✨ 慢品人间烟火色,闲观万事岁月长 🌏
🔥个人专栏:C++学习
🚀 欢迎关注:👍点赞 👂🏽留言 😍收藏 💞 💞 💞

1. 红黑树的概念
📒红黑树,是一种二叉搜索树,但在每个结点上增加一个存储位表示结点的颜色,可以是Red或Black。 通过对任何一条从根到叶子的路径上各个结点着色方式的限制,红黑树确保没有一条路径会比其他路径长出俩倍,因而是接近平衡的
📙红黑树由Rudolf Bayer在1972年发明,最初被称为平衡二叉B树(Symmetric Binary B-trees),后来被Guibas和Robert Sedgewick修改为如今的“红黑树”。

2. 红黑树的性质
节点是红色或黑色:每个节点都有一个颜色属性,颜色可以是红色或黑色。
根节点是黑色:树的根节点必须是黑色。
红色节点的子节点是黑色:如果一个节点是红色,则它的两个子节点必须是黑色(即不能有两个连续的红色节点)。
每个节点到其每个叶子节点的路径都包含相同数量的黑色节点:从任何节点到其每个叶子节点的路径上,经过的黑色节点的数量必须相同。
叶子节点是黑色:红黑树的叶子节点(通常是指空节点)被视为黑色。
3. 红黑树的节点结构及定义
红黑树节点的定义通常包含以下几个关键部分:
🧩3.1 基本元素
- _left:指向节点的左子节点的指针
- _right:指向节点的右子节点的指针
- _parent:指向节点的父节点的指针
- _kv:一个结构体或配对(pair),包含节点的键值(key)和值(value)。这取决于红黑的具体用途,可能只包含键或包含键值对。
- _col:表示当前节点的颜色。
🧩3.2 节点颜色(_col)
- 在上面的定义中,_col 成员变量用于表示节点的颜色,通过 Color 枚举类型来定义,可以是 RED 或 BLACK。
🧩3.3 构造函数
- 初始化一个新节点时,通常需要一个构造函数,它接受一个键值对(或仅键),并设置节点的左子节点、右子节点、父节点和颜色(初始化为红色)
🧩3.4 BR节点定义:
template<class K, class V> struct BSTreeNode { BSTreeNode<K, V>* _left; //左子树 BSTreeNode<K, V>* _right; //右子树 BSTreeNode<K, V>* _parent; //父亲 pair<K, V> _kv; //存放节点值的 string _col; //颜色(通过这个可以直到左右子树存在情况) //构造函数 BSTreeNode(const pair<K, V>& kv) :_left(nullptr) , _right(nullptr) , _parent(nullptr) , _kv(kv) , _col("RED") //默认颜色为红色 {} }; 红黑树的节点结构与二叉搜索树和AVL树差别不大,最大的差别就是加入了一个新的存储点——颜色
4. 红黑树的插入
🌈红黑树是在二叉搜索树的基础上加上其平衡限制条件,因此红黑树的插入可分为两步:
- 按照二叉搜索的树规则插入新节点
- 检测新节点插入后,红黑树的性质是否造到破坏
在我们进行插入操作之前,我们先定义一个红黑树的类
红黑树定义:
template<class K, class V> class RBTTree { typedef BSTreeNode<K, V> Node; public: // 其他未实现的成员函数 private: Node* _root = nullptr; }; 红黑树的插入操作类似于我们之前AVL树的插入,只不过红黑树的插入操作涉及到旋转操作以及考虑其他节点的颜色,前面的操作还是一样的
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv) { if (_root == nullptr) { _root = new Node(kv); _root->_col = BLACK; return true; } Node* parent = nullptr; Node* cur = _root; while (cur) { parent = cur; if (cur->_kv.first < kv.first) { cur = cur->_right; } else if (cur->_kv.first > kv.first) { cur = cur->_left; } else { return false; } } // 新增节点给红色 cur = new Node(kv); cur->_col = RED; if (parent->_kv.first < kv.first) { parent->_right = cur; } else { parent->_left = cur; } cur->_parent = parent; // 检测新节点插入后,红黑树的性质是否造到破坏 return true; } 🧩检测红黑树是否造到破坏
(如果遭到破坏则对当前红黑树进行变色,旋转处理)
约定:cur为当前节点,p为父节点,g为祖父节点,u为叔叔节点
🌈情况一
cur为红,p为红,g为黑,u存在且为红

解决方式:将parent,uncle改为黑,g改为红,然后把g当成cur,继续向上调整。
🌈情况二
cur为红,p为红,g为黑,u不存在/u存在且为黑
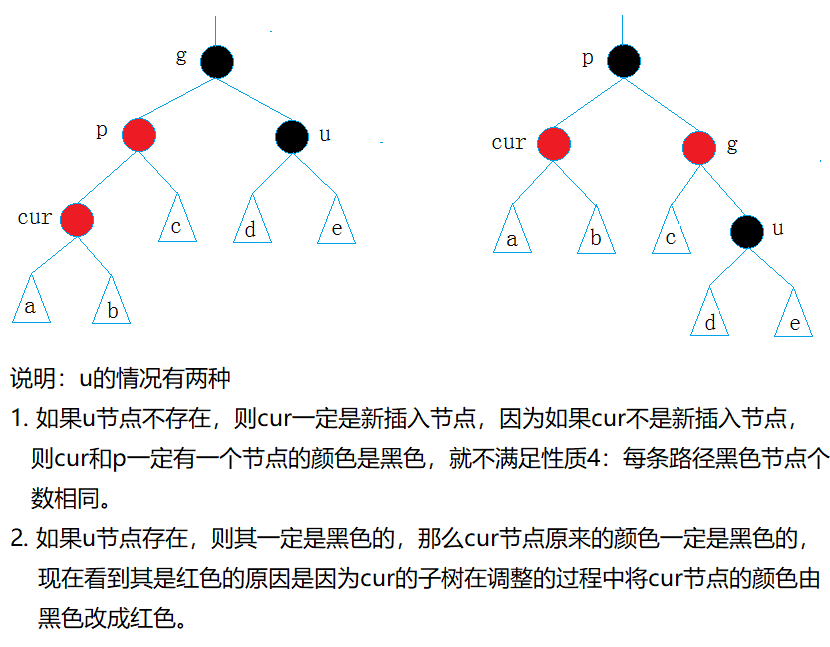
🌈情况三
cur为红,p为红,g为黑,u不存在/u存在且为黑

解决方式: p为g的左孩子,cur为p的右孩子,则针对p做左右双旋;p为g的右孩子,cur为p的左孩子,则针对p做右左旋转
cur、grandfather变色–> c变黑,p变红
检测红黑树是否造到破坏代码演示(C++):
while (parent && parent->_col == RED) //当父亲节点为红色,则出现了连续的红色,不符合条件 { Node* grandfather = parent->_parent; // g // p u if (parent == grandfather->_left) { Node* uncle = grandfather->_right; if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED) //叔叔存在并且为红 { parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK; grandfather->_col = RED; cur = grandfather; parent = cur->_parent; //往上面走 } else { //u存在且为黑或不存在 ->变色再继续往上处理 + 变色 if (cur == parent->_left) { //cur存在那么cur一定为红色 // g // p u //c //单旋,把p旋转上去,p作为子树根节点,g作为p的右 RotateR(grandfather); parent->_col = BLACK; grandfather->_col = RED; } else { // g // p u // c //双旋,将cur旋转上去,p作为cur的左,然后再旋转把cur旋转上去,g作为cur右边 RotateL(parent); RotateR(grandfather); cur->_col = BLACK; grandfather->_col = RED; } break; } } else { // g // u p Node* uncle = grandfather->_left; // 叔叔存在且为红,-》变色即可 if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED) { parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK; grandfather->_col = RED; // 继续往上处理 cur = grandfather; parent = cur->_parent; } else // 叔叔不存在,或者存在且为黑 { // 情况二:叔叔不存在或者存在且为黑 // 旋转+变色 // g // u p // c if (cur == parent->_right) { RotateL(grandfather); parent->_col = BLACK; grandfather->_col = RED; } else { // g // u p // c RotateR(parent); RotateL(grandfather); cur->_col = BLACK; grandfather->_col = RED; } break; } } } 红黑树的旋转和AVL树差不多,我们直接上代码回顾以下:
旋转代码示例(C++):
void RotateL(Node* parent) // 左旋 { Node* subR = parent->_right; Node* subRL = subR->_left; parent->_right = subRL; subR->_left = parent; Node* Parentparent = parent->_parent; parent->_parent = subR; if (subRL) subRL->_parent = parent; // 判断parent是不是根节点 if (_root == parent){ _root = subR; subR->_parent = nullptr; } else{ if (parent == Parentparent->_left) Parentparent->_left = subR; else Parentparent->_right = subR; subR->_parent = Parentparent; } } void RotateR(Node* parent) // 右旋 { Node* subL = parent->_left; Node* subLR = subL->_right; parent->_left = subLR; if (subLR) subLR->_parent = parent; Node* Parentparent = parent->_parent; subL->_right = parent; parent->_parent = subL; if(_root == parent){ _root = subL; subL->_parent = nullptr; } else{ if (parent == Parentparent->_left) Parentparent->_left = subL; else Parentparent->_right = subL; subL->_parent = Parentparent; } } 5. 红黑树的验证
📝红黑树的检测分为两步:
- 检测其是否满足二叉搜索树(中序遍历是否为有序序列)
- 检测其是否满足红黑树的性质
中序遍历代码演示(C++):
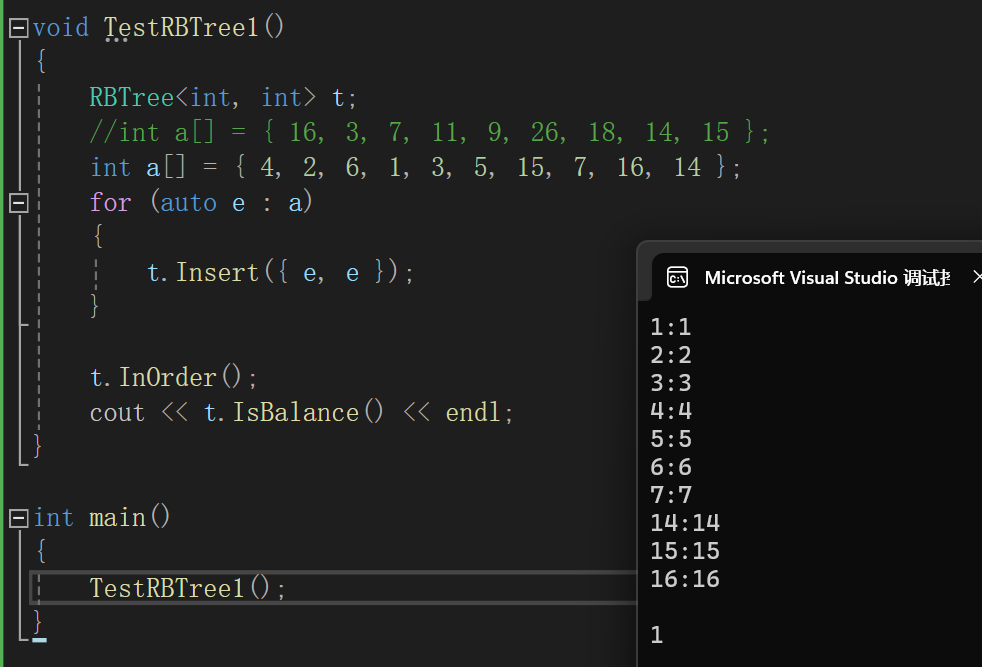
void InOrder() { _InOrder(_root); cout << endl; } void _InOrder(Node* root) { if (root == nullptr) return; _InOrder(root->_left); _cout << root->_kv.first << ":" << root->_kv.second << endl; _InOrder(root->_right); }检测其是否满足红黑树的性质(C++):
bool IsBalance() { if (_root == nullptr) return true; if (_root->_col == RED) { return false; } // 随便找条路径作为参考值 int refNum = 0; Node* cur = _root; while (cur) { if (cur->_col == BLACK) { ++refNum; } cur = cur->_left; } return Check(_root, 0, refNum); } bool Check(Node* root, int blackNum, const int refNum) { if (root == nullptr) { //cout << blackNum << endl; if (refNum != blackNum) { cout << "存在黑色节点的数量不相等的路径" << endl; return false; } return true; } if (root->_col == RED && root->_parent->_col == RED) { cout << root->_kv.first << "存在连续的红色节点" << endl; return false; } if (root->_col == BLACK) { blackNum++; } return Check(root->_left, blackNum, refNum) && Check(root->_right, blackNum, refNum); }测试代码用例及结果:
6. 红黑树的完整代码及总结
#include<iostream> #include<vector> #include<assert.h> using namespace std; enum Colour { RED, BLACK }; template<class K, class V> struct RBTreeNode { pair<K, V> _kv; RBTreeNode<K, V>* _left; RBTreeNode<K, V>* _right; RBTreeNode<K, V>* _parent; Colour _col; RBTreeNode(const pair<K, V>& kv) :_kv(kv) , _left(nullptr) , _right(nullptr) , _parent(nullptr) {} }; template<class K, class V> class RBTree { typedef RBTreeNode<K, V> Node; public: RBTree() = default; RBTree(const RBTree<K, V>& t) { _root = Copy(t._root); } RBTree<K, V>& operator=(RBTree<K, V> t) { swap(_root, t._root); return *this; } ~RBTree() { Destroy(_root); _root = nullptr; } bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv) { if (_root == nullptr) { _root = new Node(kv); _root->_col = BLACK; //根节点默认为黑色 return true; } Node* parent = nullptr; Node* cur = _root; while (cur) { parent = cur; if (cur->_kv.first < kv.first) cur = cur->_right; else if (cur->_kv.first > kv.first) cur = cur->_left; else return false; } cur = new Node(kv); // 新增节点。颜色红色给红色 cur->_col = RED; if (parent->_kv.first < kv.first) { parent->_right = cur; } else { parent->_left = cur; } cur->_parent = parent; while (parent && parent->_col == RED) //当父亲节点为红色,则出现了连续的红色,不符合条件 { Node* grandfather = parent->_parent; // g // p u if (parent == grandfather->_left) { Node* uncle = grandfather->_right; if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED) //叔叔存在并且为红 { parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK; grandfather->_col = RED; cur = grandfather; parent = cur->_parent; //往上面走 } else { //u存在且为黑或不存在 ->变色再继续往上处理 + 变色 if (cur == parent->_left) { //cur存在那么cur一定为红色 // g // p u //c //单旋,把p旋转上去,p作为子树根节点,g作为p的右 RotateR(grandfather); parent->_col = BLACK; grandfather->_col = RED; } else { // g // p u // c //双旋,将cur旋转上去,p作为cur的左,然后再旋转把cur旋转上去,g作为cur右边 RotateL(parent); RotateR(grandfather); cur->_col = BLACK; grandfather->_col = RED; } break; } } else { // g // u p Node* uncle = grandfather->_left; // 叔叔存在且为红,-》变色即可 if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED) { parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK; grandfather->_col = RED; // 继续往上处理 cur = grandfather; parent = cur->_parent; } else // 叔叔不存在,或者存在且为黑 { // 情况二:叔叔不存在或者存在且为黑 // 旋转+变色 // g // u p // c if (cur == parent->_right) { RotateL(grandfather); parent->_col = BLACK; grandfather->_col = RED; } else { // g // u p // c RotateR(parent); RotateL(grandfather); cur->_col = BLACK; grandfather->_col = RED; } break; } } } _root->_col = BLACK; //无论什么情况根节点都为黑 return true; } void InOrder() { _InOrder(_root); cout << endl; } int Height() { return _Height(_root); } int Size() { return _Size(_root); } Node* Find(const K& key) { Node* cur = _root; while (cur) { if (cur->_kv.first < key) { cur = cur->_right; } else if (cur->_kv.first > key) { cur = cur->_left; } else { return cur; } } return nullptr; } bool IsBalance() { if (_root == nullptr) return true; if (_root->_col == RED) { return false; } // 随便找条路径作为参考值 int refNum = 0; Node* cur = _root; while (cur) { if (cur->_col == BLACK) { ++refNum; } cur = cur->_left; } return Check(_root, 0, refNum); } private: bool Check(Node* root, int blackNum, const int refNum) { if (root == nullptr) { //cout << blackNum << endl; if (refNum != blackNum) { cout << "存在黑色节点的数量不相等的路径" << endl; return false; } return true; } if (root->_col == RED && root->_parent->_col == RED) { cout << root->_kv.first << "存在连续的红色节点" << endl; return false; } if (root->_col == BLACK) { blackNum++; } return Check(root->_left, blackNum, refNum) && Check(root->_right, blackNum, refNum); } int _Size(Node* root) { return root == nullptr ? 0 : _Size(root->_left) + _Size(root->_right) + 1; } int _Height(Node* root) { if (root == nullptr) return 0; int leftHeight = _Height(root->_left); int rightHeight = _Height(root->_right); return leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1; } void _InOrder(Node* root) { if (root == nullptr) { return; } _InOrder(root->_left); cout << root->_kv.first << ":" << root->_kv.second << endl; _InOrder(root->_right); } void RotateL(Node* parent) { _rotateNum++; Node* subR = parent->_right; Node* subRL = subR->_left; parent->_right = subRL; if (subRL) subRL->_parent = parent; Node* parentParent = parent->_parent; subR->_left = parent; parent->_parent = subR; if (parentParent == nullptr) { _root = subR; subR->_parent = nullptr; } else { if (parent == parentParent->_left) { parentParent->_left = subR; } else { parentParent->_right = subR; } subR->_parent = parentParent; } } void RotateR(Node* parent) { _rotateNum++; Node* subL = parent->_left; Node* subLR = subL->_right; parent->_left = subLR; if (subLR) subLR->_parent = parent; Node* parentParent = parent->_parent; subL->_right = parent; parent->_parent = subL; if (parentParent == nullptr) { _root = subL; subL->_parent = nullptr; } else { if (parent == parentParent->_left) { parentParent->_left = subL; } else { parentParent->_right = subL; } subL->_parent = parentParent; } } void Destroy(Node* root) { if (root == nullptr) return; Destroy(root->_left); Destroy(root->_right); delete root; } Node* Copy(Node* root) { if (root == nullptr) return nullptr; Node* newRoot = new Node(root->_kv); newRoot->_left = Copy(root->_left); newRoot->_right = Copy(root->_right); return newRoot; } private: Node* _root = nullptr; public: int _rotateNum = 0; }; void TestRBTree1() { RBTree<int, int> t; //int a[] = { 16, 3, 7, 11, 9, 26, 18, 14, 15 }; int a[] = { 4, 2, 6, 1, 3, 5, 15, 7, 16, 14 }; for (auto e : a) { t.Insert({ e, e }); } t.InOrder(); cout << t.IsBalance() << endl; } 以上就是红黑树的全部内容,红黑树因为其自平衡的特性,及通过节点颜色来操作其树形结构的特点,极大的提高了数据存储及处理的效率,需要我们好好掌握,希望我的博客能够帮助到你,感谢观看。