文章目录
- 前言
- 一、服务器侧等保测评项目及加固
- 1、服务器未启用密码长度以及口令复杂度、且未定期更新口令
- 2、服务器未限制非法登录次数,未设置登录连接超时自动退出
- 3、服务器只采用密码技术对用户的身份进行鉴别,未采用双因子认证;服务器未限制管理终端登录
- 4、Rc3.d文件权限过大755
- 5、未有第三方审计系统,未对审计记录进行定期备份
- 6、服务器未安装杀毒
- 二、MySql数据库等保加固
- 1、采用用户名+口令进行身份鉴别,未启用口令复杂度策略,未定期更换口令
- 2、未启用登录失败处理功能,未有登录连接超时退出策略
- 3、采用用户名+口令验证码进行身份鉴别,未实现使用两种或两种以上组合鉴别技术进行身份鉴别,未实现双因子登录;未对接入方式或网络地址范围进行限制且网络不可控
- 4、未实现管理用户的最小权限分离
- 5、未有加密技术保证数据在传输过程中的完整性;
- 6、未定期进行数据备份恢复测试功能
- 三、中间件版本过低产生的各种漏洞
- 1、nginx漏洞示例及修复
- 四、Harbor 访问控制错误漏洞
- 五、Swagger API 未授权访问漏洞
- 六、服务器常见安全加固脚本分享
- 总结
前言
安全等级测评的目的是通过对目标系统在安全技术及管理方面的测评,对目标系统的安全技术状态及安全管理状况做出初步判断,给出目标系统在安全技术及安全管理方面与其相应安全等级保护要求之间的差距。测评结论作为委托方进一步完善系统安全策略及安全技术防护措施依据
一、服务器侧等保测评项目及加固
1、服务器未启用密码长度以及口令复杂度、且未定期更新口令
整改建议: 建议修改密码长度、口令复杂度以及定期90天更换口令。 整改方法: logindefs(){ echo "---口令生存期---" cp -p /etc/login.defs /etc/login.defs_bak sed -i 's/^PASS_MAX_DAYS.*/PASS_MAX_DAYS 90/g' /etc/login.defs sed -i 's/^PASS_MIN_DAYS.*/PASS_MIN_DAYS 10/g' /etc/login.defs sed -i 's/^PASS_WARN_AGE.*/PASS_WARN_AGE 7/g' /etc/login.defs } system_auth_crack(){ echo "---口令复杂度及密码长度---" # 判断 system-auth 配置文件中是否包含 password requisite pam_cracklib.so 的配置 if grep -q 'password requisite pam_cracklib.so' /etc/pam.d/system-auth; then # 如果有,则使用 sed 命令替换原有的行 sed -i 's/^password.*requisite.*pam_cracklib.so$/& try_first_pass retry=3 dcredit=-1 lcredit=-1 ucredit=-1 ocredit=-1 minlen=8/g' /etc/pam.d/system-auth else # 如果没有,则添加新的一行 echo "password requisite pam_cracklib.so try_first_pass retry=3 dcredit=-1 lcredit=-1 ucredit=-1 ocredit=-1 minlen=8" >> /etc/pam.d/system-auth fi } 2、服务器未限制非法登录次数,未设置登录连接超时自动退出
整改建议: 建议限制非法登录次数;设置登录连接超时自动退出,如:连续登录3次锁定10分钟,并无操作10分钟自动退出。 整改方法: login_timeout(){ # 检查 /etc/profile 文件是否存在 if [ ! -f /etc/profile ]; then echo "/etc/profile 文件不存在" exit 1 fi # 使用 sed 命令检查文件末尾是否已经存在所需的两行内容,不存在则添加 if ! grep -q '^TMOUT=' /etc/profile; then echo 'TMOUT=300' >> /etc/profile else sed -i 's/^TMOUT=.*/TMOUT=300/' /etc/profile fi if ! grep -q '^export TMOUT' /etc/profile; then echo 'export TMOUT' >> /etc/profile fi } 3、服务器只采用密码技术对用户的身份进行鉴别,未采用双因子认证;服务器未限制管理终端登录
整改建议: 服务器只采用密码技术对用户的身份进行鉴别,未采用双因子认证。 因为维护的项目都是通过vpn(短信验证)-->堡垒机(短信验证)-->登录服务器,最后沟通这项可以按如下修复。即服务器配置ssh白名单,只允许堡垒机登录 整改方法: vim /etc/hosts.deny #添加以下配置 sshd:all:deny vim /etc/hosts.allow #添加以下配置 sshd:堡垒机IP:allow 4、Rc3.d文件权限过大755
整改建议: 建议修改rc3.d的读写权限为755以下 整改方法: chmod 644 -R /etc/rc.d/rc3.d 5、未有第三方审计系统,未对审计记录进行定期备份
整改建议: 未有第三方审计系统,未对审计记录进行定期备份; 整改方法: 1、服务器开启audit服务 2、使用aidutctl -l命令查看审计策略 3、使用auditctl -w 路径/文件 -p 权限 命令对文件或目录配置审计策略 补充: 使用auditctl -W 路径/文件 -p 权限 命令是取消审计策略 4、使用ausearch -f 配置的路径/文件 查看对应的审计日志 5、使用AuditLogSync.py脚本+ip_address.txt文件实现将全部服务器的audit.log日志备份并同步到日志归档服务器。脚本如下所示 6、在日志归档服务器配置定时同步,即可 [root@LogArchive]# crontab -e * */23 * * * /usr/bin/python3 -W ignore /path/AuditLogSync.py #!/usr/bin/env python3 #Date: 202403212005 import os import time import paramiko import logging from datetime import datetime import threading import inspect class AuditLogSync: def __init__(self, ip_file,audit_path,username,password,port): """ 初始化AuditLogSync类 Parameters: ip_file (str): 包含IP地址列表的文件路径 audit_path (str): 审计日志路径 username (str): 用户名 password (str): 密码 port (int): 端口 """ self.ip_file = ip_file self.audit_path=audit_path self.username = username self.password = password self.port = port #生成日期 self.current_time = datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d") #生成审计日志归档目录 self.export_dir = f"/export/AuditLogSync/{self.current_time}" #生成执行日志 self.info_log_file = "/export/AuditLogSync/sync_info.log" self.error_log_file = "/export/AuditLogSync/sync_error.log" # 设置 info 日志记录器 self.info_logger = logging.getLogger('info_logger') info_handler = logging.FileHandler(self.info_log_file) info_handler.setLevel(logging.INFO) info_formatter = logging.Formatter('%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s') info_handler.setFormatter(info_formatter) self.info_logger.addHandler(info_handler) self.info_logger.setLevel(logging.INFO) # 设置 error 日志记录器 self.error_logger = logging.getLogger('error_logger') error_handler = logging.FileHandler(self.error_log_file) error_handler.setLevel(logging.ERROR) error_formatter = logging.Formatter('%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s') error_handler.setFormatter(error_formatter) self.error_logger.addHandler(error_handler) #判断审计日志归档目录是否存在 if not os.path.exists(self.export_dir): os.makedirs(self.export_dir) def run_operations(self): """ 运行一系列操作:连接到服务器,打包日志文件,执行rsync同步 """ # 从文件中读取IP地址列表 with open(self.ip_file, 'r') as file: ip_addresses = file.readlines() threads= [] # 拿到ip地址调用连接服务器方法 for ip_address in ip_addresses: ip_address = ip_address.strip() # 创建线程并启动,不采用多线程容易卡死 thread = threading.Thread(target=self.process_server, args=(ip_address,)) threads.append(thread) thread.start() #ssh_client = self.connect_to_server(ip_address) #判断服务器连接是否成功,如果成功调用打包审计日志方法、执行rsync同步方法,最后关闭连接 #if ssh_client is not None: # self.package_logs(ssh_client, ip_address) # self.execute_rsync(ssh_client, ip_address) # ssh_client.close() # 等待所有线程完成 for thread in threads: thread.join() def process_server(self, ip_address): """ 处理单个服务器的操作 """ ssh_client = self.connect_to_server(ip_address) #判断服务器连接是否成功,如果成功调用打包审计日志方法、执行rsync同步方法,最后关闭连接 if ssh_client is not None: self.package_logs(ssh_client, ip_address) self.execute_rsync(ssh_client, ip_address) ssh_client.close() def connect_to_server(self, ip_address): """ 建立SSH连接到远程服务器 Parameters: ip_address (str): 目标服务器的IP地址 Returns: paramiko.SSHClient: SSH客户端对象 """ ssh_client = paramiko.SSHClient() ssh_client.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy()) try: ssh_client.connect(ip_address, username=self.username, password=self.password, port=self.port,timeout=20) self.info_logger.info(f"成功连接到服务器 {ip_address} - {inspect.currentframe().f_code.co_name}") except paramiko.ssh_exception.AuthenticationException: self.error_logger.error(f"连接服务器失败 {ip_address}. 请检查服务器信息是否正确 - {inspect.currentframe().f_code.co_name}") return None return ssh_client def package_logs(self, ssh_client, ip_address): """ 打包远程服务器上的日志文件 Parameters: ssh_client (paramiko.SSHClient): SSH客户端对象 ip_address (str): 目标服务器的IP地址 """ check_dir_cmd = f""" if [ -d {self.audit_path} ]; then echo 'Directory exists' else echo 'Directory does not exist' fi """ stdin, stdout, stderr = ssh_client.exec_command(check_dir_cmd) dir_check_output = stdout.read().decode('utf-8') if "Directory exists" in dir_check_output: self.info_logger.info(f"{ip_address}: 审计日志目录 {self.audit_path} 存在 - {inspect.currentframe().f_code.co_name}") tar_cmd = f"cd {self.audit_path} && tar -zcf /tmp/{ip_address}_{self.current_time}_audit.tar.gz ." stdin, stdout, stderr = ssh_client.exec_command(tar_cmd) exit_status = stdout.channel.recv_exit_status() # 判断打包是否成功 if exit_status == 0: self.info_logger.info(f"{ip_address}: 审计日志打包成功 - {inspect.currentframe().f_code.co_name}") else: self.error_logger.error(f"{ip_address}: 审计日志打包失败 - {stderr.read().decode('utf-8')} - {inspect.currentframe().f_code.co_name}") else: self.error_logger.error(f"{ip_address}: 审计日志目录 {self.audit_path} 不存在 - {inspect.currentframe().f_code.co_name}") def execute_rsync(self, ssh_client, ip_address): """ 执行rsync同步操作 Parameters: ssh_client (paramiko.SSHClient): SSH客户端对象 ip_address (str): 目标服务器的IP地址 """ rsync_check_cmd = "which rsync" stdin, stdout, stderr = ssh_client.exec_command(rsync_check_cmd) #调试 #print(f"execute_rsync_stdout: {stdout.read().decode('utf-8')}") if "rsync" not in stdout.read().decode('utf-8'): install_rsync_cmd = "yum -y install rsync" ssh_client.exec_command(install_rsync_cmd) #安装rsync命令可能需要20s左右 self.info_logger.info(f"{ip_address}: 安装rsync中,请等待... - {inspect.currentframe().f_code.co_name}") time.sleep(20) # 再次检查rsync命令是否安装成功 stdin, stdout, stderr = ssh_client.exec_command(rsync_check_cmd) if "rsync" not in stdout.read().decode('utf-8'): self.error_logger.error(f"{ip_address} 安装rsync失败 - {inspect.currentframe().f_code.co_name}") return # 已经安装rsync,执行目标服务器的操作 rsync_cmd = f"rsync -az -e 'ssh -p {self.port}' {self.username}@{ip_address}:/tmp/{ip_address}_{self.current_time}_audit.tar.gz {self.export_dir}" os.system(rsync_cmd) self.info_logger.info(f"{ip_address}: 审计日志压缩包同步成功 - {inspect.currentframe().f_code.co_name}") # 删除远程服务器上的tar包 delete_tar_cmd = f"rm /tmp/{ip_address}_{self.current_time}_audit.tar.gz" ssh_client.exec_command(delete_tar_cmd) self.info_logger.info(f"{ip_address}: 成功删除远程服务器上的tar包 - {inspect.currentframe().f_code.co_name}") def delete_old_archive_logs(self, ssh_client): # 删除旧归档日志目录方法 check_archive_cmd = f"find /export/AuditLogSync/ -mindepth 1 -maxdepth 1 -type d -mtime +7" stdin, stdout, stderr = ssh_client.exec_command(check_archive_cmd) old_archive_dirs = stdout.read().decode('utf-8').splitlines() for old_dir in old_archive_dirs: delete_cmd = f"rm -rf {old_dir}" _, stderr, _ = ssh_client.exec_command(delete_cmd) error = stderr.read().decode('utf-8') if error: self.error_logger.error(f"xx.xx.xx.xx 删除旧归档日志目录失败: {error} - {inspect.currentframe().f_code.co_name}") else: self.info_logger.info("xx.xx.xx.xx 没有7天前旧归档日志目录") # 使用AuditLogSync类来运行操作,程序执行入口 if __name__ == '__main__': auditLogSync = AuditLogSync("/export/AuditLogSync/ip_addresses.txt","/var/log/audit",'root','Dcn763#+',822) auditLogSync.run_operations() ssh_client = auditLogSync.connect_to_server("xx.xx.xx.xx") if ssh_client is not None: auditLogSync.info_logger.info(f"成功连接服务器 xx.xx.xx.xx") auditLogSync.delete_old_archive_logs(ssh_client) ssh_client.close() 6、服务器未安装杀毒
整改建议: 建议服务器安装杀毒程序,并提供最新病毒库版本 整改方法: 找服务器厂商协助安装杀毒软件(商业版),一般是深信服EDR防护 二、MySql数据库等保加固
此处mysql版本是5.7.32,其余版本请DBA判断是否能用以下配置;并且配置后不要立即重启数据库,建议跟项目侧和客户约定业务低峰期进行重启操作,一定要得到客户侧的同意再执行重启操作
1、采用用户名+口令进行身份鉴别,未启用口令复杂度策略,未定期更换口令
整改建议: 建议配置数据库口令复杂度策略,如口令长度至少8位以上且包含大写字母、小写字母、数字三种字符类型中至少两种组成 整改方法: 1、检查mysql是否已安装validate_password插件 登录mysql,执行以下命令: mysql> show plugins; 2、如果未安装该插件,执行以下命令进行安装: mysql>INSTALL PLUGIN validate_password SONAME 'validate_password.so'; 3、my.cnf添加以下配置 plugin-load-add=validate_password.so validate_password_check_user_name = ON validate_password_length = 8 validate_password_mixed_case_count = 1 validate_password_number_count = 1 validate_password_policy = medium validate_password_special_char_count = 1 2、未启用登录失败处理功能,未有登录连接超时退出策略
整改建议: 建议配置登录失败处理及登录连接超时退出策略;(如登录失败5次锁定账户20分钟,登录连接超时30分钟自动退出) 整改方法: my.cnf添加以下配置 #登录失败次数限制 max_connect_errors = 5 #登录连接超时退出策略 interactive_timeout = 1800 # 将交互式客户端的超时时间设置为 1800 秒(30 分钟) wait_timeout = 1800 # 将非交互式客户端的超时时间设置为 1800 秒(30 分钟) 3、采用用户名+口令验证码进行身份鉴别,未实现使用两种或两种以上组合鉴别技术进行身份鉴别,未实现双因子登录;未对接入方式或网络地址范围进行限制且网络不可控
整改建议: 服务器只采用密码技术对用户的身份进行鉴别,未采用双因子认证。 因为维护的项目都是通过vpn(短信验证)-->堡垒机(短信验证)-->登录服务器,最后沟通这项可以按如下修复。即服务器配置ssh白名单,只允许堡垒机登录 整改方法: vim /etc/hosts.deny #添加以下配置 sshd:all:deny vim /etc/hosts.allow #添加以下配置 sshd:堡垒机IP:allow 4、未实现管理用户的最小权限分离
整改建议: 建议创建系统管理员、审计管理员、安全管理员并划分各管理员所需管理的最小权限,实现管理用户的三权分离 整改方法: 创建系统管理员(root) 审计管理员(audit) 安全管理员(secure)并分配对应权限 5、未有加密技术保证数据在传输过程中的完整性;
整改建议: 建议采用加密技术或密码技术保证重要数据在传输过程中的完整性 整改方法: my.cnf添加以下配置 require_secure_transport=ON 6、未定期进行数据备份恢复测试功能
整改建议: 建议重要数据进行本地数据备份与恢复功能 整改方法: 添加mysql_backup_3306.py全量备份脚本,定时备份,并进行恢复测试 crontab -e * */23 * * * /usr/bin/python /path/mysql_backup_3306.py IP PORT 三、中间件版本过低产生的各种漏洞
此处就不挨个展示中间件相关的漏洞了,就拿nginx的漏洞作为示例,其余中间件的修复方法都与此处一致
1、nginx漏洞示例及修复
漏洞示例: nginx 安全漏洞(CVE-2021-23017) nginx 缓冲区错误漏洞(CVE-2022-41741) nginx 越界写入漏洞(CVE-2022-41742) Nginx 信任管理问题漏洞(CVE-2021-3618) NGINX 环境问题漏洞(CVE-2019-20372) 漏洞修复方法: 采用iptables规则或firewalld规则进行修复。我比较熟练iptables规则,因此采用iptables 只允许指定的源IP地址、源网段地址、127.0.0.1访问nginx暴露出来的端口,拒绝其余网段/ip地址的访问 iptables -A INPUT -s 10.x.xx.0/24 -p tcp -m multiport --dports 80,8999 -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -s 172.xx.xx.0/24 -p tcp -m multiport --dports 80,8999 -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -s 127.0.0.1 -p tcp -m multiport --dports 80,8999 -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m multiport --dports 80,8999 -j DROP 注意事项: 1、为什么中间件漏洞通过IPtables规则进行修复? 因为随着项目再交付期的稳定运行,客户侧已开始学习使用系统,如果升级中间件版本,后端微服务代码可能也涉及到需要更改,更改后也并不一定能保证系统平稳运行,耗时巨大,成功率不敢保证100%。一般情况下客户侧也是不同意升级版本的。如果客户侧强烈要求升级版本,那只能自求多福写升级方案并演练,演练通过后再上生产。 2、其余中间件的修复方法亦是如此,只需要确定好哪些IP地址方法该中间件端口,然后添加规则就行。 四、Harbor 访问控制错误漏洞
整改建议: 1、升级harbor版本 2、将harbor中公开的仓库全部设置为私有仓库,给pod的yaml文件中配置镜像拉取策略即可 #推荐方法2 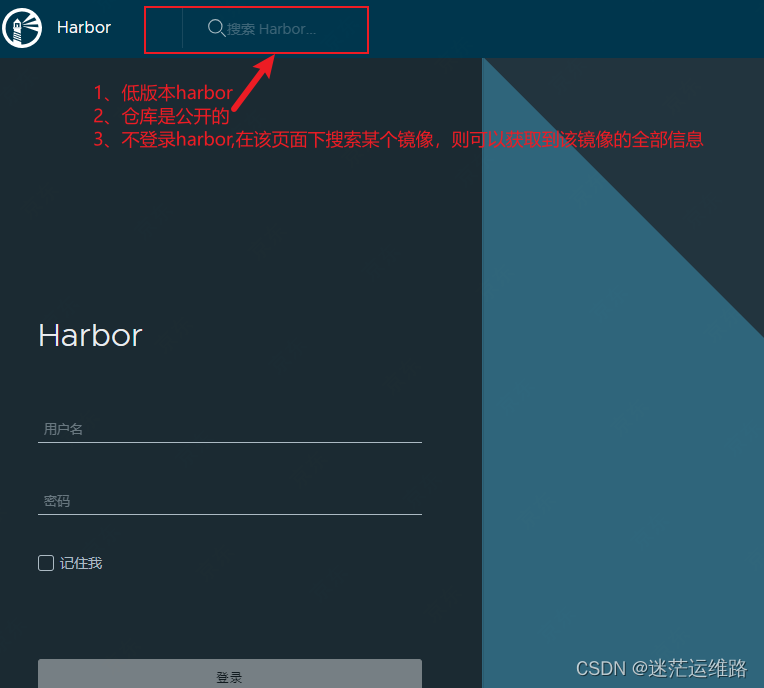
五、Swagger API 未授权访问漏洞
整改建议: 结合SpringSecurity/shiro进行认证授权,将Swagger-UI的URLs加入到各自的认证和授权过滤链中,当用户访问Swagger对应的资源时,只有通过认证授权的用户才能进行访问 整改方法: 拉通研发,进行处理即可 六、服务器常见安全加固脚本分享
一个简单的shell脚本,包含了服务器密码、连接超时、文件权限、服务器历史命令等方面的加固
#!/bin/bash #linux脆弱性加固脚本 system_auth(){ echo "---口令锁定策略---" cp -p /etc/pam.d/system-auth /etc/pam.d/system-auth_bak if grep -q 'auth required pam_tally2.so' /etc/pam.d/system-auth;then sed -i 's/^auth.*required.*pam_tally2.so$/&\nauth required pam_tally2.so deny=3 unlock_time=600 even_deny_root root_unlock_time=10/g' /etc/pam.d/system-auth else echo "auth required pam_tally2.so deny=3 unlock_time=600 even_deny_root root_unlock_time=10" >> /etc/pam.d/system-auth fi if grep -q 'account required pam_tally2.so' /etc/pam.d/system-auth;then sed -i 's/^account.*required.*pam_tally2.so$/&\n/g' /etc/pam.d/system-auth else echo "account required pam_tally2.so" >> /etc/pam.d/system-auth fi } logindefs(){ echo "---口令生存期---" cp -p /etc/login.defs /etc/login.defs_bak sed -i 's/^PASS_MAX_DAYS.*/PASS_MAX_DAYS 90/g' /etc/login.defs sed -i 's/^PASS_MIN_DAYS.*/PASS_MIN_DAYS 10/g' /etc/login.defs sed -i 's/^PASS_WARN_AGE.*/PASS_WARN_AGE 7/g' /etc/login.defs } system_auth_crack(){ echo "---口令复杂度---" # 判断 system-auth 配置文件中是否包含 password requisite pam_cracklib.so 的配置 if grep -q 'password requisite pam_cracklib.so' /etc/pam.d/system-auth; then # 如果有,则使用 sed 命令替换原有的行 sed -i 's/^password.*requisite.*pam_cracklib.so$/& try_first_pass retry=3 dcredit=-1 lcredit=-1 ucredit=-1 ocredit=-1 minlen=8/g' /etc/pam.d/system-auth else # 如果没有,则添加新的一行 echo "password requisite pam_cracklib.so try_first_pass retry=3 dcredit=-1 lcredit=-1 ucredit=-1 ocredit=-1 minlen=8" >> /etc/pam.d/system-auth fi } file_contro(){ echo "文件与目录缺省权限控制" cp -p /etc/profile /etc/profile.bak if grep -q 'umask 027' /etc/profile;then echo "已存在umask 027" else echo "umask 027" >>/etc/profile source /etc/profile } user_control(){ chmod 644 /etc/passwd chmod 400 /etc/shadow chmod 644 /etc/group chmod 644 /etc/services chmod 600 /etc/xinetd.conf chmod 600 /etc/security chattr +a /var/log/messages } security_log(){ filename="/var/adm/messages" if [ -e "${filename}" ]; then chmod 666 /var/adm/messages /etc/init.d/rsyslog restart else touch ${filename} chmod 666 /var/adm/messages echo " *.err;kern.debug;daemon.notice /var/adm/messages" >> /etc/rsyslog.conf /etc/init.d/rsyslog restart fi } login_timeout(){ # 检查 /etc/profile 文件是否存在 if [ ! -f /etc/profile ]; then echo "/etc/profile 文件不存在" exit 1 fi # 使用 sed 命令检查文件末尾是否已经存在所需的两行内容,不存在则添加 if ! grep -q '^TMOUT=' /etc/profile; then echo 'TMOUT=300' >> /etc/profile else sed -i 's/^TMOUT=.*/TMOUT=300/' /etc/profile fi if ! grep -q '^export TMOUT' /etc/profile; then echo 'export TMOUT' >> /etc/profile fi } history_set(){ # 检查 /etc/profile 文件是否存在 if [ ! -f /etc/profile ]; then echo "/etc/profile 文件不存在" exit 1 fi # 使用 sed 命令检查文件中是否已经存在所需的两行内容,不存在则添加上去 if ! grep -q '^HISTFILESIZE=' /etc/profile; then echo 'HISTFILESIZE=5' >> /etc/profile else sed -i 's/^HISTFILESIZE=.*/HISTFILESIZE=5/' /etc/profile fi if ! grep -q '^HISTSIZE=' /etc/profile; then echo 'HISTSIZE=5' >> /etc/profile else sed -i 's/^HISTSIZE=.*/HISTSIZE=5/' /etc/profile fi # 让配置生效 source /etc/profile } core_dump(){ # 检查 /etc/security/limits.conf 文件是否存在 if [ ! -f /etc/security/limits.conf ]; then echo "/etc/security/limits.conf 文件不存在" exit 1 fi # 使用 sed 命令检查文件末尾是否已经存在所需的两行内容 if ! grep -q '^\*\s\+soft\s\+core\s\+0$' /etc/security/limits.conf; then echo '* soft core 0' >> /etc/security/limits.conf else sed -i 's/^\(\*\s\+soft\s\+core\s\+\).*/\10/' /etc/security/limits.conf fi if ! grep -q '^\*\s\+hard\s\+core\s\+0$' /etc/security/limits.conf; then echo '* hard core 0' >> /etc/security/limits.conf else sed -i 's/^\(\*\s\+hard\s\+core\s\+\).*/\10/' /etc/security/limits.conf fi # 检查 /etc/profile 文件是否存在 if [ ! -f /etc/profile ]; then echo "/etc/profile 文件不存在" exit 1 fi # 使用 grep 命令检查文件中是否存在指定内容,同时注释掉对应的行 if grep -q 'ulimit\s\+-S\s\+-c\s\+0\s\+>\s\+\/dev\/null\s\+2>&1' /etc/profile; then sed -i 's/^ulimit\s\+-S\s\+-c\s\+0\s\+>\s\+\/dev\/null\s\+2>&1/#&/' /etc/profile fi } system_auth logindefs system_auth_crack file_contro user_control security_log login_timeout history_set core_dump 总结
以上就是关于常见的等保测评项及加固方法,后期遇到新的测评项及加固方法会随时更新,希望能对大家起到帮助作用,也期望大家能给文章点点赞!!!
学习网络安全技术的方法无非三种:
第一种是报网络安全专业,现在叫网络空间安全专业,主要专业课程:程序设计、计算机组成原理原理、数据结构、操作系统原理、数据库系统、 计算机网络、人工智能、自然语言处理、社会计算、网络安全法律法规、网络安全、内容安全、数字取证、机器学习,多媒体技术,信息检索、舆情分析等。
第二种是自学,就是在网上找资源、找教程,或者是想办法认识一-些大佬,抱紧大腿,不过这种方法很耗时间,而且学习没有规划,可能很长一段时间感觉自己没有进步,容易劝退。
第三种就是去找培训。

接下来,我会教你零基础入门快速入门上手网络安全。
网络安全入门到底是先学编程还是先学计算机基础?这是一个争议比较大的问题,有的人会建议先学编程,而有的人会建议先学计算机基础,其实这都是要学的。而且这些对学习网络安全来说非常重要。但是对于完全零基础的人来说又或者急于转行的人来说,学习编程或者计算机基础对他们来说都有一定的难度,并且花费时间太长。
第一阶段:基础准备 4周~6周
这个阶段是所有准备进入安全行业必学的部分,俗话说:基础不劳,地动山摇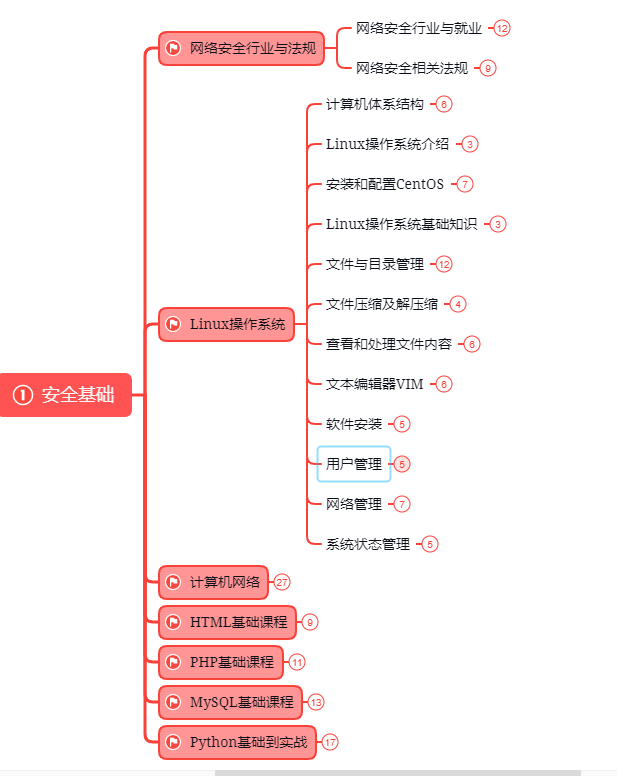
第二阶段:web渗透
学习基础 时间:1周 ~ 2周:
① 了解基本概念:(SQL注入、XSS、上传、CSRF、一句话木马、等)为之后的WEB渗透测试打下基础。
② 查看一些论坛的一些Web渗透,学一学案例的思路,每一个站点都不一样,所以思路是主要的。
③ 学会提问的艺术,如果遇到不懂得要善于提问。
配置渗透环境 时间:3周 ~ 4周:
① 了解渗透测试常用的工具,例如(AWVS、SQLMAP、NMAP、BURP、中国菜刀等)。
② 下载这些工具无后门版本并且安装到计算机上。
③ 了解这些工具的使用场景,懂得基本的使用,推荐在Google上查找。
渗透实战操作 时间:约6周:
① 在网上搜索渗透实战案例,深入了解SQL注入、文件上传、解析漏洞等在实战中的使用。
② 自己搭建漏洞环境测试,推荐DWVA,SQLi-labs,Upload-labs,bWAPP。
③ 懂得渗透测试的阶段,每一个阶段需要做那些动作:例如PTES渗透测试执行标准。
④ 深入研究手工SQL注入,寻找绕过waf的方法,制作自己的脚本。
⑤ 研究文件上传的原理,如何进行截断、双重后缀欺骗(IIS、PHP)、解析漏洞利用(IIS、Nignix、Apache)等,参照:上传攻击框架。
⑥ 了解XSS形成原理和种类,在DWVA中进行实践,使用一个含有XSS漏洞的cms,安装安全狗等进行测试。
⑦ 了解一句话木马,并尝试编写过狗一句话。
⑧ 研究在Windows和Linux下的提升权限,Google关键词:提权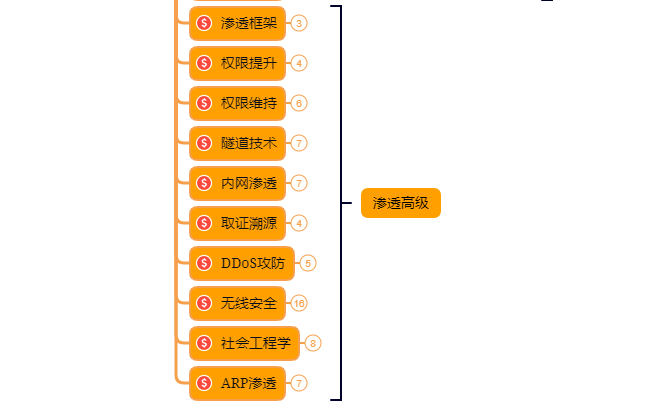
以上就是入门阶段
第三阶段:进阶
已经入门并且找到工作之后又该怎么进阶?详情看下图
给新手小白的入门建议:
新手入门学习最好还是从视频入手进行学习,视频的浅显易懂相比起晦涩的文字而言更容易吸收,这里我给大家准备了一套网络安全从入门到精通的视频学习资料包免费领取哦!