目录

引文:
我们在开发过程当中,经常会在接口响应结果中以 Json 的形式返回数据,我们也对于这种处理方式习以为常。那么大家是否想过,SpringBoot 当中将对象转为 Json 格式有几种方式?本文将介绍开发中常用的三种 Json 序列化的方式:Jackson、FastJSON、Gson。
JSON 文档:
- JSON 中文官网:http://www.json.org/json-zh.html
- JSON 官网:http://www.json.org/
一、Jackson 方案(SpringBoot默认支持)
Jackson 是用来序列化和反序列化 json 的 Java 开源框架。
1.1 Jackson 库的特点
Jackson 库具有以下特点:
- Spring MVC 的默认 json 解析器就是 Jackson。
- 与其他 Java 的 json 框架 Gson 等相比,Jackson 解析大的 json 文件速度比较快。
- Jackson 运行时内存比较低,性能比较好。
- Jackson 有灵活的 API,容易扩展和定制。
补充:SpringBoot 中 Jackson 库的依赖集成在 spring-boot-starter-web 组件中,具体位置如下图所示:
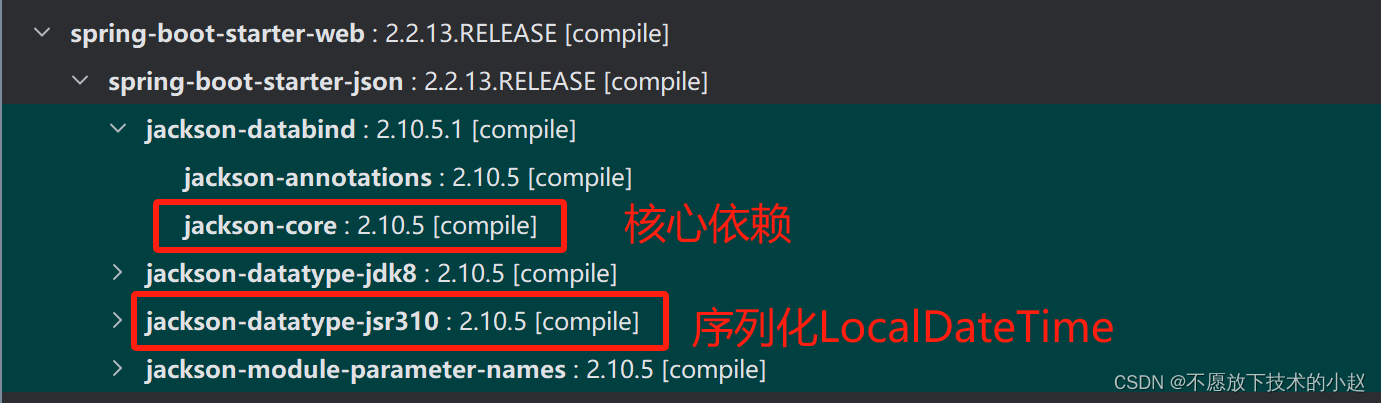
1.2 Jackson 的核心模块
Jackson 的核心模块由三部分组成:
jackson-core:核心包,提供基于 “流模式” 解析的相关 API,它包括 JsonParser 和 JsonGenerator。Jackson 内部实现正是通过高性能的流模式 API 的 JsonGenerator 和 JsonParser 来生成和解析 json。
jackson-annotations:注解包,提供标准注解功能。jackson-databind:数据绑定包,提供基于 “对象绑定” 解析的相关 API(ObjectMapper)和 “树模型” 解析的相关 API(JsonNode);基于 “对象绑定” 解析的 API 和 “树模型” 解析的 API 依赖基于 “流模式” 解析的 API。
在了解 Jackson 的概要情况之后,下面介绍 Jackson 的基本用法。
1.3 Maven依赖
<!-- Jackson库 --> <dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId> <version>2.13.5</version> <scope>compile</scope> </dependency> <!-- Jackson 支持 LocalDateTime 格式化 --> <dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-datatype-jsr310</artifactId> <version>2.13.5</version> <scope>compile</scope> </dependency> jackson-databind 依赖包含了 jackson-core 和 jackson-annotations。当添加了 jackson-databind 之后,jackson-core 和 jackson-annotations 也就添加到 Java 项目工程中了。在添加相关依赖包之后,就可以使用 Jackson。
1.4 代码示例
Jackson 最常用的 API 就是基于 “对象绑定” 的 ObjectMapper。下面是一个简单的使用示例:
Person.java
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonFormat; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.annotation.JsonDeserialize; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.annotation.JsonSerialize; import com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype.jsr310.deser.LocalDateTimeDeserializer; import com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype.jsr310.ser.LocalDateTimeSerializer; import lombok.Data; import java.time.LocalDateTime; @Data public class Person { // 字符串测试 private String name; // 空对象测试 private Integer age; // 默认值测试 private int height; // 日期测试 @JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss", timezone="GMT+8") @JsonSerialize(using = LocalDateTimeSerializer.class) @JsonDeserialize(using = LocalDateTimeDeserializer.class) private LocalDateTime createTime; } JacksonTest.java
import com.demo.model.Person; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper; import java.io.IOException; import java.time.LocalDateTime; /** * <p> @Title JacksonTest * <p> @Description Jackson库测试 * * @author ACGkaka * @date 2024/4/12 19:04 */ public class JacksonTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(); // 造数据 Person person = new Person(); person.setName("Tom"); person.setAge(40); person.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now()); // 序列化 String jsonString = mapper.writeValueAsString(person); System.out.println("序列化结果(JSON):" + jsonString); // 反序列化 Person deserializedPerson = mapper.readValue(jsonString, Person.class); System.out.println("反序列化结果(toString):" + deserializedPerson); } } 执行结果:

1.5 LocalDateTime 格式化
在上面的示例中,我们可以看到 LocaDateTime 的属性上面使用了 @JsonFormat、@JsonSerialize、@JsonDeserialize 三个注解,它们具体是什么作用呢?
@JsonFormat:重点关注日期时间类型的序列化与反序列化 格式。@JsonSerialize:指定自定义序列化逻辑,重点关注 序列化时的定制化处理。@JsonDeserialize:执行自定义反序列化逻辑,重点关注 反序列化时的定制化处理。
补充: 如果只想在 RESTful 接口返回正确的时间格式,只需要使用
@JsonFormat即可,但是如果想在代码中使用 ObjectMapper 进行序列化的话就需要使用@JsonFormat+@JsonSerialize。
在 Jackson 的 2.13.5 版本中,如果依赖中只集成了 jackson-databind 依赖,没有集成 jackson-datatype-jsr310 依赖,是无法自动将 LocalDateTime 类型的字段进行序列化的,报错如下:
- Java 8 date/time type
java.time.LocalDateTimenot supported by default: add Module “com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype:jackson-datatype-jsr310” to enable handling (through reference chain: com.demo.model.Person[“createTime”])
完整报错如下:
Exception in thread "main" com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.exc.InvalidDefinitionException: Java 8 date/time type `java.time.LocalDateTime` not supported by default: add Module "com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype:jackson-datatype-jsr310" to enable handling (through reference chain: com.demo.model.Person["createTime"]) at com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.exc.InvalidDefinitionException.from(InvalidDefinitionException.java:77) at com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.SerializerProvider.reportBadDefinition(SerializerProvider.java:1300) at com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ser.impl.UnsupportedTypeSerializer.serialize(UnsupportedTypeSerializer.java:35) at com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ser.BeanPropertyWriter.serializeAsField(BeanPropertyWriter.java:728) at com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ser.std.BeanSerializerBase.serializeFields(BeanSerializerBase.java:774) at com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ser.BeanSerializer.serialize(BeanSerializer.java:178) at com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ser.DefaultSerializerProvider._serialize(DefaultSerializerProvider.java:480) at com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ser.DefaultSerializerProvider.serializeValue(DefaultSerializerProvider.java:319) at com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper._writeValueAndClose(ObjectMapper.java:4568) at com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper.writeValueAsString(ObjectMapper.java:3821) at com.demo.test.JacksonTest.main(JacksonTest.java:27) 解决方案:
- 只需集成对应版本的
jackson-datatype-jsr310依赖即可:
<dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-datatype-jsr310</artifactId> <version>2.13.5</version> <scope>compile</scope> </dependency> 1.6 统一配置
我们在进行项目开发的时候,如果每次新增 HTTP 请求接口都要去 VO 里面增加一遍注解的话非常费时费力,我们可以在 SpringBoot 项目中增加一个 Jackson 库的统一配置类:
JacksonConfig.java
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonInclude; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.DeserializationFeature; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.module.SimpleModule; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ser.std.ToStringSerializer; import com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype.jsr310.deser.LocalDateTimeDeserializer; import com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype.jsr310.ser.LocalDateTimeSerializer; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary; import org.springframework.http.converter.json.Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder; import java.time.LocalDateTime; import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter; @Configuration public class JacksonConfig { @Bean @Primary @ConditionalOnMissingBean(ObjectMapper.class) public ObjectMapper jacksonObjectMapper(Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilder builder) { ObjectMapper objectMapper = builder.createXmlMapper(false).build(); // 全局配置序修改列化返回 Json 处理方案 objectMapper.registerModule(new SimpleModule() // Json Long --> String,防止精度丢失 .addSerializer(Long.class, ToStringSerializer.instance) // 自定义序列化时 LocalDateTime 时间日期格式 .addSerializer(LocalDateTime.class, new LocalDateTimeSerializer(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"))) // 自定义反序列化时 LocalDateTime 时间日期格式 .addDeserializer(LocalDateTime.class, new LocalDateTimeDeserializer(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")))); // 在序列化时,忽略值为 null 的属性 objectMapper.setSerializationInclusion(JsonInclude.Include.NON_NULL); // 在序列化是,忽略值为默认值的属性(例如 int 的原始类型会有默认值) objectMapper.setDefaultPropertyInclusion(JsonInclude.Include.NON_DEFAULT); // 在反序列化时,忽略在 json 中存在但 Java 对象不存在的属性。 objectMapper.configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES, false); return objectMapper; } } 修改 Person.java,去除注解:
public class Person { ... // 日期测试 private LocalDateTime createTime; } 请求接口如下:
@GetMapping("/person") @ResponseBody public Result<Object> person() { Person person = new Person(); person.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now()); return Result.succeed().setData(person); } 请求结果:

可以看到全局配置正常生效了。更多配置信息可以查看 Jackson 库中的 DeserializationFeature、SerializationFeature 和 Include 源码内容。
1.7 常用注解
Jackson 库支持使用注解调整它的序列化和序列化机制。常见的注解及用法如下:
@JsonPropertyOrder:用于类,指定属性在序列化时 json 中的顺序。@JsonIgnoreProperties:用于类,批量忽视属性,不进行序列化。@JsonNaming:用于类,在序列化与反序列化时的驼峰命名、小写字母命名转换。@JsonIgnore:用于字段,忽略属性,不进行序列化。@JsonProperty:用于字段,定制序列化的变量名。@JsonFormat:用于字段,指定时间日期字段的格式。@JsonSerialize:用于字段,指定字段的序列化方式。@JsonDeserialize:用于字段,指定字段的反序列化方式。@JsonCreator:用于构造函数,配合 @JsonProperty 使用,用于定制反序列化机制。@JsonAnyGetter:用于修饰方法,负责序列化时处理 JSON 对象中未知的键值对。@JsonAnySetter:用于修饰方法,负责反序列化时处理 JSON 对象中未知的键值对。
使用示例:
// 用于类,指定属性在序列化时 json 中的顺序 @JsonPropertyOrder({"date", "user_name"}) // 批量忽略属性,不进行序列化 @JsonIgnoreProperties(value = {"other"}) // 用于序列化与反序列化时的驼峰命名与小写字母命名转换 @JsonNaming(PropertyNamingStrategy.SnakeCaseStrategy.class) public static class User { @JsonIgnore private Map<String, Object> other = new HashMap<>(); // 正常case @JsonProperty("user_name") private String userName; // 空对象case private Integer age; @JsonFormat(timezone = "GMT+8", pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") // 日期转换case private Date date; // 默认值case private int height; public User() { } // 反序列化执行构造方法 @JsonCreator public User(@JsonProperty("user_name") String userName) { System.out.println("@JsonCreator 注解使得反序列化自动执行该构造方法 " + userName); // 反序列化需要手动赋值 this.userName = userName; } @JsonAnySetter public void set(String key, Object value) { other.put(key, value); } @JsonAnyGetter public Map<String, Object> any() { return other; } // 本文默认省略getter、setter方法 } 测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(); // 造数据 Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("user_name", "Tom"); map.put("date", "2020-07-26 19:28:44"); map.put("age", 100); map.put("demoKey", "demoValue"); String jsonString = mapper.writerWithDefaultPrettyPrinter().writeValueAsString(map); System.out.println(jsonString); System.out.println("反序列化"); User user = mapper.readValue(jsonString, User.class); System.out.println(user); System.out.println("序列化"); jsonString = mapper.writerWithDefaultPrettyPrinter().writeValueAsString(user); System.out.println(jsonString); } 执行结果:

1.8 自定义序列化和反序列化
当 Jackson 库默认序列化和反序列化的类不能满足实际需要,可以自定义新的序列化和反序列化的类。
自定义序列化类:自定义的序列化类需要直接或间接集成 StdSerializer 或 JsonSerializer,同时需要利用 JsonGenerator 生成 json,重写方法 serialize(),示例如下:
public static class CustomSerializer extends StdSerializer<Person> { protected CustomSerializer() { super(Person.class); } @Override public void serialize(Person person, JsonGenerator jgen, SerializerProvider provider) throws IOException { jgen.writeStartObject(); jgen.writeNumberField("age", person.getAge()); jgen.writeStringField("name", person.getName()); jgen.writeStringField("msg", "已被自定义序列化"); jgen.writeEndObject(); } } JsonGenerator 有多种 write 方法以支持生成复杂类型的 json,比如 writeArray()、writeTree() 等。若想单独创建 JsonGenerator,可以通过 JsonFactory() 的 createGenerator()。
自定义反序列化类:自定义的反序列化类需要直接或间接集成 StdDeserializer 或 StdDeserializer,同时需要利用 JsonParser 读取 json,重写方法 deserilize(),示例如下:
public static class CustomDeserializer extends StdDeserializer<Person> { protected CustomDeserializer() { super(Person.class); } @Override public Person deserialize(JsonParser jp, DeserializationContext ctxt) throws IOException, JsonProcessingException { JsonNode node = jp.getCodec().readTree(jp); Person person = new Person(); int age = (Integer) ((IntNode) node.get("age")).numberValue(); String name = node.get("name").asText(); person.setAge(age); person.setName(name); return person; } } JsonParser 提供很多方法来读取 json 信息,如 isClosed()、nextToken()、getValueAsString() 等。若想单独创建 JsonParser,可以通过 JsonFactory() 的 createParser()。
测试示例:
创建好自定义序列化类和自定义反序列化类,若想在程序中调用它们,还需要注册到 ObjectMapper 的 Module,示例如下:
@Test public void test9() throws IOException { ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(); // 生成 module SimpleModule module = new SimpleModule("myModule"); module.addSerializer(new CustomSerializer()); module.addDeserializer(Person.class, new CustomDeserializer()); // 注册 module mapper.registerModule(module); // 造数据 Person person = new Person(); person.setName("Tom"); person.setAge(40); person.setDate(new Date()); System.out.println("序列化"); String jsonString = mapper.writerWithDefaultPrettyPrinter().writeValueAsString(person); System.out.println(jsonString); System.out.println("反序列化"); Person deserializedPerson = mapper.readValue(jsonString, Person.class); System.out.println(deserializedPerson); } 或者也可以通过注解方式加在 java 对象的属性、方法或类上来调用它们:
- @JsonSerialize(using = CustomSerializer.class)
- @JsonDeserialize(using = CustomDeserializer.class)
1.9 Jackson 工具类
public class JacsonUtils { public static final ObjectMapper MAPPER; static { MAPPER = new ObjectMapper(); MAPPER.configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES, false); MAPPER.setSerializationInclusion(JsonInclude.Include.NON_NULL); MAPPER.setDateFormat(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")); } //===============================序列化================// @SneakyThrows public static String toString(Object obj) { if (obj == null) return null; if (obj.getClass() == String.class) return Convert.toStr(obj); return MAPPER.writeValueAsString(obj); } //==========================反序列化===============// //对象反序列化 @SneakyThrows(value={IOException.class}) public static <T> T toBean(String json, Class<T> tClass) { if(StrUtil.isEmpty(json)) return null; return MAPPER.readValue(json, tClass); } //集合反序列化 @SneakyThrows(value={IOException.class}) public static <E> List<E> toList(String json, Class<E> eClass) { if(StrUtil.isEmpty(json)) return null; JavaType javaType = MAPPER.getTypeFactory().constructParametricType(List.class, Bean.class); return MAPPER.readValue(json,javaType); } //Map集合反序列化 @SneakyThrows(value={IOException.class}) public static <K, V> Map<K, V> toMap(String json, Class<K> kClass, Class<V> vClass) { if(StrUtil.isEmpty(json)) return null; JavaType javaType = MAPPER.getTypeFactory() .constructParametricType(HashMap.class,String.class, Bean.class); return MAPPER.readValue(json, javaType); } //复杂对象反序列化 @SneakyThrows(value={IOException.class}) public static <T> T nativeRead(String json, TypeReference<T> type) { if(StrUtil.isEmpty(json)) return null; return MAPPER.readValue(json, type); } } 二、FastJSON 方案
FastJSON 是一个高性能、功能全面的 Java JSON 处理库,由 阿里巴巴 集团开发并开源。其核心功能在于高效地处理 JSON 数据与 Java 对象之间的相互转换,同时也提供了丰富的 JSON 解析、生成与操作功能。
2.1 FastJSON 的特点
- 高性能: FastJSON 以其卓越的性能著称,在处理大量 JSON 数据时表现出较高的效率。通过优化算法和底层实现,它在速度和内存占用上相比许多其它 JSON 库具有竞争优势,特别适合于高并发、大数据量的场景。
- 广泛的功能支持: 序列化与非序列化、泛型与复杂类型处理、日期与时间格式化、注解驱动配置、防止JSON注入等。
2.2 FastJSON 的核心类
FastJSON 库中我们常用的核心类有以下4个:
JSON:是 FastJSON 处理 json 的入口,相当于一个工具类,提供了以下方法来进行序列化和反序列化:序列化方法:
- toJSONString(Object object): 将给定的 Java 对象序列化为 JSON 文本字符串。
- toJSONBytes(Object object, Charset charset): 将给定的 Java 对象序列化为 JSON 字节数组,使用指定的字符集(例:StandardCharsets.UTF_8)。
反序列化方法:
- parseObject(String text, Class<T> clazz): 将给定的 JSON 文本字符串反序列化为指定的 Java 对象。
- parseArray(String text, Class<T> clazz): 将给定的 JSON 数组文本字符串反序列化为指定元素类型的 Java 对象。
JSONObject/JSONArray:解析后的对象或数组。JSONPath:采用 path 方式获取 json 值。JSONReader:json 的读取器。
2.2 Maven依赖
<!-- FastJSON --> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>fastjson</artifactId> <version>1.2.83</version> </dependency> 2.3 代码示例
User.java
import com.alibaba.fastjson.annotation.JSONField; import lombok.AllArgsConstructor; import lombok.Data; import java.time.LocalDateTime; /** * 一个简单的 Java Bean 类 */ @Data @AllArgsConstructor public class User { private int id; private String name; @JSONField(format = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") private LocalDateTime birthday; private Address address; public User(int id, String name) { this.id = id; this.name = name; } @Data @AllArgsConstructor public static class Address { private String street; private String city; } } 测试代码:
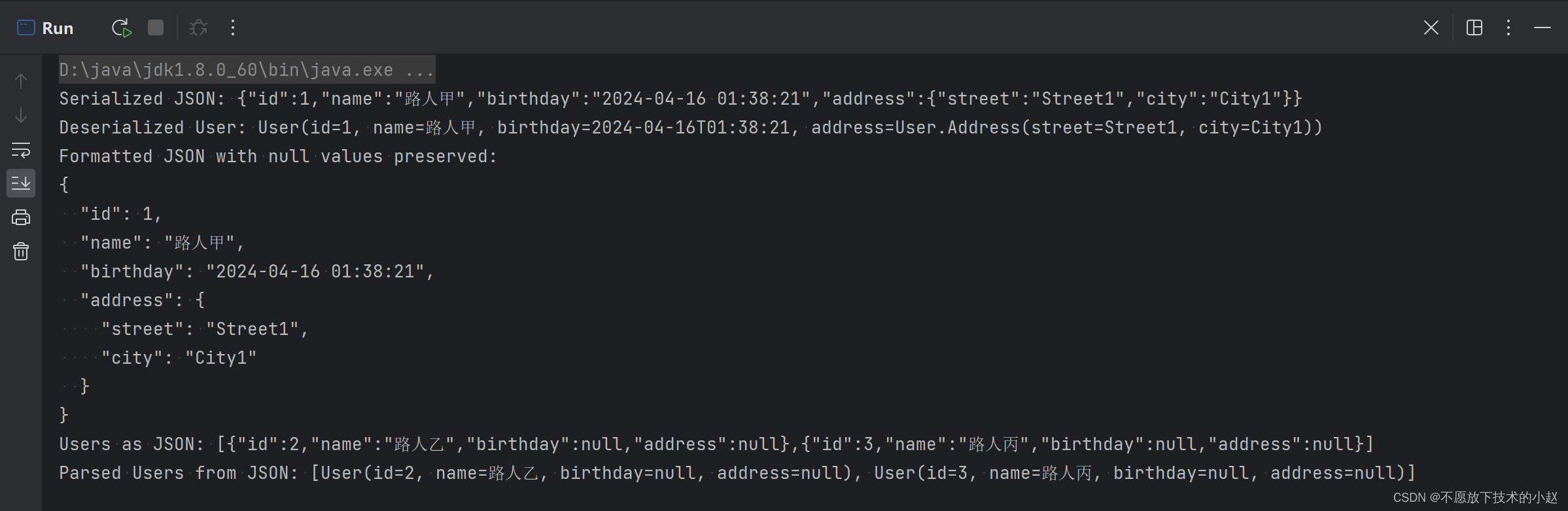
public static void main(String[] args) { // 序列化单个对象 User user = new User(1, "ACGkaka", LocalDateTime.now(), new User.Address("Street1", "City1")); String jsonString = JSON.toJSONString(user); System.out.println("Serialized JSON: " + jsonString); // 反序列化单个对象 User deserializedUser = JSON.parseObject(jsonString, User.class); System.out.println("Deserialized User: " + deserializedUser); // 序列化单个对象,保留null值和去掉空格 String formattedJson = JSON.toJSONString(user, SerializerFeature.WriteNullListAsEmpty, SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue, SerializerFeature.PrettyFormat); System.out.println("Formatted JSON with null values preserved: \n" + formattedJson); // 序列化多个对象 List<User> userList = Arrays.asList(new User(1, "Alice"), new User(2, "Bob")); String usersJson = JSON.toJSONString(userList); System.out.println("Users as JSON: " + usersJson); // 反序列化多个对象 List<User> users = JSON.parseArray(usersJson, User.class); System.out.println("Parsed Users from JSON: " + users); } 执行结果:

2.3 统一配置
一般场景下不需要配置类,采用默认的方式即可。如需配置类进行特殊配置,可以参考如下代码:
@Configuration public class FJsonConfig { @Bean public HttpMessageConverter configureMessageConverters() { FastJsonHttpMessageConverter converter = new FastJsonHttpMessageConverter(); FastJsonConfig config = new FastJsonConfig(); converter.setFastJsonConfig(config); List<MediaType> mediaTypeList = new ArrayList<>(); mediaTypeList.add(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON); converter.setSupportedMediaTypes(mediaTypeList); return converter; } } 2.4 常用注解
@JSONField:FastJSON 的核心注解,基本所有的序列化和反序列化操作都是通过这个注解实现的。注解的属性如下:
- name: 设置序列后别名。
- format: 格式化后输出日期。
- ordinal: 输出排列顺序。
- serialize: 是否序列化输出。
- deserialize: 是否反序列化载入。
2.5 SpringBoot 设置 FastJSON 为默认Json解析框架
如果我们基于某些特殊的场景,必须要使用 FastJSON 作为 SpringBoot 默认的 Json 解析框架,首先要排除 jackson 依赖:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> <!-- 排除jackson依赖 --> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> 然后,创建配置类如下所示:
DefaultJsonConfig.java
import com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer.SerializerFeature; import com.alibaba.fastjson.support.config.FastJsonConfig; import com.alibaba.fastjson.support.spring.FastJsonHttpMessageConverter; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.HttpMessageConverters; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.http.MediaType; import org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter; import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * 默认JSON框架配置类 */ @Configuration public class DefaultJsonConfig { /** * 利用 fastJSON 替换掉 jackson, */ @Bean public HttpMessageConverters fastJsonHttpMessageConverters() { // 配置StringHttpMessageConverter,解决返回中文乱码问题 StringHttpMessageConverter stringHttpMessageConverter = new StringHttpMessageConverter(StandardCharsets.UTF_8); List<MediaType> supportedMediaTypes = new ArrayList<>(); supportedMediaTypes.add(MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN); supportedMediaTypes.add(MediaType.TEXT_HTML); stringHttpMessageConverter.setSupportedMediaTypes(supportedMediaTypes); stringHttpMessageConverter.setWriteAcceptCharset(false); // 配置fastjson FastJsonHttpMessageConverter fastConverter = new FastJsonHttpMessageConverter(); FastJsonConfig fastJsonConfig = new FastJsonConfig(); config.setSerializerFeatures( // 可以配置不同的属性序列化方式 SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue, // SerializerFeature.WriteNullStringAsEmpty, // SerializerFeature.WriteNullNumberAsZero, // SerializerFeature.WriteNullListAsEmpty, // SerializerFeature.WriteNullBooleanAsFalse, SerializerFeature.DisableCircularReferenceDetect // 格式化 // SerializerFeature.PrettyFormat ); converter.setDefaultCharset(Charset.forName("UTF-8")); // 设置支持的MediaType List<MediaType> fastMediaTypes = new ArrayList<>(); fastMediaTypes.add(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON); fastMediaTypes.add(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8); fastConverter.setSupportedMediaTypes(fastMediaTypes); fastConverter.setFastJsonConfig(fastJsonConfig); return new HttpMessageConverters(fastConverter, stringHttpMessageConverter); } } 三、GSON 方案
GSON 是 Google 开发的一款强大的 Java 库,主要用于处理 JSON 数据与 Java 对象之间的序列化与反序列化。GSON 通过将 JSON 数据结构与 Java 对象模型相互转换,简化了 Java 应用中 JSON 数据的处理过程,广泛应用于 Web 服务、移动应用、数据交换等领域。
3.1 GSON 的特点
- 支持序列化、反序列化。
- 支持泛型。
- 支持 JSON 解析器(JsonParser)与生成器(JsonWriter),允许直接读写 JSON 流,适用于需要更多控制权或处理大型 JSON 文档的场景。
3.2 Maven依赖
<!-- GSON --> <dependency> <groupId>com.google.code.gson</groupId> <artifactId>gson</artifactId> <version>2.10.1</version> </dependency> 3.3 代码示例
User.java
import com.google.gson.annotations.SerializedName; import lombok.AllArgsConstructor; import lombok.Data; import java.time.LocalDateTime; /** * 一个简单的 Java Bean 类 */ @Data @AllArgsConstructor public class User { private int id; @SerializedName("name") private String name; private LocalDateTime birthday; private Address address; public User(int id, String name) { this.id = id; this.name = name; } @Data @AllArgsConstructor public static class Address { private String street; private String city; } } 测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) { // 序列化单个对象 User user = new User(1, "路人甲", LocalDateTime.now(), new User.Address("Street1", "City1")); JsonSerializer<LocalDateTime> localDateTimeSerializer = (localDateTime, type, jsonSerializationContext) -> new JsonPrimitive(localDateTime.format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"))); JsonDeserializer<LocalDateTime> localDateTimeDeserializer = (json, typeOfT, context) -> LocalDateTime.parse(json.getAsJsonPrimitive().getAsString(), DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")); Gson gson = new GsonBuilder() // 设置 LocalDateTime 序列化格式 .registerTypeAdapter(LocalDateTime.class, localDateTimeSerializer) // 设置 LocalDateTime 反序列化格式 .registerTypeAdapter(LocalDateTime.class, localDateTimeDeserializer) .serializeNulls() .create(); String jsonString = gson.toJson(user); System.out.println("Serialized JSON: " + jsonString); // 反序列化单个对象 User deserializedUser = gson.fromJson(jsonString, User.class); System.out.println("Deserialized User: " + deserializedUser); // 序列化单个对象,保留null值和去掉空格(GSON默认保留null值,格式化可使用GsonBuilder) Gson prettyGson = new GsonBuilder() .registerTypeAdapter(LocalDateTime.class, localDateTimeSerializer) .registerTypeAdapter(LocalDateTime.class, localDateTimeDeserializer) .setPrettyPrinting().create(); String formattedJson = prettyGson.toJson(user); System.out.println("Formatted JSON with null values preserved:\n" + formattedJson); // 序列化多个对象 List<User> userList = Arrays.asList(new User(2, "路人乙"), new User(3, "路人丙")); String usersJson = gson.toJson(userList); System.out.println("Users as JSON: " + usersJson); // 反序列化多个对象 Type userListType = new TypeToken<List<User>>() {}.getType(); List<User> users = gson.fromJson(usersJson, userListType); System.out.println("Parsed Users from JSON: " + users); } 执行结果:
3.4 SpringBoot 设置 GSON 为默认Json解析框架
如果我们基于某些特殊的场景,必须要使用 FastJSON 作为 SpringBoot 默认的 Json 解析框架,首先要排除 jackson 依赖:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> <!-- 排除jackson依赖 --> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> 然后,创建配置类如下所示:
DefaultJsonConfig.java
import com.google.gson.*; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.http.HttpMessageConverters; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.http.MediaType; import org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter; import org.springframework.http.converter.json.GsonHttpMessageConverter; import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets; import java.time.LocalDate; import java.time.LocalDateTime; import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; /** * 默认JSON框架配置类 */ @Configuration public class DefaultJsonConfig { /** * GSON时间日期-序列化机制 */ private final static JsonSerializer<LocalDateTime> jsonSerializerDateTime = (localDateTime, type, jsonSerializationContext) -> new JsonPrimitive(localDateTime.format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"))); private final static JsonSerializer<LocalDate> jsonSerializerDate = (localDate, type, jsonSerializationContext) -> new JsonPrimitive(localDate.format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"))); /** * GSON时间日期-反序列化机制 */ private final static JsonDeserializer<LocalDateTime> jsonDeserializerDateTime = (jsonElement, type, jsonDeserializationContext) -> LocalDateTime.parse(jsonElement.getAsJsonPrimitive().getAsString(), DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")); private final static JsonDeserializer<LocalDate> jsonDeserializerDate = (jsonElement, type, jsonDeserializationContext) -> LocalDate.parse(jsonElement.getAsJsonPrimitive().getAsString(), DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")); /** * 利用 GSON 替换掉 jackson, */ @Bean public HttpMessageConverters gsonHttpMessageConverters() { // 配置StringHttpMessageConverter,解决返回中文乱码问题 StringHttpMessageConverter stringHttpMessageConverter = new StringHttpMessageConverter(StandardCharsets.UTF_8); List<MediaType> supportedMediaTypes = new ArrayList<>(); supportedMediaTypes.add(MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN); supportedMediaTypes.add(MediaType.TEXT_HTML); stringHttpMessageConverter.setSupportedMediaTypes(supportedMediaTypes); stringHttpMessageConverter.setWriteAcceptCharset(false); // 配置gson Gson gson = new GsonBuilder() // 设置 LocalDateTime 序列化、反序列化格式 .registerTypeAdapter(LocalDateTime.class, jsonSerializerDateTime) .registerTypeAdapter(LocalDateTime.class, jsonDeserializerDateTime) // 设置 LocalDate 序列化、反序列化格式 .registerTypeAdapter(LocalDate.class, jsonSerializerDate) .registerTypeAdapter(LocalDate.class, jsonDeserializerDate) // 序列化Null值 // .serializeNulls() .create(); GsonHttpMessageConverter gsonConverter = new GsonHttpMessageConverter(); gsonConverter.setGson(gson); // 设置支持的MediaType List<MediaType> fastMediaTypes = new ArrayList<>(); fastMediaTypes.add(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON); fastMediaTypes.add(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8); gsonConverter.setSupportedMediaTypes(fastMediaTypes); gsonConverter.setDefaultCharset(StandardCharsets.UTF_8); return new HttpMessageConverters(gsonConverter, stringHttpMessageConverter); } } 整理完毕,完结撒花~🌻
参考地址:
1.SpringBoot使用Json序列化(jackson-fastjson-gson等),https://blog.csdn.net/QingChunBuSanChang/article/details/125370687
2.Jackson、gson官方文档以及下载地址,https://blog.csdn.net/banzhengyu/article/details/131168023
3.Jackson入门,https://www.cnblogs.com/mjoe/p/14930842.html
4.Spring Boot整合系列——Gson完整详细版,https://blog.csdn.net/Saykuray/article/details/110506500
5.Gson使用中LocalDateTime和String转化,https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_39406978/article/details/110929874
