程序设计之字符串2
字符串
在字符串操作后切记最后得加上字符串结束标识符 ′ \ 0 ′ '\backslash0' ′\0′ 。
用数组作为函数的形参时,可以不定义数组的行数,但一定要定义数组的列数。
问题2_1
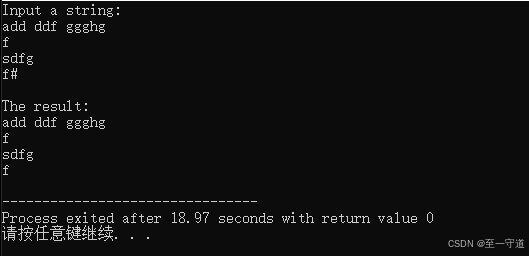
函数 f u n fun fun 的功能是:删除指针 p p p 所指字符串中的所有空白字符(包括制表符、回车符及换行符)。输入字符串时用 # 号结束输入。
代码2_1
#include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> #include<ctype.h> void fun(char *p){ int i, t; char c[80]; for(i=0,t=0; p[i]; i++){ if(!isspace(*(p+1))) c[t++] = p[i]; } c[t] = '\0'; strcpy(p, c); } void main(void){ char c, s[80]; int i=0; printf("Input a string:\n"); c = getchar(); while(c!='#'){ s[i] = c; i++; c = getchar(); } s[i] = '\0'; fun(s); printf("\nThe result:\n"); puts(s); } 结果2_1
问题2_2
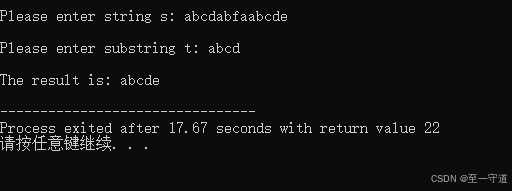
函数 f u n fun fun的功能是:求形参 s s s 所指字符串中最后一次出现的 t t t 所指字符串的地址,并通过函数值返回,在主函数中输出从此地址开始的字符串;若未找到,则函数值为 NULL。
例如: 形参 s s s 所指的字符串为 “ a b c d a b f a a b c d e ” “abcdabfaabcde” “abcdabfaabcde” , t t t 中的字符为 a b c d abcd abcd ,执行后字符串应为 " a b c d e " "abcde" "abcde" 。当 t t t 中的字符为 g h f ghf ghf ,则程序输出未找到信息 " n o t b e f o u n d ! " "not be found!" "notbefound!" 。
代码2_2
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> #include<string.h> char *fun(char *s, char *t){ char *p, *r, *a; a = NULL; while(*s){ p = s; r = t; while(*r){ if(*r==*p){ r++; p++; } else break; } if(*r=='\0') a = s; s++; } return a; } void main(void){ char s[100], t[100], *p; system("CLS"); printf("\nPlease enter string s: "); scanf("%s", s); printf("\nPlease enter substring t: "); scanf("%s", t); p = fun(s, t); if(p) printf("\nThe result is: %s\n", p); else printf("\nNot found!\n"); } 结果2_2
问题2_3
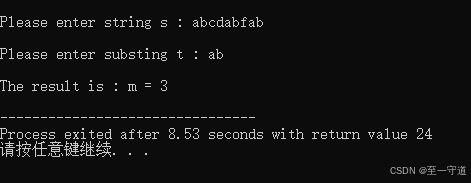
函数 f u n fun fun的功能是:在形参 s s s 所指字符串中找出 t t t 所指字符串的个数作为函数值返回。
例如: 形参 s s s 所指的字符串为 “ a b c d a b f a b ” “abcdabfab” “abcdabfab” , t t t 所指字符串的内容为 a b ab ab ,则函数返回值为 3 3 3 。
代码2_3
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #include<conio.h> #include<string.h> int fun(char *s, char *t){ int n; char *p, *r; while(*s){ p =s; r = t; while(*r){ if(*r==*p){ r++; p++; } else break; } if(*r=='\0') n++; s++; } return n; } void main(void){ char s[100], t[100]; int m; system("CLS"); printf("\nPlease enter string s : "); scanf("%s", s); printf("\nPlease enter substing t : "); scanf("%s", t); m = fun(s, t); printf("\nThe result is : m = %d \n", m); } 结果2_3
问题2_4
函数 f u n fun fun的功能是:将一个数字字符串转换为一个整数(不得调用C语言提供的将字符串转换为整数的函数)。
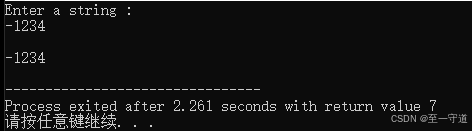
例如: 若输入字符串为 " − 1234 " "-1234" "−1234" 则函数把它转换为整数值 -1234$ 。
代码2_4
#include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> long fun(char *p){ long n=0; int flag=1; if(*p=='-'){ p++; flag = -1; } else if(*p=='+') p++; while(*p!='\0'){ n = n*10+*p-'0'; p++; } return n*flag; } void main(void){ char s[6]; long n; printf("Enter a string : \n"); gets(s); n = fun(s); printf("\n%ld\n", n); } 结果2_4
问题2_5
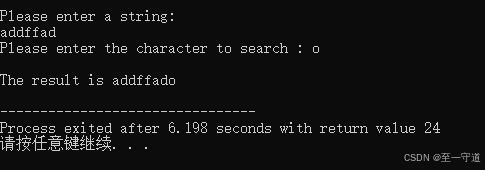
函数 f u n fun fun的功能是:判断 c h ch ch 中的字符是否与 s t r str str 所指串中的某个字符相同;若相同,什么也不做,若不同,则将其插在串的最后 。
代码2_5
#include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> void fun(char *str, char ch){ while(*str&&*str!=ch) str++; if(*str!=ch){ // 思考这里为什么是最后??? str[0] = ch; str[1] = 0; } } void main(){ char s[81], c; printf("\nPlease enter a string:\n"); gets(s); printf("Please enter the character to search : "); c = getchar(); fun(s, c); printf("\nThe result is %s\n", s); } 结果2_5
问题2_6
函数 f u n fun fun的功能是:统计一个长度为 2 的字符串在另一个字符串中出现的次数。
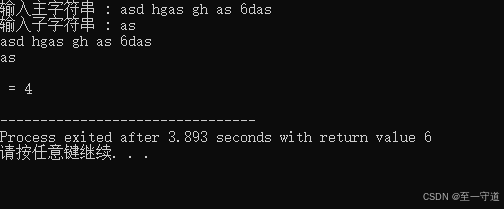
例如: 输入字符串为 " a s d h g a s g h a s 6 d a s " "asd\ hgas\ gh\ as\ 6das" "asd hgas gh as 6das" ,字符串为 " a s " "as" "as" ,则应当输出 4 。
代码2_6
#include<stdlib.h> #include<conio.h> #include<stdio.h> #include<string.h> int fun(char *str, char *substr){ int i, j; for(i=0; str[i+1]!='\0'; i++){ if(str[i]==substr[0]&&str[i+1]==substr[1]) j++; } return j; } void main(void){ char str[81], substr[3]; int n; system("CLS"); printf("输入主字符串 : "); gets(str); printf("输入子字符串 : "); gets(substr); puts(str); puts(substr); n = fun(str, substr); printf("\n = %d\n", n); } 结果2_6