阅读量:0
本文主要记录一种用于嵌入式开发中【模块测试】通用模板,使用
getopt_long()函数作为串口命令行解析的工具,从而进行测试代码逻辑的编写。本文以
ADC和uart测试为例,介绍函数的使用以及测试代码的编写
【测试环境说明 】
本文是在 rt-thread 环境下,确保已经移植好了debug串口接口。。移植过程在此不做赘述
本文主要记录 杰理蓝牙
audio接口的使用,包括ADC和DAC原理的介绍和API接口的使用。
【杰理蓝牙开发】AC695x 音频部分
0. 个人简介 && 授权须知

📋 个人简介
- 💖 作者简介:大家好,我是喜欢记录零碎知识点的菜鸟打工人。😎
- 📝 个人主页:欢迎访问我的博客主页🔥
- 🎉 支持我:点赞👍+收藏⭐️+留言📝
- 📣 系列专栏:嵌入式开发专栏 🍁 🍁
- 💬格言:写文档啊不是写文章,重要的还是直白!🔥
转载文章,禁止声明原创;不允许直接二次转载,转载请根据原文链接联系作者
若无需改版,在文首清楚标注作者及来源/原文链接,并删除【原创声明】,即可直接转载。
但对于未注明转载来源/原文链接的文章,我将保留追述的权利。作者:积跬步、至千里

1. 测试代码架构
测试时,输入的串口指令为:
test_adc -c 2 , 格式只能为这种,其他格式会报错
说明:参数分别为
test_adc:测试命令-c:表示channel通道2:具体的channel
static void cmd_test_adc(int argc, char **argv) { int c; u32 ch = 0; if (argc < 2) { // 若参数少于2个,则提示错误 cmd_adcim_usage(argv[0]); // 提示错误 return; } optind = 0; while ((c = getopt_long(argc, argv, sopts, lopts, NULL)) != -1) { switch (c) { case 'c': ch = atoi(optarg); // 解析通道 adc_dm_test(ch); continue; case 'v': continue; case 'h': default: cmd_adcim_usage(argv[0]); // 提示错误 return; } } return; } MSH_CMD_EXPORT_ALIAS(cmd_test_adc, test_adc, adcim dm device sample); // 设置测试命令行 2. 接口 getopt_long() 的分析
getopt_long() 函数是用于在 C 或 C++ 程序中解析命令行选项的一个强大工具。
#include <getopt.h> int getopt_long(int argc, char * const argv[], const char *optstring, const struct option *longopts, int *longindex); 2.1 参数说明
argc:命令行参数的数量。argv:命令行参数的数组。optstring:指定短选项的字符串。每个字符代表一个短选项,如果字符后面跟一个:,表示该选项需要一个参数。- 例如,
"ab:c"表示a选项不需要参数,b选项需要一个参数,c选项不需要参数。
- 例如,
longopts:这是一个指向struct option结构体数组的指针,用于定义长选项。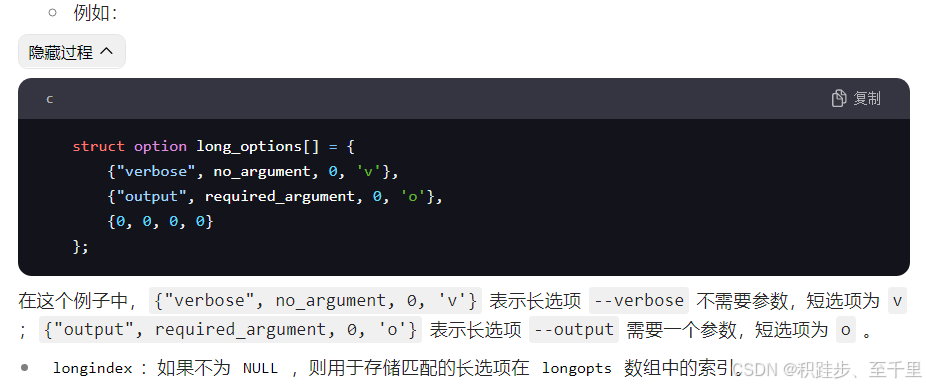
2.2 返回值说明
- 如果找到一个有效的短选项或长选项,返回选项字符。
- 如果选项需要一个参数,
optarg指针将被设置为该参数的值。 - 如果遇到选项解析错误,返回
'?'。 - 如果所有选项都已处理完毕,返回
-1
3. 接口 getopt_long() 的使用
3.1 定义 【短选项】字符串 optstring
/* c: 表示 -c 命令后边还需要一个参数 h: -h 后边不需要参数 v: -v 后边不需要参数 */ static const char sopts[] = "c:hv"; 3.2 定义【长选项】字符串 longopts
static const struct option lopts[] = { {"channel", required_argument, NULL, 'c'}, // required_argument 表示 -c 命令后边还需要一个参数 {"usage", no_argument, NULL, 'h'}, // no_argument 表示命令后边不需要参数了 {"verbose", no_argument, NULL, 'v'}, {0, 0, 0, 0} // 必须以{0,0,0,0}结尾 }; 3.3 定义提示信息
对命令参数作基本说明
static void cmd_adcim_usage(char *program) { printf("Compile time: %s %s\n", __DATE__, __TIME__); printf("Usage: %s [options]\n", program); printf("\t -c, --channel\t\tSelect one channel in [0, 15]\n"); // 表示 channel范围【0-15】 printf("\t -h, --usage \n"); printf("\n"); printf("Example: %s -c 0\n", program); // 示例 test_adc -c 0 测试通道0 } 4. 测试串口的实例
static const char sopts[] = "u:n:t:h"; // optional_argument 表示可能需要采纳数,不是必须的 static const struct option lopts[] = { {"uart", optional_argument, NULL, 'u'}, // 设置哪一个串口 {"number", optional_argument, NULL, 'n'}, // 设置串口接收数量 {"timeout", optional_argument, NULL, 't'}, // 设置接收超时时间 {"help", no_argument, NULL, 'h'}, // {0, 0, 0, 0} }; // 提示信息 static void test_uart_usage(char *program) { printf("Compile time: %s %s\n", __DATE__, __TIME__); printf("Usage: %s [options]\n", program); printf("\t -u, --uart\t\tSelect a serial port. Default as uart4\n"); printf("\t -n, --number\t\treceive max number. Default as 128\n"); printf("\t -t, --timeout\t\tSerial port receive timeout, Default as forever, unit ms\n"); printf("\t -h, --help \n"); printf("\n"); printf("Example: Serial port loopback test\n"); printf(" %s -u uart4 -n 128 -t 1000 \n", program); } int test_uart(int argc, char *argv[]) { /* argc: 参数的数量 argv:命令行参数的字符串数组 sopts:指定短选项的格式字符串 lopts:用于定义长选项 *idx:如果不为空,用于存储匹配到的长选项在 lopts 数组中的索引 */ while ((c = getopt_long(argc, argv, sopts, lopts, NULL)) != -1) { switch (c) { case 'u': rt_strncpy(uart_name, optarg, RT_NAME_MAX); printf("-u\r\n"); break; case 'n': g_recv_max = atoi(optarg); g_recv_max = g_recv_max > 128 ? 128 : g_recv_max; g_recv_max = g_recv_max < 0 ? 128 : g_recv_max; printf("-n\r\n"); break; case 't': g_timeout = atoi(optarg); g_timeout = g_timeout < 0 ? TIMEOUT_NONE : g_recv_max; printf("-t\r\n"); break; case 'h': printf("-h\r\n"); break; default: printf("-default\r\n"); test_uart_usage(argv[0]); return 0; } } } MSH_CMD_EXPORT(test_uart, MCU Chip Uart Test); 5. 一个通用的测试模板
#include <stdio.h> #include <getopt.h> int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int c; int verbose_flag = 0; char *output_file = NULL; struct option long_options[] = { {"verbose", no_argument, &verbose_flag, 1}, {"output", required_argument, 0, 'o'}, {0, 0, 0, 0} }; while ((c = getopt_long(argc, argv, "vo:", long_options, NULL))!= -1) { switch (c) { case 'v': verbose_flag = 1; break; case 'o': output_file = optarg; break; case '?': printf("Invalid option\n"); return 1; default: abort(); } } if (verbose_flag) { printf("Verbose mode enabled\n"); } if (output_file) { printf("Output file: %s\n", output_file); } for (; optind < argc; optind++) { printf("Non-option argument: %s\n", argv[optind]); } return 0; } 