阅读量:0
Method 1
# Method 1: create_sequences function def create_sequences_meth1(data, target_col, sequence_length=10): sequences = [] targets = [] for i in range(len(data) - sequence_length): seq = data[i:i + sequence_length].drop(columns=[target_col]).values label = data.iloc[i + sequence_length][target_col] sequences.append(seq) targets.append(label) return np.array(sequences), np.array(targets) scaler_meth1 = MinMaxScaler() scaled_df_meth1 = pd.DataFrame(scaler_meth1.fit_transform(df), columns=df.columns) sequence_length = 100 num_features = len(df.columns) X_meth1, y_meth1 = create_sequences_meth1(scaled_df_meth1, target_col='RH', sequence_length=sequence_length) split_ratio = 0.8 split_index = int(len(X_meth1) * split_ratio) X_train_meth1, X_test_meth1 = X_meth1[:split_index], X_meth1[split_index:] y_train_meth1, y_test_meth1 = y_meth1[:split_index], y_meth1[split_index:] X_train_meth1 = X_train_meth1.reshape((X_train_meth1.shape[0], X_train_meth1.shape[1], X_train_meth1.shape[2])) X_test_meth1 = X_test_meth1.reshape((X_test_meth1.shape[0], X_test_meth1.shape[1], X_test_meth1.shape[2])) optimizer_meth1 = Adam(lr=0.001) model_meth1 = Sequential() model_meth1.add(LSTM(32, return_sequences=True, input_shape=(X_train_meth1.shape[1], X_train_meth1.shape[2]))) model_meth1.add(Dropout(0.2)) model_meth1.add(LSTM(32)) model_meth1.add(Dropout(0.2)) model_meth1.add(Dense(1)) model_meth1.compile(loss='mse', optimizer=optimizer_meth1, metrics=['mse']) early_stopping_meth1 = EarlyStopping(monitor='val_loss', patience=10, restore_best_weights=True) history_meth1 = model_meth1.fit(X_train_meth1, y_train_meth1, epochs=200, batch_size=50, validation_data=(X_test_meth1, y_test_meth1), verbose=0, callbacks=[early_stopping_meth1], shuffle=False) plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6)) plt.plot(history_meth1.history['loss'], label='train') plt.plot(history_meth1.history['val_loss'], label='test') plt.legend() plt.show()
predictions_meth1 = model_meth1.predict(X_test_meth1) X_test_reshaped_meth1 = X_test_meth1.reshape((X_test_meth1.shape[0], X_test_meth1.shape[1] * X_test_meth1.shape[2])) inv_preds_meth1 = np.concatenate((predictions_meth1, X_test_reshaped_meth1[:, -(num_features - 1):]), axis=1) inv_preds_meth1 = scaler_meth1.inverse_transform(inv_preds_meth1) inv_preds_meth1 = inv_preds_meth1[:, 0] y_test_reshaped_meth1 = y_test_meth1.reshape((len(y_test_meth1), 1)) inv_actual_y_meth1 = np.concatenate((y_test_reshaped_meth1, X_test_reshaped_meth1[:, -(num_features - 1):]), axis=1) inv_actual_y_meth1 = scaler_meth1.inverse_transform(inv_actual_y_meth1) inv_actual_y_meth1 = inv_actual_y_meth1[:, 0] print("Predictions Method 1:", inv_preds_meth1) print("Actual values Method 1:", inv_actual_y_meth1) 58/58 [==============================] - 1s 13ms/step Predictions Method 1: [20.72510315 13.99930025 11.20439576 ... 2.88401567 0.74950135 -0.53083279] Actual values Method 1: [16.40754717 13.01509434 12.19622642 ... 3.42264151 0.61509434 0.38113208] # Evaluate Method 1 mse_meth1 = mean_squared_error(inv_actual_y_meth1, inv_preds_meth1) rmse_meth1 = np.sqrt(mse_meth1) r2_meth1 = r2_score(inv_actual_y_meth1, inv_preds_meth1) mae_meth1 = mean_absolute_error(inv_actual_y_meth1, inv_preds_meth1) print(f'Method 1 - Mean Squared Error (MSE): {mse_meth1}') print(f'Method 1 - Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE): {rmse_meth1}') print(f'Method 1 - R-squared (R2): {r2_meth1}') print(f'Method 1 - Mean Absolute Error (MAE): {mae_meth1}') Method 1 - Mean Squared Error (MSE): 6.851774623441025 Method 1 - Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE): 2.617589468087199 Method 1 - R-squared (R2): 0.9328422940803206 Method 1 - Mean Absolute Error (MAE): 1.8842330539870726 # Visualize actual vs predicted for Method 1 plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6)) plt.plot(inv_actual_y_meth1, label='Actual') plt.plot(inv_preds_meth1, label='Predicted') plt.title('Actual vs Predicted (Method 1)') plt.xlabel('Time') plt.ylabel('Value') plt.legend() plt.show()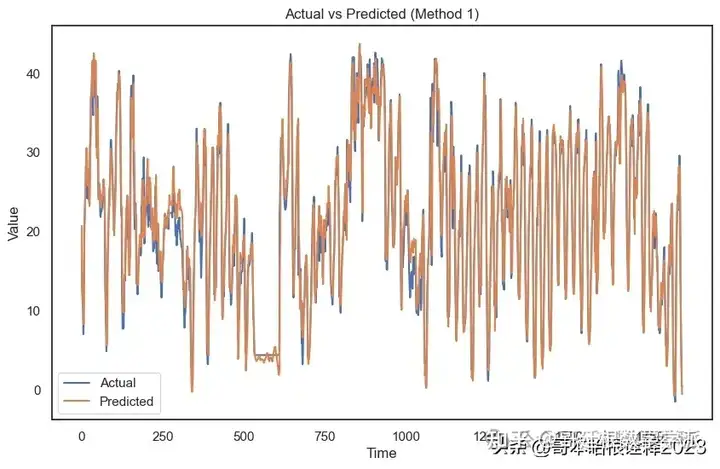
Method 2
# Method 2: making_supervised function def making_supervised_meth2(data, number_input=1, number_output=1, dropnan=True): number_variables = 1 if type(data) is list else data.shape[1] df = pd.DataFrame(data) cols, names = list(), list() for i in range(number_input, 0, -1): cols.append(df.shift(i)) names += [('var%d(t-%d)' % (j+1, i)) for j in range(number_variables)] for i in range(0, number_output): cols.append(df.shift(-i)) if i == 0: names += [('var%d(t)' % (j+1)) for j in range(number_variables)] else: names += [('var%d(t+%d)' % (j+1, i)) for j in range(number_variables)] agg = pd.concat(cols, axis=1) agg.columns = names if dropnan: agg.dropna(inplace=True) return agg scaler_meth2 = MinMaxScaler() scaled_values_meth2 = scaler_meth2.fit_transform(df.values) scaled_df_meth2 = pd.DataFrame(scaled_values_meth2, columns=df.columns) number_input = 100 number_output = 1 reframed_meth2 = making_supervised_meth2(scaled_df_meth2, number_input, number_output) target_col_index = len(df.columns) * number_input drop_columns = [i for i in range(target_col_index, reframed_meth2.shape[1]) if (i - target_col_index) % len(df.columns) != len(df.columns) - 1] reframed_meth2.drop(reframed_meth2.columns[drop_columns], axis=1, inplace=True) values_meth2 = reframed_meth2.values n_train_hours = int(len(values_meth2) * 0.8) train_meth2 = values_meth2[:n_train_hours, :] test_meth2 = values_meth2[n_train_hours:, :] X_train_meth2, y_train_meth2 = train_meth2[:, :-1], train_meth2[:, -1] X_test_meth2, y_test_meth2 = test_meth2[:, :-1], test_meth2[:, -1] X_train_meth2 = X_train_meth2.reshape((X_train_meth2.shape[0], number_input, len(df.columns))) X_test_meth2 = X_test_meth2.reshape((X_test_meth2.shape[0], number_input, len(df.columns))) optimizer_meth2 = Adam(lr=0.001) model_meth2 = Sequential() model_meth2.add(LSTM(64, return_sequences=True, input_shape=(X_train_meth2.shape[1], X_train_meth2.shape[2]))) model_meth2.add(Dropout(0.2)) model_meth2.add(LSTM(64)) model_meth2.add(Dropout(0.2)) model_meth2.add(Dense(1)) model_meth2.compile(loss='mse', optimizer=optimizer_meth2, metrics=['mse']) early_stopping_meth2 = EarlyStopping(monitor='val_loss', patience=10, restore_best_weights=True) history_meth2 = model_meth2.fit(X_train_meth2, y_train_meth2, epochs=200, batch_size=50, validation_data=(X_test_meth2, y_test_meth2), verbose=0, callbacks=[early_stopping_meth2], shuffle=False) plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6)) plt.plot(history_meth2.history['loss'], label='train') plt.plot(history_meth2.history['val_loss'], label='test') plt.legend() plt.show()
predictions_meth2 = model_meth2.predict(X_test_meth2) X_test_reshaped_meth2 = X_test_meth2.reshape((X_test_meth2.shape[0], number_input * len(df.columns))) inv_preds_meth2 = np.concatenate((predictions_meth2, X_test_reshaped_meth2[:, -(len(df.columns) - 1):]), axis=1) inv_preds_meth2 = scaler_meth2.inverse_transform(inv_preds_meth2) inv_preds_meth2 = inv_preds_meth2[:, 0] y_test_reshaped_meth2 = y_test_meth2.reshape((len(y_test_meth2), 1)) inv_actual_y_meth2 = np.concatenate((y_test_reshaped_meth2, X_test_reshaped_meth2[:, -(len(df.columns) - 1):]), axis=1) inv_actual_y_meth2 = scaler_meth2.inverse_transform(inv_actual_y_meth2) inv_actual_y_meth2 = inv_actual_y_meth2[:, 0] print("Predictions Method 2:", inv_preds_meth2) print("Actual values Method 2:", inv_actual_y_meth2) 58/58 [==============================] - 2s 20ms/step Predictions Method 2: [20.05376787 13.37555639 11.81537217 ... 4.66319288 1.91325717 -0.3942143 ] Actual values Method 2: [16.40754717 13.01509434 12.19622642 ... 3.42264151 0.61509434 0.38113208] # Evaluate Method 2 mse_meth2 = mean_squared_error(inv_actual_y_meth2, inv_preds_meth2) rmse_meth2 = np.sqrt(mse_meth2) r2_meth2 = r2_score(inv_actual_y_meth2, inv_preds_meth2) mae_meth2 = mean_absolute_error(inv_actual_y_meth2, inv_preds_meth2) print(f'Method 2 - Mean Squared Error (MSE): {mse_meth2}') print(f'Method 2 - Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE): {rmse_meth2}') print(f'Method 2 - R-squared (R2): {r2_meth2}') print(f'Method 2 - Mean Absolute Error (MAE): {mae_meth2}') Method 2 - Mean Squared Error (MSE): 5.7881381678302954 Method 2 - Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE): 2.4058549764751604 Method 2 - R-squared (R2): 0.943267532535622 Method 2 - Mean Absolute Error (MAE): 1.7095511506826195 # Visualize actual vs predicted for Method 2 plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6)) plt.plot(inv_actual_y_meth2, label='Actual') plt.plot(inv_preds_meth2, label='Predicted') plt.title('Actual vs Predicted (Method 2)') plt.xlabel('Time') plt.ylabel('Value') plt.legend() plt.show()
Comparison of Methods
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6)) plt.plot(inv_actual_y_meth1, label='Actual Method 1', linestyle='dashed') plt.plot(inv_preds_meth1, label='Predicted Method 1') plt.plot(inv_actual_y_meth2, label='Actual Method 2', linestyle='dotted') plt.plot(inv_preds_meth2, label='Predicted Method 2') plt.title('Actual vs Predicted for Both Methods') plt.xlabel('Time') plt.ylabel('Value') plt.legend() plt.show()
# Metrics from Method 1 metrics_meth1 = { "MSE": mse_meth1, "RMSE": rmse_meth1, "R2": r2_meth1, "MAE": mae_meth1 } # Metrics from Method 2 metrics_meth2 = { "MSE": mse_meth2, "RMSE": rmse_meth2, "R2": r2_meth2, "MAE": mae_meth2 } # Create DataFrame for comparison comparison_df = pd.DataFrame([metrics_meth1, metrics_meth2], index=['Method 1', 'Method 2']) print(comparison_df) MSE RMSE R2 MAE Method 1 6.851775 2.617589 0.932842 1.884233 Method 2 5.788138 2.405855 0.943268 1.709551担任《Mechanical System and Signal Processing》审稿专家,担任《中国电机工程学报》,《控制与决策》等EI期刊审稿专家,擅长领域:现代信号处理,机器学习,深度学习,数字孪生,时间序列分析,设备缺陷检测、设备异常检测、设备智能故障诊断与健康管理PHM等。 知乎学术咨询:https://www.zhihu.com/consult/people/792359672131756032?isMe=1
