阅读量:0
目录
一、LCCP方法
LCCP指的是Local Convexity-Constrained Patch,即局部凸约束补丁的意思。LCCP方法的基本思想是在图像中找到局部区域内的凸结构,并将这些结构用于分割图像或提取特征。这种方法可以帮助识别图像中的凸物体,并对它们进行分割。LCCP方法通常结合了空间和法线信息,以提高图像分割的准确性和稳定性。
LCCP算法大致可以分成两个部分:1.基于超体聚类的过分割。2.在超体聚类的基础上再聚类。
该方法流程图如下: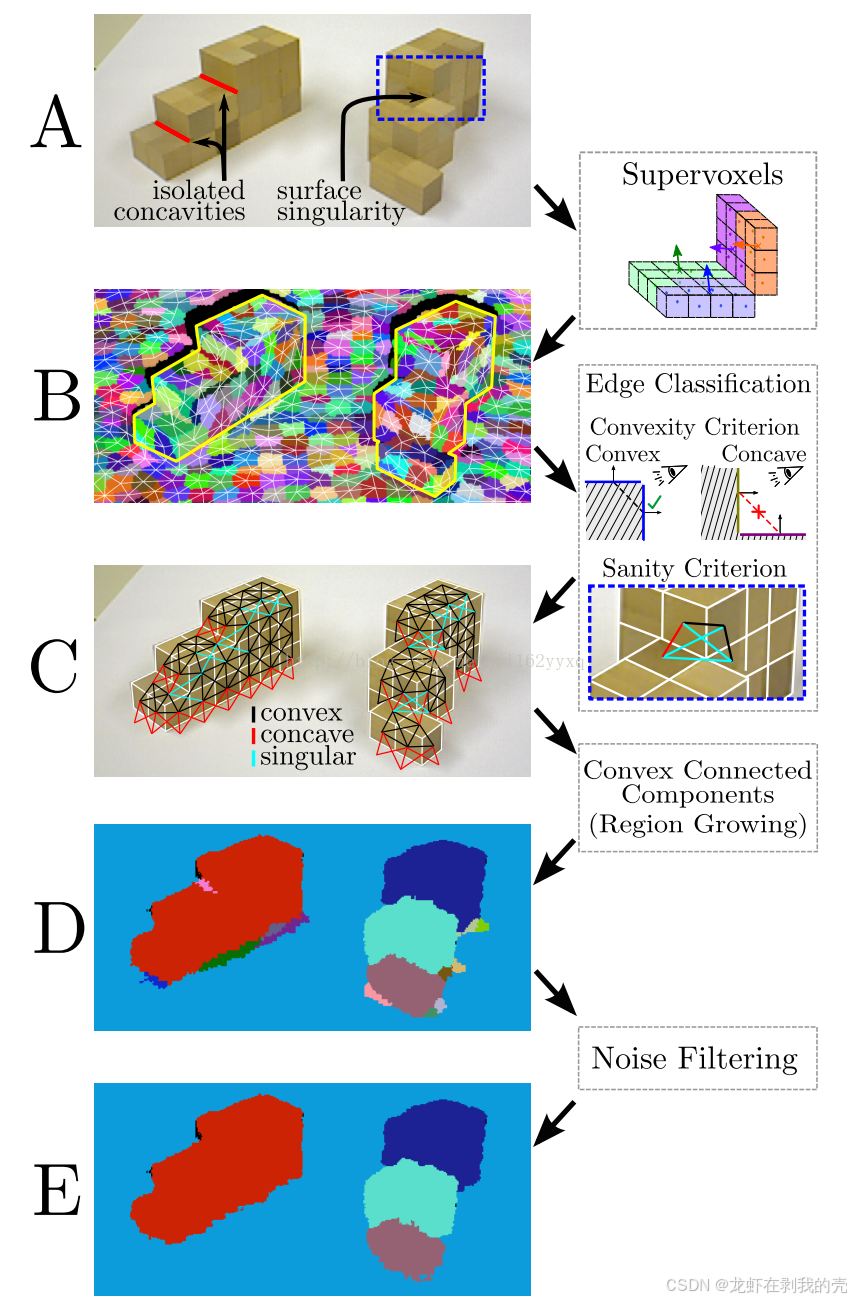
二、代码实现
#include <iostream> #include <pcl/ModelCoefficients.h> #include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h> #include <pcl/point_types.h> #include <pcl/sample_consensus/method_types.h> #include <pcl/sample_consensus/model_types.h> #include <pcl/segmentation/sac_segmentation.h> #include <pcl/visualization/cloud_viewer.h> #include <pcl/filters/extract_indices.h> #include <boost/thread/thread.hpp> #include <stdlib.h> #include <cmath> #include <limits.h> #include <boost/format.hpp> #include <pcl/console/parse.h> #include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h> #include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h> #include <pcl/visualization/point_cloud_color_handlers.h> #include <pcl/filters/passthrough.h> #include <pcl/segmentation/supervoxel_clustering.h> #include <pcl/segmentation/lccp_segmentation.h> #include <vtkPolyLine.h> #include <pcl/point_cloud.h> #include <pcl/segmentation/supervoxel_clustering.h> #include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h> using namespace std; typedef pcl::PointXYZ PointT; typedef pcl::LCCPSegmentation<PointT>::SupervoxelAdjacencyList SuperVoxelAdjacencyList; //邻接线条可视化 void addSupervoxelConnectionsToViewer(pcl::PointXYZRGBA& supervoxel_center, pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGBA>& adjacent_supervoxel_centers, std::string supervoxel_name, pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer::Ptr& viewer) { vtkSmartPointer<vtkPoints> points = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPoints>::New(); vtkSmartPointer<vtkCellArray> cells = vtkSmartPointer<vtkCellArray>::New(); vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyLine> polyLine = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyLine>::New(); for (auto adjacent_itr = adjacent_supervoxel_centers.begin(); adjacent_itr != adjacent_supervoxel_centers.end(); ++adjacent_itr) { points->InsertNextPoint(supervoxel_center.data); points->InsertNextPoint(adjacent_itr->data); } vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData> polyData = vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyData>::New(); polyData->SetPoints(points); polyLine->GetPointIds()->SetNumberOfIds(points->GetNumberOfPoints()); for (unsigned int i = 0; i < points->GetNumberOfPoints(); i++) polyLine->GetPointIds()->SetId(i, i); cells->InsertNextCell(polyLine); polyData->SetLines(cells); viewer->addModelFromPolyData(polyData, supervoxel_name); } int main(int argc, char** argv) { pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>); pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>); pcl::PCDReader reader; // 读入点云PCD文件 reader.read("E:****.pcd", *cloud); cout << "Point cloud data: " << cloud->points.size() << " points" << endl; pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr coefficients(new pcl::ModelCoefficients); pcl::PointIndices::Ptr inliers(new pcl::PointIndices); // 创建分割对象 pcl::SACSegmentation<pcl::PointXYZ> seg; // 可选择配置,设置模型系数需要优化 seg.setOptimizeCoefficients(true); // 必须配置,设置分割的模型类型、所用随机参数估计方法 seg.setModelType(pcl::SACMODEL_PLANE); seg.setMethodType(pcl::SAC_RANSAC); seg.setDistanceThreshold(0.02);// 距离阈值 单位m。距离阈值决定了点被认为是局内点时必须满足的条件 //seg.setDistanceThreshold(0.15);// 距离阈值 单位m。距离阈值决定了点被认为是局内点时必须满足的条件 //距离阈值表示点到估计模型的距离最大值。 seg.setInputCloud(cloud);//输入点云 seg.segment(*inliers, *coefficients);//实现分割,并存储分割结果到点集合inliers及存储平面模型系数coefficients if (inliers->indices.size() == 0) { PCL_ERROR("Could not estimate a planar model for the given dataset."); return (-1); } //*********************************************************************** //-----------输出平面模型的系数 a,b,c,d----------- cout << "Model coefficients: " << coefficients->values[0] << " " << coefficients->values[1] << " " << coefficients->values[2] << " " << coefficients->values[3] << endl; cout << "Model inliers: " << inliers->indices.size() << endl; //*********************************************************************** // 提取地面 pcl::ExtractIndices<pcl::PointXYZ> extract; extract.setInputCloud(cloud); extract.setIndices(inliers); extract.filter(*cloud_filtered); cout << "Ground cloud after filtering: " << endl; cout << *cloud_filtered << std::endl; pcl::PCDWriter writer; writer.write<pcl::PointXYZ>("3dpoints_ground.pcd", *cloud_filtered, false); // 提取除地面外的物体 extract.setNegative(true); extract.filter(*cloud_filtered); cout << "Object cloud after filtering: " << endl; cout << *cloud_filtered << endl; //writer.write<pcl::PointXYZ>(".pcd", *cloud_filtered, false); // 点云可视化 boost::shared_ptr<pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer>viewer0(new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer("显示点云")); //左边窗口显示输入的点云,右边的窗口显示分割后的点云 int v1(0), v2(0); viewer0->createViewPort(0, 0, 0.5, 1, v1); viewer0->createViewPort(0.5, 0, 1, 1, v2); viewer0->setBackgroundColor(0, 0, 0, v1); viewer0->setBackgroundColor(0.3, 0.3, 0.3, v2); pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointXYZ> color_in(cloud, 255, 0, 0); viewer0->addPointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>(cloud, color_in, "cloud_in", v1); viewer0->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 1, "cloud_in", v1); viewer0->addPointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>(cloud_filtered, "cloud_out", v2); viewer0->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_COLOR, 0, 255, 0, "cloud_out", v2); viewer0->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 1, "cloud_out", v2); while (!viewer0->wasStopped()) { viewer0->spinOnce(100); boost::this_thread::sleep(boost::posix_time::microseconds(1000)); } //*********************************************************************** //超体聚类 float voxel_resolution = 0.01f; // 设置体素大小,该设置决定底层八叉树的叶子尺寸 float seed_resolution = 0.15f; // 设置种子大小,该设置决定超体素的大小 float color_importance = 0.0f; // 设置颜色在距离测试公式中的权重,即颜色影响超体素分割结果的比重。 真实点云都是一个颜色,所以这个参数无作用 float spatial_importance = 0.9f; // 设置空间距离在距离测试公式中的权重,较高的值会构建非常规则的超体素,较低的值产生的体素会按照法线 float normal_importance = 4.0f; // 设置法向量的权重,即表面法向量影响超体素分割结果的比重。 bool use_single_cam_transform = false; bool use_supervoxel_refinement = false; unsigned int k_factor = 0; //voxel_resolution is the resolution (in meters) of voxels used、seed_resolution is the average size (in meters) of resulting supervoxels pcl::SupervoxelClustering<PointT> super(voxel_resolution, seed_resolution); super.setUseSingleCameraTransform(use_single_cam_transform); super.setInputCloud(cloud_filtered); //cloud_filtered super.setColorImportance(color_importance); //Set the importance of spatial distance for supervoxels. super.setSpatialImportance(spatial_importance); //Set the importance of scalar normal product for supervoxels. super.setNormalImportance(normal_importance); std::map<uint32_t, pcl::Supervoxel<PointT>::Ptr> supervoxel_clusters; super.extract(supervoxel_clusters); std::multimap<uint32_t, uint32_t> supervoxel_adjacency; super.getSupervoxelAdjacency(supervoxel_adjacency); pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>::Ptr sv_centroid_normal_cloud = pcl::SupervoxelClustering<PointT>::makeSupervoxelNormalCloud(supervoxel_clusters); cout << "超体素分割的体素个数为:" << supervoxel_clusters.size() << endl; // 获取点云对应的超体素分割标签 pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZL>::Ptr supervoxel_cloud = super.getLabeledCloud(); pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer::Ptr viewer1(new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer("VCCS")); viewer1->setWindowName("超体素分割"); viewer1->addPointCloud(supervoxel_cloud, "超体素分割"); viewer1->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 1, "超体素分割"); viewer1->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_OPACITY, 0.5, "超体素分割"); //-----------------------------------------获得体素点云的邻接单元---------------------------------------------- multimap<uint32_t, uint32_t>SupervoxelAdjacency; super.getSupervoxelAdjacency(SupervoxelAdjacency); for (auto label_itr = SupervoxelAdjacency.cbegin(); label_itr != SupervoxelAdjacency.cend();) { uint32_t super_label = label_itr->first;//获取体素单元的标签 pcl::Supervoxel<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr super_cloud = supervoxel_clusters.at(super_label);//把对应标签内的点云、体素质心、以及质心对应的法向量提取出来 pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZRGBA> adjacent_supervoxel_centers; for (auto adjacent_itr = SupervoxelAdjacency.equal_range(super_label).first; adjacent_itr != SupervoxelAdjacency.equal_range(super_label).second; ++adjacent_itr) { pcl::Supervoxel<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr neighbor_supervoxel = supervoxel_clusters.at(adjacent_itr->second); adjacent_supervoxel_centers.push_back(neighbor_supervoxel->centroid_); } std::stringstream ss; ss << "supervoxel_" << super_label; addSupervoxelConnectionsToViewer(super_cloud->centroid_, adjacent_supervoxel_centers, ss.str(), viewer1); label_itr = SupervoxelAdjacency.upper_bound(super_label); } // 等待直到可视化窗口关闭 while (!viewer1->wasStopped()) { viewer1->spinOnce(100); boost::this_thread::sleep(boost::posix_time::microseconds(1000)); } //return 0; //*********************************************************************** //LCCP分割 float concavity_tolerance_threshold = 10; float smoothness_threshold = 0.8; uint32_t min_segment_size = 0; bool use_extended_convexity = false; bool use_sanity_criterion = false; pcl::LCCPSegmentation<PointT> lccp; lccp.setConcavityToleranceThreshold(concavity_tolerance_threshold);//CC效验beta值 lccp.setSmoothnessCheck(true, voxel_resolution, seed_resolution, smoothness_threshold); lccp.setKFactor(k_factor); //CC效验的k邻点 lccp.setInputSupervoxels(supervoxel_clusters, supervoxel_adjacency); lccp.setMinSegmentSize(min_segment_size);//最小分割尺寸 lccp.segment(); pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZL>::Ptr sv_labeled_cloud = super.getLabeledCloud(); pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZL>::Ptr lccp_labeled_cloud = sv_labeled_cloud->makeShared(); lccp.relabelCloud(*lccp_labeled_cloud); SuperVoxelAdjacencyList sv_adjacency_list; lccp.getSVAdjacencyList(sv_adjacency_list); pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer::Ptr viewer2(new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer("LCCP超体素分割")); viewer2->setWindowName("LCCP超体素分割"); viewer2->addPointCloud(lccp_labeled_cloud, "LCCP超体素分割"); viewer2->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 1, "LCCP超体素分割"); viewer2->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_OPACITY, 0.5, "LCCP超体素分割"); // 等待直到可视化窗口关闭 while (!viewer2->wasStopped()) { viewer2->spinOnce(100); boost::this_thread::sleep(boost::posix_time::microseconds(1000)); } return 0; } 三、实验结果
原数据
去除地面后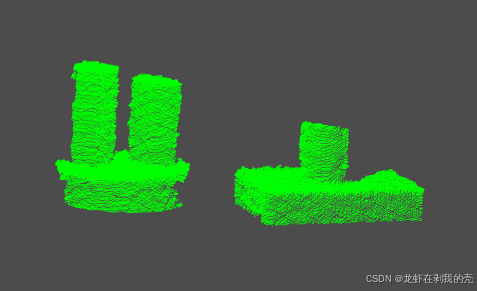
超体聚类过分割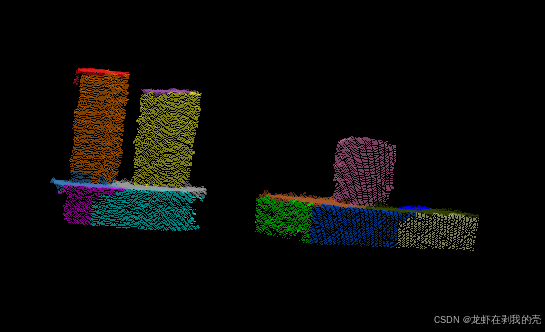
LCCP分割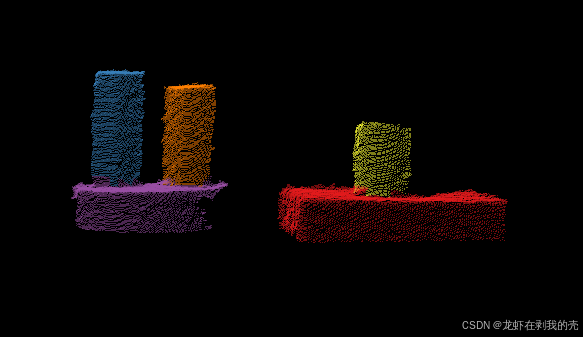
四、总结
从实验结果来看,LCCP算法在相似物体场景分割方面有着较好的表现,对于颜色类似但棱角分明的物体可使用该算法。
