PINN解偏微分方程实例1
更新:
最近使用下面代码框架求解了三个具体的偏微分方程,主要是对结果进行了可视化展示(一些漂亮的结果图),包括Diffusion,Burgers和Allen–Cahn方程;另外以burgers 方程为例,对解 PDE 反问题的结果也进行了可视化展示,具体见PINN解偏微分方程实例5.
更新:
最近使用下面代码框架求解了四个具体的偏微分方程,包括Diffusion,Burgers, Allen–Cahn和Wave方程,另外重新写了一个 求解反问题的代码框架,以burgers 方程为例,具体见PINN解偏微分方程实例4.
1. PINN简介
PINN是一种利用神经网络求解偏微分方程的方法,其计算流程图如下图所示,这里以偏微分方程(1)为例。
∂ u ∂ t + u ∂ u ∂ x = v ∂ 2 u ∂ x 2 \begin{align} \frac{\partial u}{\partial t}+u \frac{\partial u}{\partial x}=v\frac{\partial^2 u}{\partial x^2} \end{align} ∂t∂u+u∂x∂u=v∂x2∂2u
神经网络输入位置x,y,z和时间t的值,预测偏微分方程解u在这个时空条件下的数值解。
上图中可以看出,PINN的损失函数包含两部分内容,一部分是来源于训练数据误差,另一部分来源于偏微分方程误差,可以记作(2)式。
l = w d a t a l d a t a + w P D E l P D E \begin{align} \mathcal{l} = w_{data}\mathcal{l}_{data}+w_{PDE}\mathcal{l}_{PDE} \end{align} l=wdataldata+wPDElPDE
其中
l d a t a = 1 N d a t a ∑ i = 1 N d a t a ( u ( x i , t i ) − u i ) 2 l P D E = 1 N d a t a ∑ j = 1 N P D E ( ∂ u ∂ t + u ∂ u ∂ x − v ∂ 2 u ∂ x 2 ) 2 ∣ ( x j , t j ) \begin{align} \begin{aligned} \mathcal{l}_{data} &= \frac{1}{N_{data}}\sum_{i=1}^{N_{data}} (u(x_i,t_i)-u_i)^2 \\ \mathcal{l}_{PDE} &= \frac{1}{N_{data}}\sum_{j=1}^{N_{PDE}} \left( \frac{\partial u}{\partial t}+u \frac{\partial u}{\partial x}-v\frac{\partial^2 u}{\partial x^2} \right)^2|_{(x_j,t_j)} \end{aligned} \end{align} ldatalPDE=Ndata1i=1∑Ndata(u(xi,ti)−ui)2=Ndata1j=1∑NPDE(∂t∂u+u∂x∂u−v∂x2∂2u)2∣(xj,tj)
2. 偏微分方程实例
考虑偏微分方程如下:
∂ 2 u ∂ x 2 − ∂ 4 u ∂ y 4 = ( 2 − x 2 ) e − y \begin{align} \begin{aligned} \frac{\partial^2 u}{\partial x^2} - \frac{\partial^4 u}{\partial y^4} = (2-x^2)e^{-y} \end{aligned} \end{align} ∂x2∂2u−∂y4∂4u=(2−x2)e−y
考虑以下边界条件,
u y y ( x , 0 ) = x 2 u y y ( x , 1 ) = x 2 e u ( x , 0 ) = x 2 u ( x , 1 ) = x 2 e u ( 0 , y ) = 0 u ( 1 , y ) = e − y \begin{align} \begin{aligned} u_{yy}(x,0) &= x^2 \\ u_{yy}(x,1) &= \frac{x^2}{e} \\ u(x,0) &= x^2 \\ u(x,1) &= \frac{x^2}{e} \\ u(0,y) &= 0 \\ u(1,y) &= e^{-y} \\ \end{aligned} \end{align} uyy(x,0)uyy(x,1)u(x,0)u(x,1)u(0,y)u(1,y)=x2=ex2=x2=ex2=0=e−y
以上偏微分方程真解为 u ( x , y ) = x 2 e − y u(x,y)=x^2 e^{-y} u(x,y)=x2e−y,在区域 [ 0 , 1 ] × [ 0 , 1 ] [0,1]\times[0,1] [0,1]×[0,1]上随机采样配置点和数据点,其中配置点用来构造PDE损失函数 l 1 , l 2 , ⋯ , l 7 \mathcal{l}_1,\mathcal{l}_2,\cdots,\mathcal{l}_7 l1,l2,⋯,l7,数据点用来构造数据损失函数 l 8 \mathcal{l}_8 l8.
l 1 = 1 N 1 ∑ ( x i , y i ) ∈ Ω ( u ^ x x ( x i , y i ; θ ) − u ^ y y y y ( x i , y i ; θ ) − ( 2 − x i 2 ) e − y i ) 2 l 2 = 1 N 2 ∑ ( x i , y i ) ∈ [ 0 , 1 ] × { 0 } ( u ^ y y ( x i , y i ; θ ) − x i 2 ) 2 l 3 = 1 N 3 ∑ ( x i , y i ) ∈ [ 0 , 1 ] × { 1 } ( u ^ y y ( x i , y i ; θ ) − x i 2 e ) 2 l 4 = 1 N 4 ∑ ( x i , y i ) ∈ [ 0 , 1 ] × { 0 } ( u ^ ( x i , y i ; θ ) − x i 2 ) 2 l 5 = 1 N 5 ∑ ( x i , y i ) ∈ [ 0 , 1 ] × { 1 } ( u ^ ( x i , y i ; θ ) − x i 2 e ) 2 l 6 = 1 N 6 ∑ ( x i , y i ) ∈ { 0 } × [ 0 , 1 ] ( u ^ ( x i , y i ; θ ) − 0 ) 2 l 7 = 1 N 7 ∑ ( x i , y i ) ∈ { 1 } × [ 0 , 1 ] ( u ^ ( x i , y i ; θ ) − e − y i ) 2 l 8 = 1 N 8 ∑ i = 1 N 8 ( u ^ ( x i , y i ; θ ) − u i ) 2 \begin{align} \begin{aligned} \mathcal{l}_1 &= \frac{1}{N_1}\sum_{(x_i,y_i)\in\Omega} (\hat{u}_{xx}(x_i,y_i;\theta) - \hat{u}_{yyyy}(x_i,y_i;\theta) - (2-x_i^2)e^{-y_i})^2 \\ \mathcal{l}_2 &= \frac{1}{N_2}\sum_{(x_i,y_i)\in[0,1]\times\{0\}} (\hat{u}_{yy}(x_i,y_i;\theta) - x_i^2)^2 \\ \mathcal{l}_3 &= \frac{1}{N_3}\sum_{(x_i,y_i)\in[0,1]\times\{1\}} (\hat{u}_{yy}(x_i,y_i;\theta) - \frac{x_i^2}{e})^2 \\ \mathcal{l}_4 &= \frac{1}{N_4}\sum_{(x_i,y_i)\in[0,1]\times\{0\}} (\hat{u}(x_i,y_i;\theta) - x_i^2)^2 \\ \mathcal{l}_5 &= \frac{1}{N_5}\sum_{(x_i,y_i)\in[0,1]\times\{1\}} (\hat{u}(x_i,y_i;\theta) - \frac{x_i^2}{e})^2 \\ \mathcal{l}_6 &= \frac{1}{N_6}\sum_{(x_i,y_i)\in\{0\}\times [0,1]}(\hat{u}(x_i,y_i;\theta) - 0)^2 \\ \mathcal{l}_7 &= \frac{1}{N_7}\sum_{(x_i,y_i)\in\{1\}\times [0,1]}(\hat{u}(x_i,y_i;\theta) - e^{-y_i})^2 \\ \mathcal{l}_8 &= \frac{1}{N_{8}}\sum_{i=1}^{N_{8}} (\hat{u}(x_i,y_i;\theta)-u_i)^2 \end{aligned} \end{align} l1l2l3l4l5l6l7l8=N11(xi,yi)∈Ω∑(u^xx(xi,yi;θ)−u^yyyy(xi,yi;θ)−(2−xi2)e−yi)2=N21(xi,yi)∈[0,1]×{0}∑(u^yy(xi,yi;θ)−xi2)2=N31(xi,yi)∈[0,1]×{1}∑(u^yy(xi,yi;θ)−exi2)2=N41(xi,yi)∈[0,1]×{0}∑(u^(xi,yi;θ)−xi2)2=N51(xi,yi)∈[0,1]×{1}∑(u^(xi,yi;θ)−exi2)2=N61(xi,yi)∈{0}×[0,1]∑(u^(xi,yi;θ)−0)2=N71(xi,yi)∈{1}×[0,1]∑(u^(xi,yi;θ)−e−yi)2=N81i=1∑N8(u^(xi,yi;θ)−ui)2
3. 基于pytorch实现代码
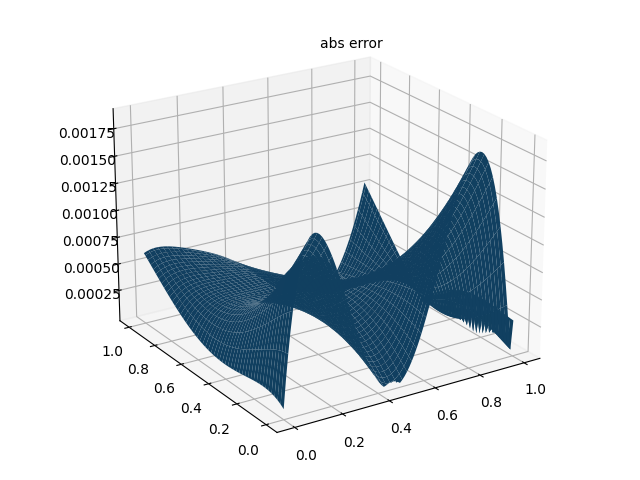
""" A scratch for PINN solving the following PDE u_xx-u_yyyy=(2-x^2)*exp(-y) Author: ST Date: 2023/2/26 """ import torch import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D epochs = 10000 # 训练代数 h = 100 # 画图网格密度 N = 1000 # 内点配置点数 N1 = 100 # 边界点配置点数 N2 = 1000 # PDE数据点 def setup_seed(seed): torch.manual_seed(seed) torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(seed) torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True # 设置随机数种子 setup_seed(888888) # Domain and Sampling def interior(n=N): # 内点 x = torch.rand(n, 1) y = torch.rand(n, 1) cond = (2 - x ** 2) * torch.exp(-y) return x.requires_grad_(True), y.requires_grad_(True), cond def down_yy(n=N1): # 边界 u_yy(x,0)=x^2 x = torch.rand(n, 1) y = torch.zeros_like(x) cond = x ** 2 return x.requires_grad_(True), y.requires_grad_(True), cond def up_yy(n=N1): # 边界 u_yy(x,1)=x^2/e x = torch.rand(n, 1) y = torch.ones_like(x) cond = x ** 2 / torch.e return x.requires_grad_(True), y.requires_grad_(True), cond def down(n=N1): # 边界 u(x,0)=x^2 x = torch.rand(n, 1) y = torch.zeros_like(x) cond = x ** 2 return x.requires_grad_(True), y.requires_grad_(True), cond def up(n=N1): # 边界 u(x,1)=x^2/e x = torch.rand(n, 1) y = torch.ones_like(x) cond = x ** 2 / torch.e return x.requires_grad_(True), y.requires_grad_(True), cond def left(n=N1): # 边界 u(0,y)=0 y = torch.rand(n, 1) x = torch.zeros_like(y) cond = torch.zeros_like(x) return x.requires_grad_(True), y.requires_grad_(True), cond def right(n=N1): # 边界 u(1,y)=e^(-y) y = torch.rand(n, 1) x = torch.ones_like(y) cond = torch.exp(-y) return x.requires_grad_(True), y.requires_grad_(True), cond def data_interior(n=N2): # 内点 x = torch.rand(n, 1) y = torch.rand(n, 1) cond = (x ** 2) * torch.exp(-y) return x.requires_grad_(True), y.requires_grad_(True), cond # Neural Network class MLP(torch.nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(MLP, self).__init__() self.net = torch.nn.Sequential( torch.nn.Linear(2, 32), torch.nn.Tanh(), torch.nn.Linear(32, 32), torch.nn.Tanh(), torch.nn.Linear(32, 32), torch.nn.Tanh(), torch.nn.Linear(32, 32), torch.nn.Tanh(), torch.nn.Linear(32, 1) ) def forward(self, x): return self.net(x) # Loss loss = torch.nn.MSELoss() def gradients(u, x, order=1): if order == 1: return torch.autograd.grad(u, x, grad_outputs=torch.ones_like(u), create_graph=True, only_inputs=True, )[0] else: return gradients(gradients(u, x), x, order=order - 1) # 以下7个损失是PDE损失 def l_interior(u): # 损失函数L1 x, y, cond = interior() uxy = u(torch.cat([x, y], dim=1)) return loss(gradients(uxy, x, 2) - gradients(uxy, y, 4), cond) def l_down_yy(u): # 损失函数L2 x, y, cond = down_yy() uxy = u(torch.cat([x, y], dim=1)) return loss(gradients(uxy, y, 2), cond) def l_up_yy(u): # 损失函数L3 x, y, cond = up_yy() uxy = u(torch.cat([x, y], dim=1)) return loss(gradients(uxy, y, 2), cond) def l_down(u): # 损失函数L4 x, y, cond = down() uxy = u(torch.cat([x, y], dim=1)) return loss(uxy, cond) def l_up(u): # 损失函数L5 x, y, cond = up() uxy = u(torch.cat([x, y], dim=1)) return loss(uxy, cond) def l_left(u): # 损失函数L6 x, y, cond = left() uxy = u(torch.cat([x, y], dim=1)) return loss(uxy, cond) def l_right(u): # 损失函数L7 x, y, cond = right() uxy = u(torch.cat([x, y], dim=1)) return loss(uxy, cond) # 构造数据损失 def l_data(u): # 损失函数L8 x, y, cond = data_interior() uxy = u(torch.cat([x, y], dim=1)) return loss(uxy, cond) # Training u = MLP() opt = torch.optim.Adam(params=u.parameters()) for i in range(epochs): opt.zero_grad() l = l_interior(u) \ + l_up_yy(u) \ + l_down_yy(u) \ + l_up(u) \ + l_down(u) \ + l_left(u) \ + l_right(u) \ + l_data(u) l.backward() opt.step() if i % 100 == 0: print(i) # Inference xc = torch.linspace(0, 1, h) xm, ym = torch.meshgrid(xc, xc) xx = xm.reshape(-1, 1) yy = ym.reshape(-1, 1) xy = torch.cat([xx, yy], dim=1) u_pred = u(xy) u_real = xx * xx * torch.exp(-yy) u_error = torch.abs(u_pred-u_real) u_pred_fig = u_pred.reshape(h,h) u_real_fig = u_real.reshape(h,h) u_error_fig = u_error.reshape(h,h) print("Max abs error is: ", float(torch.max(torch.abs(u_pred - xx * xx * torch.exp(-yy))))) # 仅有PDE损失 Max abs error: 0.004852950572967529 # 带有数据点损失 Max abs error: 0.0018916130065917969 # 作PINN数值解图 fig = plt.figure() ax = Axes3D(fig) ax.plot_surface(xm.detach().numpy(), ym.detach().numpy(), u_pred_fig.detach().numpy()) ax.text2D(0.5, 0.9, "PINN", transform=ax.transAxes) plt.show() fig.savefig("PINN solve.png") # 作真解图 fig = plt.figure() ax = Axes3D(fig) ax.plot_surface(xm.detach().numpy(), ym.detach().numpy(), u_real_fig.detach().numpy()) ax.text2D(0.5, 0.9, "real solve", transform=ax.transAxes) plt.show() fig.savefig("real solve.png") # 误差图 fig = plt.figure() ax = Axes3D(fig) ax.plot_surface(xm.detach().numpy(), ym.detach().numpy(), u_error_fig.detach().numpy()) ax.text2D(0.5, 0.9, "abs error", transform=ax.transAxes) plt.show() fig.savefig("abs error.png") 4. 数值解