阅读量:0
目录
1.安装
centos安装
安装指令:
yum -y update
yum install lua
启动指令:
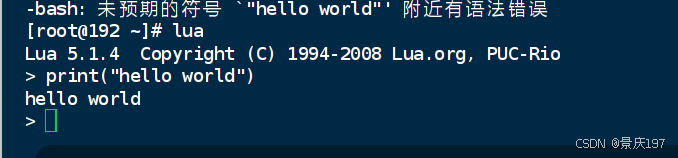
lua print("hello world")windos安装
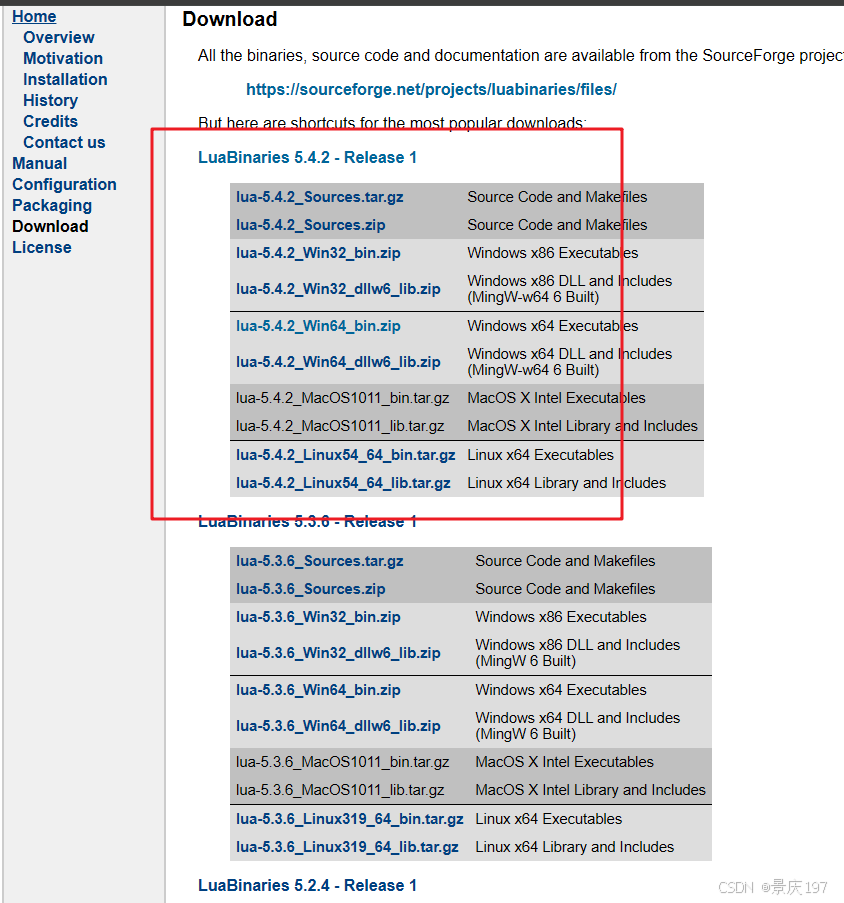
解压后在环境变量配置
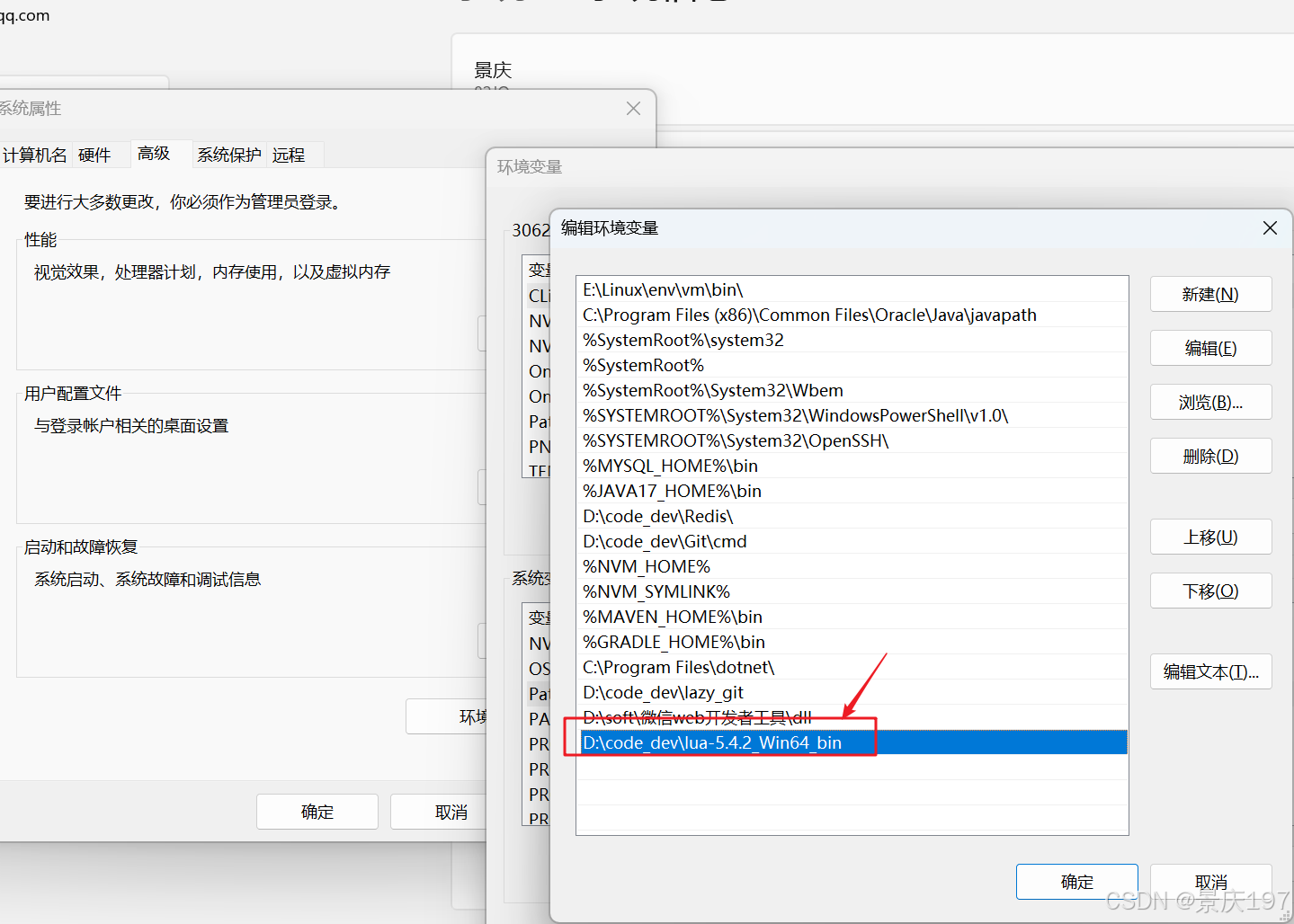
再cmd中尝试,安装成功
也可以在idea中使用
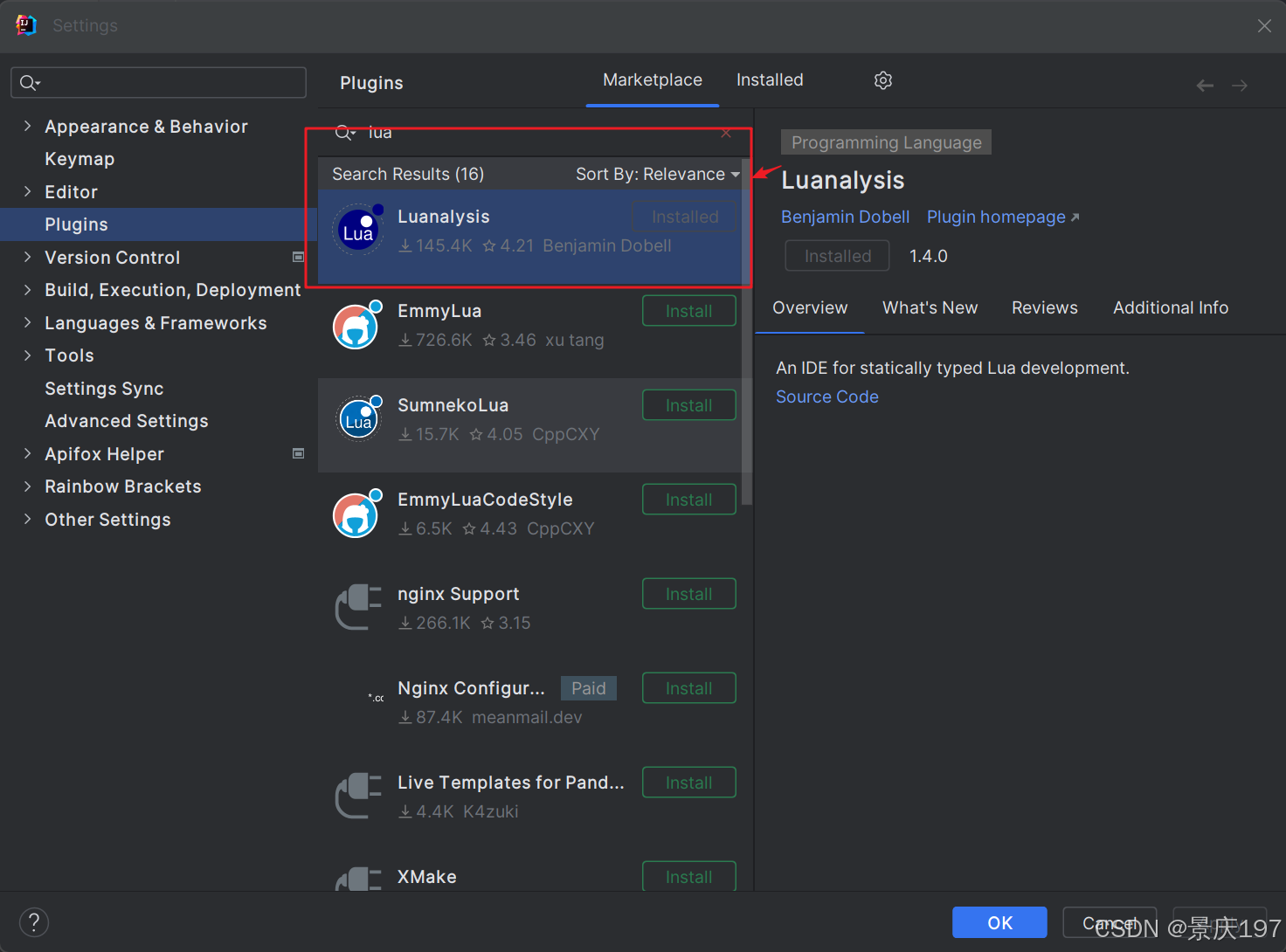
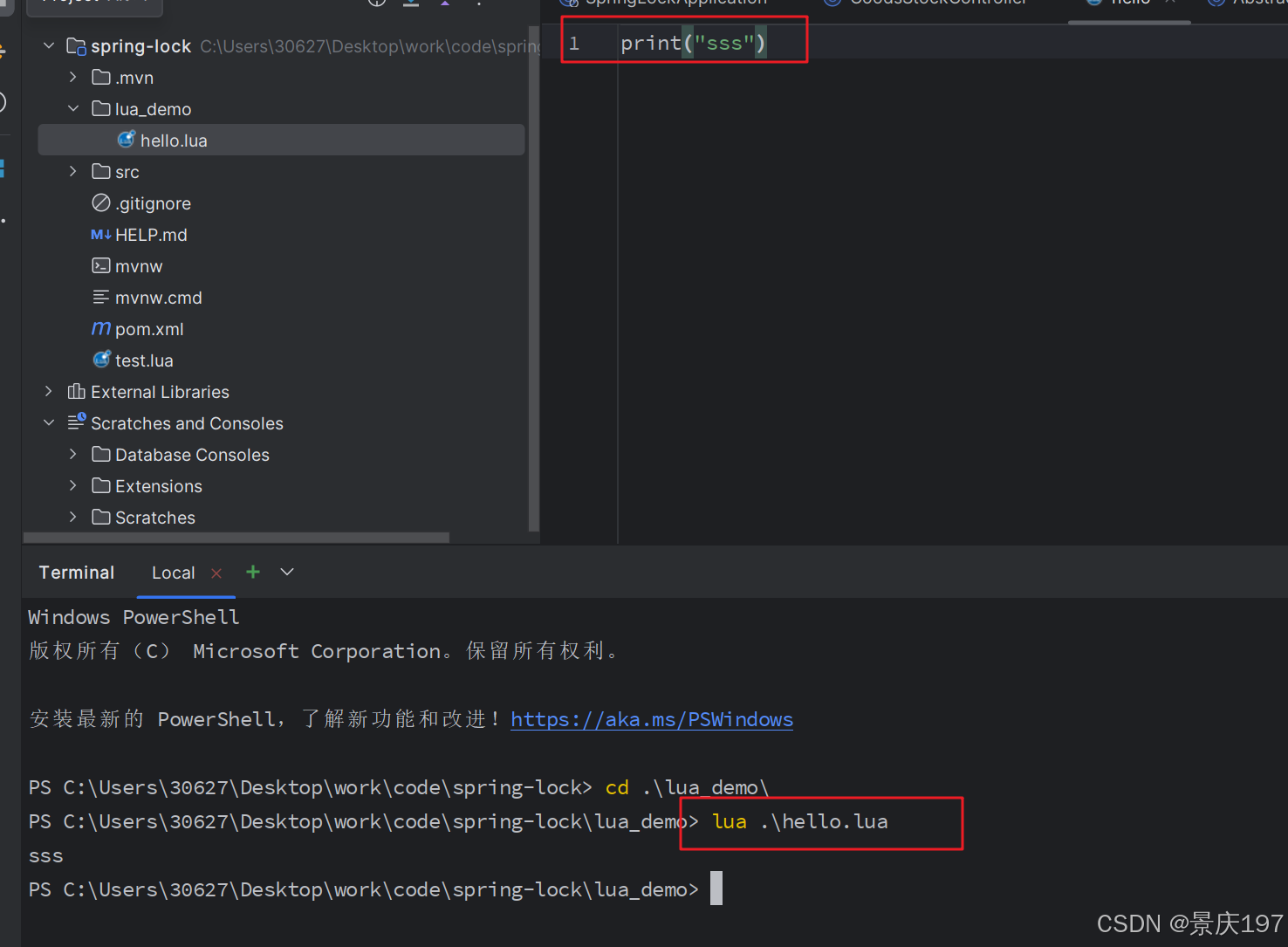
2.语法
2.1Lua数据类型
nil 表示无效值。相当于false
boolean 包含两个值:false,true
number 双精度浮点数
string 字符串由一对双引号或者单引号表示
function 由c或lua编写函数
table lua中的表(taboe) “关联数组“(associative arrays),数组的索引可以是数字、字符串或表类型。在lua里,table的创建是通过"构造表达式完成",最简单构造表达式是{}。
-- 变量 print(type(nil)) print(type(false)) print(type(1)) print(type(1.1)) print(type(type)) print(type("hello world")) print(type({1,2}))
2.2变量
Lua变量有三种类型:全局类型、局部变量、表中的域
- 没有使用local进行修饰的变量都是全局变量,使用local修饰的则为局部变量
- 局部变量的作用域为从声明位置开始到所在语句块结束
- 变量默认值都为nil
--变量 a = 5 --全局变量 print(a) -- 5 local b = 6 --局部变量 print(b) -- 6 -- 查看变量、全局变量、局部变量 do local c = 4 print(a) -- 5 print(c) -- 4 end print(c) -- nil --对多个变量同时赋值 ..表示为字符串连接 a, b, c= 1,2 -- 没有值的变量,赋值nil print(a .."-" .. b) print(c) a, b = 2,3,4 --多出来的值被省略 print(a .. "-" .. b) -- table赋值 如果key值一样后面的会覆盖前面的值 tal = {"a", "b", "3"} print(tal[1] .. tal[2] .. tal[3]) tal = {key = "xxddd", key1 = "yysss"} print(tal["key"] .. tal["key1"])2.3lua循环
--while 循环 a = 1 while(a < 5) do print(a) a = a + 1 end --for 循环,从exp1开始循环到exp2, exp3是步⻓ for var=exp1, exp2, xep3 do end for i = 1, 5, 1 do print(i) end for i = 5, 1, -1 do print(i) end --打印数组 a = {"one", "two", "three"} for i, v in ipairs(a) do print(i, v) end2.4流程控制
--流程控制 a = 9 if (a < 10) then print("⼩于10") end a = 11 if (a < 10) then print("⼩于10") else print("⼤于等于10") end a = 10 if (a < 10) then print("⼩于10") elseif (a == 10) then print("等于10") else print("⼤于10") end 2.5函数
--函数 function max(a, b) if (a < b) then print("a⼩于b") elseif(a == b) then print("a等于b") else print("a⼤于b") end end print(max(5, 5)) --函数作为参数传递给函数 myFunc = function(param) print("这是param" .. param) end function myFuncB (a, b, func) result = a + b func(result) end myFuncB(1, 2, myFunc) --可变参数函数 function aa(...) local arg={...} for i, v in pairs(arg) do print(i .. v) end end aa("a", "b", "c")2.6运算符
正常+ - * / % ^ - 特殊//整除运算符 比如5//2 输出结果为2
算数运算符号
--算术运算符 print(1 + 2) print(2 - 1) print(2 * 1) print(-10) print(10 / 6) print(10 % 6) print(10 // 6) print(10 ^ 2) 2.7关系运算符
正常 == > < >= <=
特殊:~=(不等于)
关系运算符
and or not
其他运算符号
.. 连接两个字符串
# 一元运算符,返回字符串或表的长度
#“hello” 返回5
3.lua脚本在redis中的使用
3.1lua脚本再redis简单编写
redis中支持使用EVAL关键字来使用Lua脚本
eval指令中的1 表示key的个数,以下代码实例是表示keys[1] 等于在1的后面的key1,即keys[1]=key1,但是value中是不需要声明的。
EVAL script numkeys key [key …] arg [arg …] 127.0.0.1:6379> eval "return {KEYS[1],ARGV[1],ARGV[2]}" 1 key1 arg1 arg2 1) "key1" 2) "arg1" 3) "arg2" 127.0.0.1:6379> 在redis中执行
eval 执行执行
这个keys和argv必须是大写,不然会报错
eval "return redis.call('set',KEYS[1],ARGV[1])" 1 name xiaoming也可以把指令进行缓存
script load ->evalsha 对应id
script load "return redis.call('set',KEYS[1],ARGV[1])" 返回:c686f316aaf1eb01d5a4de1b0b63cd233010e63d evalsha c686f316aaf1eb01d5a4de1b0b63cd233010e63d 1 name1 zhangsan evalsha c686f316aaf1eb01d5a4de1b0b63cd233010e63d 1 name2 zhangsan2 --判断指令是否存在 script exists c686f316aaf1eb01d5a4de1b0b63cd233010e63d --删除指令 script flush c686f316aaf1eb01d5a4de1b0b63cd233010e63d 3.2简易锁Lua脚本
加锁
ps:lua脚本中指令要对应单引号
//判断redis中是否存在key // 如果不存在,那么就使⽤set key value,并且增加过期时间,返回1. // 如果存在,直接返回0,继续循环获取锁 //正常编写 if (redis.call('exists',lockName) == 0) then redis.call('set',lockName,uuid); redis.call('pexpire',lockName,30000) return 1; else return 0; end; //替换成脚本 if (redis.call('exists',KEYS[1]) == 0) then redis.call('set',KEYS[1],ARGV[1]); redis.call('pexpire',KEYS[1],ARGV[2]) return 1; else return 0; end; 在redis中跑一遍
eval "if (redis.call('exists',KEYS[1]) == 0) then redis.call('set',KEYS[1],ARGV[1]); redis.call('pexpire',KEYS[1],ARGV[2]) return 1; else return 0; end" 1 lockName uuid 30000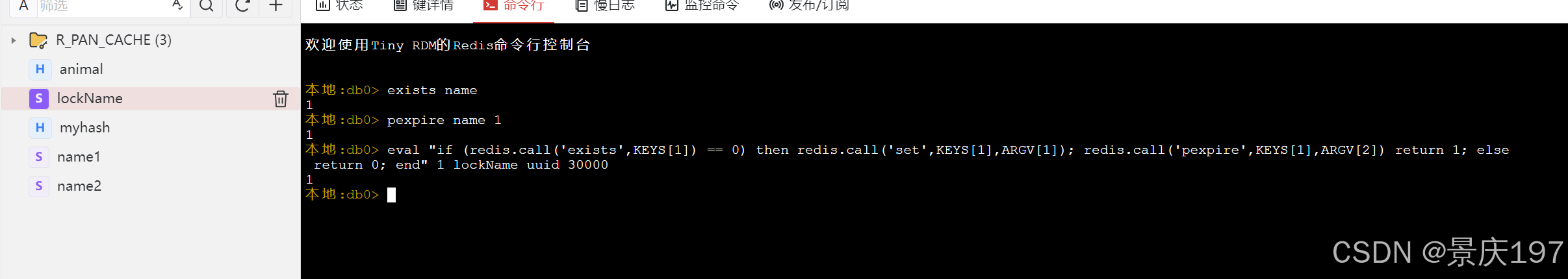
释放锁
//判断锁是否存在,如果不存在,直接返回0 //如果锁存在,判断value是否==当前线程的uuid // 如果等于,执⾏delete // 如果不等于,返回0 //正常写 if (redis.call('exists',lockName) == 0) then return 0; end; if (redis.call('get',lockName) == uuid) then redis.call('del',lockName) return 1; else return 0; end; if (redis.call('exists',KEYS[1]) == 0) then return 0; end; if (redis.call('get',KEYS[1]) == ARGV[1]) then redis.call('del',KEYS[1]) return 1; else return 0; end; reids执行脚本
eval "if (redis.call('exists', KEYS[1]) == 0) then return 0; end; if (redis.call('get', KEYS[1]) == ARGV[1]) then redis.call('del', KEYS[1]); return 1; else return 0; end;" 1 lockName uuid 3.3可重入锁lua脚本
可以通过hash的数据结构进行对锁的添加次数,和扣减测试进行设置
加锁
//redis中执⾏可重⼊加锁lua脚本 eval "if(redis.call('exists',KEYS[1]) == 0) then redis.call('hincrby',KEYS [1],ARGV[1],1); redis.call('pexpire',KEYS[1],ARGV[2]) return 1; end; if(re dis.call('hexists',KEYS[1],ARGV[1]) == 1) then redis.call('hincrby',KEYS [1],ARGV[1],1); redis.call('pexpire',KEYS[1],ARGV[2]) return 1; else retur n 0; end;" 1 lockName uuid 30000 //可重⼊加锁lua脚本 //判断锁是否存在 //如果不存在,就加锁,设置过期时间 //如果存在,判断加锁的线程是不是⾃⼰ //如果是,重⼊次数+1 //如果不是,加锁失败 if(redis.call('exists',KEYS[1]) == 0) then redis.call('hincrby',KEYS[1],ARGV[1],1); redis.call('pexpire',KEYS[1],ARGV[2]) return 1; end; if(redis.call('hexists',KEYS[1],ARGV[1]) == 1) then redis.call('hincrby',KEYS[1],ARGV[1],1); redis.call('pexpire',KEYS[1],ARGV[2]) return 1; else return 0; end; 解锁
//redis中执⾏可重⼊解锁lua脚本 eval "if(redis.call('hexists',KEYS[1],ARGV[1]) == 0) then return 0; end; l ocal lockCount = redis.call('hincrby',KEYS[1],ARGV[1],-1) if(lockCount>0)t hen redis.call('pexpire',KEYS[1],ARGV[2]); return 1; else redis.call('de l',KEYS[1]) return 1; end;" 1 lockName uuid 30000 //可重⼊解锁lua脚本 //判断锁是否存在且存在是否是本线程加的锁。也就是加锁线程是否本身 //如果不是本身,直接就return 0,解锁失败了。 //如果是本身,判断当前重⼊次数是否⼤于1 //如果⼤于1,说明存在线程多次获取⼀把锁,此时只需要减1即可 //如果不⼤于0,说明锁可以被删除了。 if(redis.call('hexists',lockName,uuid) == 0) then return 0; end; local lockCount = redis.call('hincrby',lockName,uuid,-1) if(lockCount>0) then redis.call('pexpire',lockName,time); return 1; else redis.call('del',lockName) return 1; end; 续约
//redis执⾏续约lua脚本 eval "if(redis.call('hexists',KEYS[1],ARGV[1])==0) then return 0; else red is.call('pexpire',KEYS[1],ARGV[2]) return 1; end;" 1 lockName uuid 30000 //lua脚本 //判断锁是否是本线程加锁,是的话,就⼀直延⻓时间 if(redis.call('hexists',KEYS[1],ARGV[1])==0) then return 0; else redis.call('pexpire',KEYS[1],ARGV[2]) return 1; end; 