阅读量:0
队列基本概念
首先我们要了解什么是队列,队列里面包含什么。
队列是线性表的一种是一种先进先出(First In Fi Out)的数据结构。在需要排队的场景下有很强的应用性。有数组队列也有链式队列,数组实现的队列时间复杂度太大,一般链式队列应用更为广泛。
队列里面包括队头和队尾。出队列只能在队头出(头删),入队列只能在队尾入(尾插)。
本篇要实现是单向,不带哨兵位,不循环的用链表实现的队列(此种队列应用较为广泛)
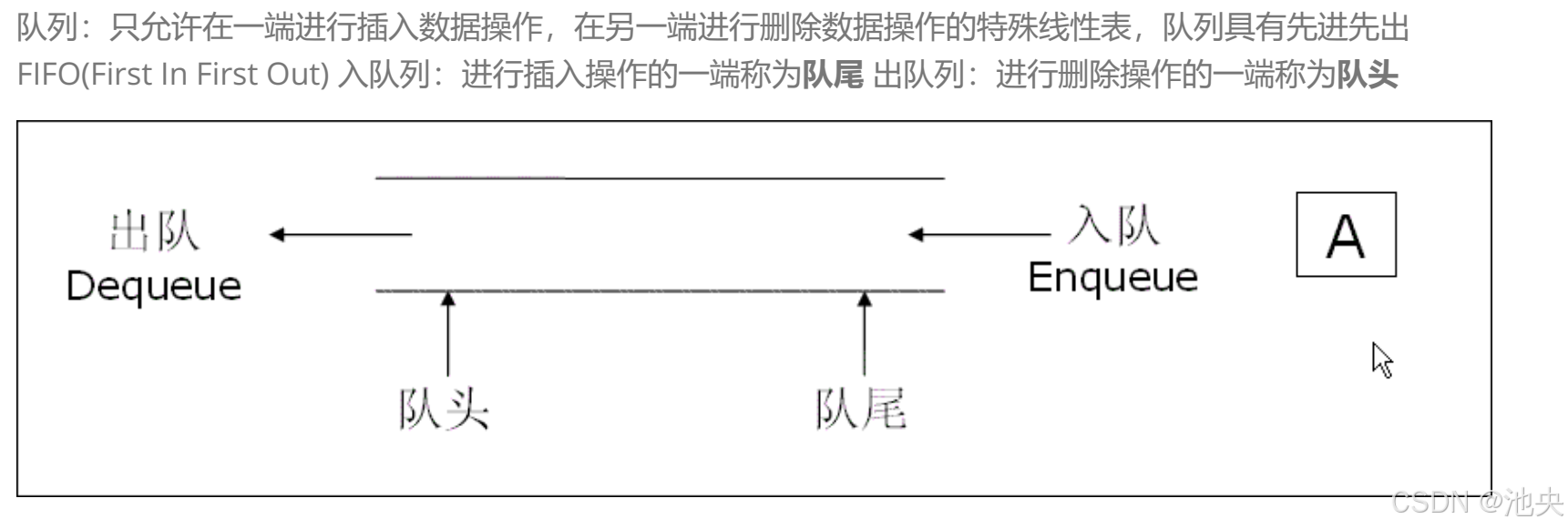
队列的定义
包括一个数据和指向下一个节点的指针
typedef int QDataType; typedef struct QueueNode { QDataType val; struct QueueNode* next; }QNode;对队列的操作
入队列与出队列
如果只有头指针那我们还是需要遍历队列才能找到队列的队尾进行入队列,而且还需要传二级指针。但是如果还有尾指针那就不需要遍历找尾,效率更高,多个指针用结构体封装,只传一级指针即可
当然在执行出入队列前我们应该先把队列初始化,但是由于说清楚为什么不用二级指针和应该有头尾指针,初始化放在后面了。

typedef struct Queue { QNode* phead; QNode* ptail; int size; }Queue;考虑到需要计算队列长度,所以在Queue结构中还加了size成员。
具体实现如下
入队列
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x) { assert(pq); //在队尾入,尾插 //创建新节点 QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode)); if (newnode == NULL) { perror("malloc fail"); return; } newnode->val = x; newnode->next = NULL; //空链表 if (QueueEmpty(pq)) { pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode; } else { pq->ptail->next = newnode; pq->ptail = newnode; } pq->size++; }此处要考虑队列为空和队列不为空两种情况,队列为空则新插入的节点即为队列的队头和队尾;
队列不为空,则队尾的next指针指向新节点,新节点成为新的队尾。
判空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); return pq->size == 0; }出队列
void QueuePop(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); //零个节点 assert(pq->phead); //一个节点 if (pq->phead->next == NULL) { free(pq->phead); pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL; } else { QNode* next = pq->phead->next; free(pq->phead); pq->phead = next; } pq->size--; }出队列要保证队头不能为空,所以要加assert(pq->phead)语句来暴力检查,队列中如果只有一个节点那么释放掉头队头节点后,把队头和队尾都置为空即可;若有多个节点,先要把队头指向的下一个节点存起来,以防释放掉队头后找不到他的下一个节点,然后让原本队头的下一个节点成为新的队头。
初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL; pq->size = 0; }取队头数据
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); assert(pq->phead); return pq->phead->val; }取队尾数据
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); assert(pq->ptail); return pq->ptail->val; }队列长度
size_t QueueLength(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); return pq->size; }销毁
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); QNode* cur = pq->phead; while (cur) { QNode* next = cur->next; free(cur); cur = next; } pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL; pq->size = 0; }完整总代码
头文件
#pragma once #include<stdio.h> #include<assert.h> #include<stdbool.h> #include<stdlib.h> typedef int QDataType; typedef struct QueueNode { QDataType val; struct QueueNode* next; }QNode; typedef struct Queue { QNode* phead; QNode* ptail; int size; }Queue; //初始化 void QueueInit(Queue* pq); //销毁 void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq); //判空 bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq); //入队列 void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x); //出队列 void QueuePop(Queue* pq); //取队头 QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq); //取队尾 QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq); //队列长度 size_t QueueLength(Queue* pq);函数定义
#include"Queue.h" //初始化 void QueueInit(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL; pq->size = 0; } //销毁 void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); QNode* cur = pq->phead; while (cur) { QNode* next = cur->next; free(cur); cur = next; } pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL; pq->size = 0; } //入队列 void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x) { assert(pq); //在队尾入,尾插 //创建新节点 QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode)); if (newnode == NULL) { perror("malloc fail"); return; } newnode->val = x; newnode->next = NULL; //空链表 if (QueueEmpty(pq)) { pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode; } else { pq->ptail->next = newnode; pq->ptail = newnode; } pq->size++; } //出队列 void QueuePop(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); //零个节点 assert(pq->phead); //一个节点 if (pq->phead->next == NULL) { free(pq->phead); pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL; } else { QNode* next = pq->phead->next; free(pq->phead); pq->phead = next; } pq->size--; } //判空 bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); return pq->size == 0; } //取队头 QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); assert(pq->phead); return pq->phead->val; } //取队尾 QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); assert(pq->ptail); return pq->ptail->val; } //队列长度 size_t QueueLength(Queue* pq) { assert(pq); return pq->size; } 测试
#include"Queue.h" void test() { Queue pq; QueueInit(&pq); QueuePush(&pq, 1); QueuePush(&pq, 2); QueuePush(&pq, 3); QueuePush(&pq, 4); while (!QueueEmpty(&pq)) { printf("%d ", QueueFront(&pq)); QueuePop(&pq); } QueueDestroy(&pq); } int main() { test(); return 0; }欢迎各位大佬一起学习交流~
有不当之处欢迎指正~
