往期回顾:
字符设备驱动开发基础—静态/动态注册设备号,使用cdev注册驱动-CSDN博客
字符设备驱动基础—sys文件系统,udev介绍,驱动模块在内核空间注册设备-CSDN博客
本文主要介绍的是 如何通过驱动进行设备的读写操作
文章目录
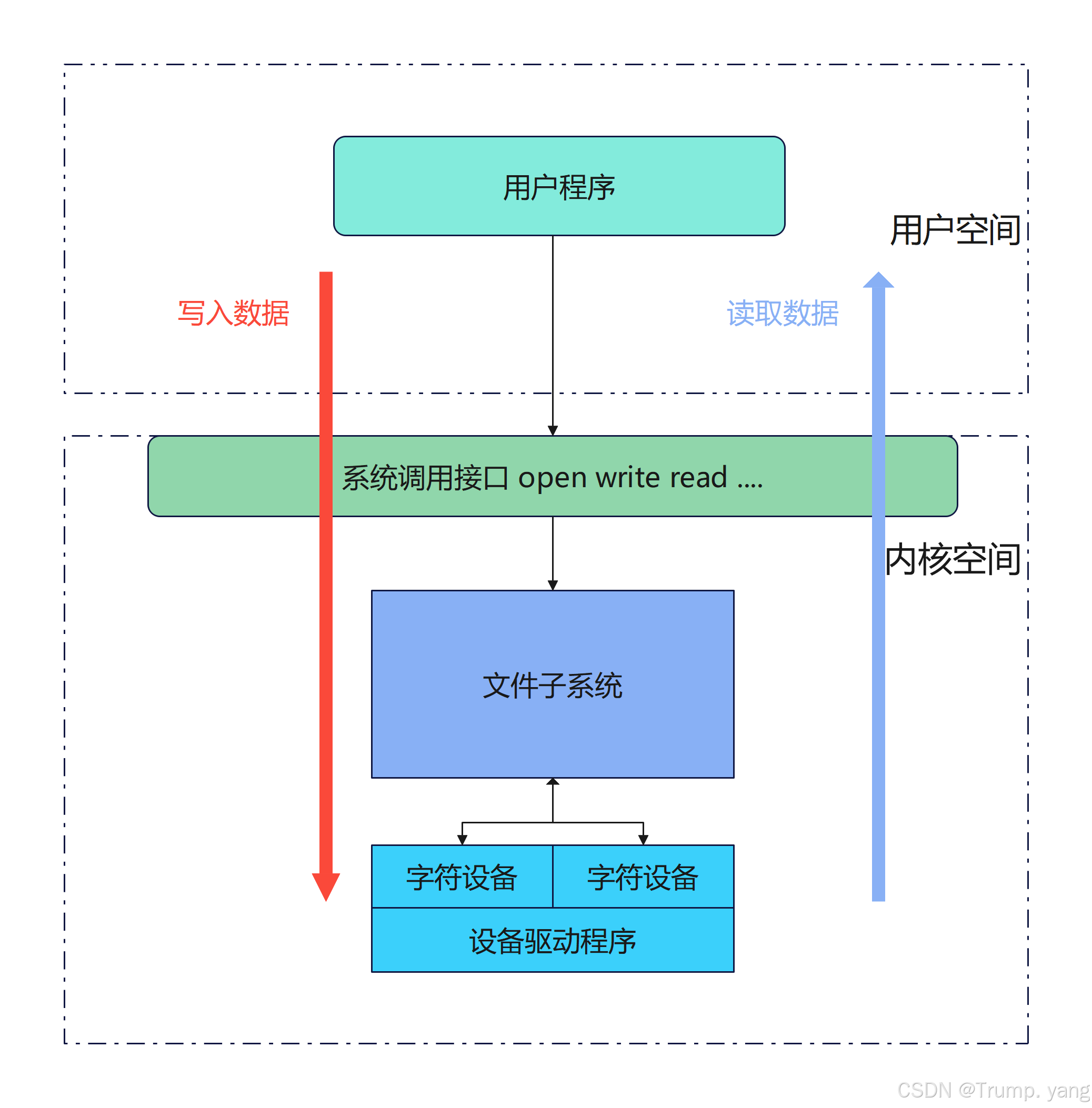
内核空间与用户空间进行数据交互
内核空间:操作系统内核运行的空间,拥有最高的权限,可以直接访问硬件资源和管理系统资源。
用户空间:用户应用程序运行的空间,权限受限,无法直接访问硬件资源,必须通过系统调用与内核交互。
交互方式:
- 系统调用(System Call):用户空间的应用程序通过系统调用请求内核执行某些操作,比如文件操作、进程管理、内存分配等。系统调用是用户空间进入内核空间的主要途径。
- 例子:
open(),read(),write(),fork()
- 例子:
系统调用
- 定义:系统调用是用户程序与操作系统内核进行交互的接口,通过系统调用,用户程序可以请求内核执行特定的服务。
- 过程:
- 用户程序发起系统调用请求。
- 处理器从用户模式切换到内核模式。
- 内核执行相应的服务程序。
- 内核模式切换回用户模式,返回结果给用户程序。
调用框架图:
注:本文只是探讨数据交互过程,没有涉及到操作寄存器,控制硬件,只是涉及到用户空间与内核空间的数据交互
驱动示例代码
#include <linux/init.h> #include <linux/module.h> #include <linux/fs.h> #include <linux/cdev.h> #include <linux/uaccess.h> #include <linux/device.h> #define DEVICE_NAME "my_char_device" #define BUF_LEN 80 static char message[BUF_LEN]; static short message_len; static int major_number; static struct class *my_class = NULL; static struct device *my_device = NULL; static struct cdev mydev; // 声明 cdev 结构体 static int device_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) { printk(KERN_INFO "Device opened\n"); return 0; } static int device_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) { printk(KERN_INFO "Device closed\n"); return 0; } static ssize_t device_read(struct file *file, char __user *user_buffer, size_t len, loff_t *offset) { int bytes_to_copy = message_len - *offset; if (bytes_to_copy < 0) bytes_to_copy = 0; if (bytes_to_copy > len) bytes_to_copy = len; if (bytes_to_copy == 0) return 0; if (copy_to_user(user_buffer, message + *offset, bytes_to_copy) != 0) { return -EFAULT; } *offset += bytes_to_copy; printk(KERN_INFO "Sent %d characters to the user\n", bytes_to_copy); return bytes_to_copy; } static ssize_t device_write(struct file *file, const char __user *user_buffer, size_t len, loff_t *offset) { int bytes_to_copy = len; if (bytes_to_copy > BUF_LEN - 1) bytes_to_copy = BUF_LEN - 1; if (copy_from_user(message, user_buffer, bytes_to_copy) != 0) { return -EFAULT; } message[bytes_to_copy] = '\0'; message_len = bytes_to_copy; printk(KERN_INFO "Received %d characters from the user\n", bytes_to_copy); return bytes_to_copy; } static struct file_operations fops = { .open = device_open, .release = device_release, .read = device_read, .write = device_write, }; static int __init test_init(void) { int retval; dev_t dev; printk(KERN_INFO "module init success\n"); // 1. 动态分配主次设备号 retval = alloc_chrdev_region(&dev, 0, 1, DEVICE_NAME); if (retval < 0) { printk(KERN_ERR "Failed to allocate major number\n"); goto fail_alloc_chrdev_region; } major_number = MAJOR(dev); printk(KERN_INFO "major number is: %d, minor number is: %d\n", major_number, MINOR(dev)); // 2. 初始化 cdev 结构体并添加到内核 cdev_init(&mydev, &fops); retval = cdev_add(&mydev, dev, 1); if (retval < 0) { printk(KERN_ERR "Failed to add cdev\n"); goto fail_cdev_add; } // 3. 创建设备类 my_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "my_class"); if (IS_ERR(my_class)) { printk(KERN_ERR "Failed to create class\n"); retval = PTR_ERR(my_class); goto fail_class_create; } // 4. 申请设备,内核空间就会通知用户空间的udev 进行创建设备,驱动程序本身自己是创建不了文件的! my_device = device_create(my_class, NULL, dev, NULL, DEVICE_NAME); if (IS_ERR(my_device)) { printk(KERN_ERR "Failed to create device\n"); retval = PTR_ERR(my_device); goto fail_device_create; } printk(KERN_INFO "my_char_device: module loaded\n"); return 0; fail_device_create: class_destroy(my_class); fail_class_create: cdev_del(&mydev); fail_cdev_add: unregister_chrdev_region(dev, 1); fail_alloc_chrdev_region: return retval; } static void __exit test_exit(void) { dev_t dev = MKDEV(major_number, 0); if (my_device) device_destroy(my_class, dev); if (my_class) class_destroy(my_class); cdev_del(&mydev); unregister_chrdev_region(dev, 1); printk(KERN_INFO "my_char_device: module unloaded\n"); } module_init(test_init); module_exit(test_exit); MODULE_AUTHOR("Marxist"); MODULE_LICENSE("GPL"); 关键解析
Linux理念:一切皆为文件,因此设备也是一种文件,也可以直接进行读写操作。
device_open 和 device_release:设备打开和关闭时的处理函数。
device_read:从设备读取数据并复制到用户空间。
device_write:从用户空间写入数据到设备。
文件操作函数实现
static int device_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) { printk(KERN_INFO "Device opened\n"); return 0; } static int device_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) { printk(KERN_INFO "Device closed\n"); return 0; } static ssize_t device_read(struct file *file, char __user *user_buffer, size_t len, loff_t *offset) { int bytes_to_copy = message_len - *offset; if (bytes_to_copy < 0) bytes_to_copy = 0; if (bytes_to_copy > len) bytes_to_copy = len; if (bytes_to_copy == 0) return 0; if (copy_to_user(user_buffer, message + *offset, bytes_to_copy) != 0) { return -EFAULT; } *offset += bytes_to_copy; printk(KERN_INFO "Sent %d characters to the user\n", bytes_to_copy); return bytes_to_copy; } static ssize_t device_write(struct file *file, const char __user *user_buffer, size_t len, loff_t *offset) { int bytes_to_copy = len; if (bytes_to_copy > BUF_LEN - 1) bytes_to_copy = BUF_LEN - 1; if (copy_from_user(message, user_buffer, bytes_to_copy) != 0) { return -EFAULT; } message[bytes_to_copy] = '\0'; message_len = bytes_to_copy; printk(KERN_INFO "Received %d characters from the user\n", bytes_to_copy); return bytes_to_copy; } 文件操作结构体
定义文件操作结构体,将文件操作函数指针绑定到对应的操作函数。
static struct file_operations fops = { .open = device_open, .release = device_release, .read = device_read, .write = device_write, }; 本文重点使用的函数:copy_to_user 和 copy_from_user
copy_to_user 用于将数据从内核空间复制到用户空间。函数原型如下:
int copy_to_user(void __user *to, const void *from, unsigned long n); to:目标用户空间地址。from:源内核空间地址。n:要复制的字节数。
如果复制成功,返回 0;如果失败,返回未能复制的字节数。
copy_from_user 用于将数据从用户空间复制到内核空间。函数原型如下:
int copy_from_user(void *to, const void __user *from, unsigned long n); to:目标内核空间地址。from:源用户空间地址。n:要复制的字节数。
如果复制成功,返回 0;如果失败,返回未能复制的字节数。
用户程序示例代码
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <errno.h> int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int fd; char buf[80] = {0}; // 检查参数数量 if (argc < 2) { fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s <r|w> [data_to_write]\n", argv[0]); return -1; } // 打开设备节点 fd = open("/dev/my_char_device", O_RDWR); if (fd < 0) { perror("open error"); return -1; } if (strcmp(argv[1], "w") == 0) { // 写操作 if (argc < 3) { fprintf(stderr, "Please provide data to write.\n"); close(fd); return -1; } strncpy(buf, argv[2], sizeof(buf) - 1); if (write(fd, buf, sizeof(buf)) < 0) { perror("write error"); close(fd); return -1; } printf("Data written: %s\n", buf); } else if (strcmp(argv[1], "r") == 0) { // 读操作 if (read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf)) < 0) { perror("read error"); close(fd); return -1; } printf("Data read: %s\n", buf); } else { fprintf(stderr, "Invalid operation. Use 'r' for read or 'w' for write.\n"); close(fd); return -1; } // 关闭设备节点 close(fd); return 0; } 实现了简单对设备的读写测试, 主要是调用了 系统调用 的 open read write 接口
实现效果
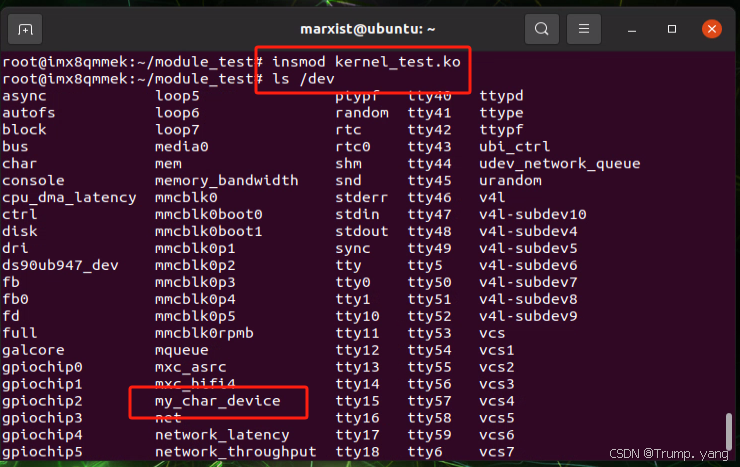
加载编译后的模块到内核,在dev目录生成了 my_char_device 设备文件
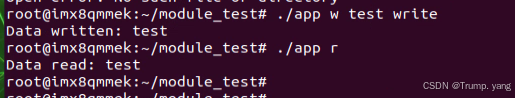
运行编译好的用户程序
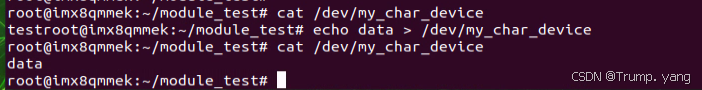
同样的也可以直接使用cat 和echo命令