阅读量:0
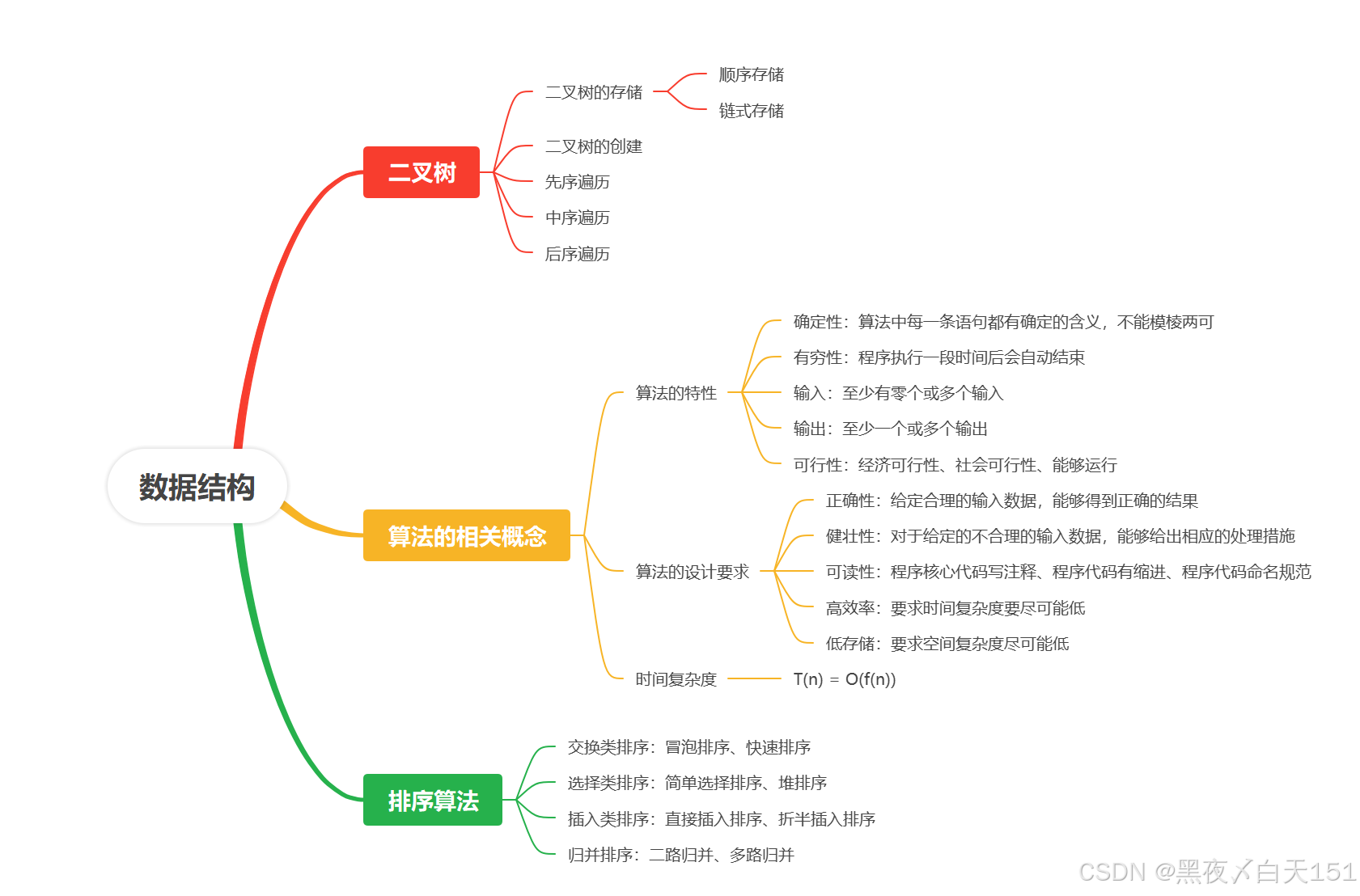
1.二叉树的创建、遍历自己实现一遍
bitree.h
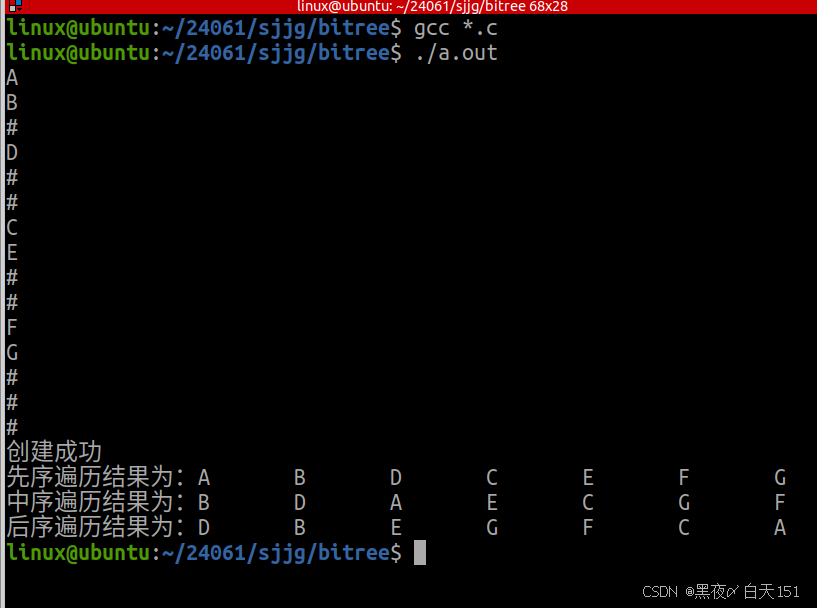
#ifndef BITREE_H #define BITREE_H #include <myhead.h> typedef char datatype; typedef struct Node { datatype data; struct Node *left_child; struct Node *right_child; }Node,*BiTreePtr; //创建二叉树 BiTreePtr tree_create(); //先序遍历 void prio_order(BiTreePtr B); //中序遍历 void in_order(BiTreePtr B); //后序遍历 void post_order(BiTreePtr B); #endif bitree.c
#include "bitree.h" //创建二叉树 BiTreePtr tree_create() { char data = 0; scanf(" %c",&data); if( data=='#') { return NULL; } BiTreePtr p = (BiTreePtr)malloc(sizeof(Node)); if( NULL==p ) { printf("节点申请失败\n"); return NULL; } p->data = data; p->left_child = tree_create(); p->right_child = tree_create(); return p; } //先序遍历 void prio_order(BiTreePtr B) { if( NULL==B ) { return ; } printf("%c\t",B->data); prio_order(B->left_child); prio_order(B->right_child); } //中序遍历 void in_order(BiTreePtr B) { if( NULL==B ) { return ; } in_order(B->left_child); printf("%c\t",B->data); in_order(B->right_child); } //后序遍历 void post_order(BiTreePtr B) { if( NULL==B ) { return ; } post_order(B->left_child); post_order(B->right_child); printf("%c\t",B->data); } main.c
#include "bitree.h" int main(int argc, const char *argv[]) { BiTreePtr B = tree_create(); if( NULL==B ) { printf("创建失败\n"); return -1; } printf("创建成功\n"); printf("先序遍历结果为:"); prio_order(B); printf("\n"); printf("中序遍历结果为:"); in_order(B); printf("\n"); printf("后序遍历结果为:"); post_order(B); printf("\n"); return 0; }2.把所有的排序算法自己实现一遍
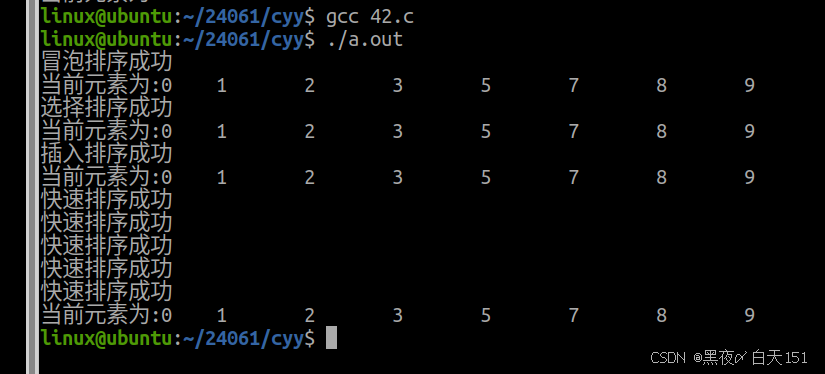
#include <myhead.h> void bubble_sort(int *arr,int n) //冒泡排序 { for(int i=1;i<n;i++) { int flag=0; for(int j=0;j<n-i;j++) { if(arr[j]>arr[j+1]) { flag=1; int temp=arr[j]; arr[j]=arr[j+1]; arr[j+1]=temp; } } if(flag==0) { break; } } printf("冒泡排序成功\n"); } void select_sort(int *arr, int n) //选择排序 { for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { int x=i; for(int j=i+1;j<n;j++) { if(arr[x]>arr[j]) { x=j; } } if(x!=i) { int temp = arr[x]; arr[x]= arr[i]; arr[i] = temp; } } printf("选择排序成功\n"); } void putout(int *arr,int n) //输出 { printf("当前元素为:"); for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { printf("%d\t",arr[i]); } printf("\n"); } void insert_sort(int *arr, int n) //插入排序 { int i,j; for(i=1;i<n;i++) { int x=arr[i]; for(j=i-1;j>=0 && arr[j]>=x;j--) { arr[j+1]=arr[j]; } arr[j+1]=x; } printf("插入排序成功\n"); } int part(int *arr,int low,int high) { int x=arr[low]; while(high>low) { while( arr[high]>=x && high>low ) { high--; } arr[low]=arr[high]; while( arr[low]<=x && high>low ) { low++; } arr[high]=arr[low]; } arr[low]=x; return low; } void quick_sort(int *arr,int low,int high) //快速排序 { if(low>=high) { return; } int mid=part(arr,low,high); quick_sort(arr,low,mid-1); quick_sort(arr,mid+1,high); printf("快速排序成功\n"); } int main(int argc,const char *argv[]) { int arr[]={7,8,5,2,3,0,1,9}; int len =sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]); bubble_sort(arr,len); putout(arr,len); int brr[]={7,8,5,2,3,0,1,9}; select_sort(brr,len); putout(brr,len); int crr[]={7,8,5,2,3,0,1,9}; insert_sort(crr,len); putout(crr,len); int drr[]={7,8,5,2,3,0,1,9}; quick_sort(drr,0,len-1); putout(drr,len); return 0; } 思维导图