目录
为了更好地理解 map 和 set 的特性,和后面讲解查找效率极高的平衡搜索二叉树,和红黑树去实现模拟,所以决定在这里对搜索二叉树进行一个讲解~
1.定义
二叉搜索树(Search Binary Tree)
每一颗子树都满足,左子树上所有节点的值都小于根节点的值,右子树都大于
所以就能得到性质:左子树的值 < 根 < 右子树的值
它也称二叉排序树或二叉查找树,最多找高度次O(N)
二叉搜索树蜕化为单边树(或类似单边),其平均比较次数为:O(N)
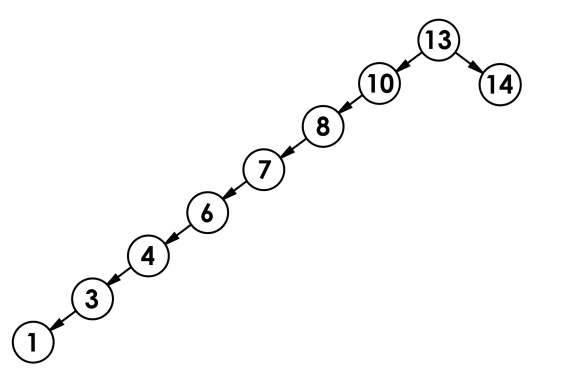
搜索二叉树由于控制不了极端情况,与 O(logN) 失之交臂了,但后面讲到的平衡二叉搜索树可以做到。
初始化
template<class K> struct BSTreeNode {//全部都共有开放的,就直接定struct BSTreeNode<K>* _left;//左结构体指针 BSTreeNode<K>* _right; K _key; BSTreeNode(const K& key) :_left(nullptr) ,_right(nullptr) ,_key(key) {} }; //定义一个树 template<class K> class BATree{ typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node; private: Node* _root = nullptr; // 这里我们构造函数都没必要写,它自己生成的就够用了 };插入
思路:
- 检查是否有根结点 _root,如果没有我们就 new 一个结点出来作为根结点。
- 插入就需要找到插入位置,我们定义一个 cur 变量,从根节点开始,
根据搜索二叉树 性质,将 cur 结点的 key 与插入的值 key 进行大小比较 - 仅仅 new 上一个新结点给 cur 是完成不了插入操作的!需要 cur 跟上一层(cur 的父亲)相链接才行!为了能找到上一层,所以我们还需要额外定义一个 parent 变量来记录 cur 的父结点
在我们更换 cur 结点时记录父结点的位置
parent=cur即可。parent 意义:确认位置,实现插入
4.比较确定 cur 应该链接父亲的左边,还是链接父亲的右边,插入即可
//插入 bool Insert(const K& key) { //没有根节点就new一个 if (_root == nullptr) { _root = new Node(key); return true; } Node* parent = nullptr; Node* cur = _root; //循环比较 while (cur) { if (cur->_key < key) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_right;//小了就应该往右找 } else if(cur->_key > key) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_left; } else { return false; }//不断比较,搜索找到了之后 } //new了一个新节点,和parent的key比较,确定插入的左右 cur = new Node(key); if (parent->_key < key) { parent->_right = cur; } else { parent->_left = cur; }//将新节点插入到二叉树里面啦 return true; }再写一个中序遍历来测试一下插入的效果:
void InOrder(Node* root) { if (root == nullptr) { return; } InOrder(root->_left); // 左 cout << root->_key << " "; // 值 InOrder(root->_right); // 右 } //测试 void TestBSTree() { BSTree<int> t; int a[] = { 8, 3, 1, 10, 6, 4, 7, 14, 13 }; for (auto e : a) { t.Insert(e); } t.InOrder(); ❌ 没法传根 }此时会出现一个问题,因为根是私有的,我们没办法把根传过去,我们可以采取 getroot,这里的话,我们将其设为内部函数即可
void InOrder() { _InOrder(_root); } private: // 改为内部函数 void _InOrder(Node* root) { if (root == nullptr) { return; } _InOrder(root->_left); cout << root->_key << " "; _InOrder(root->_right); } Node* _root = nullptr; };完整测试代码:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; template<class K> struct BSTreeNode { BSTreeNode<K>* _left; BSTreeNode<K>* _right; K _key; BSTreeNode(const K& key) : _left(nullptr) , _right(nullptr) , _key(key) {} }; template<class K> class BSTree { typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node; public: BSTree() : _root(nullptr) {} bool Insert(const K& key) { if (_root == nullptr) { _root = new Node(key); return true; } Node* parent = nullptr; Node* cur = _root; //设置结构体形的cur节点,并进行初始化 while (cur) { if (cur->_key < key) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_right; } else if (cur->_key > key) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_left; } else { return false; // Key already exists } } cur = new Node(key); if (parent->_key < key) { parent->_right = cur; } else { parent->_left = cur; } return true; } void InOrder() { _InOrder(_root); cout << endl; } private: void _InOrder(Node* root) { if (root == nullptr) { return; } _InOrder(root->_left); cout << root->_key << " "; _InOrder(root->_right); } Node* _root; }; // 测试函数 void TestBSTree() { BSTree<int> t; int a[] = { 8, 3, 1, 10, 6, 4, 7, 14, 13 }; for (auto e : a) { t.Insert(e); } t.InOrder(); } int main() { TestBSTree(); return 0; }打印:
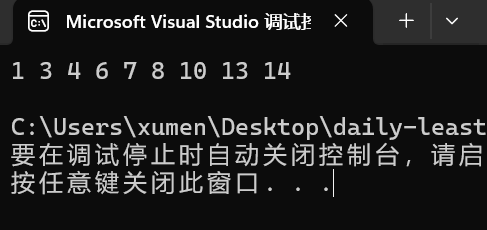
查找
从根开始,如果要查找的值大于 cur 目前的值,则让 cur 往右走,反之往左走。
当查找得值与 cur 的值相等时则说明找到了,返回 true。
当 cur 触及到空(while 循环结束)则说明找不到,返回 false。
//查找 bool Find(const K& key) { Node* cur = _root;//从根开始 while (cur) {//循环查找 if (cur->_key < key) { cur = cur->_right; } else if (cur->_key > key) { cur = cur->_left; } else { return true; //找到啦 } } return false; //为空了还没找到就退出 }删除
搜索二叉树删除的实现是有难度的,删除的实现就需要一些技巧了,断然删除会毁树。
我们可以以下面这棵树为例
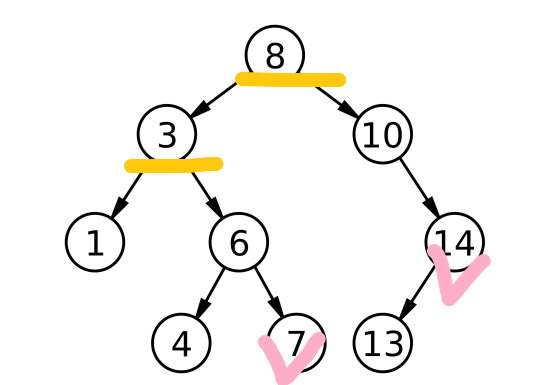
分别一次删除 7,14,3,8
7 和 14 属于直接删除的场景
3,8 属于需要替换法进行删除的场景
总结:
没有孩子,或者一个孩子都好删(直接删,托孤即可)
两个孩子以上就要采取替换法(左子树的最大节点,或者右子树的最小节点)
1.该结点无左孩子
- 若该结点为 root,直接让 root 等于它的右孩子结点。(一定要先判断)
画忘了,画成右为空了qwq,大家同理的理解一下
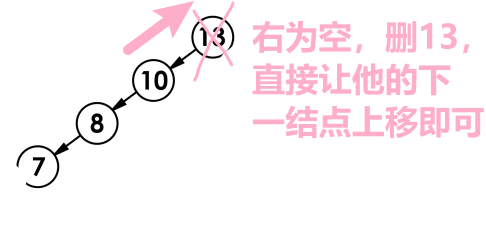
// 左为空 if (cur->_left == nullptr) { if (cur == _root) {//如果是根节点,parent就变为空了 _root = cur->_right; } else- 判断 cur 是在父节点的左还是右支,判断后将其指向parent->right/left = cur->right ,直接将右边连过去,实现重新连接的延续
- 最后删除 cur 结点
if (cur->_left == nullptr) {//该结点无左孩子 /* 判断要删除的结点是否为根结点 */ if (cur == _root) { _root = cur->_right; } else { if (cur == father->_right) { //判断他是上一个节点的左节点还是右节点 father->_right = cur->_right; } else { father->_left = cur->_right; } } delete cur; cur = nullptr; }左右都不为空--替换法
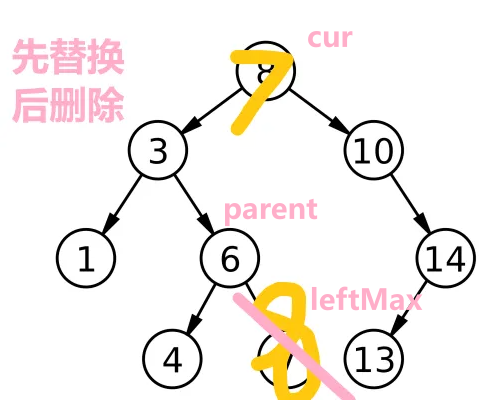
else { //查找到左边的最右节点 //右边的最左节点 //交换 //删除 // 找替代节点 Node* parent = cur; //不能设置为nullptr,循环可能不进去了 //之后要对父节点进行处理 Node* leftMax = cur->_left; //设置最大节点 while (leftMax->_right) { parent = leftMax; leftMax = leftMax->_right; //即最右节点 } //交换key swap(cur->_key, leftMax->_key);删除的判断
//将parent置空处理,断联 if (parent->_left == leftMax) { parent->_left = leftMax->_left; } else { parent->_right = leftMax->_left; } //删除cur的处理 cur = leftMax; } delete cur; return true; } } return false;完整代码
#pragma once template<class K> struct BSTreeNode { BSTreeNode<K>* _left; BSTreeNode<K>* _right; K _key; BSTreeNode(const K& key) :_left(nullptr) ,_right(nullptr) ,_key(key) {} }; template<class K> class BSTree { typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node; public: BSTree() :_root(nullptr) {} bool Insert(const K& key) { if (_root == nullptr) { _root = new Node(key); return true; } Node* parent = nullptr; Node* cur = _root; while (cur) { if (cur->_key < key) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_right; } else if(cur->_key > key) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_left; } else { return false; } } cur = new Node(key); if (parent->_key < key) { parent->_right = cur; } else { parent->_left = cur; } return true; } bool Find(const K& key) { Node* cur = _root; while (cur) { if (cur->_key < key) { cur = cur->_right; } else if (cur->_key > key) { cur = cur->_left; } else { return true; } } return false; } bool Erase(const K& key) { Node* parent = nullptr; Node* cur = _root; while (cur) { if (cur->_key < key) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_right; } else if (cur->_key > key) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_left; } else // 找到了 { // 左为空 if (cur->_left == nullptr) { if (cur == _root) { _root = cur->_right; } else { if (parent->_right == cur) { parent->_right = cur->_right; } else { parent->_left = cur->_right; } } }// 右为空 else if (cur->_right == nullptr) { if (cur == _root) { _root = cur->_left; } else { if (parent->_right == cur) { parent->_right = cur->_left; } else { parent->_left = cur->_left; } } } // 左右都不为空 else { // 找替代节点 Node* parent = cur; Node* leftMax = cur->_left; while (leftMax->_right) { parent = leftMax; leftMax = leftMax->_right; } swap(cur->_key, leftMax->_key); if (parent->_left == leftMax) { parent->_left = leftMax->_left; } else { parent->_right = leftMax->_left; } cur = leftMax; } delete cur; return true; } } return false; } void InOrder() { _InOrder(_root); cout << endl; } void _InOrder(Node* root) { if (root == NULL) { return; } //递归实现中序遍历的打印 _InOrder(root->_left); cout << root->_key << " "; _InOrder(root->_right); } private: Node* _root; };测试:
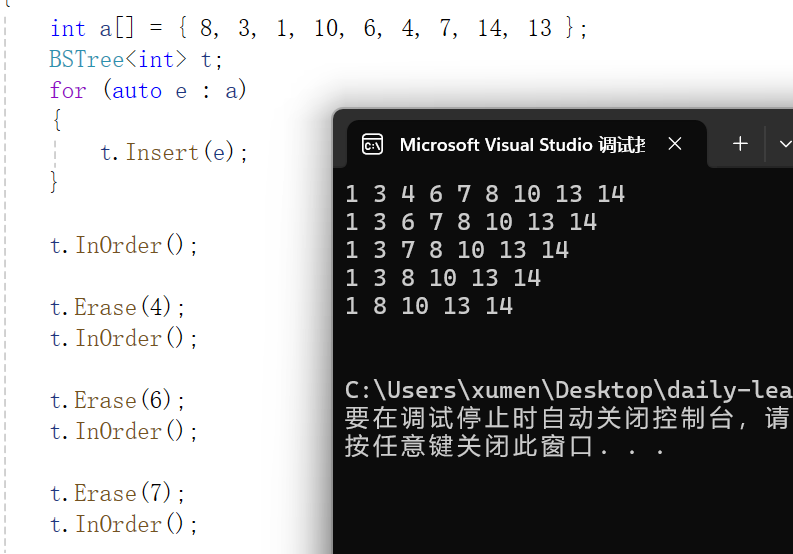
void TestBSTree1() { int a[] = { 8, 3, 1, 10, 6, 4, 7, 14, 13 }; BSTree<int> t; for (auto e : a) { t.Insert(e); } t.InOrder(); t.Erase(4); t.InOrder(); t.Erase(6); t.InOrder(); t.Erase(7); t.InOrder(); t.Erase(3); t.InOrder(); for (auto e : a) { t.Erase(e);//插入 } t.InOrder(); }运行:
2.运用
K 模型和 KV 模型详解
K 模型
K 模型指的是只有 key 作为关键码的结构,在这种结构中只存储 key。K 模型常用于需要搜索具体值的场景,比如拼写检查、数字搜索等。
示例代码:K 模型的二叉搜索树
以下是一个实现 K 模型的二叉搜索树(BST)的完整代码示例:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; template<class K> struct BSTreeNode { BSTreeNode<K>* _left; BSTreeNode<K>* _right; K _key; BSTreeNode(const K& key) : _left(nullptr) , _right(nullptr) , _key(key) {} }; template<class K> class BSTree { typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node; public: BSTree() : _root(nullptr) {} bool Insert(const K& key) { if (_root == nullptr) { _root = new Node(key); return true; } Node* parent = nullptr; Node* cur = _root; while (cur) { if (cur->_key < key) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_right; } else if (cur->_key > key) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_left; } else { return false; // Key already exists } } cur = new Node(key); if (parent->_key < key) { parent->_right = cur; } else { parent->_left = cur; } return true; } void InOrder() { _InOrder(_root); cout << endl; } private: void _InOrder(Node* root) { if (root == nullptr) { return; } _InOrder(root->_left); cout << root->_key << " "; _InOrder(root->_right); } Node* _root; }; // 测试函数 void TestBSTree() { BSTree<int> t; int a[] = { 8, 3, 1, 10, 6, 4, 7, 14, 13 }; for (auto e : a) { t.Insert(e); } t.InOrder(); } int main() { TestBSTree(); return 0; }KV 模型
KV 模型表示每一个关键码 (key) 都有与之对应的值 (value),即 <Key, Value> 的键值对。这种结构常用于字典、映射、统计等场景。
示例代码:KV 模型的二叉搜索树
以下是一个实现 KV 模型的二叉搜索树的完整代码示例:
#include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; template<class K, class V> struct BSTreeNode { BSTreeNode<K, V>* _left; BSTreeNode<K, V>* _right; K _key; V _value; BSTreeNode(const K& key, const V& value) : _left(nullptr) , _right(nullptr) , _key(key) , _value(value) {} }; template<class K, class V> class BSTree { typedef BSTreeNode<K, V> Node; public: BSTree() : _root(nullptr) {} bool Insert(const K& key, const V& value) { if (_root == nullptr) { _root = new Node(key, value); return true; } Node* parent = nullptr; Node* cur = _root; while (cur) { if (cur->_key < key) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_right; } else if (cur->_key > key) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_left; } else { cur->_value = value; // Update value if key already exists return true; } } cur = new Node(key, value); if (parent->_key < key) { parent->_right = cur; } else { parent->_left = cur; } return true; } bool Find(const K& key, V& value) { Node* cur = _root; while (cur) { if (cur->_key < key) { cur = cur->_right; } else if (cur->_key > key) { cur = cur->_left; } else { value = cur->_value; return true; } } return false; } void InOrder() { _InOrder(_root); cout << endl; } private: void _InOrder(Node* root) { if (root == nullptr) { return; } _InOrder(root->_left); cout << "<" << root->_key << ", " << root->_value << "> "; _InOrder(root->_right); } Node* _root; }; // 测试函数 void TestKVTree() { BSTree<string, string> dict; dict.Insert("apple", "苹果"); dict.Insert("banana", "香蕉"); dict.Insert("cherry", "樱桃"); string value; if (dict.Find("banana", value)) { cout << "banana: " << value << endl; } dict.InOrder(); } int main() { TestKVTree(); return 0; }代码解释
- 节点结构定义:
template<class K, class V> struct BSTreeNode { BSTreeNode<K, V>* _left; BSTreeNode<K, V>* _right; K _key; V _value; BSTreeNode(const K& key, const V& value) : _left(nullptr) , _right(nullptr) , _key(key) , _value(value) {} };- 这是一个模板结构,表示二叉搜索树的节点。每个节点包含一个键值对 (key, value) 以及指向左子节点和右子节点的指针。
- 二叉搜索树类定义:
template<class K, class V> class BSTree { typedef BSTreeNode<K, V> Node; public: BSTree() : _root(nullptr) {}- 这是一个模板类,表示二叉搜索树。包含根节点指针
_root以及插入、查找和中序遍历的方法。
- 这是一个模板类,表示二叉搜索树。包含根节点指针
- 插入方法:
bool Insert(const K& key, const V& value) { if (_root == nullptr) { _root = new Node(key, value); return true; } Node* parent = nullptr; Node* cur = _root; while (cur) { if (cur->_key < key) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_right; } else if (cur->_key > key) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_left; } else { cur->_value = value; // Update value if key already exists return true; } } cur = new Node(key, value); if (parent->_key < key) { parent->_right = cur; } else { parent->_left = cur; } return true; }- 插入方法用于将新的键值对插入到树中。通过比较键值确定新节点应该插入的位置。如果键已存在,则更新其对应的值。
- 查找方法:
bool Find(const K& key, V& value) { Node* cur = _root; while (cur) { if (cur->_key < key) { cur = cur->_right; } else if (cur->_key > key) { cur = cur->_left; } else { value = cur->_value; return true; } } return false; }- 查找方法用于查找指定键的值。如果找到该键,则返回对应的值。
- 中序遍历方法:
void InOrder() { _InOrder(_root); cout << endl; } private: void _InOrder(Node* root) { if (root == nullptr) { return; } _InOrder(root->_left); cout << "<" << root->_key << ", " << root->_value << "> "; _InOrder(root->_right); }- 中序遍历方法用于遍历树并输出键值对。递归地遍历左子树、访问根节点、然后遍历右子树。
- 测试函数:
void TestKVTree() { BSTree<string, string> dict; dict.Insert("apple", "苹果"); dict.Insert("banana", "香蕉"); dict.Insert("cherry", "樱桃"); string value; if (dict.Find("banana", value)) { cout << "banana: " << value << endl; } dict.InOrder(); } int main() { TestKVTree(); return