目录
1.什么是STL
STL(standarf template libaray-标准模板库):是C++标准库的重要组成部分,不仅是一个可复用的组件库,而且是一个包罗数据结构与算法的软件框架。
2.STL的版本
- 原始版本
Alexander Stepanov MengLee 在惠普实验室完成的原始版本,本着开源精神,他们声明允许任何人任意运用,拷贝,修改,传播,商业使用这些代码,无需付费。唯一的条件就是也需要向原始版本一样做开源使用。HP版本--所有STL实现版本的始祖。
- P.J.版本
由P.J.Plauger开发,继承自HP版本,被Windows Visual C++采用,不能公开或修改,缺陷:可读性比较低,符号命名比较怪异。
- RW版本
由Rouge Wage 公司开发,继承自HP版本,被C++ Builder 采用 ,不能公开或修改,缺陷:可读性一般
- SGL版本
由Silicon Graphics Computer Systems ,Inc公司开发,继承自HP版本。被GCC(Linux)采用,可移植性较好,可公开,修改甚至贩卖,从命名风格和编程风格上看,阅读性非常高。
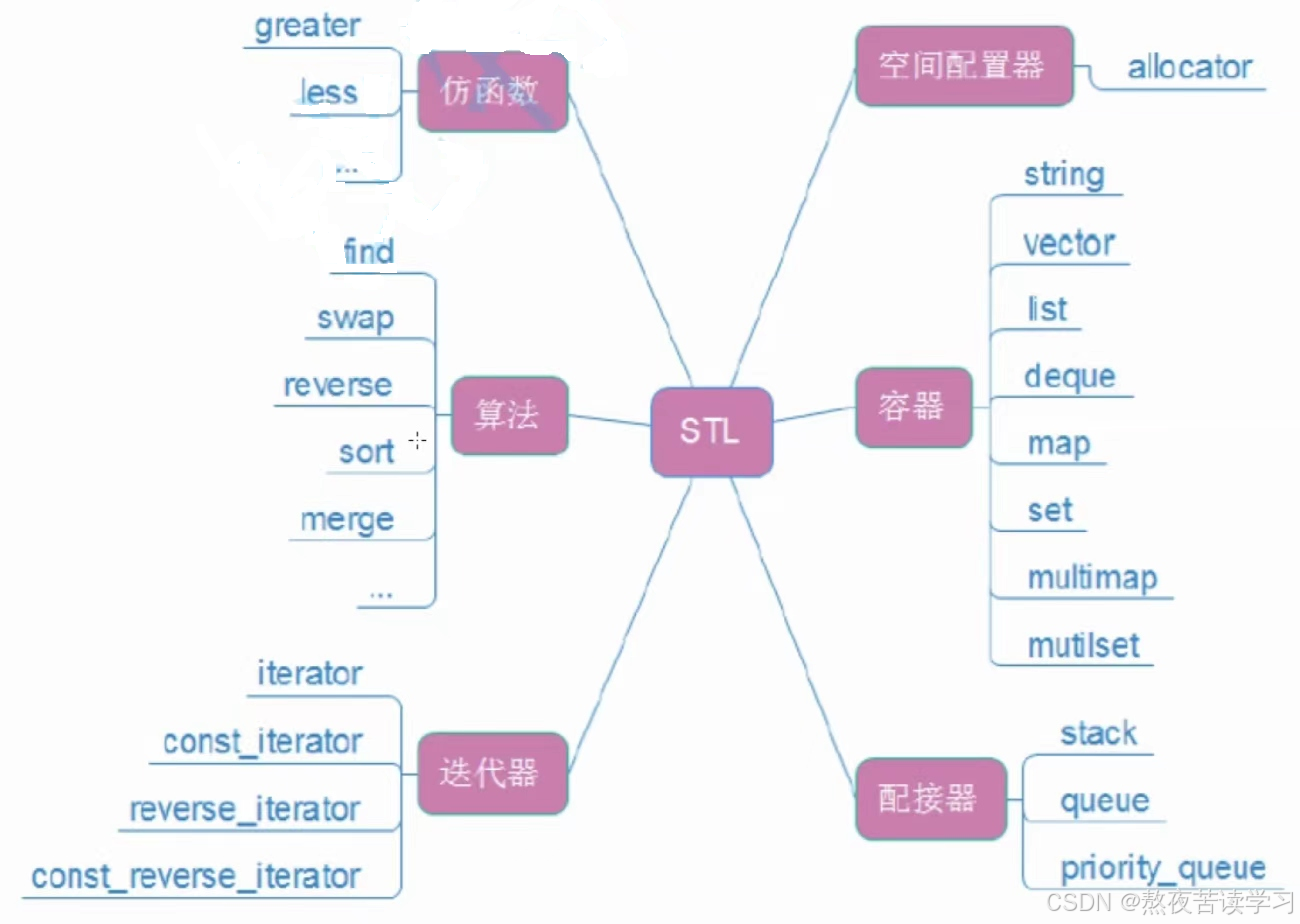
3.STL的六大组件
4.string类
4.1为什么学习string类?
C语言中,字符串是以"\0"结尾的一些字符的集合,为了方便操作,C标准库中提供了一些str系列的库函数,但是这些库函数与字符串是分开的,不太符合OOP的思想,而且底层空间需要用户自己管理,稍不留神可能还会越界访问。而且在常规工作中,为了简单,方便,快捷,基本都使用string类,很少有人使用C库中的字符串操作函数
4.2string常见接口
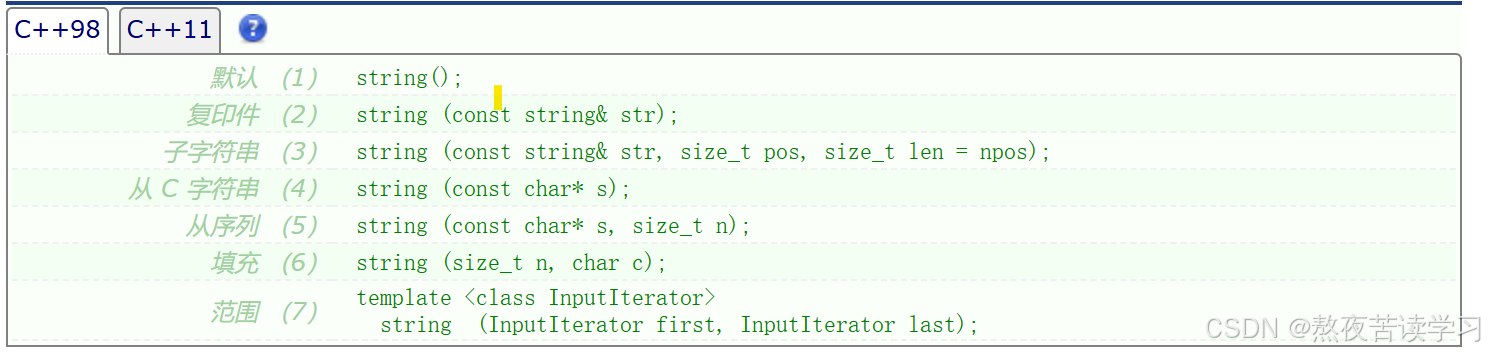
4.2.1默认构造
实例
//无参构造 //string(); string s1; //带参构造 string s2("111"); //string(const char* s); //拷贝构造 string s3(s2); //string(const string & str); string s4("123", 2, 1); //string(const string & str, size_t pos, size_t len = npos); //复制str中从字符下标位置 pos 开始的len个 字符进行拷贝构造(如果任一 str 太短或 len 为 string::npos,则复制到str 的末尾)。 string s5("123",0 ,string:: npos); // string(const char* s, size_t n); string s6("123", 2); //从 s 指向的字符数组中复制前 n 个字符。 //string(size_t n, char c); //用连续的n个c字符去初始化 string s7(3, 'c'); //template <class InputIterator> //string(InputIterator first, InputIterator last);4.2.2析构函数

Element access:
4.2.3 []
获取字符串的字符

利用[]来进行读写,下标+[]遍历
int main() { string s1("abcd"); //写 s1[0] ='*'; //将下标为0的元素修改为1 cout << s1 << endl; //读 for (int i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++) { cout << s1[i] ; } return 0; } 
[]原型
class string { public: char& operator[](size_t i) { return _str[i]; } private: char* _str; size_t _size; size_t _capacity; };4.2.4迭代器
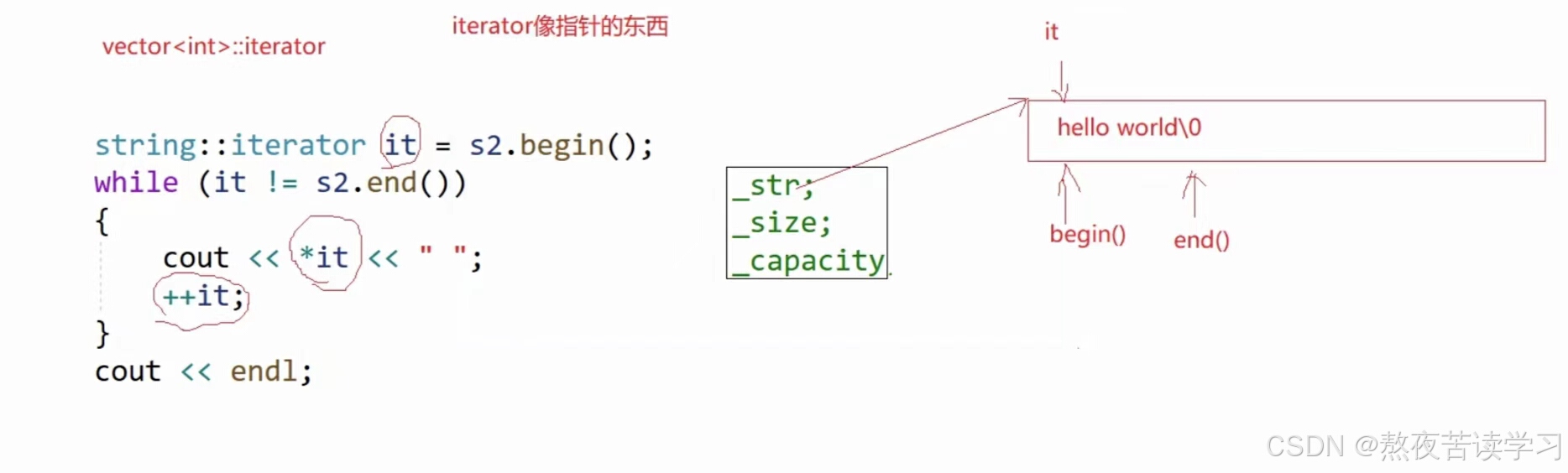
在 STL 中,迭代器(Iterator)用来访问和检查 STL 容器中元素的对象,它的行为模式和指针类似,但是它封装了一些有效性检查,并且提供了统一的访问格式。他的底层是指针
迭代器遍历
int main() { string s1("abcd"); string::iterator it = s1.begin(); while (it != s1.end()) { cout << *it <<" " ; ++it; } return 0; }auto
补充一个C++小语法
auto可自动推导类型,极大程度简化代码
const string s3("hello ward!"); //string::const_iterator cit=s3.begin(); 可简写成: auto cit = s3.begin();auto声明方式
auto 变量名 ;
auto 函数名 (形参列表)
{
//函数体
}
auto的实例
int fun() { return 10; } int main() { int a=10; auto b = a; auto c = 'a'; auto d = fun(); auto& e = a; auto* f = &a; cout << typeid(a).name() << endl; cout << typeid(b).name()<< endl; cout << typeid(c).name() << endl; cout << typeid(d).name() << endl; cout << typeid(e).name() << endl; cout << typeid(f).name() << endl; return 0; }
- 在早期C/C++中auto的含义是:使用auto修饰的变量,是具有自动存储的局部变量,后来这个不重要了,C++11中,标准委员会被废为宝赋予了auto全新的含义即:auto不再是一个存储类型指示符,而是作为一个新的类型指示符来指示编译器,auto声明的变量必须由编译器在编译时期推导而得
- 用auto声明指针类型时,用auto和auto*没有任何区别,但用auto声明引用类型时必须加&
- 当在同一行声明多个变量时,这些变量必须是相同的类型,否则编译器会报错,因为编译器实际只对第一个类型进行推导,然后用推导出来的类型定义其他变量
- auto不能作为函数的参数,可以做返回值,但是谨慎使用
- aoto不能直接用来声明数组
范围for遍历
aoto自动推导,字符赋值,自动迭代,自动判断结束,底层上也是迭代器,所有的容器都支持范围for,因为所有的容器都支持迭代器
4.2.4.1 begin和end
1.begin
返回第一个字符的正向迭代器
int main() { string s1("abcd"); cout<<* s1.begin(); return 0; } 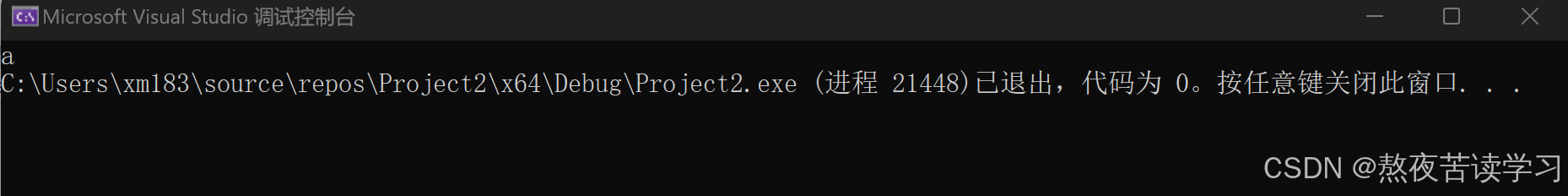
2. end 返回最后一个字符的正向迭代器
可配合起来正向遍历
int main() { string s1("abcdef"); string::const_iterator it = s1.begin(); while (it != s1.end()) { cout << *it << " "; it++; } return 0; } 
4.2.4.2.regin和rend
regin 返回最后一个的反向迭代器
rend 返回第一个字符的反向迭代器

配合起来可支持反向遍历
int main() { string s1("abcdef"); string::const_reverse_iterator it = s1.rbegin(); while (it != s1.rend()) { cout << *it << " "; it++; } return 0; } 
Capacity:
4.2.5.3 size

返回字符串的长度,不包括'\0'
int main() { string s1("abcd"); cout << s1.size(); return 0; }
4.2.6 lenth
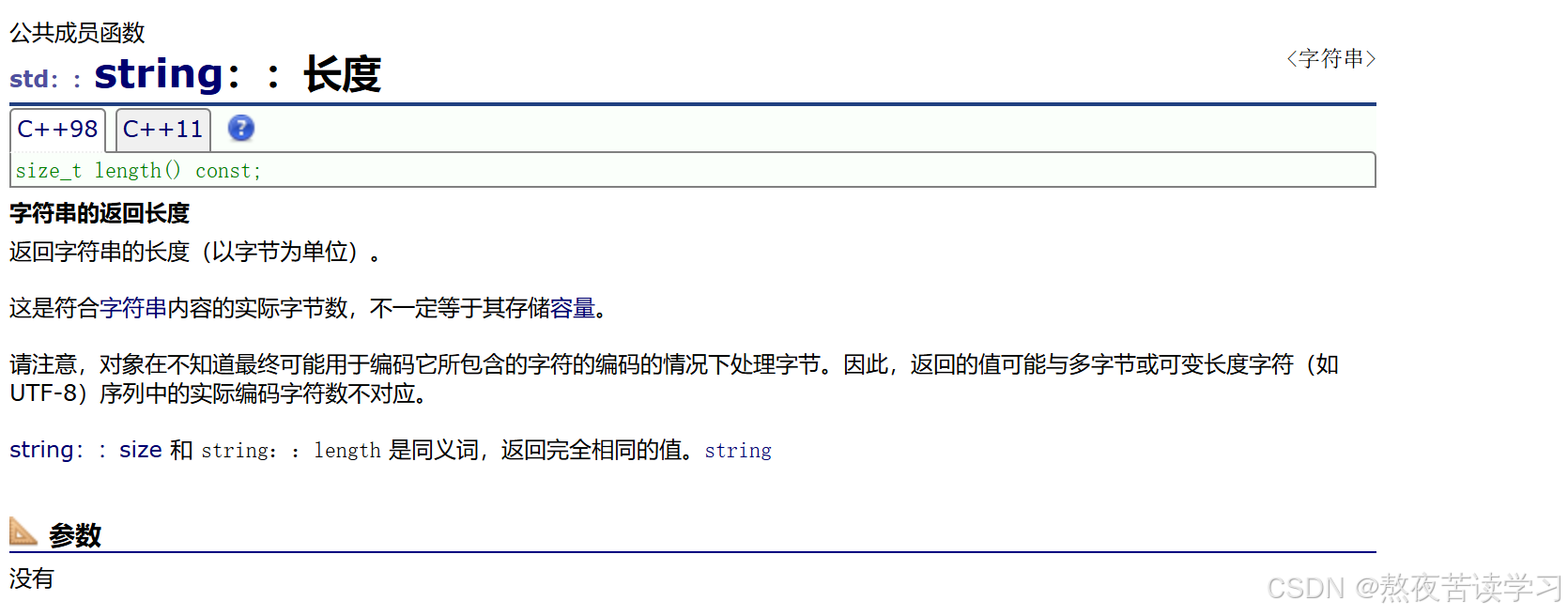
返回以字节为单位的长度,不包括"\0"
int main() { string s1("abcdef"); cout << s1.length()<<endl; return 0; } 
4.2.7capacity
l返回容量大小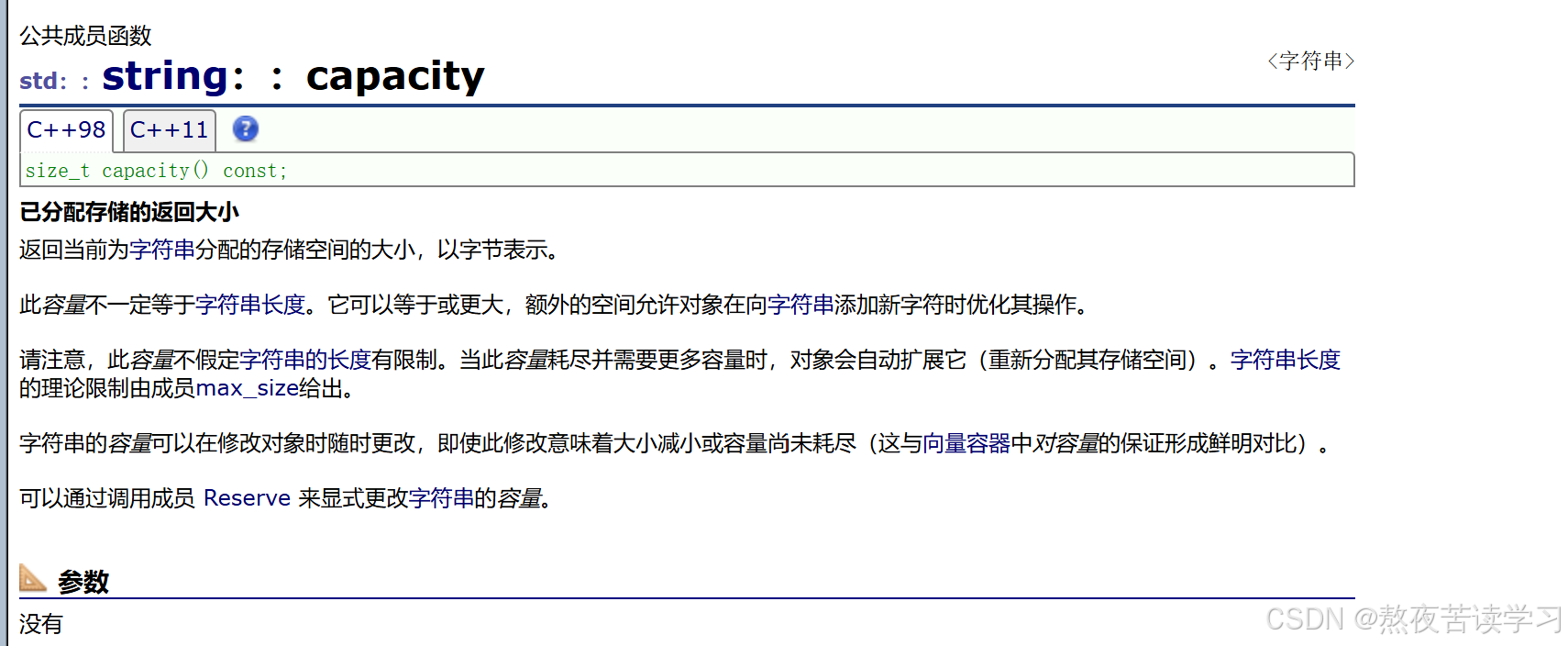
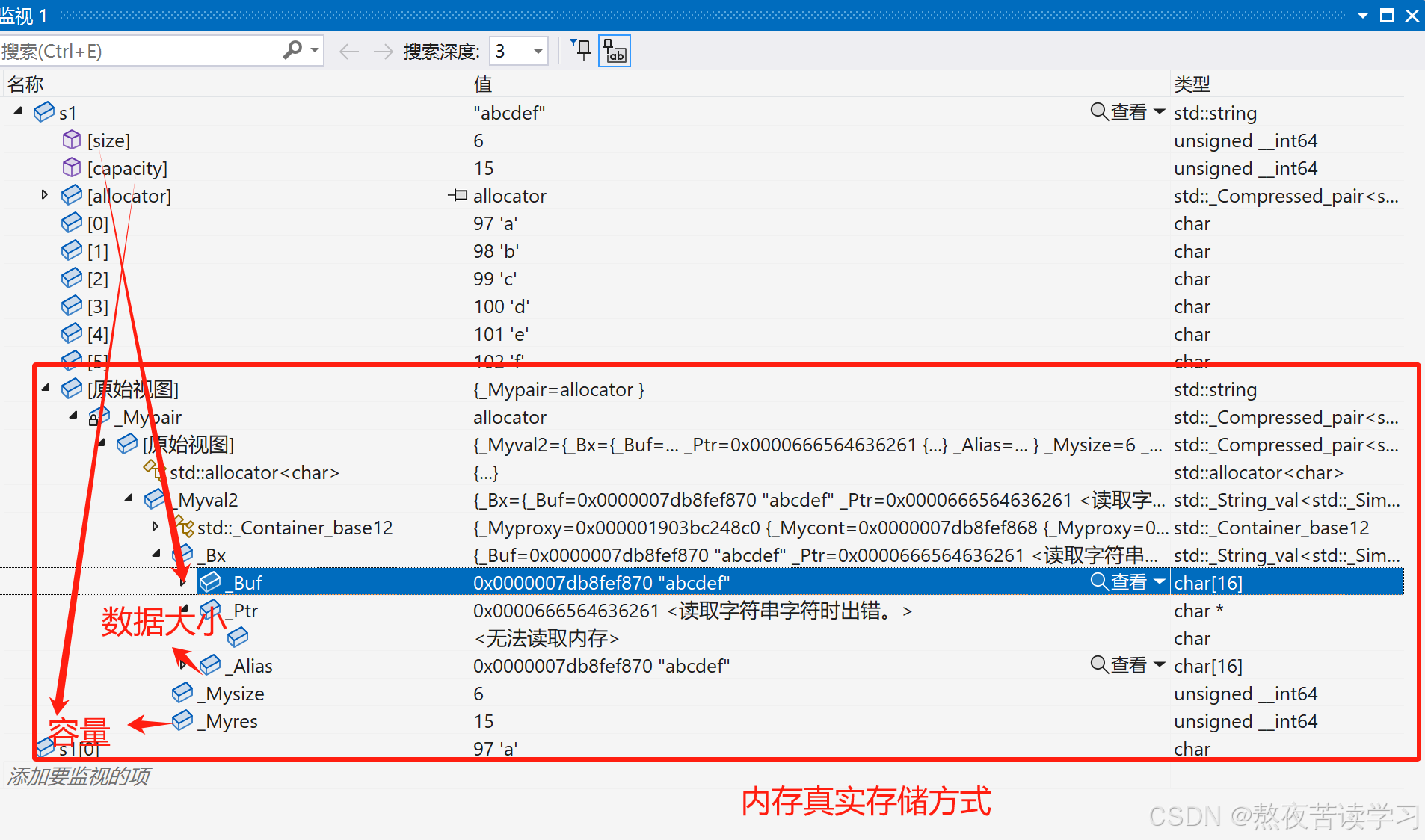
4.2.7reserve

保留预留,提前开空间,避免扩容,提高效率
int main() { string s1("abcdef"); cout << s1.capacity() << endl; s1.reserve(100); cout << s1.capacity()<<endl; //可以扩容,>=100 s1.reserve(50); cout << s1.capacity() << endl; //一般不会缩容 return 0; }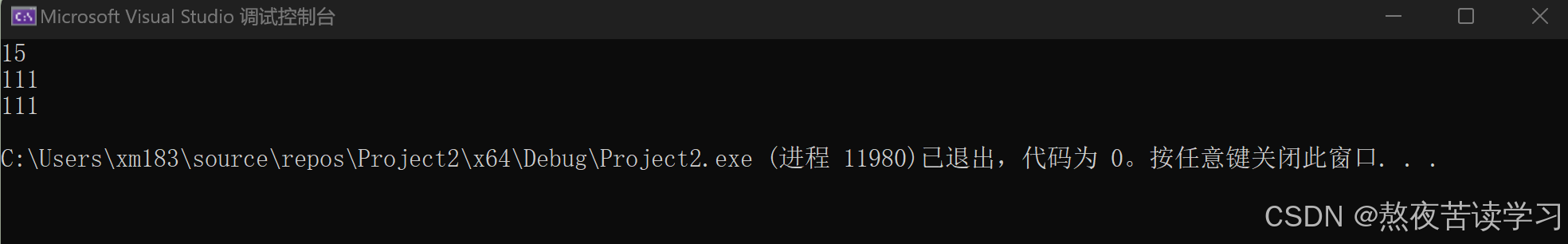
4.2.7 cleart
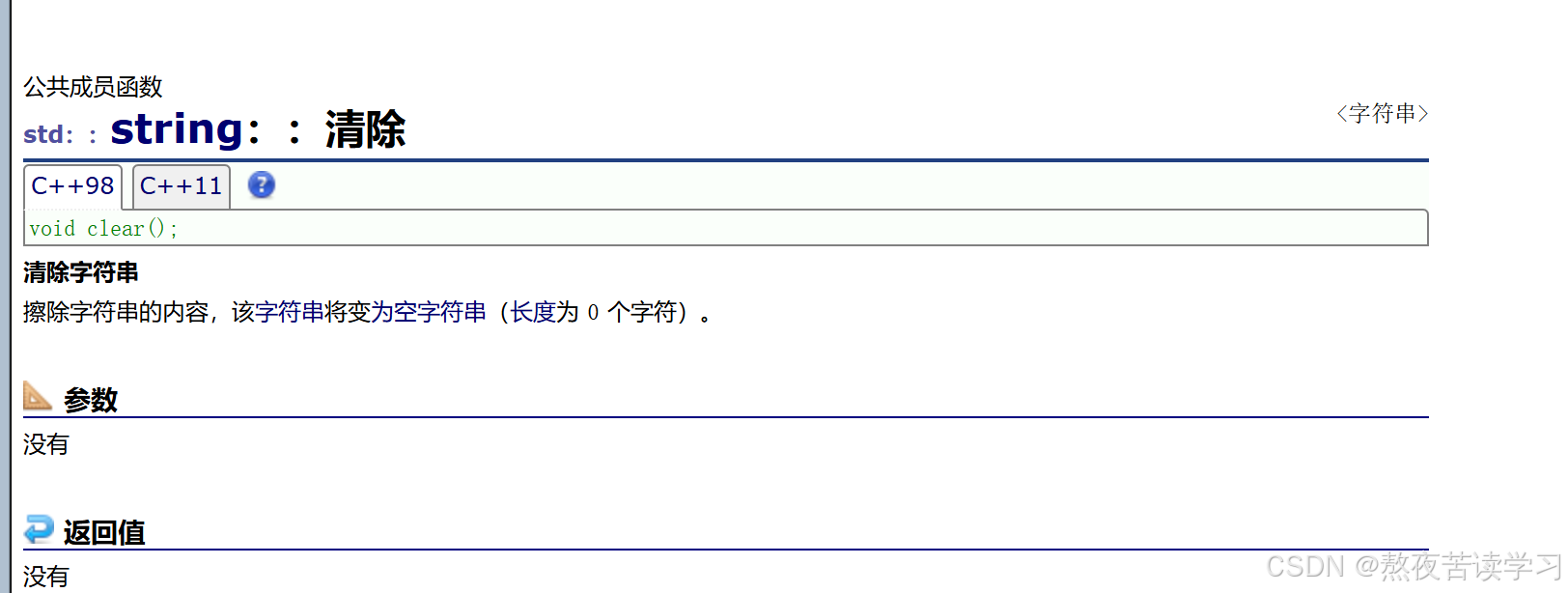 清除数据,一般不清除容量
清除数据,一般不清除容量
int main() { string s1("abcdef"); cout << s1.capacity() << endl; cout << s1.size() << endl; s1.clear(); cout << s1.capacity() << endl; cout << s1.size() << endl; //一般不会缩容 return 0; } 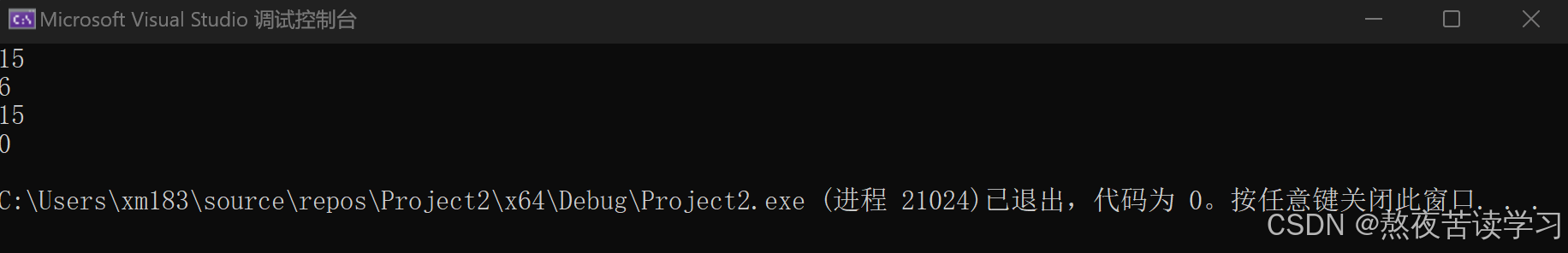
Modifiers:
4.2.7 apend
字符串追加
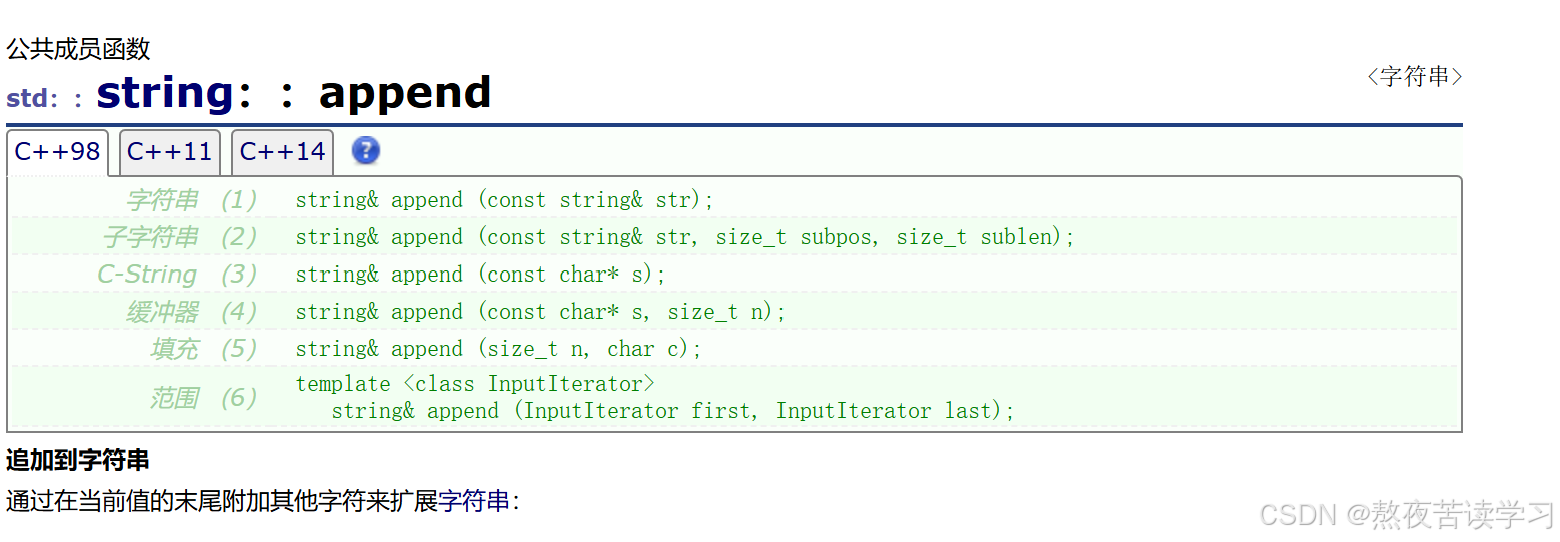
int main() { string s1("abcdef"); //string& append(const string & str); s1.append("yyy"); cout << s1 << endl; // string& append(const string & str, size_t subpos, size_t sublen); //追加 str 子字符串的副本。子字符串是 str 中从字符位置 subpos 开始并跨越 sublen 字符的部分(或者直到 str 的末尾,如果任一 str 太短或 sublen 是 string::npos)。 s1.append("aaaa", 2, 1); cout << s1 << endl; return 0; } 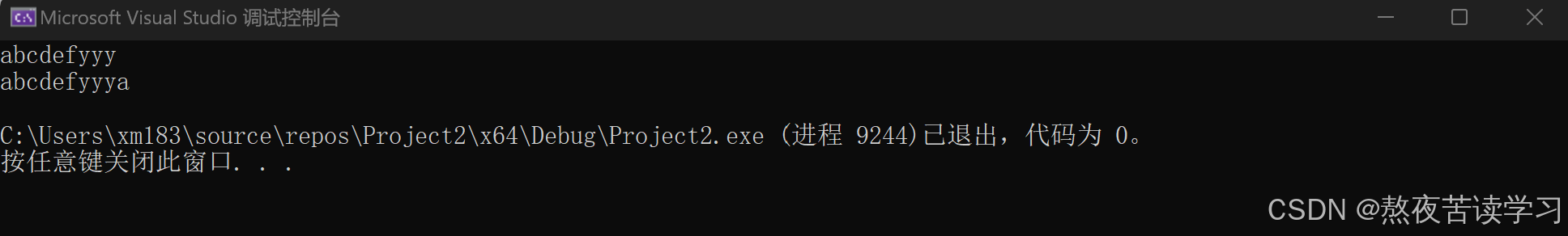
4.2.8 +=
字符串拼接,尾插
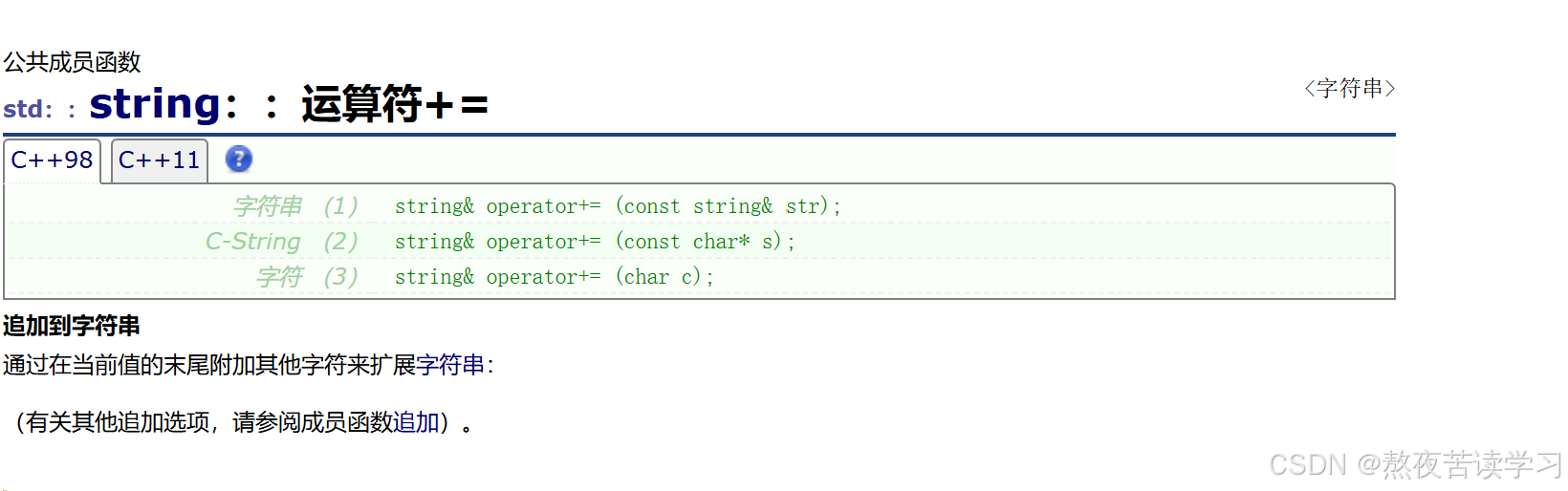
int main() { string s1("abcdef"); string s2("123"); //string& operator+= (const string & str); s1 += s2; s1 += 'a'; //string& operator+= (char c); s1 += "aaa"; //string & operator+= (const char* s); return 0; } int main() { string s1("abcdef"); string s2("123"); //string& insert(size_t pos, const string & str); // 在pos之前插入str s1.insert(0, "abc"); //string& insert(size_t pos, const string & str, size_t subpos, size_t sublen); //在下标pos位置之前插入str下表中subpos到下标sublen位置的元素 s2.insert(0, "abcdd", 0, 4); cout << s2 << endl; //string & insert(size_t pos, const char* s); //在pos位置之前插入s //string& insert(size_t pos, const char* s, size_t n); //从在下标为pos的位置插入s的n个字符 //string& insert(size_t pos, size_t n, char c); //在pos位置之前插入n个c字符 //void insert(iterator p, size_t n, char c); //在迭代器的位置之前插入n个字符c //iterator insert(iterator p, char c); //在迭代器的位置之前插入字符c s1.insert(s1.begin(), '*'); cout << s1 << endl; return 0; }4.2.9 erase
头删

int main() { string s1("abcdef"); string s2("123"); //string& erase(size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos); //擦除字符串值中从字符位置 pos 开始并到 len 字符的部分不包括len(如果内容太短或 len 为 string::npos,则擦除字符串值的末尾。 s1.erase(0, 2); //iterator erase(iterator p); //擦除 p 指向的字符。 s1.erase(s1.begin()); //iterator erase(iterator first, iterator last); //擦除[first,last] 范围内的字符序列 s1.erase(s1.begin(), s2.end()); cout << s1 << endl; return 0; } 4.2.10 replace
替换
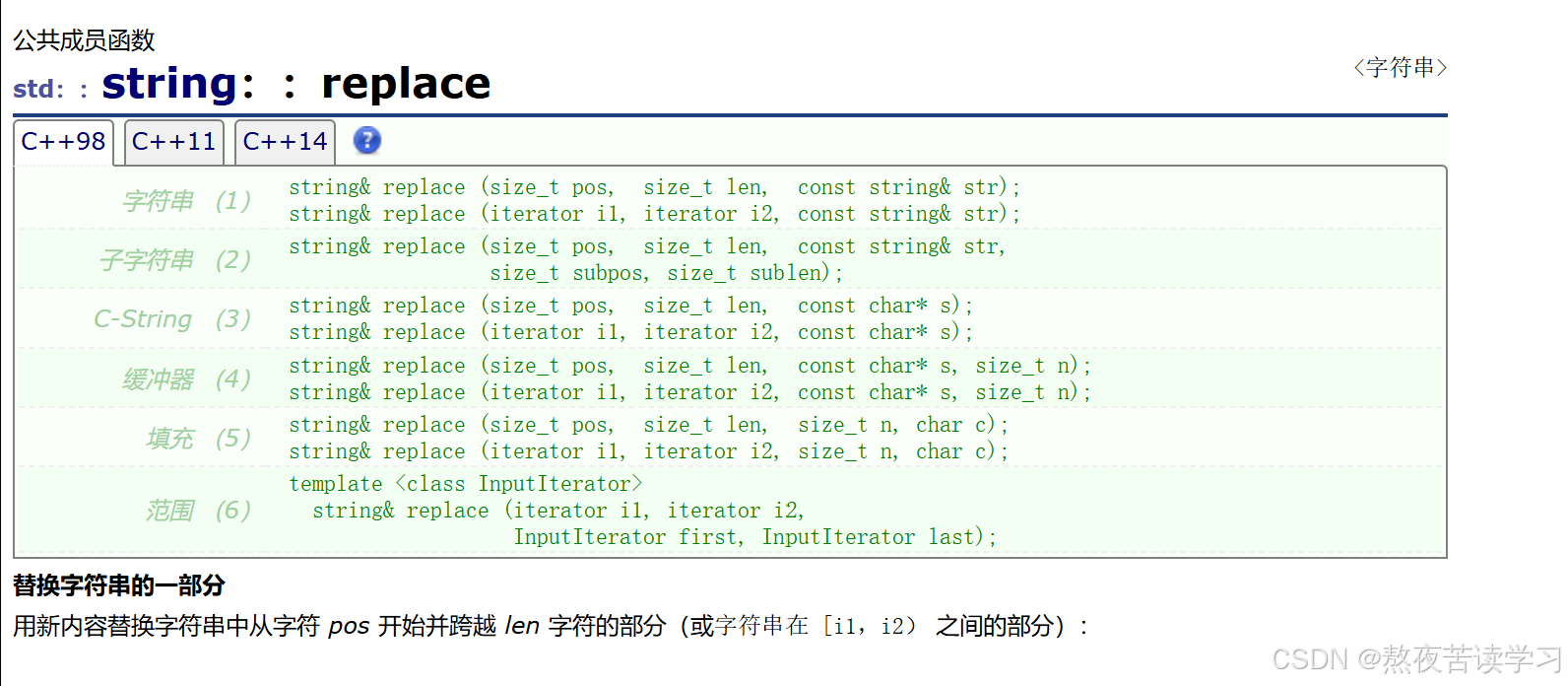
int main() { string s1("abcdef"); string s2("123"); //string & replace(size_t pos, size_t len, const char* s); //string& replace(size_t pos, size_t len, const string & str); //把pos位置到len位置替换成str //string& replace(iterator i1, iterator i2, const char* s); //string& replace(iterator i1, iterator i2, const string & str); //把i1到i2之间的迭代器换成str //string& replace(size_t pos, size_t len, size_t n, char c); //string& replace(size_t pos, size_t len, const char* s, size_t n); //把pos位置到len位置替换成str中的前n个 //string& replace(iterator i1, iterator i2, const char* s, size_t n); //把i1到i2之间的迭代器换成str中的前n个 //string& replace(iterator i1, iterator i2, size_t n, char c); //把i1到i2之间的迭代器换成n个字符c //string& replace(iterator i1, iterator i2, //InputIterator first, InputIterator last); //将迭代器输入到范围内的初始位置和最终位置。使用的范围是 [first,last),它包括 first 和 last 之间的所有字符,包括 first 指向的字符,但不包括 last 指向的字符 return 0; }String operations:
4.2.11 find
查找
返回第一个匹配的第一个字符的位置。
如果未找到匹配项,该函数将返回 string::npos。(整型最大值)
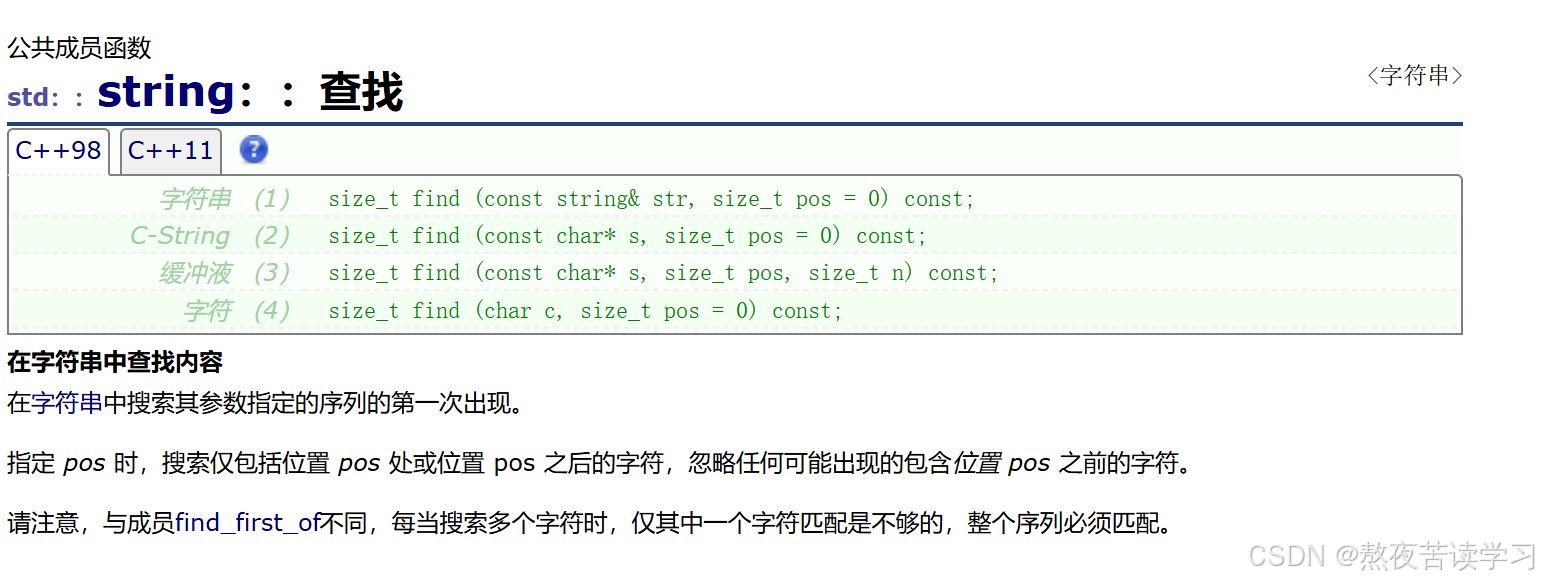
int main() { string s1("abcdef"); string s2("123"); //size_t find(const string & str, size_t pos = 0) const; s1.find("bce"); // size_t find(const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const; //在pos位置找s s1.find('a'); // size_t find(const char* s, size_t pos, size_t n) const; //从pos位置找s的前n个 cout<< s1.find("aaa", 1, 2); // size_t find(char c, size_t pos = 0) const; //从pos位置开始搜索字符c return 0; }4.2.12 substr
获得对于位置以后的子串然后重新构成string类返回
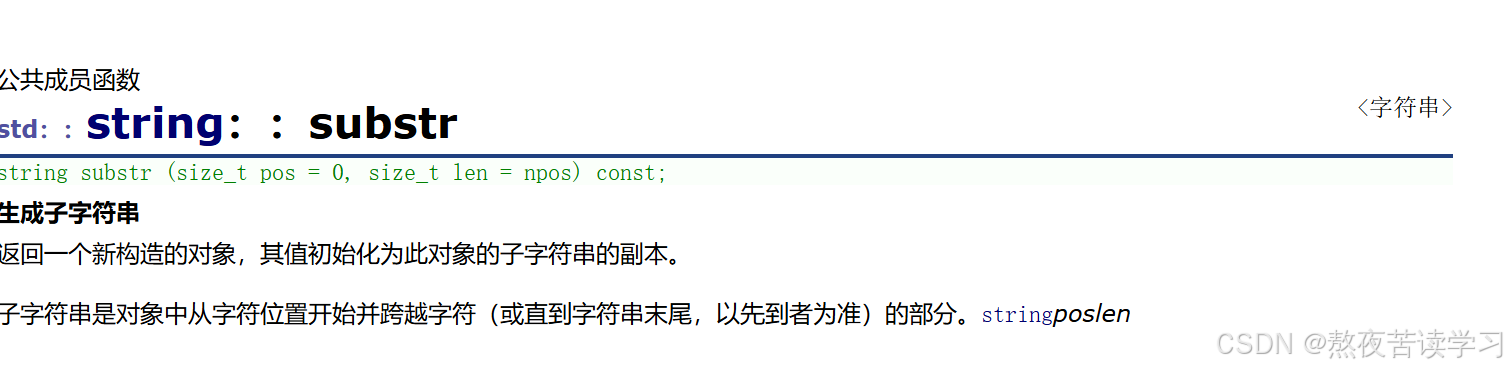
int main() { string s1("abcdef"); //tring substr(size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos) const; //从pos位置开始的len个字符重新构建成string再返回 s1.substr(3, 4); return 0; }实例
int main() { string s("text.cpp"); size_t pos = s.rfind('.'); string suffix = s.substr(pos); cout << suffix << endl;; return 0; } 
4.2.13 find_first_of
顺着找字符串中的字符,找到返回第一个出现的下标

int main() { string s1("abcdef"); //ze_t find_first_of(const string & str, size_t pos = 0) const; //ize_t find_first_of(const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const; //ize_t find_first_of(char c, size_t pos = 0) const; //在pos位置开始找str中的字符 s1.find_first_of("abc"); //ize_t find_first_of(const char* s, size_t pos, size_t n) const; //在pos位置找s的前n个 return 0; }4.2.14 find_ last_of
倒着找字符串中的字符,找到返回第一个出现的下标

int main() { string s1("abcdef"); //size_t find_last_of(const string & str, size_t pos = npos) const; // //size_t find_last_of(char c, size_t pos = npos) const; // size_t find_last_of(const char* s, size_t pos = npos) const; //从最后一个位置向前找str中的字符 s1.find_last_of("Abc",2,4); //size_t find_last_of(const char* s, size_t pos, size_t n) const; //从最后一个位置向前找str中的n个字符 return 0; }分割文件
void SplitFilename(const std::string & str) { std::cout << "Splitting:" << str << endl; std::size_t found = str.find_last_of(" / \\"); std::cout << "path:" << str.substr(0, found) << endl; std::cout << "file:" << str.substr(found + 1) << endl; } int main() { string str1("windows\\winhelp.exe"); string str2("/url/bin/man"); SplitFilename(str1); cout << endl; SplitFilename(str2); return 0; }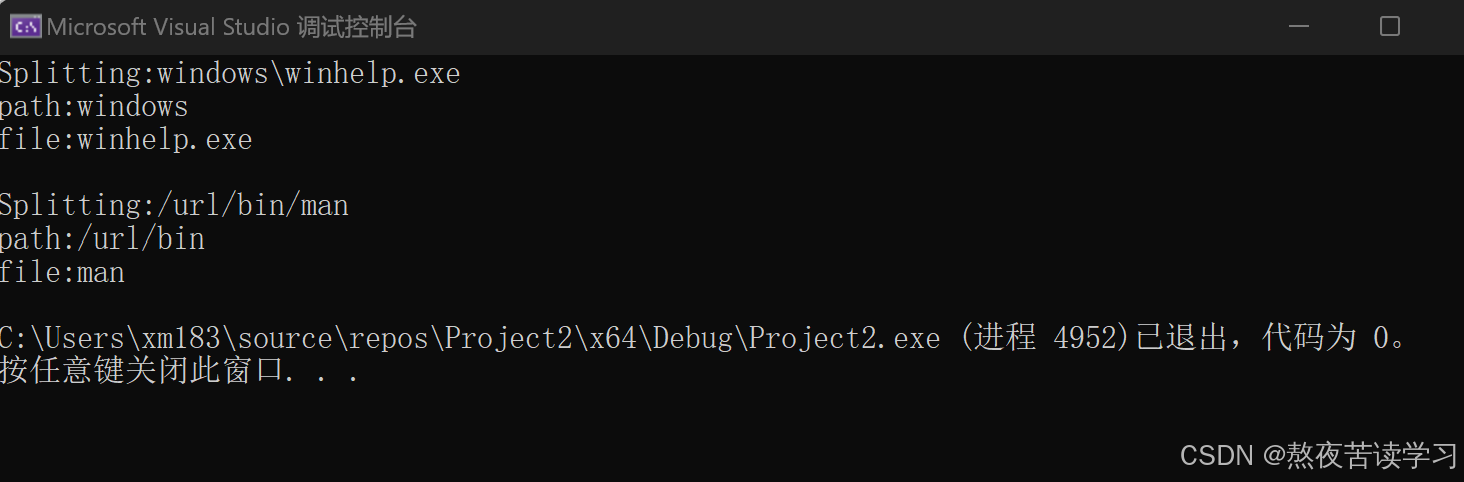
4.2.15 find_first_not_of
没找到就返回,顺着找返回第一个不匹配的对应下标

int main() { string s1("abcdef"); //size_t find_first_not_of(const string & str, size_t pos = 0) const; //size_t find_first_not_of(const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const; // //size_t find_first_not_of(char c, size_t pos = 0) const; //从第一个位置向前找str中的n个字符找到第一个不匹配的元素下标,找不到就返回 // //size_t find_first_not_of(const char* s, size_t pos, size_t n) const; //从第一个位置向后找中第一个不匹配的字符str中的前n个的字符 return 0; } 实例
int main() {// string str("Please, replace the vowels in this sentence by asterisks."); //除了"abcdef"以外全部替换成* std::size_t found = str.find_first_not_of("abcdef"); while (found != std::string::npos) { str[found] = '*' ; found = str.find_first_not_of("abcdef", found + 1); } std::cout << str; return 0; } 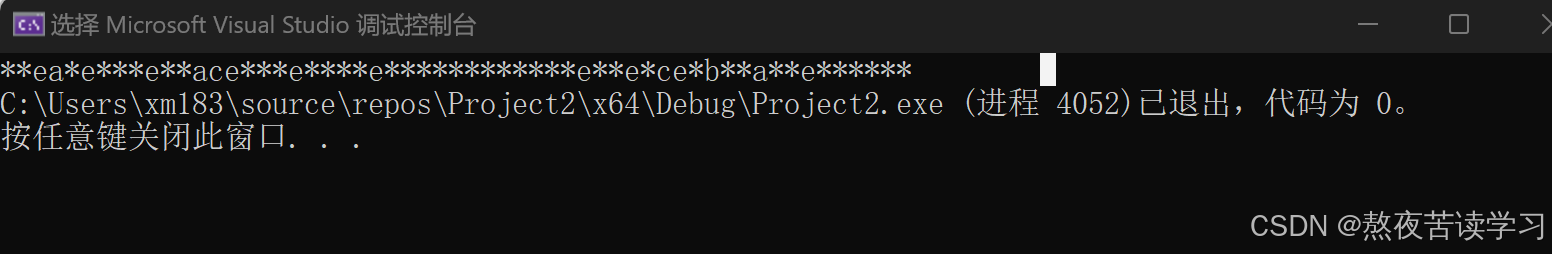
4.2.16 find_last_not_of
倒着找,找到第一个不匹配返回下标

int main() { //ize_t find_first_not_of(const string & str, size_t pos = 0) const; // size_t find_first_not_of(const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const; //size_t find_first_not_of(char c, size_t pos = 0) const; // 从最后一个位置向前找第一个不匹配str中的字符的下标 //size_t find_first_not_of(const char* s, size_t pos, size_t n) const; //从最后一个位置向前找第一个不匹配str中的前n个字符的下标,找不到就返回 return 0; }