温馨提示:文末有 CSDN 平台官方提供的学长 QQ 名片 :)
1. 项目简介
农作物病害不仅影响产量,还会导致严重的经济损失。传统的病害检测方法通常依赖人工专家进行目视检查,这种方法费时费力且容易受到主观因素的影响。近年来,深度学习技术的快速发展为植物病害的自动化检测提供了新的解决方案。本项目基于迁移学习策略,以VGG卷积神经网络为 base 模型,利用 TensorFlow、Keras 等工具构建面向植物疾病监测的卷积神经网络,通过模型训练、验证测试,预测准确率达到90%。利用 Flask、Bootstrap等框架搭建交互分析平台,用户通过上传植物叶片图像,实现疾病的在线诊断。
B站详情与代码下载:基于深度学习的植物疾病检测识别系统_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
基于深度学习的植物疾病检测识别系统
2. 植物疾病数据集读取与可视化
利用 opencv工具读取图像数据,并利用 matplotlib 进行样本的可视化:
import cv2 # 用于图像处理 from tqdm import tqdm # 用于显示进度条 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 用于绘制图像 # 加载训练集图像 train_images = [] for name in tqdm(p_train['image_id']): # p_train['image_id'] 应该是一个包含图像ID的 pandas Series path = './dataset/images/' + name + '.jpg' # 构建文件路径 img = cv2.imread(path) # 使用 OpenCV 读取图像 image = cv2.resize(img, (img_size, img_size), interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA) # 调整图像大小 train_images.append(image) # 将调整后的图像添加到列表中 # 显示四张样本训练图像 fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 4, figsize=(15, 15)) # 创建一个子图网格 for i in range(4): ax[i].set_axis_off() # 关闭坐标轴标记 ax[i].imshow(train_images[i]) # 在子图上显示图像 plt.show() # 显示绘图 # 加载测试集图像 test_images = [] for name in tqdm(p_test['image_id']): # p_test['image_id'] 应该是一个包含图像ID的 pandas Series path = './dataset/images/' + name + '.jpg' # 构建文件路径 img = cv2.imread(path) # 使用 OpenCV 读取图像 image = cv2.resize(img, (img_size, img_size), interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA) # 调整图像大小 test_images.append(image) # 将调整后的图像添加到列表中 # 显示四张样本测试图像 fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 4, figsize=(15, 15)) # 创建一个子图网格 for i in range(4): ax[i].set_axis_off() # 关闭坐标轴标记 ax[i].imshow(test_images[i]) # 在子图上显示图像 plt.show() # 显示绘图

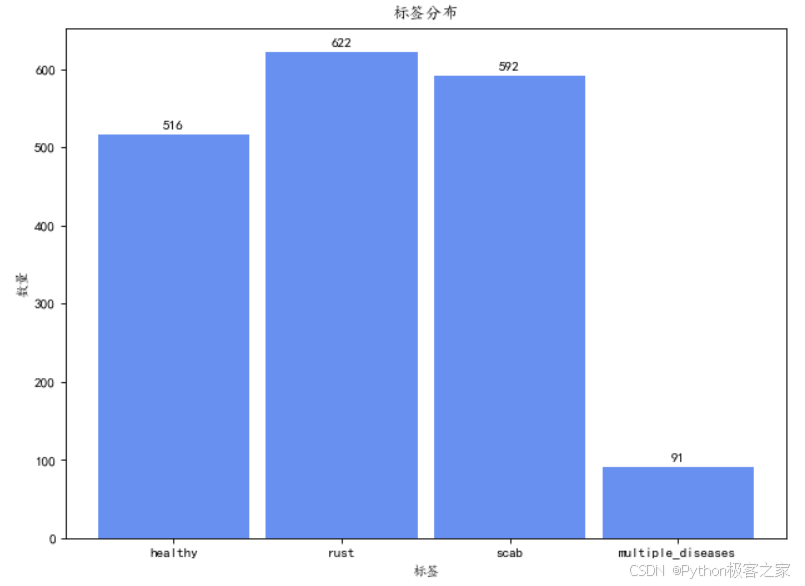
该数据集的标签包括:healthy、multiple_diseases、rust、scab,以此是一个多标签的图像分类问题,其样本数量分布如下:
3. 缓解类别不均衡问题
类别不平衡问题,顾名思义,即数据集中存在某一类样本,其数量远多于或远少于其他类样本,从而导致一些机器学习模型失效的问题。本文采用 SMOTE 上采样算法,缓解样本类别不均衡。
SMOTE 算法(Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique)是一种用于处理数据集中类别不平衡问题的技术。当数据集中某个类别的样本数量远少于其他类别时,这被称为类别不平衡问题。这种不平衡可能会导致机器学习模型偏向于多数类,从而忽视少数类的预测准确率。
from imblearn.over_sampling import SMOTE sm = SMOTE(random_state = 115) x_train, y_train = sm.fit_resample(x_train.reshape((-1, img_size * img_size * 3)), y_train) x_train = x_train.reshape((-1, img_size, img_size, 3)) x_train.shape, y_train.sum(axis=0)4. 构建卷积神经网络
本项目以VGG16(也可以选择其他模型)为base模型,构建卷积神经网络:
input_shape=(img_size, img_size, 3) base_model = tf.keras.applications.vgg16.VGG16( weights='./pretrained_models/vgg16_weights_tf_dim_ordering_tf_kernels_notop.h5', include_top=False, input_shape=input_shape ) base_model.trainable = False model = tf.keras.Sequential() model.add(base_model) model.add(tf.keras.layers.Flatten()) ...... model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(0.001), metrics=['acc']) model.summary()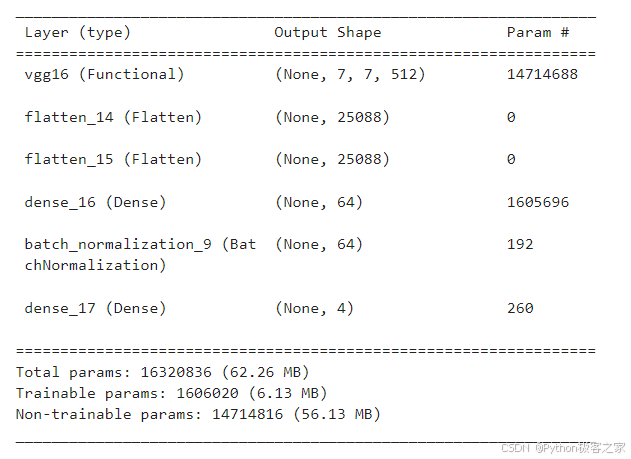
5. 模型训练与验证
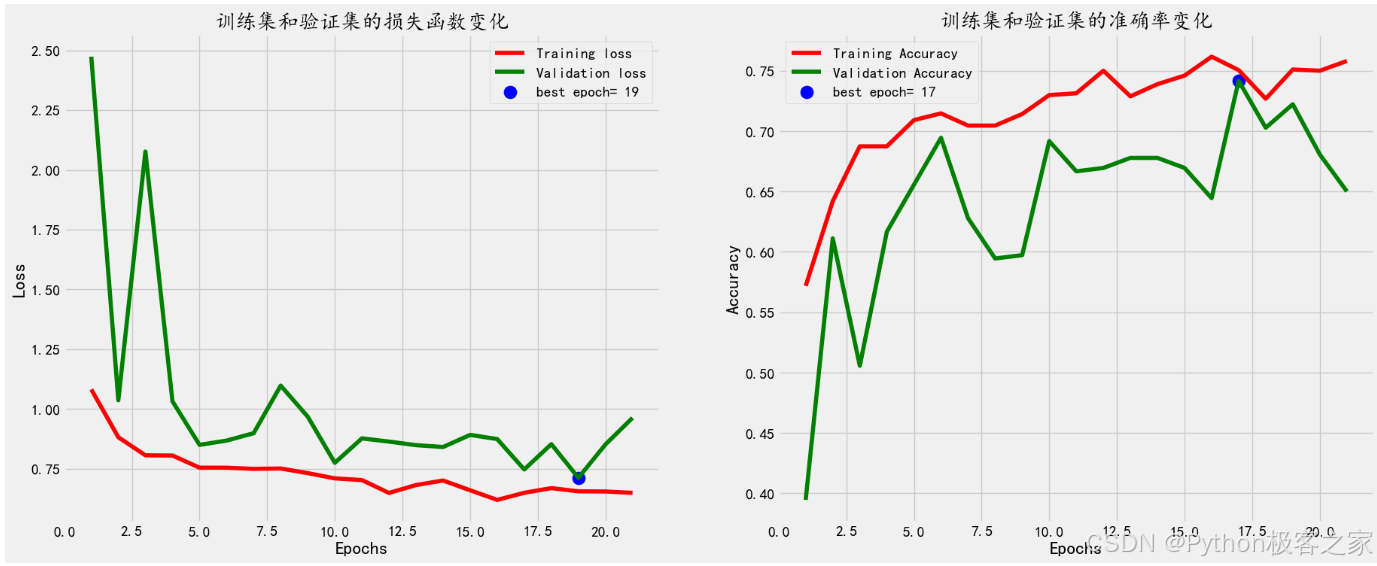
datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rotation_range=45, # shear_range=.25, # zoom_range=.25, width_shift_range=.25, height_shift_range=.25, # brightness_range=[.5,1.5], horizontal_flip=True, vertical_flip=True ) epochs = 50 batch_size = 24 checkpoint = tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint('save_models/best_model.h5', monitor='val_acc', verbose=1, mode='max',save_best_only=True) early = tf.keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(monitor="acc", mode="max",restore_best_weights=True, patience=5) callbacks_list = [checkpoint, early] history = model.fit_generator(datagen.flow(x_train, y_train, batch_size=batch_size), epochs=epochs, steps_per_epoch=x_train.shape[0] // batch_size, verbose=1, callbacks=callbacks_list, validation_data=datagen.flow(x_val, y_val,batch_size=batch_size), validation_steps=x_val.shape[0]//batch_size )Epoch 1/50 83/83 [==============================] - ETA: 0s - loss: 1.0818 - acc: 0.5717 Epoch 1: val_acc improved from -inf to 0.39444, saving model to save_models\best_model.h5 83/83 [==============================] - 318s 4s/step - loss: 1.0818 - acc: 0.5717 - val_loss: 2.4739 - val_acc: 0.3944 Epoch 2/50 83/83 [==============================] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.8818 - acc: 0.6419 Epoch 2: val_acc improved from 0.39444 to 0.61111, saving model to save_models\best_model.h5 83/83 [==============================] - 268s 3s/step - loss: 0.8818 - acc: 0.6419 - val_loss: 1.0368 - val_acc: 0.6111 ...... Epoch 16/50 83/83 [==============================] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.6197 - acc: 0.7616 Epoch 16: val_acc did not improve from 0.69444 83/83 [==============================] - 275s 3s/step - loss: 0.6197 - acc: 0.7616 - val_loss: 0.8742 - val_acc: 0.6444 Epoch 17/50 83/83 [==============================] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.6494 - acc: 0.7505 Epoch 17: val_acc improved from 0.69444 to 0.74167, saving model to save_models\best_model.h5 83/83 [==============================] - 409s 5s/step - loss: 0.6494 - acc: 0.7505 - val_loss: 0.7470 - val_acc: 0.7417 Epoch 18/50 83/83 [==============================] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.6689 - acc: 0.7268 Epoch 18: val_acc did not improve from 0.74167 83/83 [==============================] - 391s 5s/step - loss: 0.6689 - acc: 0.7268 - val_loss: 0.8530 - val_acc: 0.7028 ...... CPU times: total: 11h 1min 29s Wall time: 1h 47min 10s
 模型完成训练后,利用验证集进行性能评估:
模型完成训练后,利用验证集进行性能评估:
from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score pred_test = model.predict(x_val) roc_sum = 0 for i in range(4): score = roc_auc_score(y_val[:, i], pred_test[:, i]) roc_sum += score print(f'{score:.3f}') roc_sum /= 4 print(f'预测的验证集 AUC:{roc_sum:.3f}')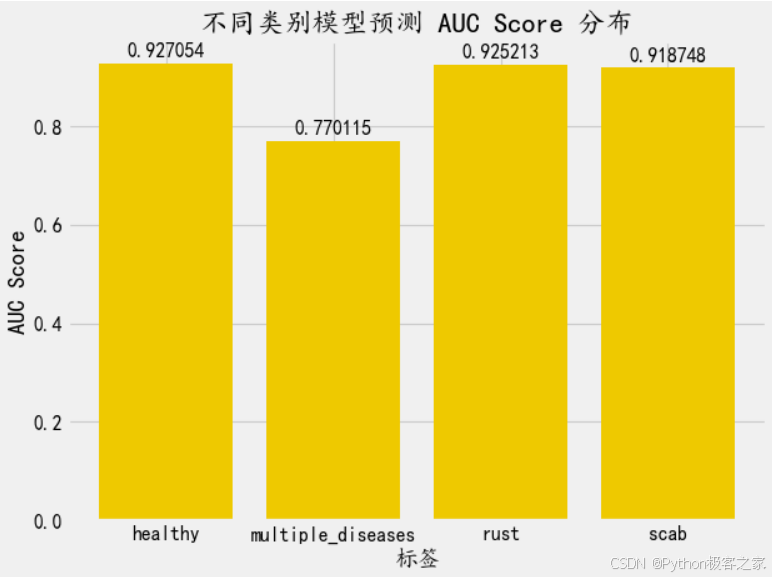
可以看出,healthy, rust, scab 类别预测 AUC 均达到 92%左右,multiple_diseases 由于样本过少,AUC 为 77%,可以通过进一步扩充 multiple_diseases 类别的样本来进行优化。
6. 基于深度学习的植物疾病检测识别系统
6.1 系统首页

6.2 模型介绍

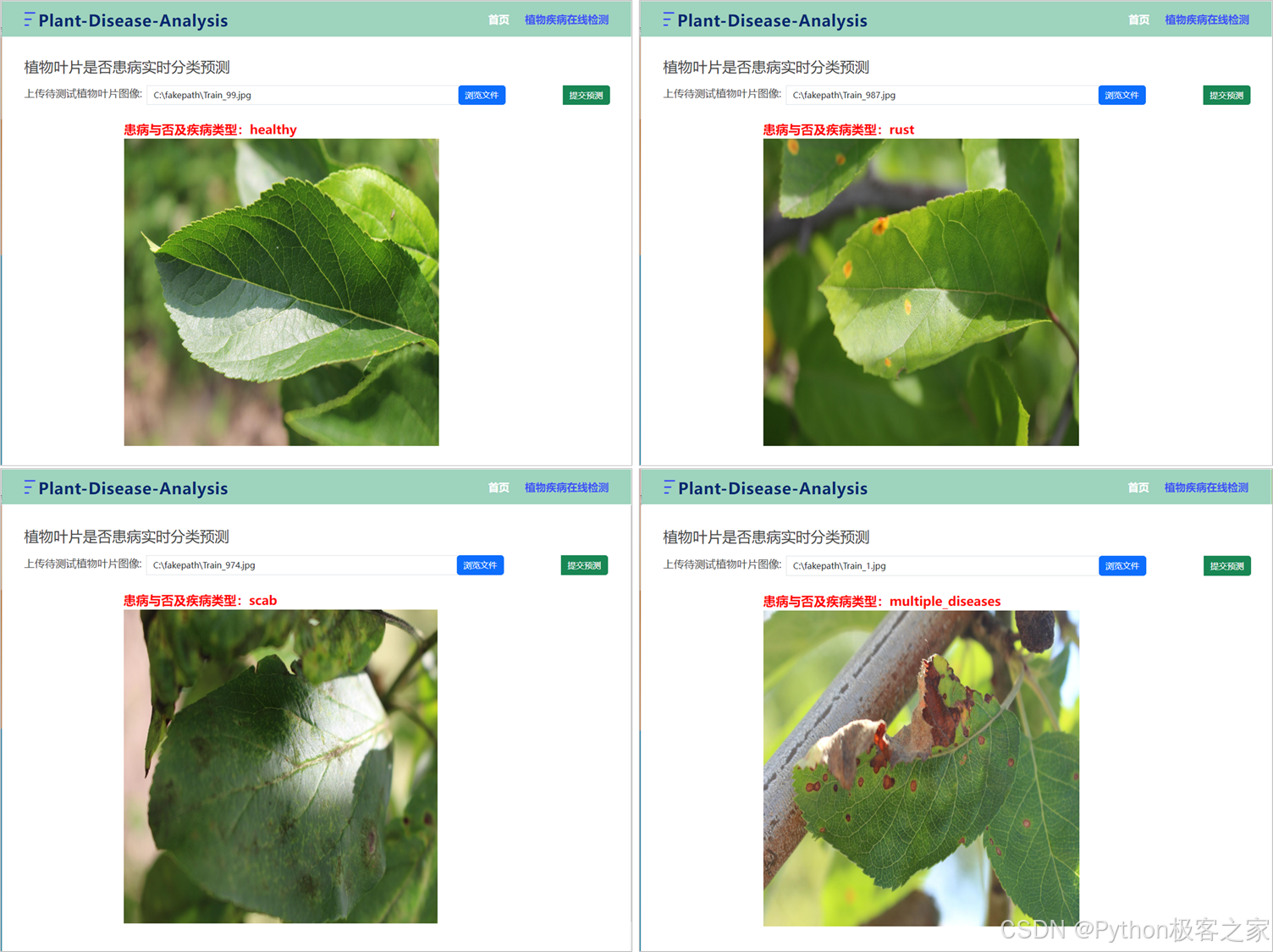
6.3 植物疾病在线检测
7. 结论
本项目基于迁移学习策略,以VGG卷积神经网络为 base 模型,利用 TensorFlow、Keras 等工具构建面向植物疾病监测的卷积神经网络,通过模型训练、验证测试,预测准确率达到90%。利用 Flask、Bootstrap等框架搭建交互分析平台,用户通过上传植物叶片图像,实现疾病的在线诊断。该系统不仅可以提高病害检测的效率和准确性,还可以为农民提供及时有效的防治建议,从而减少农作物损失。
欢迎大家点赞、收藏、关注、评论啦 ,由于篇幅有限,只展示了部分核心代码。技术交流、源码获取认准下方 CSDN 官方提供的学长 QQ 名片 :)
精彩专栏推荐订阅: