阅读量:0
目录
前言
关于该注解的学习,主要来源项目中涉及,对此进行查漏补缺
@Accessors 注解通常用于简化实体类的代码,使其更加简洁和易读。
1. 概念
@Accessors 是 Lombok(一种Java库)提供的注解之一,用于自动生成 getter 和 setter 方法,并可以配置一些属性。
以下是关于 @Accessors 注解的详细解释
常用属性:
- fluent:如果设置为 true,生成的 getter 方法会移除 get 前缀,setter 方法移除 set 前缀。
- chain:如果设置为 true,生成的 setter 方法会返回当前对象,支持方法链调用。
- prefix:为生成的 getter 和 setter 方法添加指定前缀。
类似如下例子:
import lombok.AccessLevel; import lombok.Setter; import lombok.ToString; import lombok.experimental.Accessors; @ToString @Accessors(chain = true, fluent = true) public class Example { @Setter(AccessLevel.PROTECTED) private String name; private int age; } 在上面的例子中,@Accessors 注解配置了 chain = true 和 fluent = true,表示生成的 setter 方法支持方法链调用,并移除了 get 和 set 前缀。
通过源码也可看出其配置的属性:
/** * A container for settings for the generation of getters and setters. * <p> * Complete documentation is found at <a href="https://projectlombok.org/features/experimental/Accessors">the project lombok features page for @Accessors</a>. * <p> * Using this annotation does nothing by itself; an annotation that makes lombok generate getters and setters, * such as {@link lombok.Setter} or {@link lombok.Data} is also required. */ @Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.FIELD}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE) public @interface Accessors { /** * If true, accessors will be named after the field and not include a {@code get} or {@code set} * prefix. If true and {@code chain} is omitted, {@code chain} defaults to {@code true}. * <strong>default: false</strong> * * @return Whether or not to make fluent methods (named {@code fieldName()}, not for example {@code setFieldName}). */ boolean fluent() default false; /** * If true, setters return {@code this} instead of {@code void}. * <strong>default: false</strong>, unless {@code fluent=true}, then <strong>default: true</strong> * * @return Whether or not setters should return themselves (chaining) or {@code void} (no chaining). */ boolean chain() default false; /** * If present, only fields with any of the stated prefixes are given the getter/setter treatment. * Note that a prefix only counts if the next character is NOT a lowercase character or the last * letter of the prefix is not a letter (for instance an underscore). If multiple fields * all turn into the same name when the prefix is stripped, an error will be generated. * * @return If you are in the habit of prefixing your fields (for example, you name them {@code fFieldName}, specify such prefixes here). */ String[] prefix() default {}; } 2. 属性
默认fluent、chain 都是false
对于false,其设定的值跟往常差不多!
举例如下:(主要为了区分fluent、chain以及prefix三个属性)
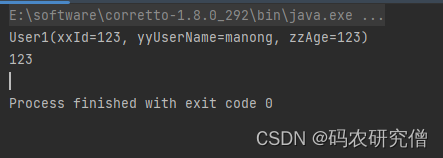
@Data //@AllArgsConstructor //@NoArgsConstructor @TableName("test_user1") @Accessors(chain = false,fluent = false) public class User1 { @TableId(value = "id", type = IdType.AUTO) private int xxId; private String yyUserName; private int zzAge; // 其他字段... public static void main(String[] args) { User1 user1 = new User1(); user1.setXxId(123); user1.setYyUserName("manong"); user1.setZzAge(123); System.out.println(user1); // User1(xxId=123, yyUserName=manong, zzAge=123) System.out.println(user1.getZzAge()); // 123 } } 截图如下:
2.1 fluent属性
为了方便测试,原先fluent默认就是false,当修改为true的时候:
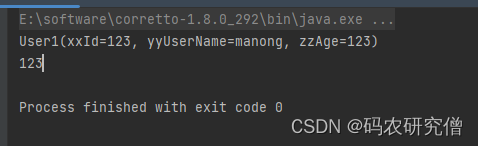
@Data @TableName("test_user1") @Accessors(fluent = true) public class User1 { @TableId(value = "id", type = IdType.AUTO) private int id; private String username; private int age; // 其他字段... public static void main(String[] args) { User1 user1 = new User1(); System.out.println(user1.id()); // 这个返回的值是int值,因为id为int类型 System.out.println(user1.id(123)); // 这个返回的对象值是类 System.out.println(user1.id()); // 再次看看id的属性为,123 System.out.println(user1.age()); // 查看其age属性,发现为0 } } 截图如下:

对应的属性有如下:
- 返回属性值
- 返回对象
可以通过得到对象再去检查其他的属性:
2.2 chain属性
chain的区别在于可以链式设定值!
代码如下:
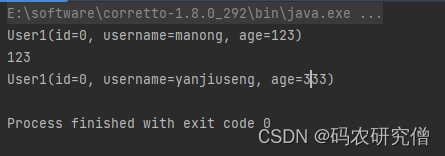
@Data @TableName("test_user1") @Accessors(chain = true) public class User1 { @TableId(value = "id", type = IdType.AUTO) private int id; private String username; private int age; // 其他字段... public static void main(String[] args) { User1 user1 = new User1(); // System.out.println(user1.setId(123)); // 返回对象 user1.setAge(123).setUsername("manong"); System.out.println(user1); // User1(id=0, username=manong, age=123) System.out.println(user1.getAge()); // 123 User1 user2 = new User1().setAge(333).setUsername("yanjiuseng"); System.out.println(user2); // User1(id=0, username=yanjiuseng, age=333) } } 截图如下:
2.3 prefix属性
注意属性中的前缀后要开头大写!此处的前缀必须为string类型
比如id属性,为了加一个前缀xx,则属性值应该为xxId,如果为xxid代码会错!
代码如下:
@Data @TableName("test_user1") @Accessors(prefix = {"xx","yy","zz"}) public class User1 { @TableId(value = "id", type = IdType.AUTO) private int xxId; private String yyUserName; private int zzAge; // 其他字段... public static void main(String[] args) { User1 user1 = new User1(); user1.setId(123); user1.setUserName("manong"); user1.setAge(123); System.out.println(user1); // User1(xxId=123, yyUserName=manong, zzAge=123) System.out.println(user1.getAge()); // 123 } } 截图如下: