阅读量:0
文章目录
tls.go中的流程梳理
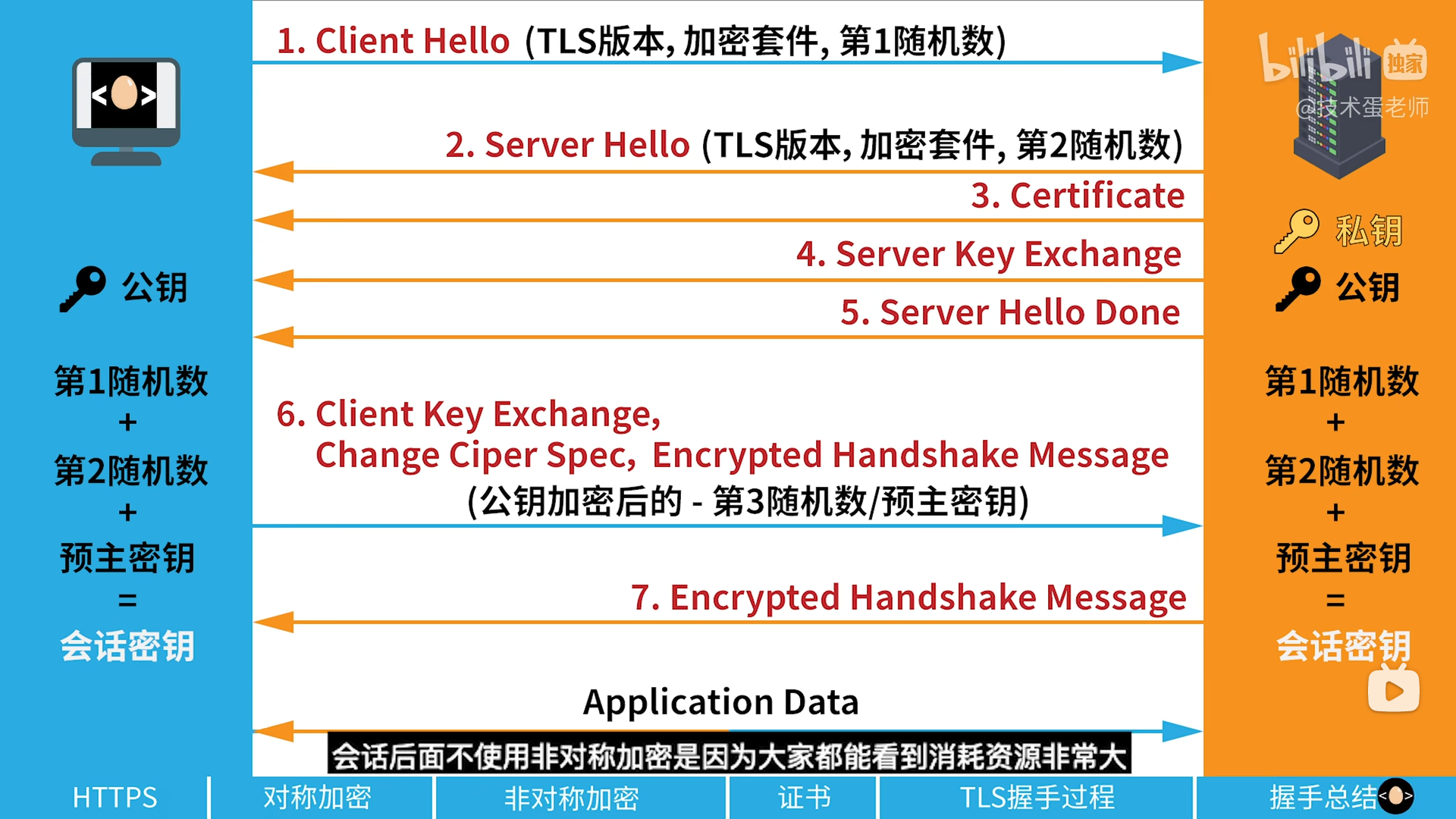
b站博主的 tls 加密过程
- 客户端发送
ClentHello(tls版本 +加密套件+ 随机数1) - 服务器发送
ServerHello(tls版本 + 加密套件 +随机数2)- 这个阶段之后,双方都知道了tls版本,选定的加密算法,两个随机数
- 服务器发送一个
X.509证书,客户端用于验证且知道了服务器的公钥,用于后续传输数据加密 - 服务器发送它自己的公钥,若上一步有,则这一步不需要
- 服务器发送
server Hello Done - 客户端生成 随机数3(预主密钥),并用服务器公钥发送给客户端
- 至此 双方都知道了3个随机数,根据3个随机数得到对称加密的秘钥
Change Cipher Spec表示随后的信息都将用双方商定的加密方法和密钥发送
自己推理的过程(未完待续)
发送ClientHello
- 客户端发送
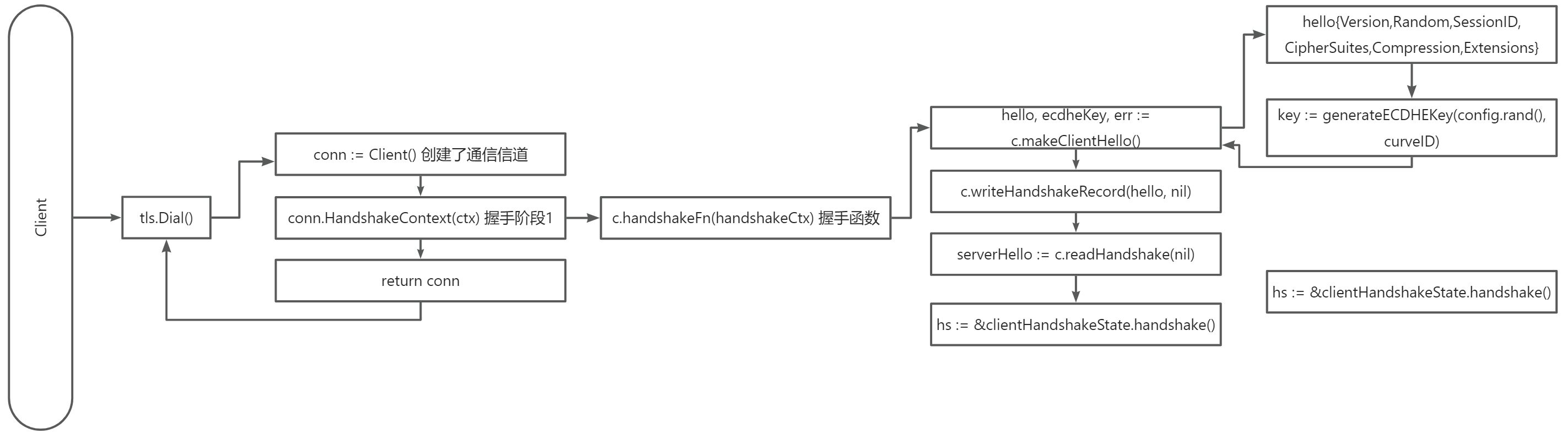
Dial(network, addr string, config *Config) (*Conn, error)
首先调用了Dialer拨号方法得到了 rawConn,然后通过Client(conn net.Conn, config *Config)封装了tls包下的Conn结构。然后进行握手c.HandshakeContext
// 重要代码 ctx context.Context func dial(ctx context.Context, netDialer *net.Dialer, network, addr string, config *Config) (*Conn, error) { rawConn, err := netDialer.DialContext(ctx, network, addr) // 获取主机名 hostname colonPos := strings.LastIndex(addr, ":") if colonPos == -1 { colonPos = len(addr) } hostname := addr[:colonPos] // 握手阶段 此处初始化了Client conn := Client(rawConn, config) if err := conn.HandshakeContext(ctx); err != nil { rawConn.Close() return nil, err } return conn, nil } - 分析
conn := Client(rawConn, config)
发现有一个函数 c.handshakeFn = c.clientHandshake 后续要用到
func Client(conn net.Conn, config *Config) *Conn { c := &Conn{ conn: conn, config: config, isClient: true, } c.handshakeFn = c.clientHandshake return c } - 点到
conn.HandshakeContext(ctx)分析
// 删掉无关代码 func (c *Conn) handshakeContext(ctx context.Context) (ret error) { // 在此处做了 client 的 handshake c.handshakeErr = c.handshakeFn(handshakeCtx) } - 点到
c.handshakeFn(handshakeCtx)
func (c *Conn) clientHandshake(ctx context.Context) (err error) { // 此处初始化了 hello 报文 hello, ecdheKey, err := c.makeClientHello() } // 下面的函数生成了 hello 报文 包括密钥空间 密钥等等 func (c *Conn) makeClientHello() (*clientHelloMsg, *ecdh.PrivateKey, error) { hello := &clientHelloMsg{ vers: clientHelloVersion, compressionMethods: []uint8{compressionNone}, random: make([]byte, 32), extendedMasterSecret: true, ocspStapling: true, scts: true, serverName: hostnameInSNI(config.ServerName), supportedCurves: config.curvePreferences(), supportedPoints: []uint8{pointFormatUncompressed}, secureRenegotiationSupported: true, alpnProtocols: config.NextProtos, supportedVersions: supportedVersions, } var key *ecdh.PrivateKey return hello, key, nil } - 生成
hello报文后,调用函数c.writeHandshakeRecord发送数据,c.readHandshake读取数据
func (c *Conn) clientHandshake(ctx context.Context) (err error) { hello, ecdheKey, err := c.makeClientHello() if _, err := c.writeHandshakeRecord(hello, nil); err != nil { return err } // serverHelloMsg is not included in the transcript msg, err := c.readHandshake(nil) serverHello, ok := msg.(*serverHelloMsg) return nil } 获取ServerHello
如上:在发送完ClientHello信息后使用c.readHandshake(),获取从服务器过来的ServerHello信息。然后是使用类型强转serverHello, ok := msg.(*serverHelloMsg)
然后根据SeverHello中选择的TLS版本和ClientHello中的版本范围进行校验。看服务器发送过来的TLS版本是否在ClientHello指定的范围中。
