阅读量:0
最近在看矩阵,顺路记录一下复习吧
1.矩阵变换- 平移
- 向量矩阵转换在计算机图形学和游戏开发中起着非常重要的作用,它被广泛应用于以下几个方面:
- 坐标变换:通过向量矩阵转换,可以实现物体在不同坐标系之间的变换,包括平移、旋转和缩放等操作。例如,在游戏中,通过将一个模型的顶点坐标乘以一个变换矩阵,可以实现该模型的移动、旋转和缩放。
- 镜头变换:在计算机图形学中,相机(或镜头)的位置和方向对于视图的呈现至关重要。通过将相机的位置和方向与场景中的物体进行转换,可以实现正交投影或透视投影,从而获得不同的视角和观察效果。
- 物体变形:通过应用变换矩阵,可以实现对物体的形态进行自由的变形。例如,在角色动画和变形动画中,通过对关节和骨骼进行变换,可以实现角色的运动和形态的变化。
- 碰撞检测和物理模拟:向量矩阵转换可以应用于碰撞检测和物理模拟中,以便计算物体之间的相对位置、方向和速度等信息,并进行相应的碰撞判断和物理计算。
- 先来复习一下矩阵相乘的条件,左边的列数和右边的行数相等时才可进行相乘,得出来的结果矩阵行数是左边决定,列数是右边决定,所以所产生了以下区别
- 对于一个4x4的矩阵
- 他的第1 2 3行或列(unity中是列矩阵)代表了x y z轴的坐标基向量,是轴的向量,也代表了轴旋转,第四行或列一般是表示坐标平移信息
- 行向量 是 左乘矩阵(行向量x行矩阵)Unity不是用行矩阵的
- 示例
- 设本地坐标向量为 v = (vx, vy, vz, vw),变换矩阵为 M,计算向量 v 乘以变换矩阵 M 得到 v'
[ m1 m2 m3 m4 ] [ m11 m12 m13 m14 ] [ m21 m22 m23 m24 ] [ m31 m32 m33 m34 ] v'x = m1 * vx + m11 * vy + m21 * vz + m31 * vw v'y = m2 * vx + m12 * vy + m22 * vz + m32 * vw v'z = m3 * vx + m13 * vy + m23 * vz + m33 * vw v'w = m4 * vx + m14 * vy + m24 * vz + m34 * vw- 列向量是右乘矩阵 (列矩阵x列向量) Unity里面一般就是列向量,所以Matrix4x4*Vector4只能右乘
- 示例
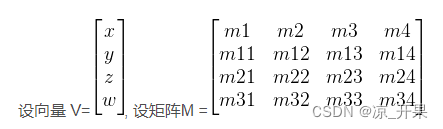
- 结果为:M*V=v'为以下结果
v'x = m1*vx + m2*vy + m3*vz + m4*vw v'y = m11*vx + m12*vy + m13*vz + m14*vw v'z = m21*vx + m22*vy + m23*vz + m24*vw v'w = m31*vx + m32*vy + m33*vz + m34*vw- 示例2 对于大多数常见的欧几里德变换(如平移、旋转和缩放),向量的第四个分量 w 通常设置为 1 这里w值只是计算示
[ 1 2 3 4 ] [ 5 6 7 8 ] [ 9 10 11 12 ] [ 13 14 15 16 ] 向量 v = (1, 2, 3, 1) v'x = 1*1 + 2*2 + 3*3 + 4*1 = 19 v'y = 5*1 + 6*2 + 7*3 + 8*1 = 47 v'z = 9*1 + 10*2 + 11*3 + 12*1 = 75 v'w = 13*1 + 14*2 + 15*3 + 16*1 = 103 向量乘法结果为 v' = (19, 47, 75, 103)- Unity示例:
using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using UnityEngine; public class MatrixDemo : MonoBehaviour { public Matrix4x4 matrix1; public Vector4 MovePoint; // Start is called before the first frame update void Start() { //这里是赋值整个变换矩阵 M=T*R*S matrix1.SetTRS(transform.position,transform.rotation,transform.localScale); } // Update is called once per frame void Update() { if (Input.GetKeyDown(KeyCode.Q)) { OnMatrix4x4Move(); } } /// <summary> /// 矩阵平移,第四列是标记坐标信息的 /// </summary> public void OnMatrix4x4Move() { Vector4 v4 = new Vector4(0,0,0,1); matrix1[0, 3] = MovePoint.x; matrix1[1, 3] = MovePoint.y; matrix1[2, 3] = MovePoint.z; v4 = matrix1 * v4; transform.position = new Vector3(v4.x,v4.y,v4.z); } }
2.矩阵变换-旋转
- 三维图形的旋转可以绕三个坐标轴进行,以下是左手法则的旋转变换矩阵分别为:

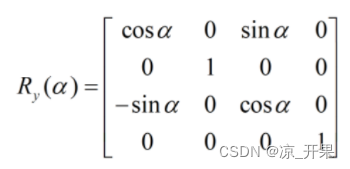
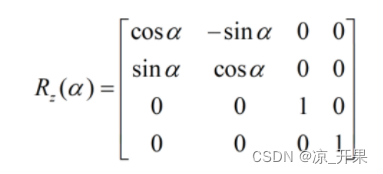
- 四元数的转换
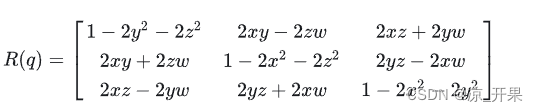
- 根据上面可以推导出,这里w的tr(r)是矩阵的迹,也就是矩阵对角元素的和

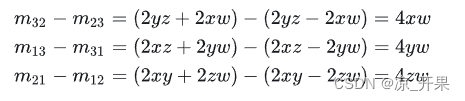
- Unity示例:
using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using UnityEngine; public class MatrixDemo : MonoBehaviour { public Matrix4x4 matrix1; // public Matrix4x4 matrixRotate; public Vector4 MovePoint; public Vector3 RotateData; // Start is called before the first frame update void Start() { //这里是赋值整个变换矩阵 M=T*R*S matrix1.SetTRS(transform.position, transform.rotation, transform.localScale); } // Update is called once per frame void Update() { if (Input.GetKeyDown(KeyCode.Q)) { OnMatrix4x4Move(); } if (Input.GetKeyDown(KeyCode.W)) { OnMatrix4x4Rotate(); } } /// <summary> /// 矩阵平移,第四列是标记坐标信息的 /// </summary> public void OnMatrix4x4Move() { Vector4 v4 = new Vector4(0, 0, 0, 1); matrix1[0, 3] = MovePoint.x; matrix1[1, 3] = MovePoint.y; matrix1[2, 3] = MovePoint.z; v4 = matrix1 * v4; transform.position = new Vector3(v4.x, v4.y, v4.z); } /// <summary> /// 矩阵旋转,这里是按本地旋转来的,例如先转x轴30再转Y,这里Y是基于X30度去转的 /// </summary> public void OnMatrix4x4Rotate() { Matrix4x4 matrixRotateX = Matrix4x4.identity; Matrix4x4 matrixRotateY = Matrix4x4.identity; Matrix4x4 matrixRotateZ = Matrix4x4.identity; Matrix4x4 matrixRotate = Matrix4x4.identity; // if (RotateData.x != 0) { matrixRotateX[1, 1] = Mathf.Cos(RotateData.x * Mathf.Deg2Rad); matrixRotateX[2, 1] = Mathf.Sin(RotateData.x * Mathf.Deg2Rad); matrixRotateX[1, 2] = -Mathf.Sin(RotateData.x * Mathf.Deg2Rad); matrixRotateX[2, 2] = Mathf.Cos(RotateData.x * Mathf.Deg2Rad); } // if (RotateData.y != 0) { matrixRotateY[0, 0] = Mathf.Cos(RotateData.y * Mathf.Deg2Rad); matrixRotateY[2, 0] = -Mathf.Sin(RotateData.y * Mathf.Deg2Rad); matrixRotateY[0, 2] = Mathf.Sin(RotateData.y * Mathf.Deg2Rad); matrixRotateY[2, 2] = Mathf.Cos(RotateData.y * Mathf.Deg2Rad); } // if (RotateData.z != 0) { matrixRotateZ[0, 0] = Mathf.Cos(RotateData.z * Mathf.Deg2Rad); matrixRotateZ[1, 0] = Mathf.Sin(RotateData.z * Mathf.Deg2Rad); matrixRotateZ[0, 1] = -Mathf.Sin(RotateData.z * Mathf.Deg2Rad); matrixRotateZ[1, 1] = Mathf.Cos(RotateData.z * Mathf.Deg2Rad); } matrixRotate = matrixRotateX * matrixRotateY * matrixRotateZ; float vW = Mathf.Sqrt(matrixRotate.m00 + matrixRotate.m11 + matrixRotate.m22 + 1) / 2; float w = vW * 4; float vX = (matrixRotate.m21 - matrixRotate.m12) / w; float vY = (matrixRotate.m02 - matrixRotate.m20) / w; float vZ = (matrixRotate.m10 - matrixRotate.m01) / w; transform.rotation= new Quaternion(vX, vY, vZ, vW); } }3.矩阵变换-缩放
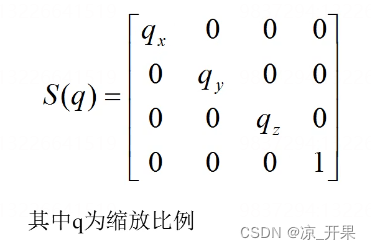
- 也是乘法的用向量代表缩放,
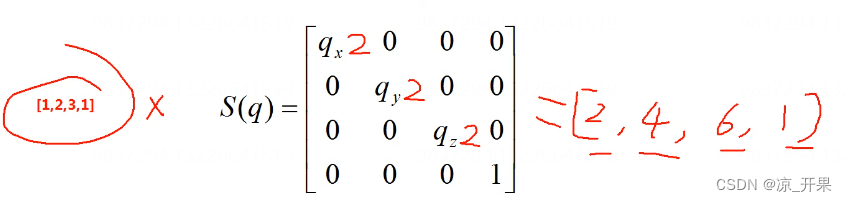
- 上方向量经过缩放两倍从 [1,2,3,1]变成了[2,4,6,1]
- 如果是unity注意是要右乘,因为他是用的列矩阵
- Unity示例
using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using UnityEngine; public class MatrixDemo : MonoBehaviour { public Matrix4x4 matrix1; // public Matrix4x4 matrixRotate; public Vector4 MovePoint; public Vector3 RotateData; public Vector3 ScaleData=Vector3.one; // Start is called before the first frame update void Start() { //这里是赋值整个变换矩阵 M=T*R*S matrix1.SetTRS(transform.position, transform.rotation, transform.localScale); } // Update is called once per frame void Update() { if (Input.GetKeyDown(KeyCode.Q)) { OnMatrix4x4Move(); } if (Input.GetKeyDown(KeyCode.W)) { OnMatrix4x4Rotate(); } if (Input.GetKeyDown(KeyCode.E)) { OnMatrix4x4Scale(); } } /// <summary> /// 矩阵平移,第四列是标记坐标信息的 /// </summary> public void OnMatrix4x4Move() { Vector4 v4 = new Vector4(0, 0, 0, 1); matrix1[0, 3] = MovePoint.x; matrix1[1, 3] = MovePoint.y; matrix1[2, 3] = MovePoint.z; v4 = matrix1 * v4; transform.position = new Vector3(v4.x, v4.y, v4.z); } /// <summary> /// 矩阵旋转,这里是按本地旋转来的,例如先转x轴30再转Y,这里Y是基于X30度去转的 /// </summary> public void OnMatrix4x4Rotate() { Matrix4x4 matrixRotateX = Matrix4x4.identity; Matrix4x4 matrixRotateY = Matrix4x4.identity; Matrix4x4 matrixRotateZ = Matrix4x4.identity; Matrix4x4 matrixRotate = Matrix4x4.identity; // if (RotateData.x != 0) { matrixRotateX[1, 1] = Mathf.Cos(RotateData.x * Mathf.Deg2Rad); matrixRotateX[2, 1] = Mathf.Sin(RotateData.x * Mathf.Deg2Rad); matrixRotateX[1, 2] = -Mathf.Sin(RotateData.x * Mathf.Deg2Rad); matrixRotateX[2, 2] = Mathf.Cos(RotateData.x * Mathf.Deg2Rad); } // if (RotateData.y != 0) { matrixRotateY[0, 0] = Mathf.Cos(RotateData.y * Mathf.Deg2Rad); matrixRotateY[2, 0] = -Mathf.Sin(RotateData.y * Mathf.Deg2Rad); matrixRotateY[0, 2] = Mathf.Sin(RotateData.y * Mathf.Deg2Rad); matrixRotateY[2, 2] = Mathf.Cos(RotateData.y * Mathf.Deg2Rad); } // if (RotateData.z != 0) { matrixRotateZ[0, 0] = Mathf.Cos(RotateData.z * Mathf.Deg2Rad); matrixRotateZ[1, 0] = Mathf.Sin(RotateData.z * Mathf.Deg2Rad); matrixRotateZ[0, 1] = -Mathf.Sin(RotateData.z * Mathf.Deg2Rad); matrixRotateZ[1, 1] = Mathf.Cos(RotateData.z * Mathf.Deg2Rad); } matrixRotate = matrixRotateX * matrixRotateY * matrixRotateZ; float vW = Mathf.Sqrt(matrixRotate.m00 + matrixRotate.m11 + matrixRotate.m22 + 1) / 2; float w = vW * 4; float vX = (matrixRotate.m21 - matrixRotate.m12) / w; float vY = (matrixRotate.m02 - matrixRotate.m20) / w; float vZ = (matrixRotate.m10 - matrixRotate.m01) / w; transform.rotation= new Quaternion(vX, vY, vZ, vW); } /// <summary> /// 矩阵缩放 /// </summary> public void OnMatrix4x4Scale() { Matrix4x4 matrixScale = Matrix4x4.identity; Vector4 v4 = new Vector4(1, 1, 1, 1); matrixScale.m00 = ScaleData.x; matrixScale.m11 = ScaleData.y; matrixScale.m22 = ScaleData.z; v4 = matrixScale * v4; transform.localScale = new Vector3(v4.x, v4.y, v4.z); } } 