文章目录
聚合操作
聚合操作允许用户处理多个文档并返回计算结果。
聚合操作包含三类:单一作用聚合、聚合管道、MapReduce。我们主要掌握其中的聚合管道方式即可。
-
单一作用聚合
提供了对常见聚合过程的简单访问,操作都从单个集合聚合文档。
MongoDB提供
db.collection.estimatedDocumentCount(), db.collection.countDocument(), db.collection.distinct()这类单一作用的聚合函数。 -
聚合管道
一个数据聚合的框架,模型基于数据处理流水线的概念。文档进入多级管道,将文档转换为聚合结果。
-
MapReduce
操作具有两个阶段:处理每个文档并向每个输入文档发射一个或多个对象的map阶段,以及reduce组合map操作的输出阶段。
从MongoDB 5.0开始,map-reduce操作已被弃用。聚合管道比映射-reduce操作提供更好的性能和可用性。
MongoDB 6.0在原有聚合功能的基础上,推出了如下新特性以及优化项:
- 分片集群实例支持 l o o k u p 和 lookup和 lookup和graphLookup。
- 改进$lookup对JOINS的支持。
- 改进$graphLookup对图遍历的支持。
- 提升$lookup性能,部分场景中性能提升可达百倍。
聚合管道
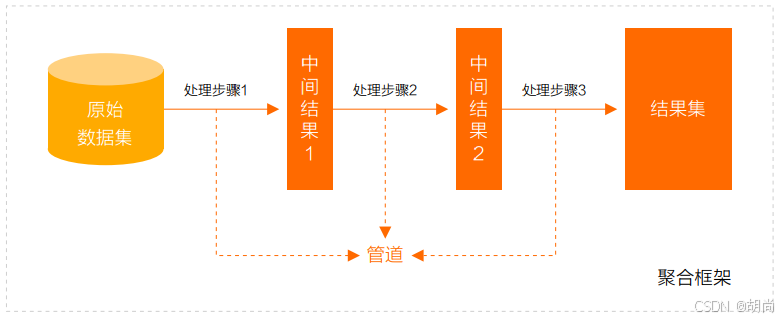
管道(Pipeline)和阶段(Stage)
整个聚合运算过程称为管道(Pipeline),它是由多个阶段(Stage)组成的, 每个管道:
- 接受一系列文档(原始数据);
- 每个阶段对这些文档进行一系列运算;
- 结果文档输出给下一个阶段;
聚合管道操作语法:
pipeline = [$stage1, $stage2, ...$stageN]; db.collection.aggregate(pipeline, {options}) - pipelines 一组数据聚合阶段。除
$out、$Merge、$geonear阶段之外,每个阶段都可以在管道中出现多次。 - options 可选,聚合操作的其他参数。包含:查询计划、是否使用临时文件、 游标、最大操作时间、读写策略、强制索引等等
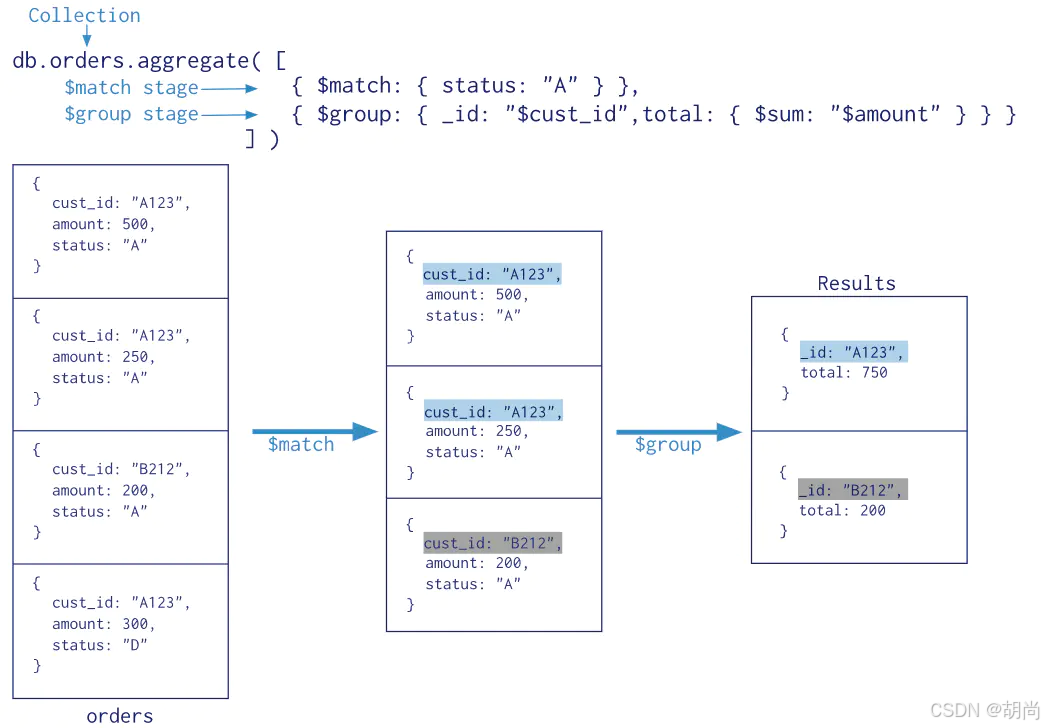
案例:先匹配出status字段为A的文档,再通过_id进行分组,并对amount字段进行求和,将求和的结果取一个别名total
在下面分组的阶段中,我们的字段名都是这种格式"$字段名"
常用的聚合阶段运算符
文档:Aggregation Pipeline Stages — MongoDB Manual
| 阶段运算符 | 描述 | SQL等价运算符 |
|---|---|---|
| $match | 筛选条件 | WHERE |
| $project | 投影 | AS |
| $lookup | 左外连接 | LEFT OUTER JOIN |
| $sort | 排序 | ORDER BY |
| $group | 分组 | GROUP BY |
| $skip + $limit | 分页 | |
| $unwind | 展开数组 | 把多个值展开为多个文档 |
| $graphLookup | 图搜索 | |
| f a c e t / facet/ facet/bucket | 分面搜索 |
聚合表达式
获取字段信息
$<field> : 用 $ 指示字段路径 $<field>.<sub field> : 使用 $ 和 . 来指示内嵌文档的路径 常量表达式
$literal :<value> : 指示常量 <value> 系统变量表达式
$$<variable> 使用 $$ 指示系统变量 $$CURRENT 指示管道中当前操作的文档 准备数据集,执行脚本
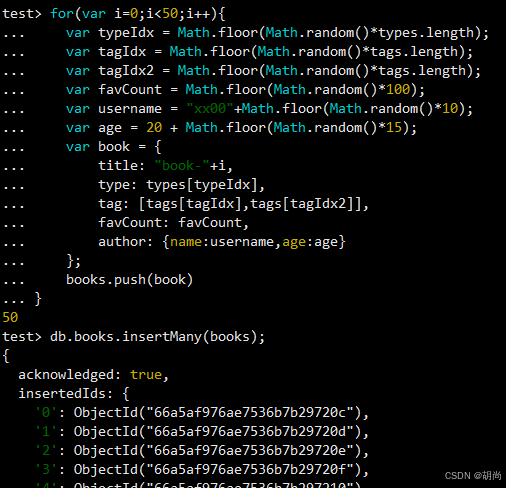
var tags = ["nosql","mongodb","document","developer","popular"]; var types = ["technology","sociality","travel","novel","literature"]; var books=[]; for(var i=0;i<50;i++){ var typeIdx = Math.floor(Math.random()*types.length); var tagIdx = Math.floor(Math.random()*tags.length); var tagIdx2 = Math.floor(Math.random()*tags.length); var favCount = Math.floor(Math.random()*100); var username = "xx00"+Math.floor(Math.random()*10); var age = 20 + Math.floor(Math.random()*15); var book = { title: "book-"+i, type: types[typeIdx], tag: [tags[tagIdx],tags[tagIdx2]], favCount: favCount, author: {name:username,age:age} }; books.push(book) } db.books.insertMany(books); 为接下来的测试案例,可以直接在mondosh命令行执行,当然也可以创建js文件,通过db.load()方式执行
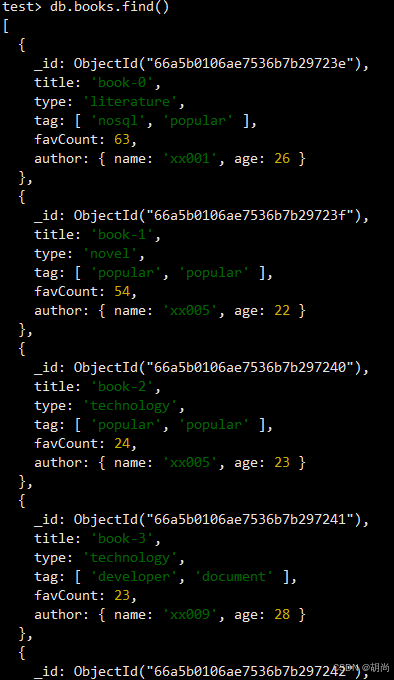
插入之后的数据
$project
投影操作, 将原始字段投影成指定名称,也就是mysql中的字段别名功能。 如将集合中的 title 投影成 name
db.books.aggregate([{ $project: { name: "$title" } }]) 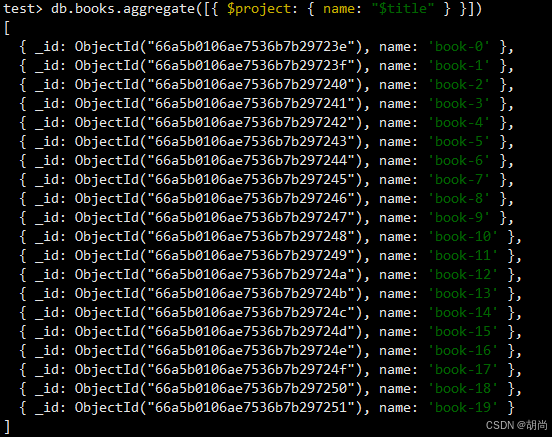
$project 可以灵活控制输出文档的格式,也可以剔除不需要的字段
db.books.aggregate([ { $project: { _id: 0, author: 1, type: 1 } } ]) 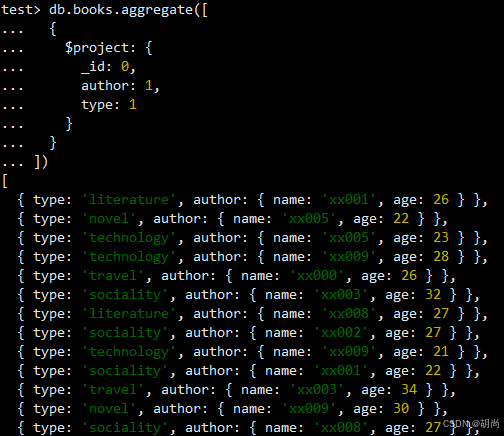
从嵌套文档中排除字段
db.books.aggregate([ { $project: { _id: 0, "author.name": 1, type: 1 } } ]) # 或者使用下面这种写法 db.books.aggregate([ { $project: { _id: 0, type: 1, author: { name: 1 } } } ]) $match
$match用于对文档进行筛选,之后可以在得到的文档子集上做聚合。也就是类似于Mysql的where功能
在实际应用中尽可能将$match放在管道的前面位置
# 查找type字段为novel的文档 db.books.aggregate([ {$match: {type: "novel"}} ]) 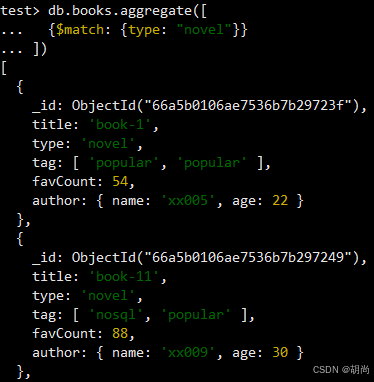
筛选管道操作和其他管道操作配合时候时,尽量放到开始阶段,这样可以减少后续管道操作符要操作的文档数,提升效率
# 先查询type字段为novel的文档,然后再投影,只显示某些字段 db.books.aggregate([ {$match: {type: "novel"}}, {$project: {_id:0, title:1, type:1, favCount:1}} ]) $count
计数并返回与查询匹配的结果数
# 先查询type字段为novel的文档,然后再统计个数,并将该值分配给type_count db.books.aggregate([ {$match: {type: "novel"}}, {$count: "type_count"} ]) # 执行结果 [ { type_count: 9 } ] $group
按指定的表达式对文档进行分组,并将每个不同分组的文档输出到下一个阶段
使用 $group 管道阶段中的 _id 字段来设置组键。也就是说我想按照什么来进行分组就需要在_id中设置
# 标准格式 { $group: { _id: <expression>, // Group key <field1>: { <accumulator1> : <expression1> }, ... } } 常用的accumulator操作符如下所示
| 名称 | 描述 | 类比sql |
|---|---|---|
| $avg | 计算均值 | avg |
| $first | 返回每组第一个文档,如果有排序,按照排序,如果没有按照默认的存储的顺序的第一个文档。 | limit 0,1 |
| $last | 返回每组最后一个文档,如果有排序,按照排序,如果没有按照默认的存储的顺序的最后个文档。 | - |
| $max | 根据分组,获取集合中所有文档对应值得最大值。 | max |
| $min | 根据分组,获取集合中所有文档对应值得最小值。 | min |
| $push | 将指定的表达式的值添加到一个数组中。 | - |
| $addToSet | 将表达式的值添加到一个集合中(无重复值,无序)。 | - |
| $sum | 计算总和 | sum |
| $stdDevPop | 返回输入值的总体标准偏差(population standard deviation) | - |
| $stdDevSamp | 返回输入值的样本标准偏差(the sample standard deviation) | - |
$group阶段的内存限制为100M。
默认情况下,如果stage超过此限制, g r o u p 将产生错误。但是,要允许处理大型数据集,请将 a l l o w D i s k U s e 选项设置为 t r u e 以启用 group将产生错误。但是,要允许处理大型数据集,请将allowDiskUse选项设置为true以启用 group将产生错误。但是,要允许处理大型数据集,请将allowDiskUse选项设置为true以启用group操作以写入临时文件。
# book的数量,收藏总数和平均值 这里就不需要进行分组了 db.books.aggregate([ { $group: { _id: null, bookcountSum: { $sum: 1 }, favCountSum: { $sum: "$favCount" }, favCountAvg: { $avg: "$favCount" } } } ]) # 执行结果 [ { _id: null, bookcountSum: 50, favCountSum: 2349, favCountAvg: 46.98 } # 统计每个作者的book收藏总数 db.books.aggregate([ { $group: { _id: "$author.name", bookFavSum: { $sum: "$favCount" } } } ]) # 执行结果 [ { _id: 'xx000', bookFavSum: 373 }, { _id: 'xx004', bookFavSum: 173 }, { _id: 'xx009', bookFavSum: 313 }, { _id: 'xx001', bookFavSum: 143 }, { _id: 'xx002', bookFavSum: 377 }, { _id: 'xx005', bookFavSum: 245 }, { _id: 'xx003', bookFavSum: 137 }, { _id: 'xx008', bookFavSum: 187 }, { _id: 'xx006', bookFavSum: 198 }, { _id: 'xx007', bookFavSum: 203 } ] # 统计每个作者的每本book的收藏数 db.books.aggregate([ { $group: { _id: {name: "$author.name",book: "$title"}, bookFavSum: {$sum: "$favCount"} } } ]) # 执行结果 [ { _id: { name: 'xx001', book: 'book-0' }, bookFavSum: 63 }, { _id: { name: 'xx009', book: 'book-8' }, bookFavSum: 62 }, { _id: { name: 'xx002', book: 'book-22' }, bookFavSum: 39 }, { _id: { name: 'xx008', book: 'book-12' }, bookFavSum: 37 }, { _id: { name: 'xx006', book: 'book-33' }, bookFavSum: 9 }, { _id: { name: 'xx002', book: 'book-7' }, bookFavSum: 69 }, { _id: { name: 'xx005', book: 'book-38' }, bookFavSum: 27 }, { _id: { name: 'xx004', book: 'book-23' }, bookFavSum: 85 }, { _id: { name: 'xx007', book: 'book-34' }, bookFavSum: 26 }, { _id: { name: 'xx004', book: 'book-21' }, bookFavSum: 78 }, { _id: { name: 'xx000', book: 'book-29' }, bookFavSum: 54 }, { _id: { name: 'xx006', book: 'book-40' }, bookFavSum: 93 }, { _id: { name: 'xx000', book: 'book-27' }, bookFavSum: 93 }, { _id: { name: 'xx002', book: 'book-24' }, bookFavSum: 63 }, { _id: { name: 'xx006', book: 'book-41' }, bookFavSum: 1 }, { _id: { name: 'xx005', book: 'book-45' }, bookFavSum: 56 }, { _id: { name: 'xx009', book: 'book-46' }, bookFavSum: 3 }, { _id: { name: 'xx007', book: 'book-28' }, bookFavSum: 10 }, { _id: { name: 'xx006', book: 'book-49' }, bookFavSum: 6 }, { _id: { name: 'xx006', book: 'book-17' }, bookFavSum: 32 } ] # 每个作者book 的type合集 db.books.aggregate([ { $group: { _id: {name: "$author.name"}, typeList: {$addToSet: "$type"} } } ]) # 执行结果为 [ { _id: { name: 'xx000' }, typeList: [ 'technology', 'literature', 'travel', 'novel' ] }, { _id: { name: 'xx004' }, typeList: [ 'technology', 'literature' ] }, { _id: { name: 'xx009' }, typeList: [ 'novel', 'technology', 'literature', 'sociality' ] }, { _id: { name: 'xx001' }, typeList: [ 'literature', 'sociality', 'technology' ] }, ...... ] $unwind
可以将数组拆分为单独的文档
# 您可以将数组字段路径传递给 $unwind。使用该语法时,如果字段值为 null、缺失或空数组,则 $unwind 不会输出文档。 # 如需指定字段路径,在字段名称前加上美元符号 $,并用引号括起来。 { $unwind: <field path> } v3.2+支持如下语法:
{ $unwind: { #要指定字段路径,在字段名称前加上$符并用引号括起来。 path: <field path>, #可选,一个新字段的名称用于存放元素的数组索引。该名称不能以$开头。 includeArrayIndex: <string>, #可选,default :false,若为true,如果路径为空,缺少或为空数组,则$unwind输出文档 preserveNullAndEmptyArrays: <boolean> } } # 姓名为xx006的作者的book的tag数组拆分为多个文档 db.books.aggregate([ {$match: {"author.name": "xx006"}}, {$unwind: "$tag"} ]) # 或者是下面这种写法 db.books.aggregate([ {$match: {"author.name": "xx006"}}, { $unwind: { path: "$tag", includeArrayIndex: "tagIndex", preserveNullAndEmptyArrays: true } } ]) # 输出结果为 [ ..... { _id: ObjectId("66a5b0106ae7536b7b29726f"), title: 'book-49', type: 'travel', tag: 'nosql', favCount: 6, author: { name: 'xx006', age: 30 }, tagIndex: Long("0") # tagIndex为我自定义的字段名 原数组索引下标 }, { _id: ObjectId("66a5b0106ae7536b7b29726f"), title: 'book-49', type: 'travel', tag: 'developer', favCount: 6, author: { name: 'xx006', age: 30 }, tagIndex: Long("1") # 原数组索引下标 } ] # 每个作者的book的tag合集 db.books.aggregate([ {$unwind: {path: "$tag"}}, { $group: { _id: "$author.name", types: {$addToSet: "$tag"} } } ]) # 输出结果 [ { _id: 'xx000', types: [ 'document', 'mongodb', 'nosql', 'popular', 'developer' ] }, { _id: 'xx004', types: [ 'mongodb', 'nosql', 'developer', 'popular' ] }, { _id: 'xx001', types: [ 'document', 'mongodb', 'nosql', 'popular', 'developer' ] }, { _id: 'xx003', types: [ 'mongodb', 'developer', 'nosql', 'popular' ] }, ...... ] 案例
示例数据
# tag为[]空数组、没有tag字段、tag数组有值 三种情况 db.books.insert([ { "title" : "book-51", "type" : "technology", "favCount" : 11, "tag":[], "author" : { "name" : "hushang", "age" : 28 } },{ "title" : "book-52", "type" : "technology", "favCount" : 15, "author" : { "name" : "hushang", "age" : 28 } },{ "title" : "book-53", "type" : "technology", "tag" : [ "nosql", "document" ], "favCount" : 20, "author" : { "name" : "hushang", "age" : 28 } }]) 测试
# 只要作者为hushang的文档 使用includeArrayIndex选项来输出数组元素的数组索引 db.books.aggregate([ {$match: {"author.name": "hushang"}}, {$unwind: { path: "$tag", includeArrayIndex: 'tagIndex' }} ]) # 执行结果,只有两条数据 [ { _id: ObjectId("66a5cf9fe78ef1c1a23525b3"), title: 'book-53', type: 'technology', tag: 'nosql', favCount: 20, author: { name: 'hushang', age: 28 }, tagIndex: Long("0") # 源数组下标索引 }, { _id: ObjectId("66a5cf9fe78ef1c1a23525b3"), title: 'book-53', type: 'technology', tag: 'document', favCount: 20, author: { name: 'hushang', age: 28 }, tagIndex: Long("1") # 源数组下标索引 } ] # 使用preserveNullAndEmptyArrays选项在输出中包含缺少path字段,null或空数组的文档 db.books.aggregate([ {$match: {"author.name": "hushang"}}, {$unwind: { path: "$tag", includeArrayIndex: 'tagIndex', preserveNullAndEmptyArrays: true }} ]) # 此时的执行结果就有四条数据了,将另外两个tag字段为空数组 或者 null 也一起输出了 [ { # 没有tag字段,并且tagIndex为null _id: ObjectId("66a5cf9fe78ef1c1a23525b1"), title: 'book-51', type: 'technology', favCount: 11, author: { name: 'hushang', age: 28 }, tagIndex: null }, { # 没有tag字段,并且tagIndex为null _id: ObjectId("66a5cf9fe78ef1c1a23525b2"), title: 'book-52', type: 'technology', favCount: 15, author: { name: 'hushang', age: 28 }, tagIndex: null }, { _id: ObjectId("66a5cf9fe78ef1c1a23525b3"), title: 'book-53', type: 'technology', tag: 'nosql', favCount: 20, author: { name: 'hushang', age: 28 }, tagIndex: Long("0") }, { _id: ObjectId("66a5cf9fe78ef1c1a23525b3"), title: 'book-53', type: 'technology', tag: 'document', favCount: 20, author: { name: 'hushang', age: 28 }, tagIndex: Long("1") } ] $limit
限制传递到管道中下一阶段的文档数
db.books.aggregate([ {$limit: 5} ]) 此操作仅返回管道传递给它的前5个文档。 $limit对其传递的文档内容没有影响。
注意:当$sort在管道中的$limit之前出现时,$sort操作只会在过程中维持前n个结果,其中n是指定的限制,而MongoDB只需要将n个项存储在内存中。
$skip
跳过进入stage的指定数量的文档,并将其余文档传递到管道中的下一个阶段
此操作将跳过管道传递给它的前5个文档。 $skip对沿着管道传递的文档的内容没有影响。
db.books.aggregate([ { $skip : 5 } ]); $sort
将所有输入文档进行排序,然后按照排序将其返回至管道。
语法:
{ $sort: { <field1>: <sort order>, <field2>: <sort order> ... } } $sort 接受指定要作为排序依据的字段以及相应排序顺序的文档。
- field表示要排序依据的字段
- sort order,如果为1表示升序排序,-1表示降序排序
如果对多个字段进行排序,则按从左到右的顺序进行排序。
db.books.aggregate([ {$sort: {favCount: 1,"author.age": -1}} ]) $lookup
5.1 版本中进行了更改。可以将 $lookup 与分片集合一起使用。
对同一 数据库中的一个集合执行左外连接,以过滤“已连接”集合中的文档以便进行处理。
$lookup 阶段向每个输入文档添加一个新的数组字段,(可根据需要命名新key )。数组列存放的数据是来自被Join集合的适配文档,如果没有,集合为空(即 为[ ])
db.collection.aggregate([{ $lookup: { from: "<collection to join>", localField: "<field from the input documents>", foreignField: "<field from the documents of the from collection>", as: "<output array field>" } }) | 关键字 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| from | 同一个数据库下等待被Join的集合。 |
| localField | 源集合中的match值,如果输入的集合中,某文档没有 localField这个Key(Field),在处理的过程中,会默认为此文档含有 localField:null的键值对。 |
| foreignField | 待Join的集合的match值,如果待Join的集合中,文档没有foreignField值,在处理的过程中,会默认为此文档含有 foreignField:null的键值对。 |
| as | 为输出文档的新增值命名。如果输入的集合中已存在该值,则会覆盖掉 |
注意:null = null 此为真
案例:
数据准备
db.orders.insertMany( [ { "_id" : 1, "item" : "almonds", "price" : 12, "quantity" : 2 }, { "_id" : 2, "item" : "pecans", "price" : 20, "quantity" : 1 }, { "_id" : 3 } ] ) db.inventory.insertMany( [ { "_id" : 1, "sku" : "almonds", "description": "product 1", "instock" : 120 }, { "_id" : 2, "sku" : "bread", "description": "product 2", "instock" : 80 }, { "_id" : 3, "sku" : "cashews", "description": "product 3", "instock" : 60 }, { "_id" : 4, "sku" : "pecans", "description": "product 4", "instock" : 70 }, { "_id" : 5, "sku": null, "description": "Incomplete" }, { "_id" : 6 } ] ) orders 集合的字段 item 和来自 inventory 集合的 sku 字段,将来自 orders 的文档与来自 inventory 集合的文档联接在一起:
# orders集合的item字段 inventory集合的sku字段 db.orders.aggregate( [ { $lookup: { from: "inventory", localField: "item", foreignField: "sku", as: "inventory_docs" } } ] ) # 该操作对应于如下伪 SQL 语句: SELECT *, inventory_docs FROM orders WHERE inventory_docs IN ( SELECT * FROM inventory WHERE sku = orders.item ) # 输出结果为下面三行,注意最后一行,null == null 条件成立的结果 [ { _id: 1, item: 'almonds', price: 12, quantity: 2, inventory_docs: [ { _id: 1, sku: 'almonds', description: 'product 1', instock: 120 } ] }, { _id: 2, item: 'pecans', price: 20, quantity: 1, inventory_docs: [ { _id: 4, sku: 'pecans', description: 'product 4', instock: 70 } ] }, { _id: 3, inventory_docs: [ { _id: 5, sku: null, description: 'Incomplete' }, { _id: 6 } ] } ] 聚合操作案例1
原始数据
test> db.books.find() [ { _id: ObjectId("66a5b0106ae7536b7b29723e"), title: 'book-0', type: 'literature', tag: [ 'nosql', 'popular' ], favCount: 63, author: { name: 'xx001', age: 26 } }, { _id: ObjectId("66a5b0106ae7536b7b29723f"), title: 'book-1', type: 'novel', tag: [ 'popular', 'popular' ], favCount: 54, author: { name: 'xx005', age: 22 } }, { _id: ObjectId("66a5b0106ae7536b7b297240"), title: 'book-2', type: 'technology', tag: [ 'popular', 'popular' ], favCount: 24, author: { name: 'xx005', age: 23 } }, ...... ] # 统计每个分类的book文档数量 db.books.aggregate([ {$group:{ _id: "$type", bookcount: {$count: {}} }}, {$sort:{bookcount: -1}} ]) # 输出结果 [ { _id: 'technology', bookcount: 15 }, { _id: 'sociality', bookcount: 11 }, { _id: 'literature', bookcount: 11 }, { _id: 'novel', bookcount: 9 }, { _id: 'travel', bookcount: 7 } ] # 标签的热度排行,标签的热度则按其关联book文档的收藏数(favCount)来计算 db.books.aggregate([ {$match:{favCount: {$gt: 0}}}, {$unwind:{ path: "$tag", includeArrayIndex: "arrayIndex", preserveNullAndEmptyArrays: true }}, {$group:{ _id: "$tag", countSum: {$sum: "$favCount"} }}, {$sort:{countSum: -1}} ] - 过滤掉favCount=0的文档
- 将tag标签中的数组拆分为一个个的文档,这样一个包含3个标签的文档会被拆解为3个条目。
- 再按照tag分组,并求出各个标签订阅的总数
- 对总数排序
# 执行结果 [ { _id: 'popular', total: 1159 }, { _id: 'nosql', total: 1095 }, { _id: 'developer', total: 1014 }, { _id: 'mongodb', total: 872 }, { _id: 'document', total: 598 } ] 聚合操作案例2
导入邮政编码数据集:https://media.mongodb.org/zips.json
使用mongoimport工具导入数据
mongoimport -h 192.168.75.100 -d test -u hushang -p 123456 --authenticationDatabase=admin -c zips --file D:\downfile\goodle下载\zips.json h,–host :代表远程连接的数据库地址,默认连接本地Mongo数据库;
–port:代表远程连接的数据库的端口,默认连接的远程端口27017;
-u,–username:代表连接远程数据库的账号,如果设置数据库的认证,需要指定用户账号;
-p,–password:代表连接数据库的账号对应的密码;
-d,–db:代表连接的数据库;
-c,–collection:代表连接数据库中的集合;
-f, --fields:代表导入集合中的字段;
–type:代表导入的文件类型,包括csv和json,tsv文件,默认json格式;
–file:导入的文件名称
–headerline:导入csv文件时,指明第一行是列名,不需要导入;
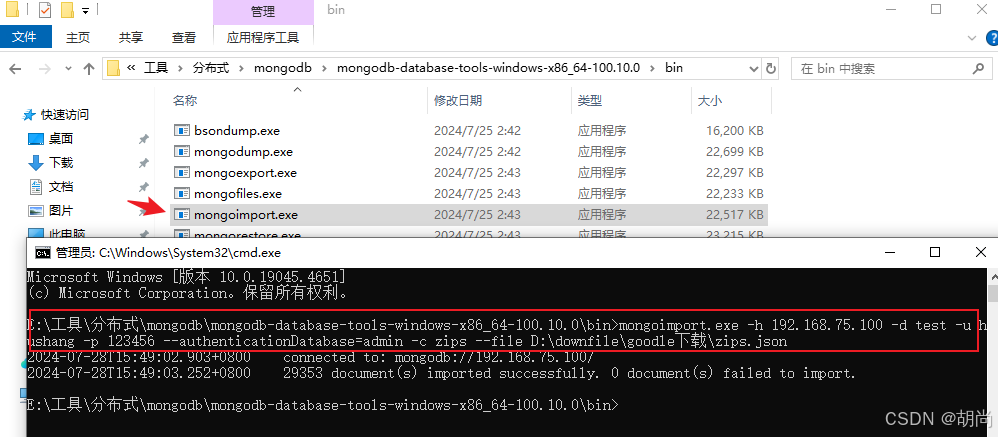
test> show collections books emp zips test> db.zips.countDocuments() 29353 # 原始数据 test> db.zips.find() [ { _id: '01035', city: 'HADLEY', loc: [ -72.571499, 42.36062 ], pop: 4231, state: 'MA' }, { _id: '01030', city: 'FEEDING HILLS', loc: [ -72.675077, 42.07182 ], pop: 11985, state: 'MA' }, { _id: '01026', city: 'CUMMINGTON', loc: [ -72.905767, 42.435296 ], pop: 1484, state: 'MA' }, ...... ] # 返回人口超过1000万的州 db.zips.aggregate([ { $group: { _id: "$state", popSum: { $sum: "$pop" } } }, { $match: { popSum: { $gte: 1000000 } } } ]) # 返回各州中各个城市平均人口 db.zips.aggregate([ { $group: { _id: { state: "$state", city: "$city" }, cityPop: { $sum: "$pop" } } }, { $group: { _id: "$_id.state", avgCityPop: { $avg: "$cityPop" } } } ]) # 按州返回人口最大和最小的城市 db.zips.aggregate( [ # 计算出各个州下 各个城市的人数 { $group: { _id: { state: "$state", city: "$city" }, pop: { $sum: "$pop" } } }, # 对人数进行排序 { $sort: { pop: 1 } }, # 取排序后的第一个数据和最后一个数据 { $group: { _id : "$_id.state", biggestCity: { $last: "$_id.city" }, biggestPop: { $last: "$pop" }, smallestCity: { $first: "$_id.city" }, smallestPop: { $first: "$pop" } } }, # 对输出的内容包装一下 { $project: { _id: 0, state: "$_id", biggestCity: { name: "$biggestCity", pop: "$biggestPop" }, smallestCity: { name: "$smallestCity", pop: "$smallestPop" } } } ] ) 聚合优化
https://www.mongodb.com/docs/manual/core/aggregation-pipeline-optimization/
聚合优化的三大目标:
- 尽可能利用索引完成搜索和排序
- 尽早尽多减少数据量,比如使用$match
- 尽可能减少执行步骤
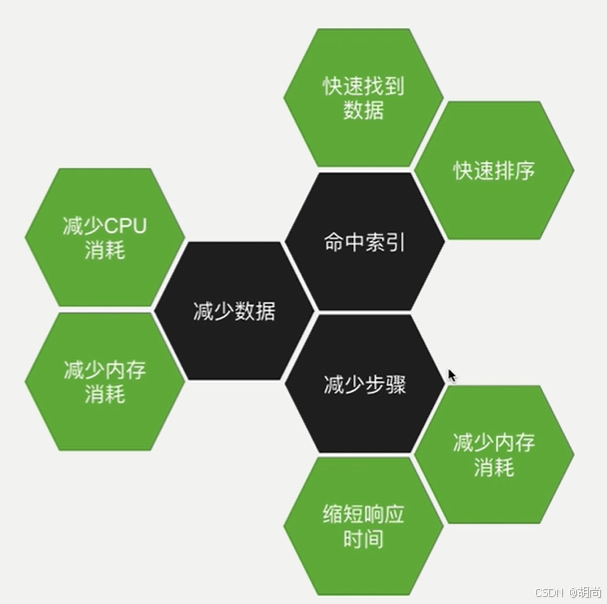
执行顺序
$match/$sort vs $project/$addFields
为了使查询能够命中索引,$match/$sort步骤需要在最前面,该原则适用于MongoDB <=3.4版本。MongoDB 3.6开始具备一定的自动优化能力。
$project + $skip/$limit
$skip/$limit应该尽可能放在$project之前,减少$project投影的工作量 。3.6开始自动完成这个优化。
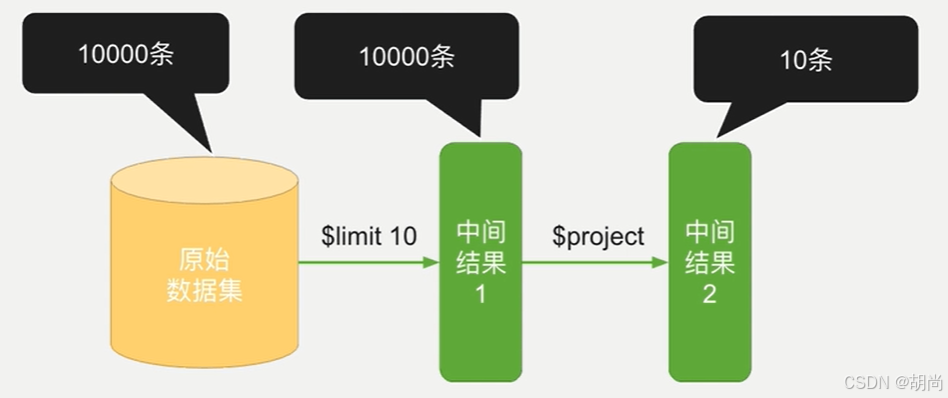
内存排序
在没有索引支持的情况下,MongoDB最多只支持使用100MB内存进行排序。
假设总共可用内存为16GB,一个请求最多可以使用100MB内存排序,总共可以有16000/ 100= 160个请求同时执行。
内存排序消耗的不仅是内存,还有大量CPU
方案一: $sort + $limit
只排Top N ,只要N条记录总和不超过100MB即可
方案二: {allowDiskUse: true}
使用磁盘作为交换空间完成全量,超出100MB部分与磁盘交换排序
方案三: 索引排序
使用索引完成排序,没有内存限制
整合Springboot进行聚合操作
SpringBoot整合MongoDB的详细流程请参考上文《SpringBoot整合MongoDB》
MongoTemplate提供了aggregate方法来实现对数据的聚合操作。
基于聚合管道mongodb提供的可操作的内容:
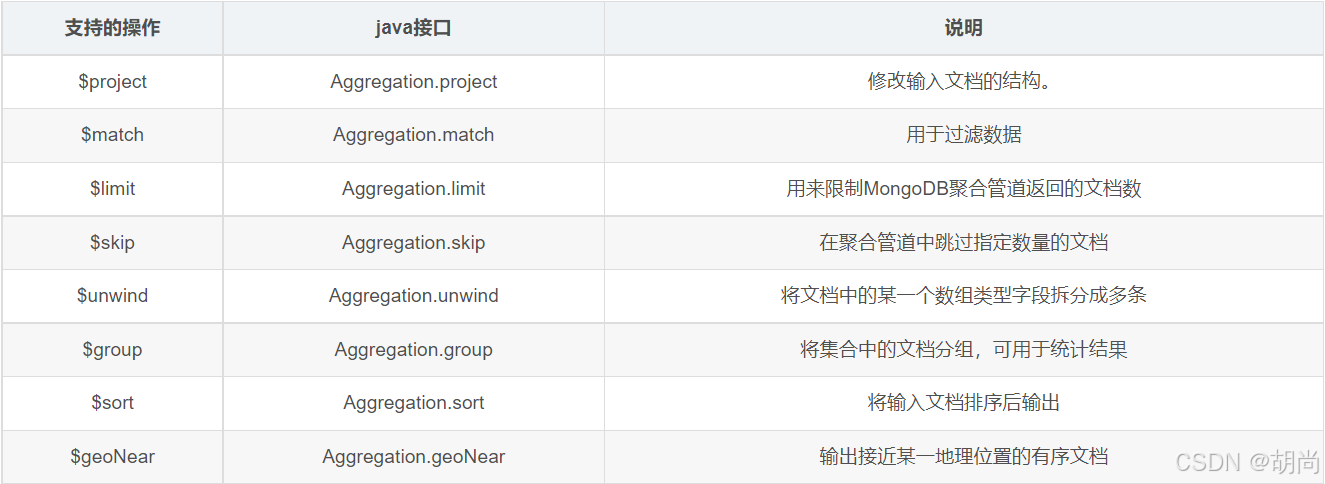
基于聚合操作Aggregation.group,mongodb提供可选的表达式
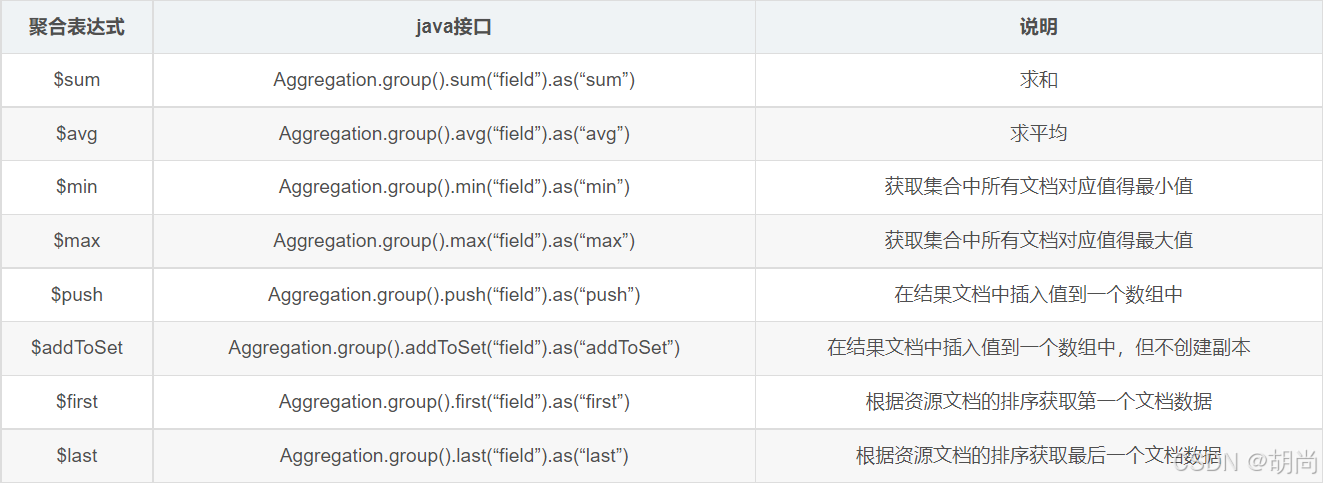
案例一
返回人口超过1000万的州
db.zips.aggregate([ { $group: { _id: "$state", popSum: { $sum: "$pop" } } }, { $match: { popSum: { $gte: 1000000 } } } ]) import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.aggregation.*; import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.query.Criteria; /** * 返回人口超过1000万的州 * 先对州进行分组 * 求和,州的总人数 * 筛选、匹配、过滤 */ @Test public void testGtPop() { //$group GroupOperation groupOperation = Aggregation.group("state") .sum("pop") .as("popSum"); //$match Criteria criteria = Criteria.where("popSum").gte(1000000); MatchOperation matchOperation = Aggregation.match(criteria); // 按顺序组合每一个聚合步骤 TypedAggregation<Zips> zipsTypedAggregation = Aggregation.newAggregation(Zips.class, groupOperation, matchOperation); // 执行聚合操作,如果不使用 Map,也可以使用自定义的实体类来接收数据 AggregationResults<Map> aggregationResults = mongoTemplate.aggregate(zipsTypedAggregation, Map.class); // 取出最终结果 List<Map> mappedResults = aggregationResults.getMappedResults(); mappedResults.forEach(System.out::println); } 案例二
返回各州中各个城市平均人口
db.zips.aggregate([ { $group: { _id: { state: "$state", city: "$city" }, cityPop: { $sum: "$pop" } } }, { $group: { _id: "$_id.state", avgCityPop: { $avg: "$cityPop" } } }, {$sort: {avgCityPop: -1}} ]) /** * 返回各州中各个城市平均人口 * 先安装州、城市进行分组 * 得到哥走中各个城市的人口 * 再求平均值 */ @Test public void testPopAvg(){ //$group GroupOperation cityGroup = Aggregation.group("state", "city").sum("pop").as("cityPop"); GroupOperation avgCityGroup = Aggregation.group("_id.state").avg("cityPop").as("avgCityPop"); // $sort SortOperation sortOperation = Aggregation.sort(Sort.Direction.DESC, "avgCityPop"); // 按顺序组合每一个聚合步骤 TypedAggregation<Zips> zipsTypedAggregation = Aggregation.newAggregation(Zips.class, cityGroup, avgCityGroup, sortOperation); // 执行聚合操作,如果不使用 Map,也可以使用自定义的实体类来接收数据 AggregationResults<Map> aggregationResults = mongoTemplate.aggregate(zipsTypedAggregation, Map.class); // 取出最终结果 List<Map> mappedResults = aggregationResults.getMappedResults(); mappedResults.forEach(System.out::println); } 案例三
按州返回人口最大和最小的城市
# 按州返回人口最大和最小的城市 db.zips.aggregate( [ { $group: { _id: { state: "$state", city: "$city" }, pop: { $sum: "$pop" } } }, { $sort: { pop: 1 } }, { $group: { _id : "$_id.state", biggestCity: { $last: "$_id.city" }, biggestPop: { $last: "$pop" }, smallestCity: { $first: "$_id.city" }, smallestPop: { $first: "$pop" } } }, { $project: { _id: 0, state: "$_id", biggestCity: { name: "$biggestCity", pop: "$biggestPop" }, smallestCity: { name: "$smallestCity", pop: "$smallestPop" } } }, { $sort: { state: 1 } } ] ) @Test public void testMinMaxPop(){ // $group GroupOperation cityPopGroup = Aggregation.group("state", "city").sum("pop").as("pop"); // $sort SortOperation popSort = Aggregation.sort(Sort.Direction.ASC, "pop"); // $group GroupOperation lastFirstGroup = Aggregation.group("_id.state") .last("_id.city").as("biggestCity") .last("pop").as("biggestPop") .first("_id.city").as("smallestCity") .first("pop").as("smallestPop"); // $project ProjectionOperation projectionOperation = Aggregation.project("state", "biggestCity", "smallestCity") .and("_id").as("state") .andExpression("{ name: \"$biggestCity\", pop: \"$biggestPop\" }") .as("biggestCity") .andExpression("{ name: \"$smallestCity\", pop: \"$smallestPop\" }") .as("smallestCity"); // $sort SortOperation stateSort = Aggregation.sort(Sort.Direction.ASC, "state"); // 按顺序组合每一个聚合步骤 TypedAggregation<Zips> zipsTypedAggregation = Aggregation.newAggregation(Zips.class, cityPopGroup, popSort, lastFirstGroup, projectionOperation, stateSort); // 执行聚合操作,如果不使用 Map,也可以使用自定义的实体类来接收数据 AggregationResults<Map> aggregationResults = mongoTemplate.aggregate(zipsTypedAggregation, Map.class); // 取出最终结果 List<Map> mappedResults = aggregationResults.getMappedResults(); mappedResults.forEach(System.out::println); } 