学个damn!
给我狠狠玩好嘛别卷我啊
知道的是图书馆,不知道的还以为开演唱会呢!
八点啊,那可是八点,才八点!

不是哥们下午两点半开馆即满人啊我靠?
只能去儿童区学我说不是?


别拷打我了我真碎了哥

说说自主shell编写吧(要不然进程控制不白学了)
自主shell首先得有打印命令行提示符吧,命令行提示符构成是这样的:用户名+主机名+当前所处路径,我们都封装成函数:
const char* GetUserName() { const char* name = getenv("USER"); if (name == NULL) { return "None"; } return name; } const char* GetHostName() { const char* hostname = getenv("HOSTNAME"); if (hostname == NULL) { return "None"; } return hostname; } const char* GetCwd() { const char* cwd = getenv("PWD"); if (cwd == NULL) { return "None"; } return cwd; }分别获取到了对应的字符串,我们还需要一个函数把这些字符串拼接起来,这个功德圆满的函数就是:sprintf!
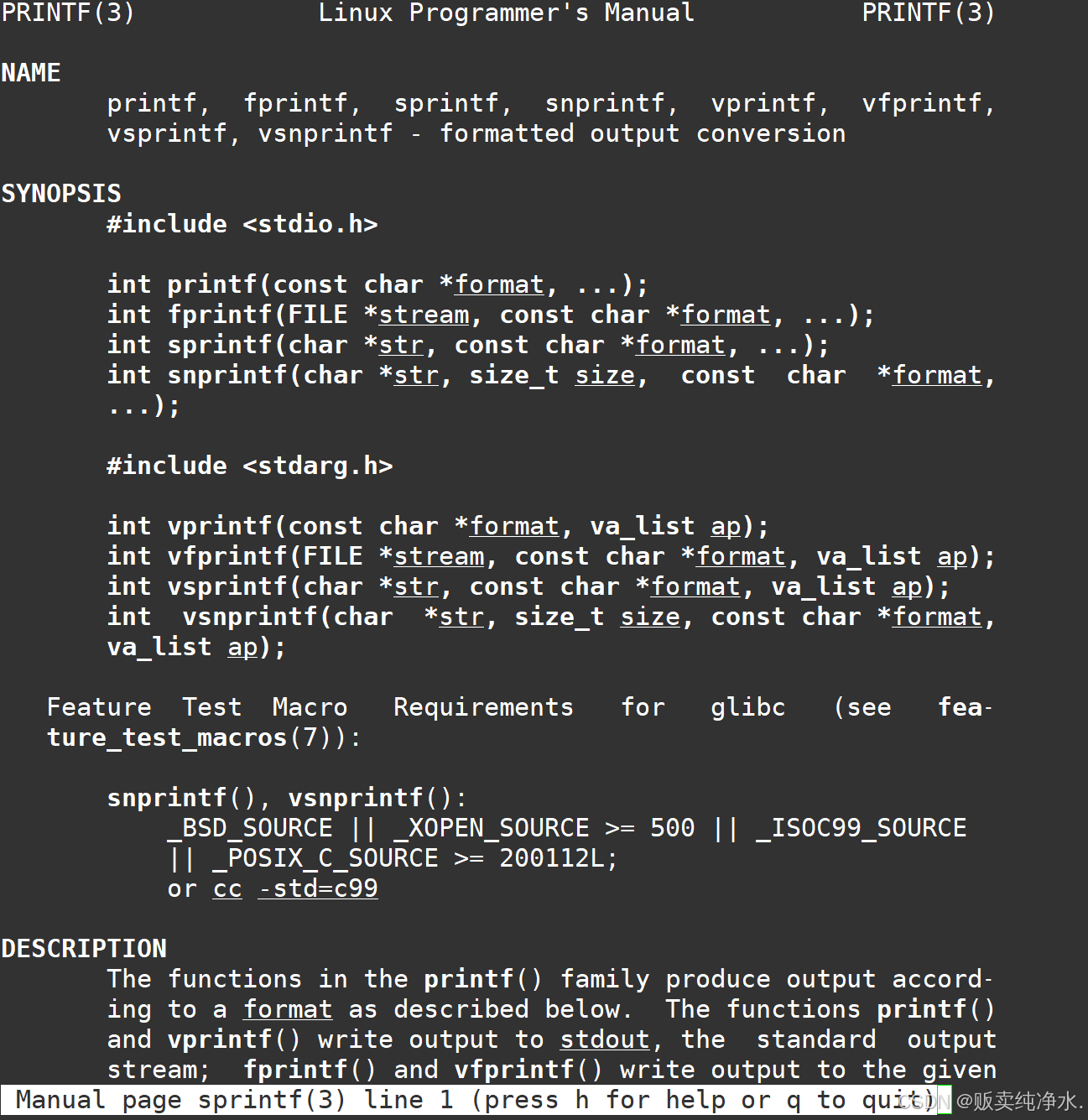
sprintf是个怎样的函数呢?
sprintf是一个可以向内存空间写入的printf
而snprintf是给定大小的更安全的向内存空间中写入的printf(写到缓冲区)
void MakeCommandLine(char line[], size_t size) { const char* username = GetUserName(); const char* hostname = GetHostName(); const char* cwd = GetCwd(); snprintf(line, size, "[%s@%s %s]#", username, hostname, cwd); fflush(stdout); }搞完哩, ,,
![]()
命令行已经输出了,我们需要获取用户的命令
而像ls -a -l -i这种命令本质上是字符串嘞,不能直接用scanf获取,因为scanf空格作为分割,但是我们输入命令是不知道有多少空格的输入,按照行获取有木有?
有哇,fgets啊
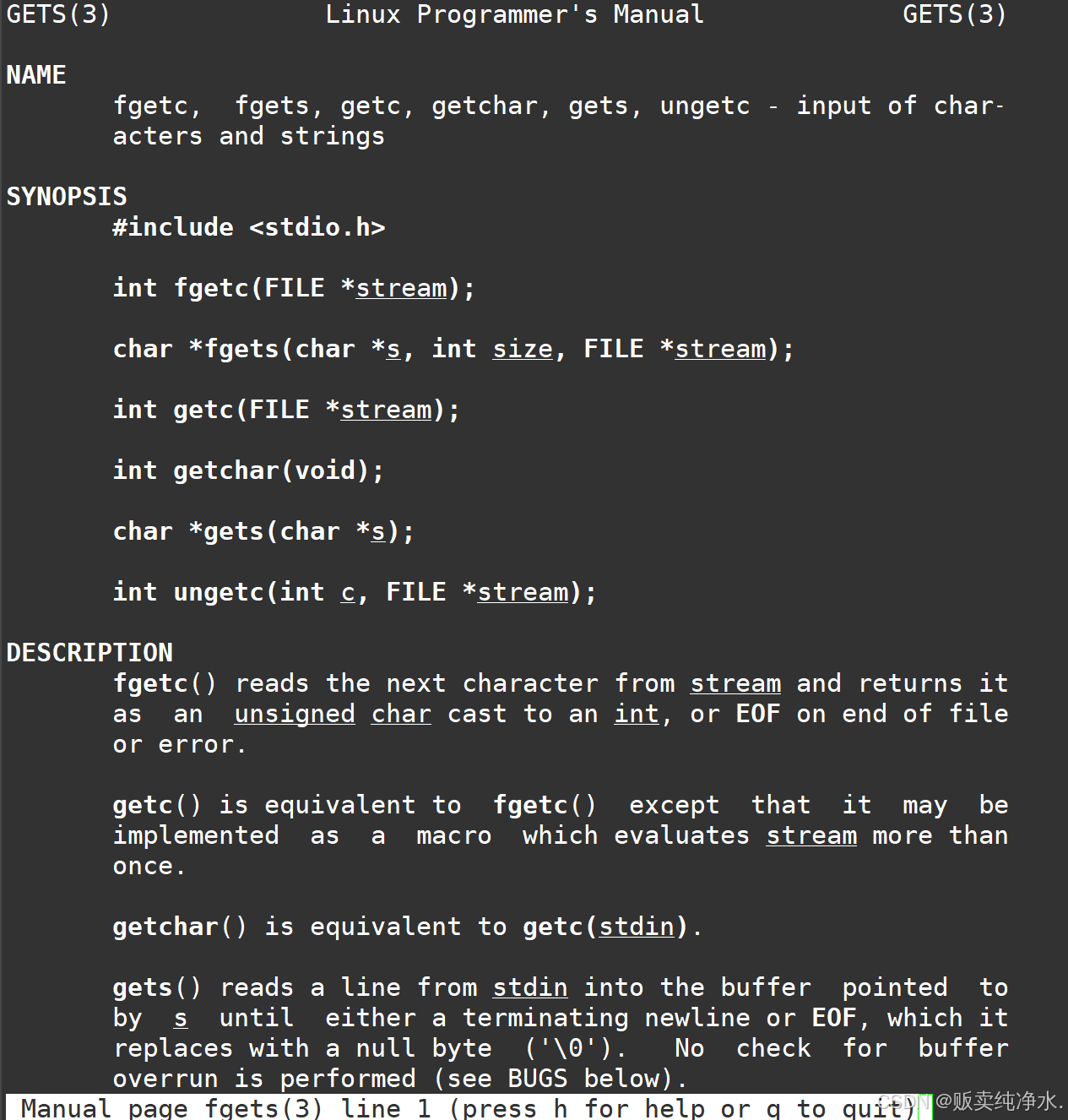
为何偏偏是它
乐意,,,
#include<stdio.h> #include<unistd.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<sys/types.h> #include<sys/wait.h> #define SIZE 512 const char* GetUserName() { const char* name = getenv("USER"); if (name == NULL) { return "None"; } return name; } const char* GetHostName() { const char* hostname = getenv("HOSTNAME"); if (hostname == NULL) { return "None"; } return hostname; } const char* GetCwd() { const char* cwd = getenv("PWD"); if (cwd == NULL) { return "None"; } return cwd; } void MakeCommandLine() { char line[SIZE]; const char* username = GetUserName(); const char* hostname = GetHostName(); const char* cwd = GetCwd(); snprintf(line, sizeof(line), "[%s@%s %s]#", username, hostname, cwd); printf("%s", line); fflush(stdout); } int main() { MakeCommandLine(); char usercommand[SIZE]; char* s = fgets(usercommand, sizeof(usercommand), stdin); if (s == NULL) { return 1; } printf("echo:%s\n", usercommand); return 0; }为什么这多输出了一个空行(因为多有了一个\n啊)
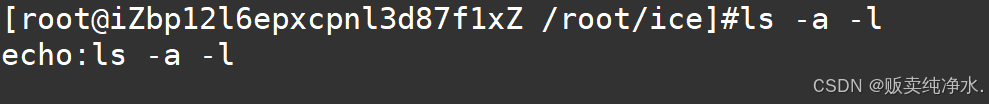
为了剔除这个\n,可以这样干:
#include<stdio.h> #include<unistd.h> #include<string.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<sys/types.h> #include<sys/wait.h> #define SIZE 512 #define ZERO '\0' const char* GetUserName() { const char* name = getenv("USER"); if (name == NULL) { return "None"; } return name; } const char* GetHostName() { const char* hostname = getenv("HOSTNAME"); if (hostname == NULL) { return "None"; } return hostname; } const char* GetCwd() { const char* cwd = getenv("PWD"); if (cwd == NULL) { return "None"; } return cwd; } void MakeCommandLine() { char line[SIZE]; const char* username = GetUserName(); const char* hostname = GetHostName(); const char* cwd = GetCwd(); snprintf(line, sizeof(line), "[%s@%s %s]#", username, hostname, cwd); printf("%s", line); fflush(stdout); } int main() { MakeCommandLine(); char usercommand[SIZE]; char* s = fgets(usercommand, sizeof(usercommand), stdin); if (s == NULL) { return 1; } usercommand[strlen(usercommand) - 1] = ZERO; printf("echo:%s\n", usercommand); return 0; }写成接口就是:
int GetUserCommand(char command[], size_t n) { char* s = fgets(command, n, stdin); if (s == NULL) { return -1; } command[strlen(command) - 1] = ZERO; return strlen(command); }接下来需要做的是命令行字符串分割
我们无需再进行手搓函数,有个函数已经提供了分割的功能了:strtok
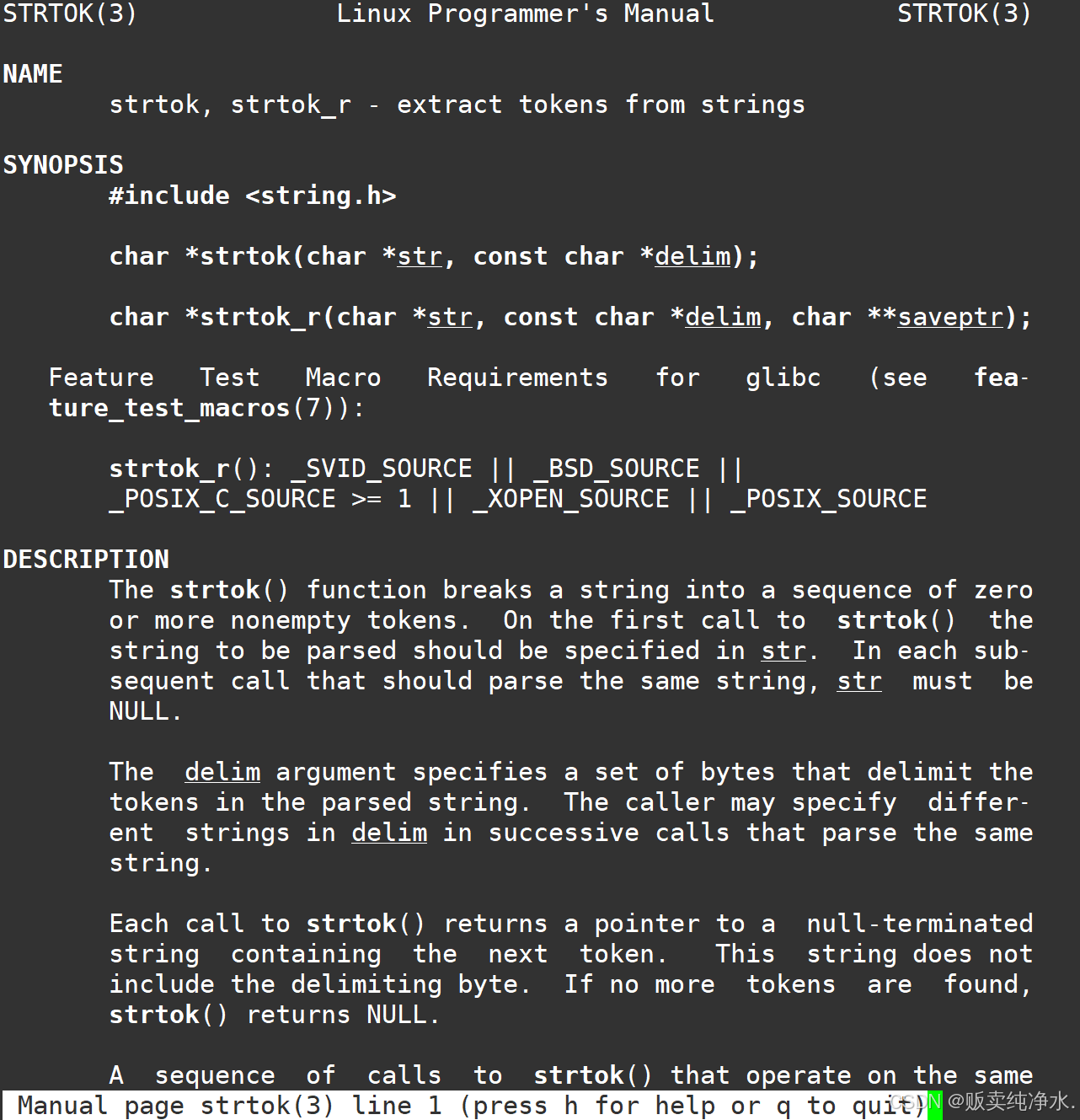
字符串函数们的使用和模拟实现-CSDN博客![]() https://blog.csdn.net/chestnut_orenge/article/details/135351316 这样赋值,先判断,分割后strtok会返回NULL,刚好让gArgv的最后一个元素是NULL,并且while判断结束
https://blog.csdn.net/chestnut_orenge/article/details/135351316 这样赋值,先判断,分割后strtok会返回NULL,刚好让gArgv的最后一个元素是NULL,并且while判断结束
void splitCommand(char command[], size_t n) { gArgv[0] = strtok(command, SEP); int index = 1; while ((gArgv[index++] = strtok(NULL, SEP))); }命令行字符串分割后要执行相应的命令,但是我们不能让该程序执行(代码替换完之后就无了),所以要创建紫禁城帮助我们执行相应的命令
之前学过exec相关函数,我们所获得的命令串都是系统中的,所以默认去环境变量中寻找即可(带p的),又因为获取的是命令串,所以要带v的(容器)
现在大致是这样的:
#include<stdio.h> #include<unistd.h> #include<string.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<sys/types.h> #include<errno.h> #include<sys/wait.h> #define SIZE 512 #define ZERO '\0' #define SEP " " #define NUM 32 void Die() { } const char* GetUserName() { const char* name = getenv("USER"); if (name == NULL) { return "None"; } return name; } const char* GetHostName() { const char* hostname = getenv("HOSTNAME"); if (hostname == NULL) { return "None"; } return hostname; } const char* GetCwd() { const char* cwd = getenv("PWD"); if (cwd == NULL) { return "None"; } return cwd; } void MakeCommandLine() { char line[SIZE]; const char* username = GetUserName(); const char* hostname = GetHostName(); const char* cwd = GetCwd(); snprintf(line, sizeof(line), "[%s@%s %s]#", username, hostname, cwd); printf("%s", line); fflush(stdout); } int GetUserCommand(char command[], size_t n) { char* s = fgets(command, n, stdin); if (s == NULL) { return -1; } command[strlen(command) - 1] = ZERO; return strlen(command); } char* gArgv[NUM]; void splitCommand(char command[], size_t n) { gArgv[0] = strtok(command, SEP); int index = 1; while ((gArgv[index++] = strtok(NULL, SEP))); } int main() { MakeCommandLine(); char usercommand[SIZE]; GetUserCommand(usercommand, sizeof(usercommand)); splitCommand(usercommand, sizeof(usercommand)); for (int i = 0; gArgv[i]; i++) { printf("gArgv[%d]:%s\n", i, gArgv[i]); } pid_t id = fork(); if (id < 0) { Die(); } else if (id == 0) { execvp(gArgv[0], gArgv); exit(errno); } else { int status = 0; pid_t rid = waitpid(id,&status,0); if (rid > 0) { } } return 0; }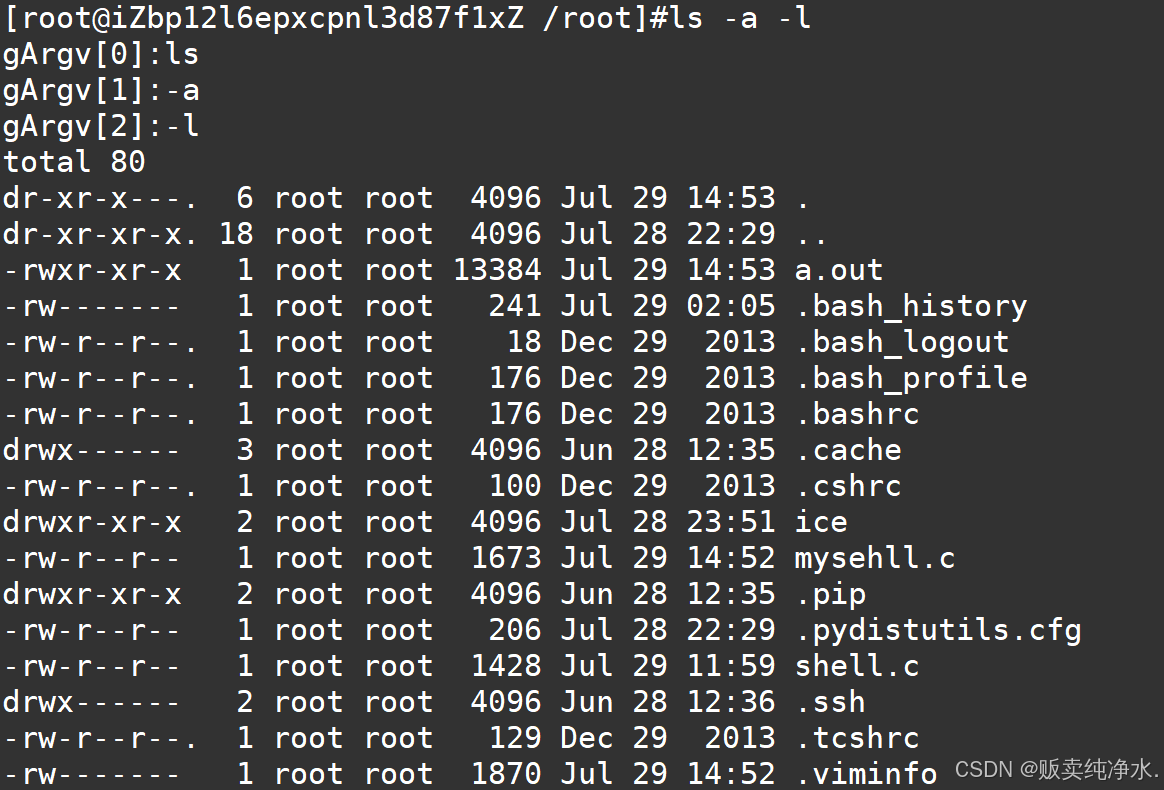
但是我们自己编写的这个shell只能运行一次,我们想要让它一直运行执行命令
于是封装+循环写个简单的shell就好:
#include<stdio.h> #include<unistd.h> #include<string.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<sys/types.h> #include<errno.h> #include<sys/wait.h> #define SIZE 512 #define ZERO '\0' #define SEP " " #define NUM 32 void Die() { } const char* GetUserName() { const char* name = getenv("USER"); if (name == NULL) { return "None"; } return name; } const char* GetHostName() { const char* hostname = getenv("HOSTNAME"); if (hostname == NULL) { return "None"; } return hostname; } const char* GetCwd() { const char* cwd = getenv("PWD"); if (cwd == NULL) { return "None"; } return cwd; } void MakeCommandLine() { char line[SIZE]; const char* username = GetUserName(); const char* hostname = GetHostName(); const char* cwd = GetCwd(); snprintf(line, sizeof(line), "[%s@%s %s]#", username, hostname, cwd); printf("%s", line); fflush(stdout); } int GetUserCommand(char command[], size_t n) { char* s = fgets(command, n, stdin); if (s == NULL) { return -1; } command[strlen(command) - 1] = ZERO; return strlen(command); } char* gArgv[NUM]; void splitCommand(char command[], size_t n) { gArgv[0] = strtok(command, SEP); int index = 1; while ((gArgv[index++] = strtok(NULL, SEP))); } void ExecuteCommand() { pid_t id = fork(); if (id < 0) { Die(); } else if (id == 0) { execvp(gArgv[0], gArgv); exit(errno); } else { int status = 0; pid_t rid = waitpid(id, &status, 0); if (rid > 0) { } } } int main() { int quit = 0; while (!quit) { MakeCommandLine(); char usercommand[SIZE]; GetUserCommand(usercommand, sizeof(usercommand)); splitCommand(usercommand, sizeof(usercommand)); ExecuteCommand(); } return 0; }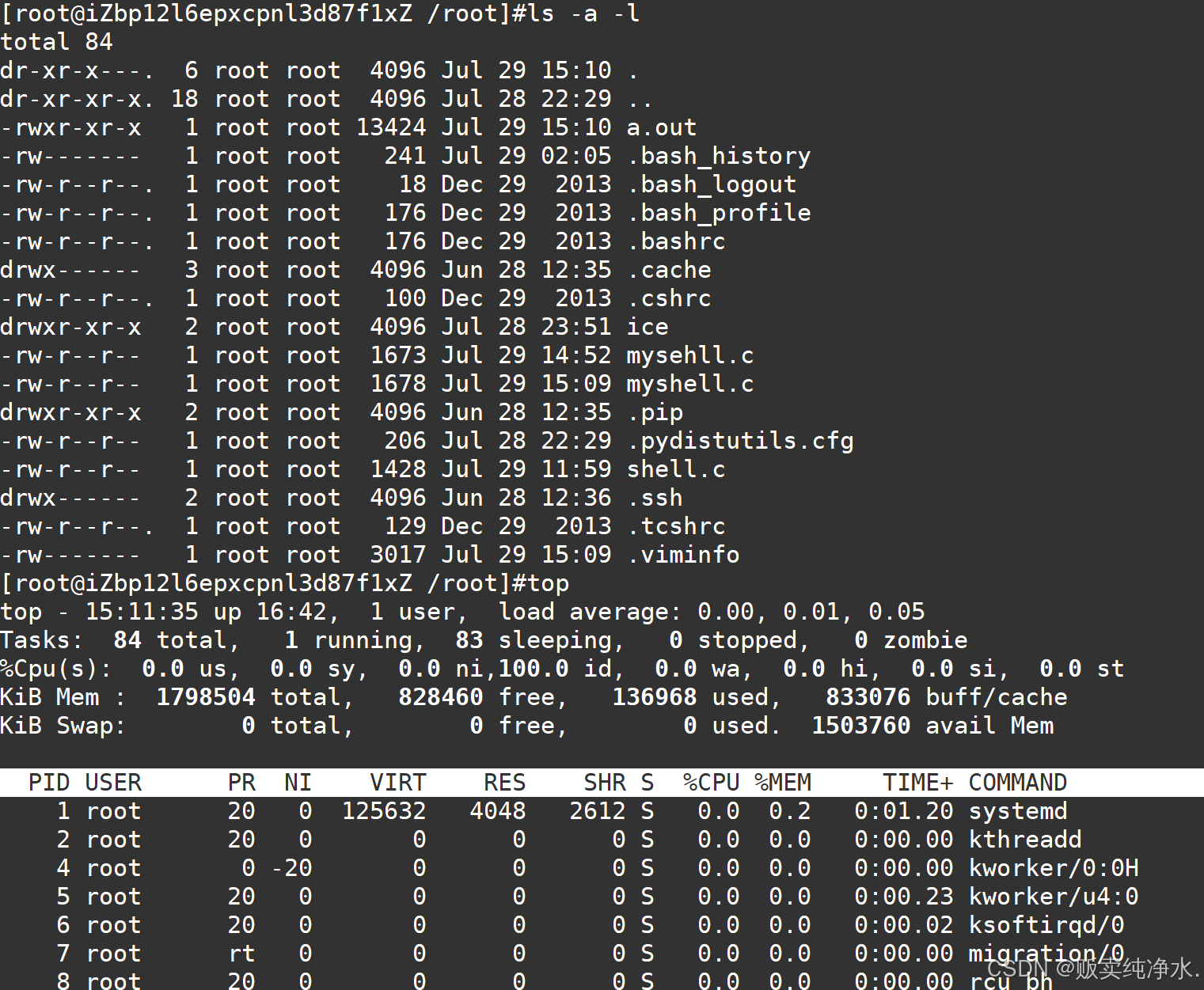
大致没问题,但是有个命令跑起来有问题:cd
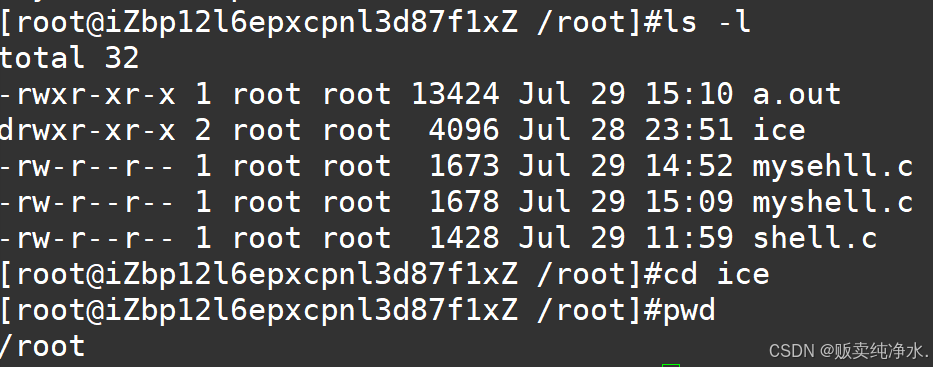
我们的shell没法进行路径的切换和回退
每个进程都会记录自己当前所处的路径(父进程有,紫禁城也有)
紫禁城确实是执行了路径切换的命令,但是和父进程没什么关系,而打印命令行是父进程负责的
我们需要让cd交给父进程去执行,也就是所谓的内建命令
所以我们在执行命令前要检查是否是内建命令,由于命令已经被分割,所以直接检查
在获取完用户命令后,进行切换命令需要用到系统调用的接口chdir
写完了一串代码,会发现cd倒是能用,只不过命令行打印不正常罢了,所以这意味着我们需要对环境变量进行更新
#include<stdio.h> #include<unistd.h> #include<string.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<sys/types.h> #include<errno.h> #include<sys/wait.h> #define SIZE 512 #define ZERO '\0' #define SEP " " #define NUM 32 void Die() { } const char* Home() { const char* home = getenv("HOME"); if (home == NULL) { return "/"; } return home; } void Cd() { const char* path = gArgv[1]; if (path == NULL) { path = Home(); } chdir(path); } const char* GetUserName() { const char* name = getenv("USER"); if (name == NULL) { return "None"; } return name; } const char* GetHostName() { const char* hostname = getenv("HOSTNAME"); if (hostname == NULL) { return "None"; } return hostname; } const char* GetCwd() { const char* cwd = getenv("PWD"); if (cwd == NULL) { return "None"; } return cwd; } void MakeCommandLine() { char line[SIZE]; const char* username = GetUserName(); const char* hostname = GetHostName(); const char* cwd = GetCwd(); snprintf(line, sizeof(line), "[%s@%s %s]#", username, hostname, cwd); printf("%s", line); fflush(stdout); } int GetUserCommand(char command[], size_t n) { char* s = fgets(command, n, stdin); if (s == NULL) { return -1; } command[strlen(command) - 1] = ZERO; return strlen(command); } char* gArgv[NUM]; void splitCommand(char command[], size_t n) { gArgv[0] = strtok(command, SEP); int index = 1; while ((gArgv[index++] = strtok(NULL, SEP))); } void ExecuteCommand() { pid_t id = fork(); if (id < 0) { Die(); } else if (id == 0) { execvp(gArgv[0], gArgv); exit(errno); } else { int status = 0; pid_t rid = waitpid(id, &status, 0); if (rid > 0) { } } } int CheckBuildin() { int yes = 0; const char* enter_cmd = gArgv[0]; if (strcmp(enter_cmd, "cd") == 0) { yes = 1; Cd(); } return yes; } int main() { int quit = 0; while (!quit) { MakeCommandLine(); char usercommand[SIZE]; int n = GetUserCommand(usercommand, sizeof(usercommand)); if (n < 0) { return 1; } splitCommand(usercommand, sizeof(usercommand)); n = CheckBuildin(); if (n) { continue; } ExecuteCommand(); } return 0; }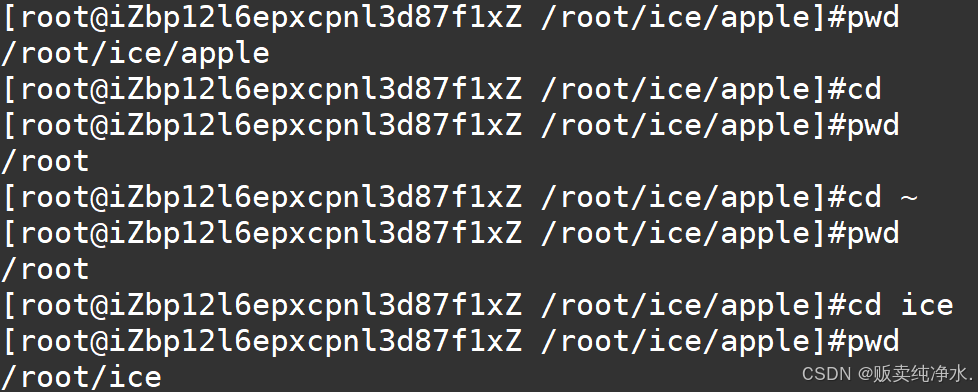
需要注意的是,我们需要刷新环境变量,以保证出来的都是绝对路径
改完之后除了cd -不支持,其他都支持(cd -需要保存最近一次所处路径)
#include<stdio.h> #include<unistd.h> #include<string.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<sys/types.h> #include<errno.h> #include<sys/wait.h> #define SIZE 512 #define ZERO '\0' #define SEP " " #define NUM 32 char cwd[SIZE * 2]; char* gArgv[NUM]; void Die() { exit(1); } const char* Home() { const char* home = getenv("HOME"); if (home == NULL) { return "/"; } return home; } void Cd() { const char* path = gArgv[1]; if (path == NULL) { path = Home(); } chdir(path); char temp[SIZE * 2]; getcwd(temp, sizeof(temp)); snprintf(cwd, sizeof(cwd), "PWD=%s", temp); putenv(cwd); } const char* GetUserName() { const char* name = getenv("USER"); if (name == NULL) { return "None"; } return name; } const char* GetHostName() { const char* hostname = getenv("HOSTNAME"); if (hostname == NULL) { return "None"; } return hostname; } const char* GetCwd() { const char* cwd = getenv("PWD"); if (cwd == NULL) { return "None"; } return cwd; } void MakeCommandLine() { char line[SIZE]; const char* username = GetUserName(); const char* hostname = GetHostName(); const char* cwd = GetCwd(); snprintf(line, sizeof(line), "[%s@%s %s]#", username, hostname, cwd); printf("%s", line); fflush(stdout); } int GetUserCommand(char command[], size_t n) { char* s = fgets(command, n, stdin); if (s == NULL) { return -1; } command[strlen(command) - 1] = ZERO; return strlen(command); } void splitCommand(char command[], size_t n) { gArgv[0] = strtok(command, SEP); int index = 1; while ((gArgv[index++] = strtok(NULL, SEP))); } void ExecuteCommand() { pid_t id = fork(); if (id < 0) { Die(); } else if (id == 0) { execvp(gArgv[0], gArgv); exit(errno); } else { int status = 0; pid_t rid = waitpid(id, &status, 0); if (rid > 0) { } } } int CheckBuildin() { int yes = 0; const char* enter_cmd = gArgv[0]; if (strcmp(enter_cmd, "cd") == 0) { yes = 1; Cd(); } return yes; } int main() { int quit = 0; while (!quit) { MakeCommandLine(); char usercommand[SIZE]; int n = GetUserCommand(usercommand, sizeof(usercommand)); if (n < 0) { return 1; } splitCommand(usercommand, sizeof(usercommand)); n = CheckBuildin(); if (n) { continue; } ExecuteCommand(); } return 0; }插个眼我很好奇为什么编译不过去
我们自己创建的shell在打印命令行的时候保存的是一串路径,但是正常的shell在保存路径的时候只会保存当前路径,那应该怎么办捏?
就是设个指针让它前移,但是需要做一些特殊处理,在一般情况下打印路径分割符后的内容,在特殊情况下只打印路径分隔符
使用宏是因为要单独对指针进行操作
用do...while(0)是因为可以形成代码块,且do...while(0)后面可加;
在使用时可当做函数,且可应对分支情况的出现
然后还需要接着判断其他的内建命令
#include<stdio.h> #include<unistd.h> #include<string.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<sys/types.h> #include<errno.h> #include<sys/wait.h> #define SkipPath(p) do{ p += (strlen(p) - 1); while (*p != '/')p--;}while(0) #define SIZE 512 #define ZERO '\0' #define SEP " " #define NUM 32 char cwd[SIZE * 2]; char* gArgv[NUM]; void Die() { exit(1); } const char* Home() { const char* home = getenv("HOME"); if (home == NULL) { return "/"; } return home; } void Cd() { const char* path = gArgv[1]; if (path == NULL) { path = Home(); } chdir(path); char temp[SIZE * 2]; getcwd(temp, sizeof(temp)); snprintf(cwd, sizeof(cwd), "PWD=%s", temp); putenv(cwd); } const char* GetUserName() { const char* name = getenv("USER"); if (name == NULL) { return "None"; } return name; } const char* GetHostName() { const char* hostname = getenv("HOSTNAME"); if (hostname == NULL) { return "None"; } return hostname; } const char* GetCwd() { const char* cwd = getenv("PWD"); if (cwd == NULL) { return "None"; } return cwd; } void MakeCommandLine() { char line[SIZE]; const char* username = GetUserName(); const char* hostname = GetHostName(); const char* cwd = GetCwd(); SkipPath(cwd); snprintf(line, sizeof(line), "[%s@%s %s]#", username, hostname, strlen(cwd) == 1 ? "/" : cwd + 1); printf("%s", line); fflush(stdout); } int GetUserCommand(char command[], size_t n) { char* s = fgets(command, n, stdin); if (s == NULL) { return -1; } command[strlen(command) - 1] = ZERO; return strlen(command); } void splitCommand(char command[], size_t n) { gArgv[0] = strtok(command, SEP); int index = 1; while ((gArgv[index++] = strtok(NULL, SEP))); } void ExecuteCommand() { pid_t id = fork(); if (id < 0) { Die(); } else if (id == 0) { execvp(gArgv[0], gArgv); exit(errno); } else { int status = 0; pid_t rid = waitpid(id, &status, 0); if (rid > 0) { } } } int CheckBuildin() { int yes = 0; const char* enter_cmd = gArgv[0]; if (strcmp(enter_cmd, "cd") == 0) { yes = 1; Cd(); } return yes; } int main() { int quit = 0; while (!quit) { MakeCommandLine(); char usercommand[SIZE]; int n = GetUserCommand(usercommand, sizeof(usercommand)); if (n < 0) { return 1; } splitCommand(usercommand, sizeof(usercommand)); n = CheckBuildin(); if (n) { continue; } ExecuteCommand(); } return 0; }判断echo命令
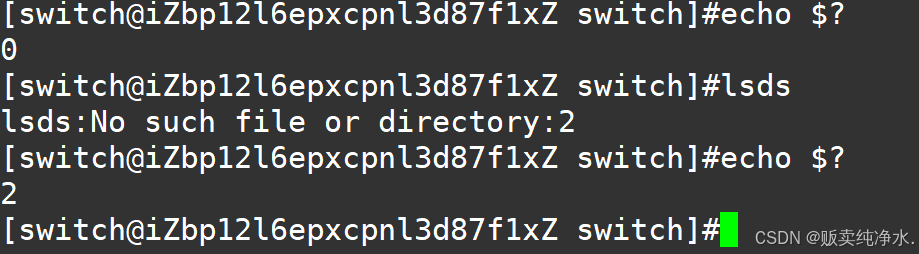
这是记录最近一次的返回值(echo $?)啊麻烦死了自己实现shell
忙活半天只能做个青春版,还不能查历史输入的命令
#include<stdio.h> #include<unistd.h> #include<string.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<sys/types.h> #include<errno.h> #include<sys/wait.h> #define SkipPath(p) do{ p += (strlen(p) - 1); while (*p != '/')p--;}while(0) #define SIZE 512 #define ZERO '\0' #define SEP " " #define NUM 32 int lastcode = 1; char cwd[SIZE * 2]; char* gArgv[NUM]; void Die() { exit(1); } const char* Home() { const char* home = getenv("HOME"); if (home == NULL) { return "/"; } return home; } void Cd() { const char* path = gArgv[1]; if (path == NULL) { path = Home(); } chdir(path); char temp[SIZE * 2]; getcwd(temp, sizeof(temp)); snprintf(cwd, sizeof(cwd), "PWD=%s", temp); putenv(cwd); } const char* GetUserName() { const char* name = getenv("USER"); if (name == NULL) { return "None"; } return name; } const char* GetHostName() { const char* hostname = getenv("HOSTNAME"); if (hostname == NULL) { return "None"; } return hostname; } const char* GetCwd() { const char* cwd = getenv("PWD"); if (cwd == NULL) { return "None"; } return cwd; } void MakeCommandLine() { char line[SIZE]; const char* username = GetUserName(); const char* hostname = GetHostName(); const char* cwd = GetCwd(); SkipPath(cwd); snprintf(line, sizeof(line), "[%s@%s %s]#", username, hostname, strlen(cwd) == 1 ? "/" : cwd + 1); printf("%s", line); fflush(stdout); } int GetUserCommand(char command[], size_t n) { char* s = fgets(command, n, stdin); if (s == NULL) { return -1; } command[strlen(command) - 1] = ZERO; return strlen(command); } void splitCommand(char command[], size_t n) { gArgv[0] = strtok(command, SEP); int index = 1; while ((gArgv[index++] = strtok(NULL, SEP))); } void ExecuteCommand() { pid_t id = fork(); if (id < 0) { Die(); } else if (id == 0) { execvp(gArgv[0], gArgv); exit(errno); } else { int status = 0; pid_t rid = waitpid(id, &status, 0); if (rid > 0) { lastcode = WEXITSTATUS(status); if (lastcode != 0) { printf("%s:%s:%d\n", gArgv[0], strerror(lastcode), lastcode); } } } } int CheckBuildin() { int yes = 0; const char* enter_cmd = gArgv[0]; if (strcmp(enter_cmd, "cd") == 0) { yes = 1; Cd(); } else if (strcmp(enter_cmd, "echo") == 0 && strcmp(gArgv[1], "$?") == 0) { yes = 1; printf("%d\n", lastcode); lastcode = 0; } return yes; } int main() { int quit = 0; while (!quit) { MakeCommandLine(); char usercommand[SIZE]; int n = GetUserCommand(usercommand, sizeof(usercommand)); if (n < 0) { return 1; } splitCommand(usercommand, sizeof(usercommand)); n = CheckBuildin(); if (n) { continue; } ExecuteCommand(); } return 0; }在shell中建立环境变量表也是默认创建指针
是一个缓冲区,可以自己申请,环境变量表是char* env[32],而定义开个空间就直接自己设置就好:
char** env = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char*)*32);自己写个shell就对它怎样执行命令认识的更加深刻了
