阅读量:0
跳表(Skip List)是一种用于有序数据存储的数据结构,它在链表的基础上增加了多级索引,从而提高了查找、插入和删除操作的效率。跳表的平均时间复杂度为 O ( log n ) O(\log n) O(logn),与平衡二叉搜索树(如 AVL 树、红黑树)相当,但实现和维护相对简单。
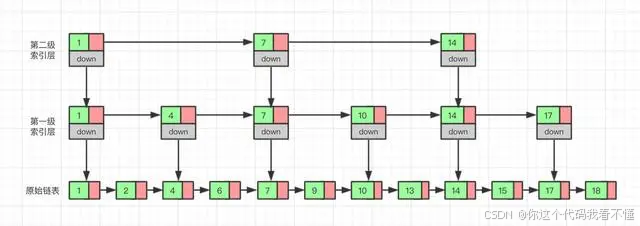
跳表的结构
跳表由多层链表组成,每一层都是一个有序链表。最底层(Level 0)包含所有元素,每一层的元素是下一层元素的子集。通过在多层链表中进行跳跃,可以快速定位到目标元素。
- Level 0:包含所有元素的有序链表。
- Level 1:包含部分元素的有序链表,通常是 Level 0 的元素的子集。
- Level 2:包含更少元素的有序链表,通常是 Level 1 的元素的子集。
- …
跳表的操作
查找:
从最高层开始,逐层向下查找,直到找到目标元素或确定元素不存在。每层查找时,如果当前元素小于目标元素,则向右移动;否则,向下移动到下一层。插入:
首先找到插入位置,然后在每一层随机决定是否插入新元素。插入时,需要更新相应层的前后指针。删除:
首先找到要删除的元素,然后在每一层删除该元素,并更新相应层的前后指针。
跳表的优点
- 高效:跳表的查找、插入和删除操作的平均时间复杂度为 O ( log n ) O(\log n) O(logn)。
- 简单:相比于平衡二叉树,跳表的实现和维护相对简单。
- 动态性:跳表可以动态调整索引层数,适应数据的变化。
跳表的实现
以下是一个简单的跳表实现示例(Java 代码):
import java.util.Random; class SkipListNode { int value; SkipListNode[] forward; public SkipListNode(int value, int level) { this.value = value; this.forward = new SkipListNode[level + 1]; } } public class SkipList { private static final int MAX_LEVEL = 16; private final SkipListNode head = new SkipListNode(-1, MAX_LEVEL); private int level = 0; private final Random random = new Random(); public void insert(int value) { SkipListNode[] update = new SkipListNode[MAX_LEVEL + 1]; SkipListNode current = head; for (int i = level; i >= 0; i--) { while (current.forward[i] != null && current.forward[i].value < value) { current = current.forward[i]; } update[i] = current; } int newLevel = randomLevel(); if (newLevel > level) { for (int i = level + 1; i <= newLevel; i++) { update[i] = head; } level = newLevel; } SkipListNode newNode = new SkipListNode(value, newLevel); for (int i = 0; i <= newLevel; i++) { newNode.forward[i] = update[i].forward[i]; update[i].forward[i] = newNode; } } public boolean search(int value) { SkipListNode current = head; for (int i = level; i >= 0; i--) { while (current.forward[i] != null && current.forward[i].value < value) { current = current.forward[i]; } } current = current.forward[0]; return current != null && current.value == value; } public void delete(int value) { SkipListNode[] update = new SkipListNode[MAX_LEVEL + 1]; SkipListNode current = head; for (int i = level; i >= 0; i--) { while (current.forward[i] != null && current.forward[i].value < value) { current = current.forward[i]; } update[i] = current; } current = current.forward[0]; if (current != null && current.value == value) { for (int i = 0; i <= level; i++) { if (update[i].forward[i] != current) { break; } update[i].forward[i] = current.forward[i]; } while (level > 0 && head.forward[level] == null) { level--; } } } private int randomLevel() { int newLevel = 0; while (random.nextInt(2) == 0 && newLevel < MAX_LEVEL) { newLevel++; } return newLevel; } public static void main(String[] args) { SkipList skipList = new SkipList(); skipList.insert(1); skipList.insert(2); skipList.insert(3); System.out.println(skipList.search(1)); // true System.out.println(skipList.search跳表(Skip List)是一种基于链表的数据结构,旨在提高有序链表的查找效率。它通过在链表上建立多级索引,使得查找、插入和删除操作的时间复杂度从 $O(n)$ 降低到 $O(\log n)$,接近于平衡树的性能,但实现和维护相对简单。 ### 跳表的结构 跳表由多层链表组成,每一层都是一个有序链表。最底层(Level 0)包含所有元素,而每一层的元素是下一层元素的子集。每个元素在跳表中的层数是随机确定的,通常遵循几何分布。 - **Level 0**:包含所有元素。 - **Level 1**:包含部分元素,作为 Level 0 的索引。 - **Level 2**:包含更少的元素,作为 Level 1 的索引。 - **...** - **Level k**:包含最少的元素,作为 Level k-1 的索引。 ### 跳表的操作 1. **查找**: 从最高层开始,逐层向下查找,直到找到目标元素或确定元素不存在。每一层的查找都是线性的,但由于层数较少,总体查找效率较高。 2. **插入**: 插入元素时,首先确定该元素在每一层的位置,然后在相应层次插入该元素。插入时需要更新相应的索引。 3. **删除**: 删除元素时,首先在每一层查找到该元素的位置,然后在相应层次删除该元素。删除时需要更新相应的索引。 ### 跳表的时间复杂度 - **查找**:$O(\log n)$ - **插入**:$O(\log n)$ - **删除**:$O(\log n)$ ### 跳表的优点 - **简单性**:跳表的实现和维护相对简单,代码量较少。 - **高效性**:跳表的查找、插入和删除操作的时间复杂度接近于平衡树。 - **动态性**:跳表可以动态调整,不需要复杂的旋转操作。 ### 跳表的实现示例(Java) 以下是一个简单的跳表实现示例: ```java import java.util.Random; class SkipListNode { int value; SkipListNode[] forward; public SkipListNode(int value, int level) { this.value = value; this.forward = new SkipListNode[level + 1]; } } public class SkipList { private static final int MAX_LEVEL = 16; private SkipListNode head; private int level; private Random random; public SkipList() { this.head = new SkipListNode(-1, MAX_LEVEL); this.level = 0; this.random = new Random(); } private int randomLevel() { int lvl = 0; while (random.nextInt(2) == 1 && lvl < MAX_LEVEL) { lvl++; } return lvl; } public void insert(int value) { SkipListNode[] update = new SkipListNode[MAX_LEVEL + 1]; SkipListNode x = head; for (int i = level; i >= 0; i--) { while (x.forward[i] != null && x.forward[i].value < value) { x = x.forward[i]; } update[i] = x; } int lvl = randomLevel(); if (lvl > level) { for (int i = level + 1; i <= lvl; i++) { update[i] = head; } level = lvl; } x = new SkipListNode(value, lvl); for (int i = 0; i <= lvl; i++) { x.forward[i] = update[i].forward[i]; update[i].forward[i] = x; } } public boolean search(int value) { SkipListNode x = head; for (int i = level; i >= 0; i--) { while (x.forward[i] != null && x.forward[i].value < value) { x = x.forward[i]; } } x = x.forward[0]; return x != null && x.value == value; } public void delete(int value) { SkipListNode[] update = new SkipListNode[MAX_LEVEL + 1]; SkipListNode x = head; for (int i = level; i >= 0; i--) { while (x.forward[i] != null && x.forward[i].value < value) { x = x.forward[i]; } update[i] = x; } x = x.forward[0]; if (x != null && x.value == value) { for (int i = 0; i <= level; i++) { if (update[i].forward[i] != x) { break; } update[i].forward[i] = x.forward[i]; } while (level > 0 && head.forward[level] == null) { level--; } } } public static void main(String[] args) { SkipList skipList = new SkipList(); skipList.insert(1); skipList.insert(2); skipList.insert(3); System.out.println(skipList.search(1)); // true System.out.println(skipList.search(4)); // false skipList.delete(1); System.out.println(skipList.search(1)); // false } } 这个示例展示了跳表的基本操作,包括插入、查找和删除。通过使用多级索引,跳表可以在保持简单性的同时提供高效的查找、插入和删除操作。
