阅读量:0
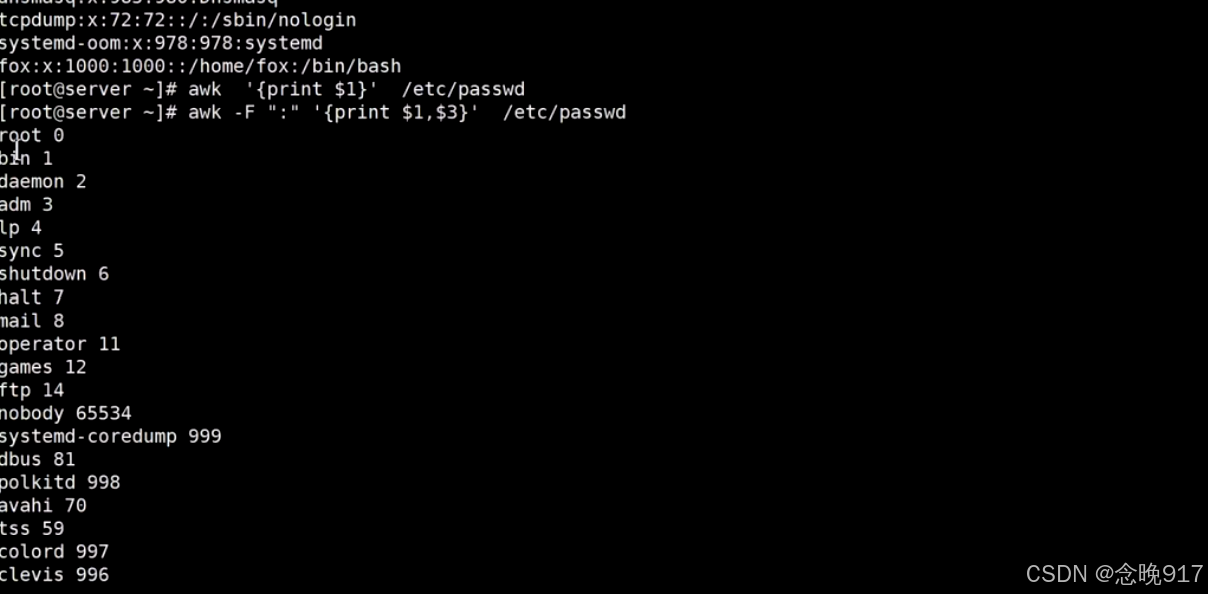
用法 awk 'BEGIN{ commands } pattern{ commands } END{ commands }' [INPUTFILE…] awk的输出 (1) print item1,item2,…… 各项目之间使用逗号隔开,而输出时则以空白字符分隔; 输出的item可以为字符串或数值、当前记录的字段(如$1)、变量或awk的表达式;数值会先转换为 字符串,然后再输出;print命令后面的item可以省略,此时其功能相当于print $0, 因此,如果想输出空白行,则需要使 用print “ ”;[root@localhost ~]# awk 'BEGIN { print "line one\nline two\nline three"}' line one line two line three [root@localhost ~]# awk 'BEGIN{print "This","is","test"}' This is test [root@localhost ~]# awk -F: '{print $1,$3}' /etc/passwd | head -n 3 root 0 bin 1 daemon 2 [root@localhost ~]# awk -F: '{printf "%-15s %i\n",$1,$3}' /etc/passwd |head -n 3 root 0 bin 1 daemon 2
输出重定向 print items > output-file print items >> output-file print items | commandroot@localhost ~]# awk -F: '{printf "%-15s %i\n",$1,$3 > "test1" }' /etc/passwd
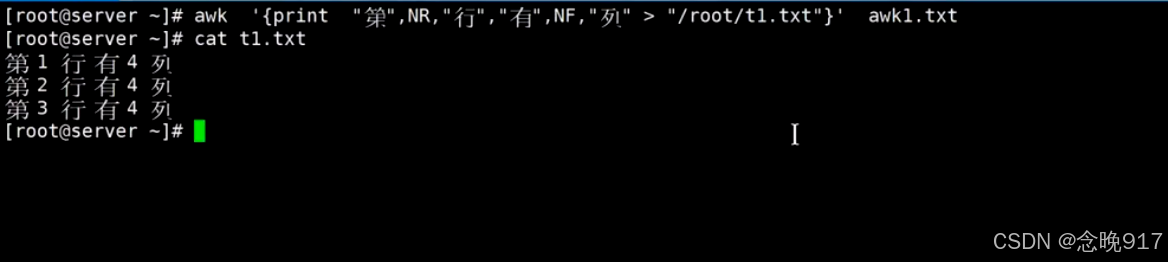
# awk命令调用脚本
[root@server ~]# awk -f test.awk awk2.txt
```
```bash
# OFS设置输出结果的间隔符为\t
[root@server ~]# awk -F ":" 'BEGIN {OFS="\t"} {print $1,$2}' /etc/passwd
```
```bash
#查看文件中所有空白行的行号
[root@server ~]# awk '/^$/{print NR}' /root/anaconda-ks.cfg
```
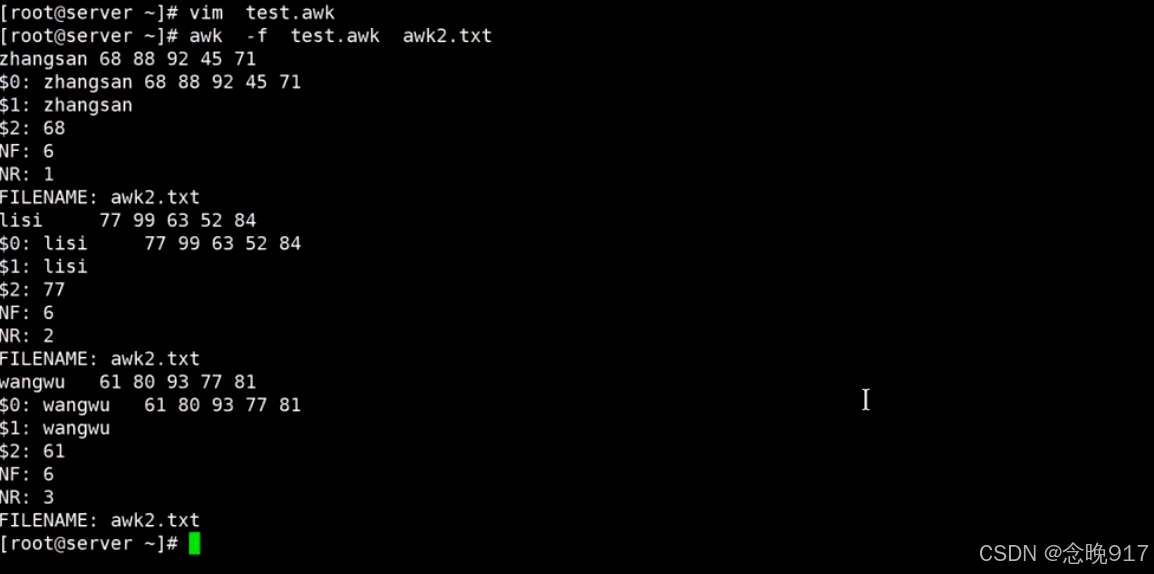

用户自定义变量:
awk允许用户自定义自己的变量以便在程序代码中使用
变量名命名规则与大多数编程语言相同,只能使用字母、数字和下划线,且不能以数字开头
awk变量名称区分字符大小写
[root@server ~l# awk 'BEGIN{test="hello world" ; print test}'#变量定义在BEGIN中
hello world
[root@server ~]# awk -v test="hello world" BEGIN'{ print test}'# 变量定义在-V参数后,
hello world
