printk("device create is error\n"); ret = EIO; goto ERR5; } } return 0; //!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!一定不能省略!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ERR5: //如果第一个设备节点和第二个设备节点创建成功,第三个设备节点创建失败,取消向上层提交第一个和第二个设备节点信息 for(--i;i>=0;i--) { device_destroy(cls, MKDEV(major,i)); //取消向上层提交设备节点信息 } class_destroy(cls); //取消向上层提交目录信息 ERR4: cdev_del(cdev); //对象注销 ERR3: unregister_chrdev_region(MKDEV(major,minor), count); //注销设备号 ERR2: kfree(cdev); //释放结构体指针 ERR1: return ret; } //出口 static void __exit demo_exit(void) { int i = 0; for(i=0;i<count;i++) { device_destroy(cls, MKDEV(major,i)); //取消向上层提交设备节点信息 } class_destroy(cls); //取消向上层提交目录信息 cdev_del(cdev); //对象注销 unregister_chrdev_region(MKDEV(major,minor), count); //注销设备号 kfree(cdev); //释放结构体指针 } module_init(demo_init); //指定入口地址 module_exit(demo_exit); //指定出口地址 MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");//许可证