java:EasyExcel使用(一)读excel
1 前言
EasyExcel相比于传统使用poi进行excel文件读写,编程使用操作上更加方便快捷,且对于内存溢出进行了优化处理。本文是EasyExcel读excel操作。
Java解析、生成Excel比较有名的框架有Apache poi、jxl。但他们都存在一个严重的问题就是非常的耗内存,poi有一套SAX模式的API可以一定程度的解决一些内存溢出的问题,但POI还是有一些缺陷,比如07版Excel解压缩以及解压后存储都是在内存中完成的,内存消耗依然很大。
easyexcel重写了poi对07版Excel的解析,一个3M的excel用POI sax解析依然需要100M左右内存,改用easyexcel可以降低到几M,并且再大的excel也不会出现内存溢出;03版依赖POI的sax模式,在上层做了模型转换的封装,让使用者更加简单方便。
EasyExcel官方文档:
https://easyexcel.opensource.alibaba.com/ 进入maven.org,自动跳转如下进行maven仓库查询:
https://central.sonatype.com/?smo=true 搜索easyexcel:
pom文件添加如下依赖:
<dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>easyexcel</artifactId> <version>3.3.4</version> </dependency> 2 使用(Excel读取)
2.1 读Excel
GoodsDto:
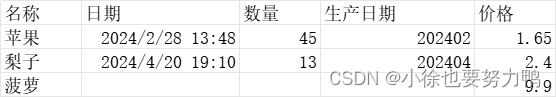
package com.xiaoxu.excel.readE; import lombok.EqualsAndHashCode; import lombok.Getter; import lombok.Setter; import java.util.Date; /** * @author xiaoxu * @date 2024-04-26 22:32 * learn_java:com.xiaoxu.excel.readE.GoodsDto */ @Getter @Setter @EqualsAndHashCode public class GoodsDto { private String name; private Date date; private long count; private Date produceDate; private double price; } 在桌面准备的excel文件,test.xlsx:
excel读取方式一:
TestExcelRead,读取excel(JDK8.0+,不用额外写ReadListener,since: 3.0.0-beta1):
package com.xiaoxu.excel.readE; import com.alibaba.excel.EasyExcel; import com.alibaba.excel.read.listener.PageReadListener; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON; import javax.swing.filechooser.FileSystemView; import java.io.File; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; /** * @author xiaoxu * @date 2024-04-27 14:53 * learn_java:com.xiaoxu.excel.readE.TestExcelRead */ public class TestExcelRead { public static void main(String[] args) { // C:\Users\****\Desktop File homeDirectory = FileSystemView .getFileSystemView().getHomeDirectory(); String fileName = "test"; // 读取桌面路径excel文件 String file = homeDirectory.getAbsolutePath() + File.separator + fileName + ".xlsx"; EasyExcel.read(file, GoodsDto.class, new PageReadListener<GoodsDto>(dataList -> { for (GoodsDto goodsDto : dataList) { System.out.println("读取到excel数据:" + JSON.toJSONString(goodsDto)); SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat( "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS"); if (null != goodsDto.getDate()) { System.out.println("日期:" + sdf.format(goodsDto.getDate())); } if (null != goodsDto.getProduceDate()) { System.out.println("生产日期:" + sdf.format(goodsDto.getProduceDate())); } } })).sheet().doRead(); } } 执行excel读取结果如下:
读取到excel数据: {"count":45,"date":1709099280000, "name":"苹果","price":1.65,"produceDate":15278342400000} 日期:2024-02-28 13:48:00.000 生产日期:2454-02-25 00:00:00.000 读取到excel数据:{"count":13,"date":1713611400000, "name":"梨子","price":2.4,"produceDate":15278515200000} 日期:2024-04-20 19:10:00.000 生产日期:2454-02-27 00:00:00.000 读取到excel数据:{"count":0,"name":"菠萝","price":9.9} 日期转换说明,需要按照excel的日期格式来写,
上述结果表明,如果是引用类型,那么excel的cell值为null时,不会为实体类赋值;如果实体类是primitive类型数据,同时excel的cell值为null时,会将null转换成该primitive的默认值,比如实体类的count属性为long时,默认值就是0,所以也会赋值(因为包装类的值为null时,直接转换成primitive类型值时,不可以为其赋值为null,必须转换成其对应的默认值,否则将会抛出异常)。
同时注意,上述的实体类的字段,和excel的每一列是按顺序一一对应定义的。否则可能会抛出ExcelDataConvertException转换异常(Excel的值类型需要和实体类字段类型一一对应)。
excel读取方式二:
TestExcelRead2,读取excel(定义监听器GoodsDtoListener读取excel):
GoodsDtoListener:
package com.xiaoxu.excel.readE; import com.alibaba.excel.context.AnalysisContext; import com.alibaba.excel.read.listener.ReadListener; import com.alibaba.excel.util.ListUtils; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON; import java.util.List; /** * @author xiaoxu * @date 2024-04-26 22:42 * learn_java:com.xiaoxu.excel.readE.GoodsDtoListener */ public class GoodsDtoListener implements ReadListener<GoodsDto> { /** * 每隔5条存储数据库,实际使用中可以100条,然后清理list ,方便内存回收 */ private static final int BATCH_COUNT = 100; /** * 缓存数据 */ private List<GoodsDto> cache = ListUtils .newArrayListWithExpectedSize(BATCH_COUNT); /** * 假设这个是一个DAO, * 当然有业务逻辑这个也可以是一个service。 * 当然如果不用存储这个对象没用。 */ private GoodsDAO goodsDAO; public GoodsDtoListener() { // 这里是demo,所以随便new一个。 // 实际使用如果到了spring,请使用下面的有参构造函数 this.goodsDAO = new GoodsDAO(); } public GoodsDtoListener(GoodsDAO goodsDAO) { // 如果使用了spring,请使用这个构造方法。 // 每次创建Listener的时候需要把spring管理的类传进来 this.goodsDAO = goodsDAO; } /** * @param goodsDto one row value. * Is is same * as {@link AnalysisContext#readRowHolder()} * @param analysisContext 这个每一条数据解析都会来调用 */ @Override public void invoke(GoodsDto goodsDto, AnalysisContext analysisContext) { System.out.println( String.format( "解析到数据: %s.", JSON.toJSONString(goodsDto))); cache.add(goodsDto); // 达到BATCH_COUNT了,需要去存储一次数据库, // 防止数据几万条数据在内存,容易OOM if (cache.size() >= BATCH_COUNT) { saveData(); // cache置为空List,方便gc work cache = ListUtils.newArrayListWithExpectedSize(BATCH_COUNT); } } private void saveData() { System.out.println("开始存储数据数数据:" + cache.size()); goodsDAO.save(cache); } /** * @param analysisContext 所有数据处理完,调用这里 */ @Override public void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext analysisContext) { // 这里也要保存数据, // 确保最后遗留的数据也存储到数据库 System.out.println("最终数据存储:"); saveData(); System.out.println("所有数据解析完成!"); } } GoodsDAO :
public class GoodsDAO { public void save(List<GoodsDto> goodsDtoList) { // 如果是mybatis,尽量别直接调用多次insert, // 自己写一个mapper里面新增一个方法batchInsert, // 所有数据一次性插入 // batchInsert的插入性能更好 System.out.println("存储数据成功~"); } } TestExcelRead2:
package com.xiaoxu.excel.readE; import com.alibaba.excel.EasyExcel; import javax.swing.filechooser.FileSystemView; import java.io.File; /** * @author xiaoxu * @date 2024-04-27 16:37 * learn_java:com.xiaoxu.excel.readE.TestExcelRead2 */ public class TestExcelRead2 { public static void main(String[] args) { // C:\Users\****\Desktop File homeDirectory = FileSystemView .getFileSystemView().getHomeDirectory(); String fileName = "test"; // 读取桌面路径excel文件 String file = homeDirectory.getAbsolutePath() + File.separator + fileName + ".xlsx"; // 有个很重要的点 GoodsDtoListener 不能被spring管理, // 要每次读取excel都要new,然后里面用到spring可以构造方法传进去 // excel有多个Sheet,可以通过 .sheet("Sheet1")指定sheet名称 // 或者可以通过.sheet(0)指定读取第1个sheet // 如果sheet名称不存在,那么不会报错,也不会读取到数据 EasyExcel.read(file, GoodsDto.class, new GoodsDtoListener()) .sheet("Sheet1").doRead(); } } 执行结果如下:
解析到数据: {"count":45,"date":1709099280000, "name":"苹果","price":1.65,"produceDate":1746545644800000}. 解析到数据: {"count":13,"date":1713611400000, "name":"梨子","price":2.4,"produceDate":1746563788800000}. 解析到数据: {"count":0,"name":"菠萝","price":9.9}. 最终数据存储: 开始存储数据数数据:3 存储数据成功~ 所有数据解析完成! 注意:excel文件有多个sheet时,.sheet()表示读取第1个sheet的内容。若需要指定sheet名称读取,则使用.sheet(“Sheet1”)即可指定名称为Sheet1的sheet进行读取,若不知道sheet名称,那么可以通过.sheet(0)读取第1个sheet,.sheet(1)读取第2个sheet等等的方式来进行读取,下标从0开始。如果sheet的名称不存在,或者sheet的索引下标不存在(比如总共只有3个sheet,但是读取为.sheet(3)第4个sheet)时,不会抛出异常,只是无法读取到对应数据。并且EasyExcel读取sheet的数据时,表头不会进入Listener回调中,而是从第二行的内容数据开始进入回调。
excel读取方式三:
TestExcelRead3,读取excel(通过ExcelReader、ReadSheet读取excel文件):
package com.xiaoxu.excel.readE; import com.alibaba.excel.EasyExcel; import com.alibaba.excel.ExcelReader; import com.alibaba.excel.read.metadata.ReadSheet; import javax.swing.filechooser.FileSystemView; import java.io.File; /** * @author xiaoxu * @date 2024-04-27 19:32 * learn_java:com.xiaoxu.excel.readE.TestExcelRead3 */ public class TestExcelRead3 { public static void main(String[] args) { // C:\Users\****\Desktop File homeDirectory = FileSystemView .getFileSystemView().getHomeDirectory(); String fileName = "test"; // 读取桌面路径excel文件 String file = homeDirectory.getAbsolutePath() + File.separator + fileName + ".xlsx"; // 一个文件一个reader try (ExcelReader excelReader = EasyExcel .read(file, GoodsDto.class, new GoodsDtoListener()).build()) { // 构建一个sheet 这里可以指定名字或者no ReadSheet readSheet = EasyExcel.readSheet(0).build(); // 读取一个sheet excelReader.read(readSheet); } } } 读取结果同读取方式二一致。
2.2 指定列的下标或者列名
前面提到了,实体类的字段必须按照顺序和excel的列一一对应,否则可能出现转换异常或者赋值与实际字段不匹配的情况。但是这种情况也有解决方式,即使用EasyExcel提供的@ExcelProperty注解。
GoodsDtoProperty:
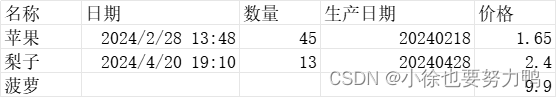
package com.xiaoxu.excel.cols; import com.alibaba.excel.annotation.ExcelProperty; import lombok.EqualsAndHashCode; import lombok.Getter; import lombok.Setter; import java.util.Date; /** * @author xiaoxu * @date 2024-04-27 20:36 * learn_java:com.xiaoxu.excel.cols.GoodsDtoPropertty */ @Getter @Setter @EqualsAndHashCode public class GoodsDtoProperty { // 注解的默认值是value,这里表示excel的表头的列名称 @ExcelProperty("售卖日期") private Date date; @ExcelProperty(index = 99) private long count; private Date produceDate; // index表示读取第几列,0表示第一列,1表示第二列... // 这里price属性是实体类第四个属性,没有 @ExcelProperty表示和第4列对应 // 这里表示和excel的第5列对应 @ExcelProperty(index = 4) private double price; @ExcelProperty(value = "名称") private String name; } excel数据如下:
TestExcelReadProp:
package com.xiaoxu.excel.cols; import com.alibaba.excel.EasyExcel; import com.alibaba.excel.read.listener.PageReadListener; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON; import javax.swing.filechooser.FileSystemView; import java.io.File; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; /** * @author xiaoxu * @date 2024-04-27 20:46 * learn_java:com.xiaoxu.excel.cols.TestExcelReadProp */ public class TestExcelReadProp { public static void main(String[] args) { // C:\Users\****\Desktop File homeDirectory = FileSystemView .getFileSystemView().getHomeDirectory(); String fileName = "test"; // 读取桌面路径excel文件 String file = homeDirectory.getAbsolutePath() + File.separator + fileName + ".xlsx"; EasyExcel.read(file, GoodsDtoProperty.class, new PageReadListener<GoodsDtoProperty>(dataList -> { for (GoodsDtoProperty goodsDtoProp : dataList) { System.out.println("读取到excel数据:" + JSON.toJSONString(goodsDtoProp)); SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat( "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS"); if (null != goodsDtoProp.getDate()) { System.out.println("日期:" + sdf.format(goodsDtoProp.getDate())); } if (null != goodsDtoProp.getProduceDate()) { System.out.println("生产日期:" + sdf.format(goodsDtoProp.getProduceDate())); } } })).sheet().doRead(); } } 执行结果:
读取到excel数据:{"count":0,"name":"苹果", "price":1.65,"produceDate":1709099280000} 生产日期:2024-02-28 13:48:00.000 读取到excel数据:{"count":0,"name":"梨子", "price":2.4,"produceDate":1713611400000} 生产日期:2024-04-20 19:10:00.000 读取到excel数据:{"count":0,"name":"菠萝","price":9.9} 上述表明,如果实体类中使用了@ExcelProperty注解,那么最好是全部属性都加上,这样方便和excel需要的属性列一一对应,否则可能出现部分值胡乱匹配excel列值的情况。同时,如果注解的value值随意填写,即excel的匹配列名不存在,或者index超越索引上限,都不会报错。同时index索引也是从0开始,0表示excel的第1列,1表示excel的第2列,以此类推。
2.3 读多个sheet
2.3.1 读取全部sheet
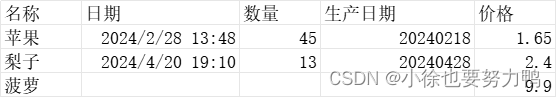
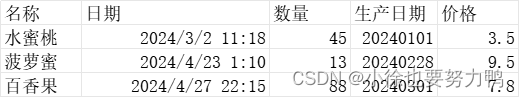
准备excel文件中存在多个Sheet,文件为test3.xlsx:
Sheet1:
Sheet2:
提取读取桌面文件工具类:
package com.xiaoxu.excel; import javax.swing.filechooser.FileSystemView; import java.io.File; /** * @author xiaoxu * @date 2024-04-27 22:00 * learn_java:com.xiaoxu.excel.DeskTool */ public class DeskTool { public static String getPath(String fileName) { // C:\Users\****\Desktop File homeDirectory = FileSystemView .getFileSystemView().getHomeDirectory(); // 读取桌面路径excel文件 return homeDirectory.getAbsolutePath() + File.separator + fileName + ".xlsx"; } } GoodsDtoNew:
package com.xiaoxu.excel.multiSht; import com.alibaba.excel.annotation.ExcelProperty; import lombok.EqualsAndHashCode; import lombok.Getter; import lombok.Setter; import java.util.Date; /** * @author xiaoxu * @date 2024-04-27 22:17 * learn_java:com.xiaoxu.excel.multiSht.GoodsDtoNew */ @Getter @Setter @EqualsAndHashCode public class GoodsDtoNew { // 注解的默认值是value,这里表示excel的表头的列名称 @ExcelProperty("日期") private Date date; @ExcelProperty("生产日期") private Date produceDate; @ExcelProperty("价格") private double price; @ExcelProperty("数量") private long count; @ExcelProperty(value = "名称") private String name; } GoodsDtoNewListener:
package com.xiaoxu.excel.multiSht; import com.alibaba.excel.context.AnalysisContext; import com.alibaba.excel.read.listener.ReadListener; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON; /** * @author xiaoxu * @date 2024-04-27 22:20 * learn_java:com.xiaoxu.excel.multiSht.GoodsDtoNewListener */ public class GoodsDtoNewListener implements ReadListener<GoodsDtoNew> { @Override public void invoke(GoodsDtoNew goodsDtoNew, AnalysisContext analysisContext) { System.out.println("扫描数据:" + JSON.toJSONString(goodsDtoNew)); } @Override public void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext analysisContext) { System.out.println("所有数据解析完成!"); } } TestExcelReadMultiSheetAll:
package com.xiaoxu.excel.multiSht; import com.alibaba.excel.EasyExcel; import com.xiaoxu.excel.DeskTool; /** * @author xiaoxu * @date 2024-04-27 21:57 * learn_java:com.xiaoxu.excel.multiSht.TestExcelReadMultiSheetAll */ public class TestExcelReadMultiSheetAll { public static void main(String[] args) { String file = DeskTool.getPath("test3"); // 读取全部sheet // 这里需要注意 GoodsDtoNewListener的doAfterAllAnalysed // 会在每个sheet读取完毕后调用一次。 // 然后所有sheet都会往同一个GoodsDtoNewListener里面写(或者读) EasyExcel.read(file, GoodsDtoNew.class, new GoodsDtoNewListener()) .doReadAll(); } } 执行结果:
扫描数据:{"count":45,"date":1709099280000, "name":"苹果","price":1.65,"produceDate":1746545644800000} 扫描数据:{"count":13,"date":1713611400000, "name":"梨子","price":2.4,"produceDate":1746563788800000} 扫描数据:{"count":0,"name":"菠萝","price":9.9} 所有数据解析完成! 扫描数据:{"count":45,"date":1709349480000, "name":"水蜜桃","price":3.5,"produceDate":1746535536000000} 扫描数据:{"count":13,"date":1713805800000, "name":"菠萝蜜","price":9.5,"produceDate":1746546508800000} 扫描数据:{"count":88,"date":1714227300000, "name":"百香果","price":7.8,"produceDate":1746552816000000} 所有数据解析完成! 所有数据解析完成! 上述表明,doReadAll()方法会处理全部的Sheet数据,且全部sheet的数据是同一个listener处理的,并且doAfterAllAnalysed()最终读取完毕的回调方法,3个sheet分别调用了3次(因为上述的excel文件还有一个空的Sheet3)。
2.3.2 读取部分sheet
准备excel文件中存在多个Sheet,多个Sheet结构不同(对应不同监听器),文件为test2.xlsx:
Sheet1:
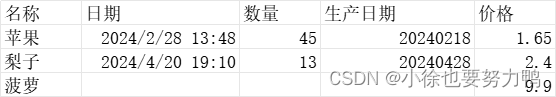
Sheet2:

MerchantDto:
package com.xiaoxu.excel.multiSht; import com.alibaba.excel.annotation.ExcelProperty; import lombok.EqualsAndHashCode; import lombok.Getter; import lombok.Setter; /** * @author xiaoxu * @date 2024-04-28 8:23 * learn_java:com.xiaoxu.excel.multiSht.MerchantDto */ @Getter @Setter @EqualsAndHashCode public class MerchantDto { @ExcelProperty("商户名称") private String merchantName; @ExcelProperty("商户库存") private long merchantInventory; } MerchantDtoListener:
package com.xiaoxu.excel.multiSht; import com.alibaba.excel.context.AnalysisContext; import com.alibaba.excel.read.listener.ReadListener; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON; /** * @author xiaoxu * @date 2024-04-28 8:25 * learn_java:com.xiaoxu.excel.multiSht.MerchantDtoListener */ public class MerchantDtoListener implements ReadListener<MerchantDto> { @Override public void invoke(MerchantDto merchantDto, AnalysisContext analysisContext) { System.out.println("扫描商户数据:" + JSON.toJSONString(merchantDto)); } @Override public void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext analysisContext) { System.out.println("商户所有数据解析完成!"); } } TestExcelReadMultiSheet:
package com.xiaoxu.excel.multiSht; import com.alibaba.excel.EasyExcel; import com.alibaba.excel.ExcelReader; import com.alibaba.excel.read.metadata.ReadSheet; import com.xiaoxu.excel.DeskTool; /** * @author xiaoxu * @date 2024-04-27 21:56 * learn_java:com.xiaoxu.excel.multiSht.TestExcelReadMultiSheet */ public class TestExcelReadMultiSheet { public static void main(String[] args) { String file = DeskTool.getPath("test2"); // 一个文件一个reader try (ExcelReader excelReader = EasyExcel .read(file).build()) { // 可以注册同样的head和Listener 自己使用功能使用不同的Listener // 构建一个sheet 这里可以指定名字或者no ReadSheet readSheet = EasyExcel.readSheet(0) .head(GoodsDtoNew.class) .registerReadListener(new GoodsDtoNewListener()) .build(); ReadSheet readSheet2 = EasyExcel.readSheet(1) .head(MerchantDto.class) .registerReadListener(new MerchantDtoListener()) .build(); // 这里注意 一定要把sheet1 sheet2 一起传进去, // 不然有个问题就是03版的excel 会读取多次,浪费性能 excelReader.read(readSheet, readSheet2); } } } 执行结果:
扫描数据:{"count":45,"date":1709099280000, "name":"苹果","price":1.65,"produceDate":1746545644800000} 扫描数据:{"count":13,"date":1713611400000, "name":"梨子","price":2.4,"produceDate":1746563788800000} 扫描数据:{"count":0,"name":"菠萝","price":9.9} 所有数据解析完成! 扫描商户数据:{"merchantInventory":150,"merchantName":"天天水果"} 扫描商户数据:{"merchantInventory":500,"merchantName":"只爱水果"} 商户所有数据解析完成! 2.4 日期、数字或者自定义格式转换
test4.xlsx:

ConverterData:
package com.xiaoxu.excel.format; import com.alibaba.excel.annotation.ExcelProperty; import com.alibaba.excel.annotation.format.DateTimeFormat; import com.alibaba.excel.annotation.format.NumberFormat; import lombok.Getter; import lombok.Setter; /** * @author xiaoxu * @date 2024-04-29 20:01 * learn_java:com.xiaoxu.excel.format.ConverterData */ @Setter @Getter public class ConverterData { /** * 定义 转换器 */ @ExcelProperty(value = "信息", converter = CustomStringConverter.class) private String message; /** * 这里用string 去接日期才能格式化。接收年月日格式 */ @DateTimeFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日HH时mm分ss秒SSS毫秒") @ExcelProperty("日期") private String date; /** * 接收百分比的数字 */ @NumberFormat("#.##%") @ExcelProperty("价格") private String price; } CustomStringConverter,日期、数字或者自定义格式转换:
package com.xiaoxu.excel.format; import com.alibaba.excel.converters.Converter; import com.alibaba.excel.converters.ReadConverterContext; import com.alibaba.excel.converters.WriteConverterContext; import com.alibaba.excel.enums.CellDataTypeEnum; import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.data.WriteCellData; /** * @author xiaoxu * @date 2024-04-29 20:05 * learn_java:com.xiaoxu.excel.format.CustomStringConverter */ public class CustomStringConverter implements Converter<String> { @Override public Class<?> supportJavaTypeKey() { return String.class; } @Override public CellDataTypeEnum supportExcelTypeKey() { return CellDataTypeEnum.STRING; } /** * @param context * @return * @throws Exception 读的时候调用 */ @Override public String convertToJavaData( ReadConverterContext<?> context) throws Exception { String str = context.getReadCellData().getStringValue(); char[] chars = str.toCharArray(); int left = 0; int right = chars.length - 1; while (left < right) { char temp = chars[left]; chars[left] = chars[right]; chars[right] = temp; left++; right--; } return new String(chars); } /** * @param context * @return * @throws Exception 写的时候调用,这里不涉及写 */ @Override public WriteCellData<?> convertToExcelData( WriteConverterContext<String> context) throws Exception { return new WriteCellData<>(context.getValue()); } } TestExcelConverter:
public class TestExcelConverter { public static void main(String[] args) { String file = DeskTool.getPath("test4"); EasyExcel.read(file, ConverterData.class, // 这里注意 我们也可以registerConverter来指定自定义转换器, // 但是这个转换变成全局了,所有java为string, // excel为string的都会用这个转换器。 // 如果就想单个字段使用请使用@ExcelProperty 指定converter // .registerConverter(new CustomStringStringConverter()) new PageReadListener<ConverterData> ((list) -> { for (ConverterData c : list) { System.out.println("读取到excel数据:" + JSON.toJSONString(c)); } })).sheet().doRead(); } } 执行结果:
读取到excel数据:{"date":"2024年02月28日13时48分00秒000毫秒", "message":"ebab好你","price":"980%"} 读取到excel数据:{"date":"2024年04月08日11时20分00秒000毫秒", "message":"EBABEFAC","price":"570%"} 上述convertToJavaData对String类型数据,进行字符串反转。
上述字符串反转,还可以使用下面的方式,效果一致:
String str = context.getReadCellData().getStringValue(); char[] chars = str.toCharArray(); int left = 0; int right = chars.length - 1; while (left < right) { chars[left] ^= chars[right]; chars[right] ^= chars[left]; chars[left] ^= chars[right]; left++; right--; } return new String(chars); 2.5 多行头
test5.xlsx:
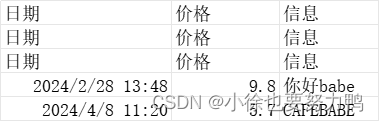
TestMultiHead:
public class TestMultiHead { public static void main(String[] args) { String file = DeskTool.getPath("test5"); EasyExcel.read(file, ConverterData.class, new PageReadListener<ConverterData> ((list) -> { for (ConverterData c : list) { System.out.println("读取到excel数据:" + JSON.toJSONString(c)); } })).sheet().doRead(); } } 执行结果:
读取到excel数据:{"date":"日期","message":"息信","price":"价格"} 读取到excel数据:{"date":"日期","message":"息信","price":"价格"} 读取到excel数据:{"date":"2024年02月28日13时48分00秒000毫秒", "message":"ebab好你","price":"980%"} 读取到excel数据:{"date":"2024年04月08日11时20分00秒000毫秒", "message":"EBABEFAC","price":"570%"} 默认就是如下的.headRowNumber(1),表头一般是1行:
String file = DeskTool.getPath("test5"); EasyExcel.read(file, ConverterData.class, new PageReadListener<ConverterData> ((list) -> { for (ConverterData c : list) { System.out.println("读取到excel数据:" + JSON.toJSONString(c)); } })).sheet().headRowNumber(1).doRead(); 如果上述有3行表头,我们希望都去掉,那么修改如下:
String file = DeskTool.getPath("test5"); EasyExcel.read(file, ConverterData.class, new PageReadListener<ConverterData> ((list) -> { for (ConverterData c : list) { System.out.println("读取到excel数据:" + JSON.toJSONString(c)); } })).sheet().headRowNumber(3).doRead(); 3行表头场景,希望都去掉表头,使用.headRowNumber(3)即可,执行结果如下:
读取到excel数据:{"date":"2024年02月28日13时48分00秒000毫秒", "message":"ebab好你","price":"980%"} 读取到excel数据:{"date":"2024年04月08日11时20分00秒000毫秒", "message":"EBABEFAC","price":"570%"} 2.6 同步的返回
test6.xlsx:
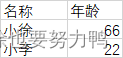
PeopleDto:
@Setter @Getter public class PeopleDto { @ExcelProperty("名称") private String name; @ExcelProperty("年龄") private int age; } TestSyncRead:
String file = DeskTool.getPath("test6"); // synchronous,同步的返回,不推荐使用, // 如果数据量大会把数据放到内存里面 List<PeopleDto> peopleDtos = EasyExcel.read(file).head(PeopleDto.class) .sheet().doReadSync(); for (PeopleDto p : peopleDtos) { System.out.println("读取到excel数据:" + JSON.toJSONString(p)); } // 这里 也可以不指定class,返回一个list, // 然后读取第一个sheet 同步读取会自动finish List<Map<Integer, String>> listMap = EasyExcel.read(file).sheet().doReadSync(); for (Map<Integer, String> data : listMap) { // 返回每条数据的键值对 表示所在的列 和所在列的值 System.out.println("读取到数据:" + JSON.toJSONString(data)); } 执行结果:
读取到excel数据:{"age":66,"name":"小徐"} 读取到excel数据:{"age":22,"name":"小李"} 读取到数据:{0:"小徐",1:"66"} 读取到数据:{0:"小李",1:"22"} 2.7 读取表头数据
监听器重写invokeHeadMap方法即可:
PeopleDtoListener监听器:
import com.alibaba.excel.context.AnalysisContext; import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.data.ReadCellData; import com.alibaba.excel.read.listener.ReadListener; import com.alibaba.excel.util.ConverterUtils; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON; import com.google.common.collect.Lists; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; /** * @author xiaoxu * @date 2024-04-30 * java_demo:com.xiaoxu.test.excel.sync.PeopleDtoListener */ public class PeopleDtoListener implements ReadListener<PeopleDto> { List<PeopleDto> peopleDtos = Lists.newArrayListWithCapacity(2); @Override public void invoke(PeopleDto peopleDto, AnalysisContext analysisContext) { peopleDtos.add(peopleDto); } @Override public void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext analysisContext) { } @Override public void invokeHead(Map<Integer, ReadCellData<?>> headMap, AnalysisContext context) { Map<Integer, String> head = ConverterUtils.convertToStringMap(headMap, context); System.out.println("读取到表头数据:" + JSON.toJSONString(head)); // 如果想转成成 Map<Integer,String> // 方案1: 不要implements ReadListener 而是 extends AnalysisEventListener // 方案2: 调用 ConverterUtils.convertToStringMap(headMap, context) 自动会转换 } } excel的head表头数据处理:
String file = DeskTool.getPath("test6"); // synchronous,同步的返回,不推荐使用, // 如果数据量大会把数据放到内存里面 // 表头数据读取 List<PeopleDto> peopleDtos = EasyExcel.read(file).head(PeopleDto.class) .registerReadListener(new PeopleDtoListener()) .sheet().doReadSync(); for (PeopleDto p : peopleDtos) { System.out.println("读取到excel数据:" + JSON.toJSONString(p)); } 执行结果:
读取到表头数据:{0:"名称",1:"年龄"} 读取到excel数据:{"age":66,"name":"小徐"} 读取到excel数据:{"age":22,"name":"小李"} 2.8 额外信息(批注、超链接、合并单元格信息读取)
since 2.0.0-beta1
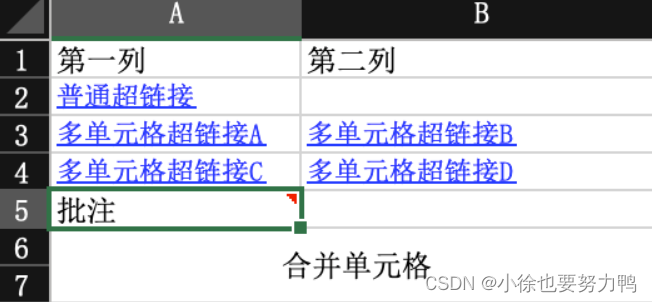
对象:
@Getter @Setter @EqualsAndHashCode public class DemoExtraData { private String row1; private String row2; } 监听器:
@Slf4j public class DemoExtraListener implements ReadListener<DemoExtraData> { @Override public void invoke(DemoExtraData data, AnalysisContext context) {} @Override public void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext context) {} @Override public void extra(CellExtra extra, AnalysisContext context) { log.info("读取到了一条额外信息:{}", JSON.toJSONString(extra)); switch (extra.getType()) { case COMMENT: log.info("额外信息是批注,在rowIndex:{},columnIndex;{},内容是:{}", extra.getRowIndex(), extra.getColumnIndex(), extra.getText()); break; case HYPERLINK: if ("Sheet1!A1".equals(extra.getText())) { log.info("额外信息是超链接,在rowIndex:{},columnIndex;{},内容是:{}", extra.getRowIndex(), extra.getColumnIndex(), extra.getText()); } else if ("Sheet2!A1".equals(extra.getText())) { log.info( "额外信息是超链接,而且覆盖了一个区间,在firstRowIndex:{},firstColumnIndex;{},lastRowIndex:{},lastColumnIndex:{}," + "内容是:{}", extra.getFirstRowIndex(), extra.getFirstColumnIndex(), extra.getLastRowIndex(), extra.getLastColumnIndex(), extra.getText()); } else { Assert.fail("Unknown hyperlink!"); } break; case MERGE: log.info( "额外信息是超链接,而且覆盖了一个区间,在firstRowIndex:{},firstColumnIndex;{},lastRowIndex:{},lastColumnIndex:{}", extra.getFirstRowIndex(), extra.getFirstColumnIndex(), extra.getLastRowIndex(), extra.getLastColumnIndex()); break; default: } } } /** * 额外信息(批注、超链接、合并单元格信息读取) * <p> * 由于是流式读取,没法在读取到单元格数据的时候直接读取到额外信息,所以只能最后通知哪些单元格有哪些额外信息 * * <p> * 1. 创建excel对应的实体对象 参照{@link DemoExtraData} * <p> * 2. 由于默认异步读取excel,所以需要创建excel一行一行的回调监听器,参照{@link DemoExtraListener} * <p> * 3. 直接读即可 * * @since 2.2.0-beat1 */ @Test public void extraRead() { String fileName = TestFileUtil.getPath() + "demo" + File.separator + "extra.xlsx"; // 这里 需要指定读用哪个class去读,然后读取第一个sheet EasyExcel.read(fileName, DemoExtraData.class, new DemoExtraListener()) // 需要读取批注 默认不读取 .extraRead(CellExtraTypeEnum.COMMENT) // 需要读取超链接 默认不读取 .extraRead(CellExtraTypeEnum.HYPERLINK) // 需要读取合并单元格信息 默认不读取 .extraRead(CellExtraTypeEnum.MERGE).sheet().doRead(); } test7.xlsx:
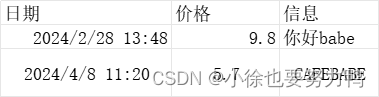
ConverterData:
@Setter @Getter public class ConverterData { /** * 定义 转换器 */ @ExcelProperty(value = "信息", converter = CustomStringConverter.class) private String message; /** * 这里用string 去接日期才能格式化。接收年月日格式 */ @DateTimeFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日HH时mm分ss秒SSS毫秒") @ExcelProperty("日期") private String date; /** * 接收百分比的数字 */ @NumberFormat("#.##%") @ExcelProperty("价格") private String price; } MergeDataListener:
package com.xiaoxu.excel.merge; import com.alibaba.excel.context.AnalysisContext; import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.CellExtra; import com.alibaba.excel.read.listener.ReadListener; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON; import com.xiaoxu.excel.format.ConverterData; import java.text.MessageFormat; /** * @author xiaoxu * @date 2024-04-30 22:13 * learn_java:com.xiaoxu.excel.merge.MergeDataListener */ public class MergeDataListener implements ReadListener<ConverterData> { @Override public void invoke(ConverterData converterData, AnalysisContext analysisContext) { System.out.println("读取正常数据:" + JSON.toJSONString(converterData)); } @Override public void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext analysisContext) { } @Override public void extra(CellExtra extra, AnalysisContext context) { System.out.println("读取额外数据:" + JSON.toJSONString(extra)); switch (extra.getType()) { case MERGE: System.out.println(MessageFormat .format("额外信息是合并单元格," + "覆盖区间:firstRowIndex:{0}," + "firstColumnIndex:{1}," + "lastRowIndex:{2},lastColumnIndex:{3}.", extra.getFirstRowIndex(), extra.getFirstColumnIndex(), extra.getLastRowIndex(), extra.getLastColumnIndex())); } } } TestMerge:
// 这种写法只会输出正常读取的数据,而不会输出合并的单元格等数据 // 批注、超链接、合并单元格默认不读取 // EasyExcel.read(file).head(ConverterData.class) // .registerReadListener(new MergeDataListener()) // .sheet().headRowNumber(1).doRead(); EasyExcel.read(file).head(ConverterData.class) .registerReadListener(new MergeDataListener()) .extraRead(CellExtraTypeEnum.MERGE) .sheet().headRowNumber(1).doRead(); 执行结果:
读取正常数据:{"date":"2024年02月28日13时48分00秒000毫秒", "message":"ebab好你","price":"980%"} 读取正常数据:{"date":"2024年04月08日11时20分00秒000毫秒", "message":"EBABEFAC","price":"570%"} 读取额外数据:{"columnIndex":0,"firstColumnIndex":0, "firstRowIndex":2,"lastColumnIndex":0, "lastRowIndex":3,"rowIndex":2,"type":"MERGE"} 额外信息是合并单元格,覆盖区间:firstRowIndex:2,firstColumnIndex:0, lastRowIndex:3,lastColumnIndex:0. 2.9 读取公式和单元格类型
test8.xlsx:
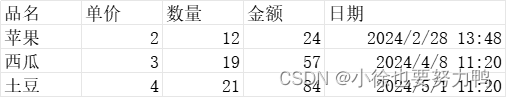
其中金额是公式生成的,是单价*数量计算出来的。
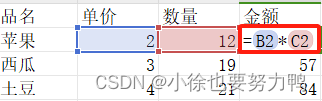
公式操作如下,在第一列数据的金额列下,输入=号,然后选中苹果的单价列,输入*表示乘,再选中苹果的数量列,按下enter即公式配置成功,下拉苹果列的金额,即可自动填充后续列的公式:
CellDataReadData:
package com.xiaoxu.excel.formula; import com.alibaba.excel.annotation.ExcelProperty; import com.alibaba.excel.metadata.data.CellData; import lombok.EqualsAndHashCode; import lombok.Getter; import lombok.Setter; import java.util.Date; /** * @author xiaoxu * @date 2024-05-01 10:22 * learn_java:com.xiaoxu.excel.formula.CellDataReadData */ @Getter @Setter @EqualsAndHashCode public class CellDataReadData { @ExcelProperty("品名") private CellData<String> name; @ExcelProperty("单价") private CellData<Long> price; @ExcelProperty("数量") private CellData<Long> number; @ExcelProperty("金额") private CellData<Long> money; @ExcelProperty("日期") private CellData<Date> date; } CellDataListener:
public class CellDataListener implements ReadListener<CellDataReadData> { @Override public void invoke(CellDataReadData cellDataReadData, AnalysisContext analysisContext) { System.out.println("读取正常数据:" + JSON.toJSONString(cellDataReadData, true)); } @Override public void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext analysisContext) { } } TestCellData:
String file = DeskTool.getPath("test8"); EasyExcel.read(file).head(CellDataReadData.class) .registerReadListener(new CellDataListener()) .extraRead(CellExtraTypeEnum.MERGE) .sheet().headRowNumber(1).doRead(); 执行结果:
读取正常数据:{ "date":{ "data":1709099280000, "dataFormatData":{ "format":"yyyy-m-d h:mm", "index":22 }, "numberValue":45350.575, "originalNumberValue":45350.575, "type":"NUMBER" }, "money":{ "data":24, "dataFormatData":{ "format":"General", "index":0 }, "formulaData":{ "formulaValue":"B2*C2" }, "numberValue":24, "originalNumberValue":24, "type":"NUMBER" }, "name":{ "data":"苹果", "dataFormatData":{ "format":"General", "index":0 }, "stringValue":"苹果", "type":"STRING" }, "number":{ "data":12, "dataFormatData":{ "format":"General", "index":0 }, "numberValue":12, "originalNumberValue":12, "type":"NUMBER" }, "price":{ "data":2, "dataFormatData":{ "format":"General", "index":0 }, "numberValue":2, "originalNumberValue":2, "type":"NUMBER" } } 读取正常数据:{ "date":{ "data":1712546400000, "dataFormatData":{ "format":"yyyy-m-d h:mm", "index":22 }, "numberValue":45390.4722222222, "originalNumberValue":45390.4722222222, "type":"NUMBER" }, "money":{ "data":57, "dataFormatData":{ "format":"General", "index":0 }, "formulaData":{ "formulaValue":"B3*C3" }, "numberValue":57, "originalNumberValue":57, "type":"NUMBER" }, "name":{ "data":"西瓜", "dataFormatData":{ "format":"General", "index":0 }, "stringValue":"西瓜", "type":"STRING" }, "number":{ "data":19, "dataFormatData":{ "format":"General", "index":0 }, "numberValue":19, "originalNumberValue":19, "type":"NUMBER" }, "price":{ "data":3, "dataFormatData":{ "format":"General", "index":0 }, "numberValue":3, "originalNumberValue":3, "type":"NUMBER" } } 读取正常数据:{ "date":{ "data":1714533600000, "dataFormatData":{ "format":"yyyy-m-d h:mm", "index":22 }, "numberValue":45413.4722222222, "originalNumberValue":45413.4722222222, "type":"NUMBER" }, "money":{ "data":84, "dataFormatData":{ "format":"General", "index":0 }, "formulaData":{ "formulaValue":"B4*C4" }, "numberValue":84, "originalNumberValue":84, "type":"NUMBER" }, "name":{ "data":"土豆", "dataFormatData":{ "format":"General", "index":0 }, "stringValue":"土豆", "type":"STRING" }, "number":{ "data":21, "dataFormatData":{ "format":"General", "index":0 }, "numberValue":21, "originalNumberValue":21, "type":"NUMBER" }, "price":{ "data":4, "dataFormatData":{ "format":"General", "index":0 }, "numberValue":4, "originalNumberValue":4, "type":"NUMBER" } } 2.10 数据转换等异常处理
test9.xlsx:

数据转换等异常处理,在监听器中重写onException方法即可:
ErrorListener,在转换异常 获取其他异常下会调用本接口,抛出异常则停止读取,如果这里不抛出异常则继续读取下一行:
package com.xiaoxu.excel.exp; import com.alibaba.excel.context.AnalysisContext; import com.alibaba.excel.exception.ExcelDataConvertException; import com.alibaba.excel.read.listener.ReadListener; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON; /** * @author xiaoxu * @date 2024-05-01 11:07 * learn_java:com.xiaoxu.excel.exp.ErrorListener */ public class ErrorListener implements ReadListener<ErrorObj> { @Override public void onException(Exception exception, AnalysisContext context) throws Exception { System.out.println("解析失败,继续下一行数据解析:" + exception.getMessage()); if (exception instanceof ExcelDataConvertException) { ExcelDataConvertException exp = (ExcelDataConvertException) exception; System.out.println(String.format("格式转换异常," + "第%s行,第%s列解析异常,数据为:%s.", exp.getRowIndex(), exp.getColumnIndex(), exp.getCellData().getStringValue())); } } @Override public void invoke(ErrorObj errorObj, AnalysisContext analysisContext) { System.out.println("读取数据:" + JSON.toJSONString(errorObj, true)); } @Override public void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext analysisContext) { } } ErrorObj:
@Setter @Getter public class ErrorObj { @ExcelProperty("数目") private long count; } TestErrorObj:
String file = DeskTool.getPath("test9"); EasyExcel.read(file).head(ErrorObj.class) .registerReadListener(new ErrorListener()) .sheet().headRowNumber(1).doRead(); 执行结果:
解析失败,继续下一行数据解析: Convert data com.alibaba.excel.metadata.data.ReadCellData@dc8f2848 to long error 格式转换异常,第1行,第0列解析异常,数据为:苹果. 读取数据:{ "count":120 } 2.11 不创建对象的读
不创建对象的场景下读取数据,可以使用Map<Integer, String>来存储读取的数据:
@Slf4j public class NoModelDataListener extends AnalysisEventListener<Map<Integer, String>> { /** * 每隔5条存储数据库,实际使用中可以100条,然后清理list ,方便内存回收 */ private static final int BATCH_COUNT = 5; private List<Map<Integer, String>> cachedDataList = ListUtils.newArrayListWithExpectedSize(BATCH_COUNT); @Override public void invoke(Map<Integer, String> data, AnalysisContext context) { log.info("解析到一条数据:{}", JSON.toJSONString(data)); cachedDataList.add(data); if (cachedDataList.size() >= BATCH_COUNT) { saveData(); cachedDataList = ListUtils.newArrayListWithExpectedSize(BATCH_COUNT); } } @Override public void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext context) { saveData(); log.info("所有数据解析完成!"); } /** * 加上存储数据库 */ private void saveData() { log.info("{}条数据,开始存储数据库!", cachedDataList.size()); log.info("存储数据库成功!"); } } 不创建对象读取:
/** * 不创建对象的读 */ @Test public void noModelRead() { String fileName = TestFileUtil.getPath() + "demo" + File.separator + "demo.xlsx"; // 这里 只要,然后读取第一个sheet 同步读取会自动finish EasyExcel.read(fileName, new NoModelDataListener()).sheet().doRead(); } 2.12 web中的读
参考EasyExcel的读取文件方法,可以传入InputStream进行读取,那么可以结合Spring的web读取excel数据:
public static ExcelReaderBuilder read(InputStream inputStream, Class head, ReadListener readListener) { ExcelReaderBuilder excelReaderBuilder = new ExcelReaderBuilder(); excelReaderBuilder.file(inputStream); if (head != null) { excelReaderBuilder.head(head); } if (readListener != null) { excelReaderBuilder.registerReadListener(readListener); } return excelReaderBuilder; } web读取如下:
/** * 文件上传 * <p> * 1. 创建excel对应的实体对象 参照{@link UploadData} * <p> * 2. 由于默认一行行的读取excel,所以需要创建excel一行一行的回调监听器,参照{@link UploadDataListener} * <p> * 3. 直接读即可 */ @PostMapping("upload") @ResponseBody public String upload(MultipartFile file) throws IOException { EasyExcel.read(file.getInputStream(), UploadData.class, new UploadDataListener(uploadDAO)).sheet().doRead(); return "success"; } 