一、所用工具
1、芯片:STM32F407ZGT6
2、CubeMX
3、KEIL5
4、OpenMV
5、舵机
二、实现功能
利用由两个自由舵机组装而成的二维云台来控制OpenMV的位置,以实现追踪指定阈值色块的效果。
三、CubeMX配置
3.1 初始化配置
3.2 定时器配置(PWM波输出)
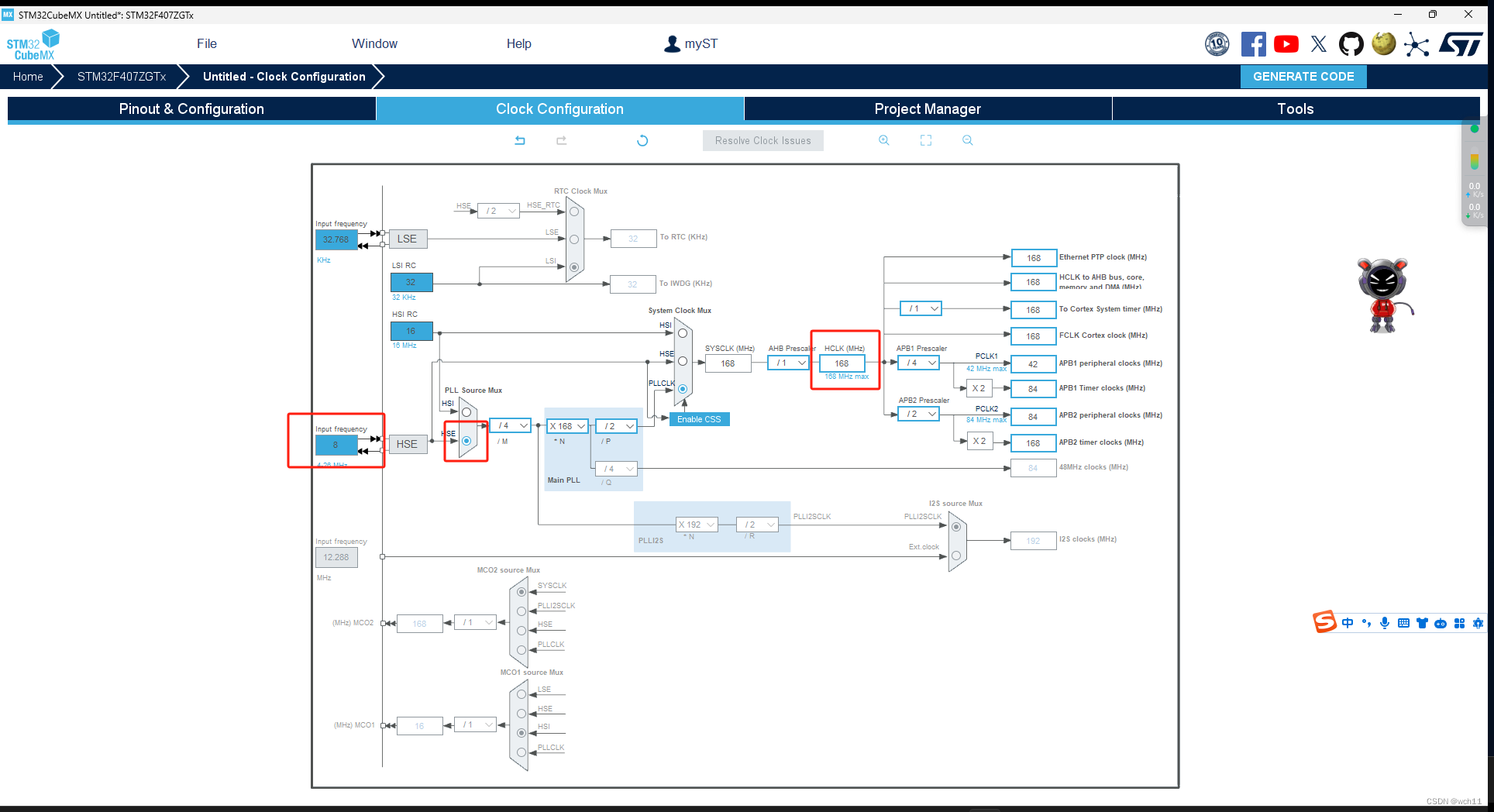
这里我使用TIM3的通道1和TIM4的通道1分别实现对两个舵机的控制,由于我购买的舵机所需要的频率为50Hz(如下图)所以下面的PWM频率均是按照50Hz配置的。

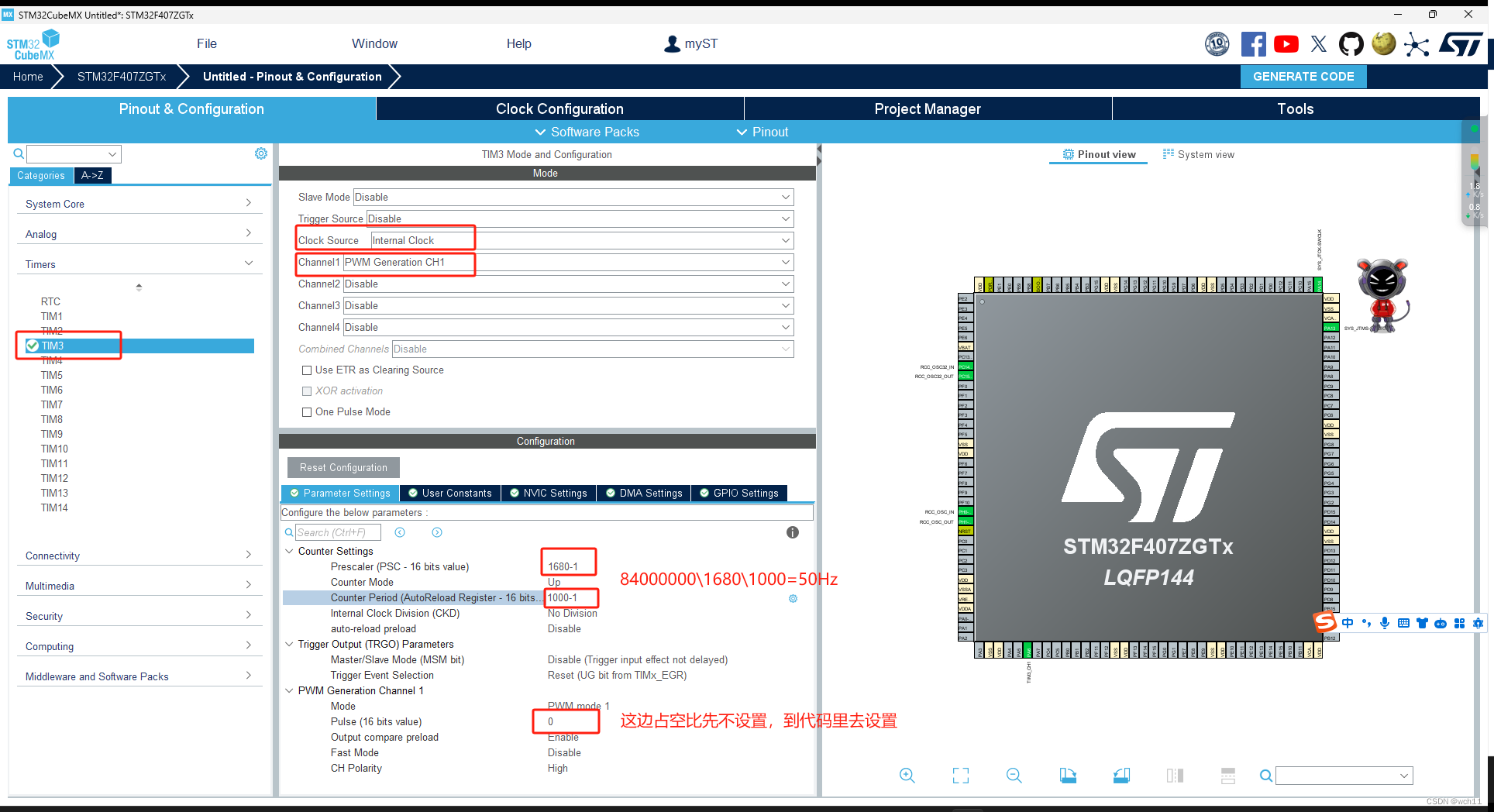
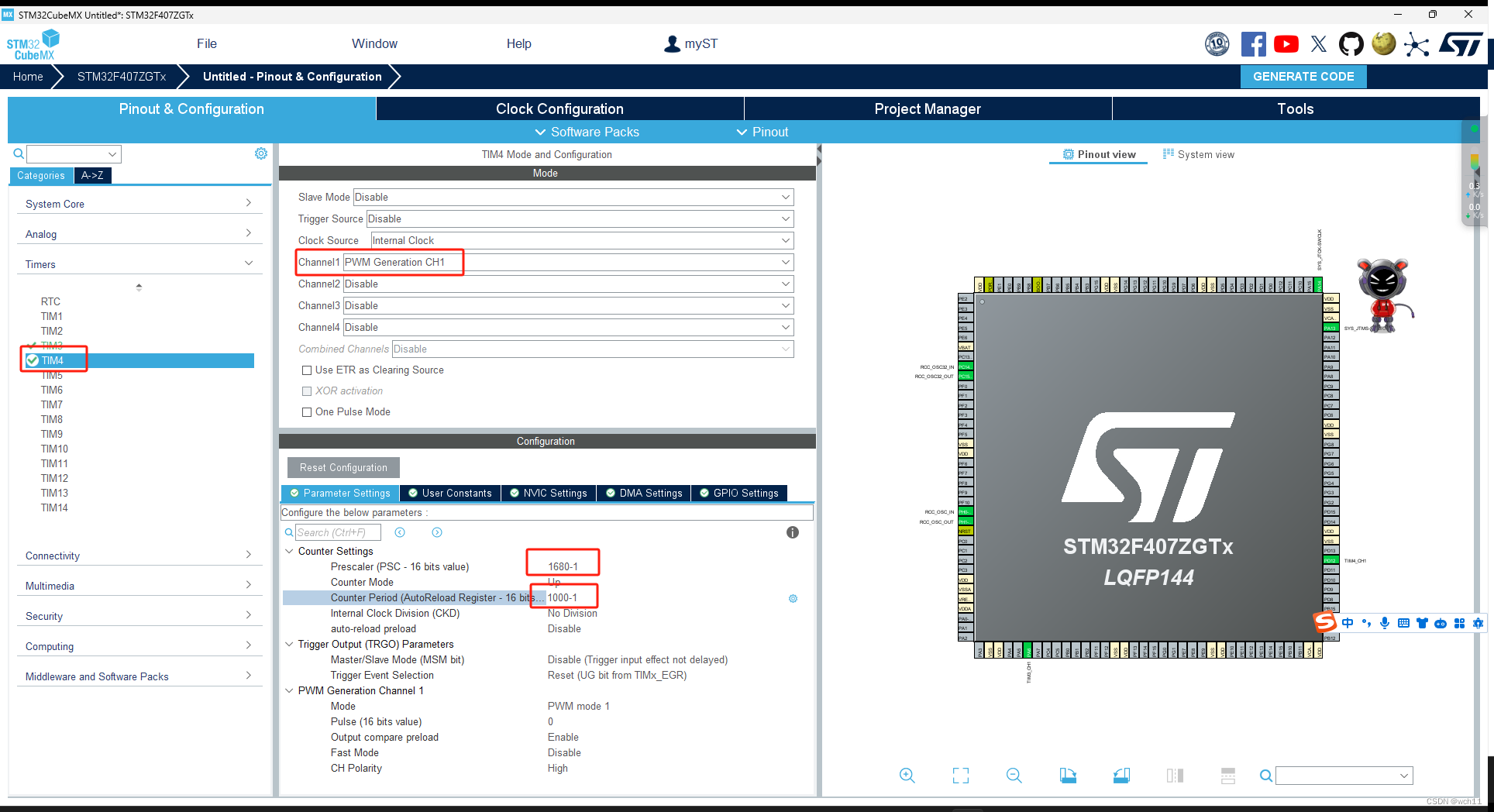
TIM4的配置同理。
3.3 串口通信配置(与OpenMV和电脑通信)
为了方便后续的调试,所以建议同时开启与OpenMV和电脑的通信,即打开两个串口。USART1是用来和电脑通信的,USART2是用来与OpenMV通信的。
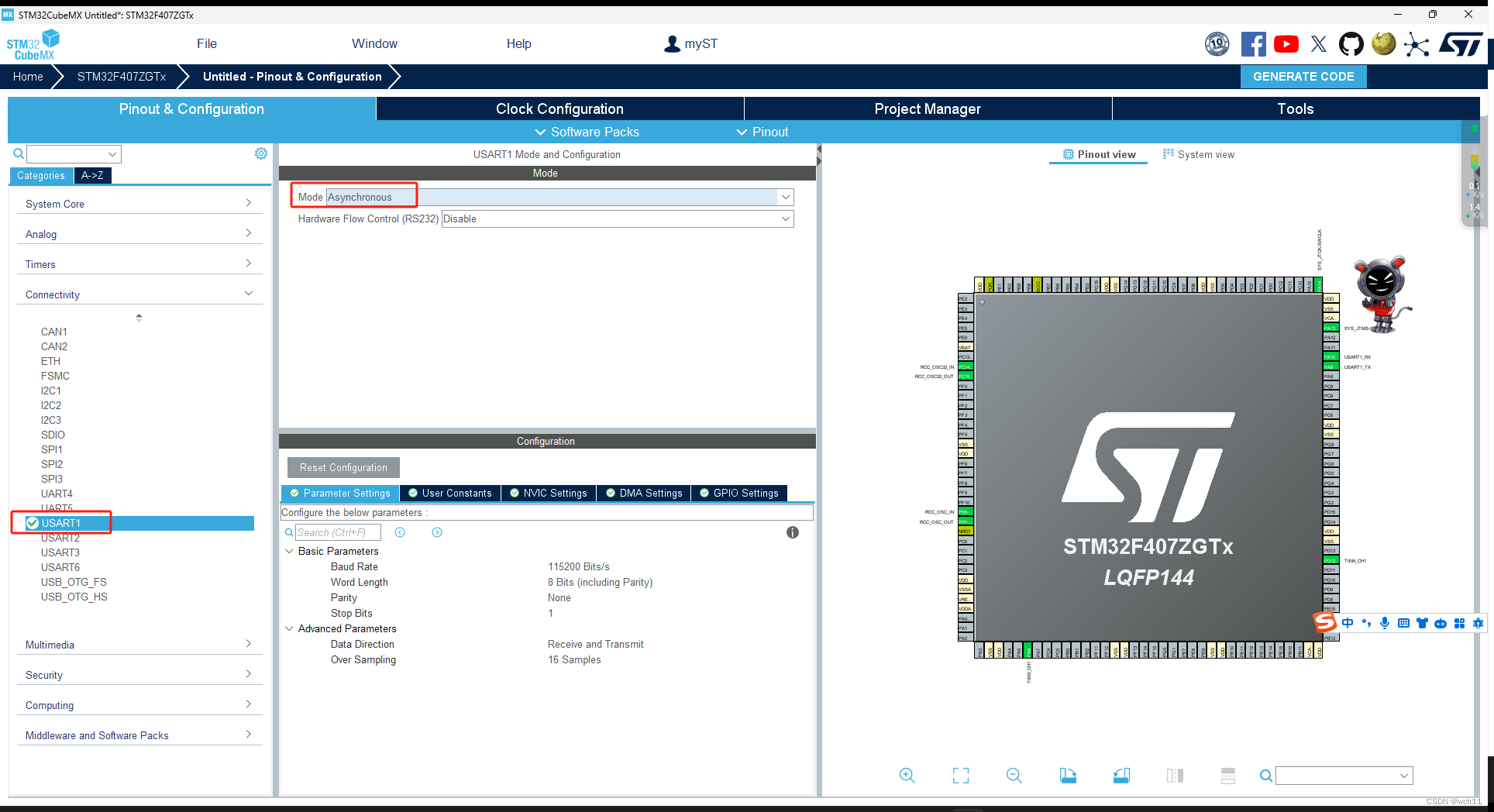
USART2的配置同理。
四、OpenMV配置
这是OpenMV中寻找色块,并通过串口PA4,PA5发送中心点位置以及长度和宽度的代码,可以直接复制到OpenMV IDE中。需要注意的是,在OpenMV中UART_RX—P5 ------ UART_TX—P4。
import time import sensor import math import image import ustruct from pyb import UART uart = UART(3, 115200, timeout_char=200) uart.init(115200, bits=8, parity=None, stop=1) # init with given parameters threshold_index = 0 # 0 for red, 1 for green, 2 for blue thresholds = [ (30, 100, 15, 127, 15, 127), # generic_red_thresholds (30, 100, -64, -8, -32, 32), # generic_green_thresholds (0, 30, 0, 64, -128, 0), # generic_blue_thresholds (82, 100, 75, -49, -22, 31), # generic_white_thresholds (21, 83, 32, 65, 31, 63), ] sensor.reset() sensor.set_pixformat(sensor.RGB565) sensor.set_framesize(sensor.QVGA)# QVGA的中心坐标:160,120 sensor.skip_frames(time=2000) # 跳过2000毫秒的帧让相机图像在改变相机设置后稳定下来 sensor.set_auto_gain(False) # 必须关闭才能进行颜色跟踪 sensor.set_auto_whitebal(False) # 必须关闭才能进行颜色跟踪 clock = time.clock() def find_max(blobs): max_size=0 for blob in blobs: if blob.pixels() > max_size: max_blob = blob max_size = blob.pixels() return max_blob def send_data(x,y,w,h): global uart; FH = bytearray([0xb3,0xb3]) # 帧头 uart.write(FH) # 写到串口 uart.write(str(x)) uart.write(bytearray([0x20])) # 发送空格 uart.write(str(y)) uart.write(bytearray([0x20])) uart.write(str(w)) uart.write(bytearray([0x20])) uart.write(str(h)) uart.write(bytearray([0x20])) FH = bytearray([0x0d,0x0a]) # 帧尾,换行和回车的ascll uart.write(FH) while True: clock.tick() img = sensor.snapshot() blobs = img.find_blobs([thresholds[threshold_index]]) #如果找到了目标颜色 if blobs: max_blob = find_max(blobs) cx=max_blob[5] cy=max_blob[6] cw=max_blob[2] ch=max_blob[3] # 这些值取决于max_blob不是圆形的,否则它们将不稳定. # 检查max_blob是否显著偏离圆形 if max_blob.elongation() > 0.5: img.draw_edges(max_blob.min_corners(), color=(255, 0, 0)) img.draw_line(max_blob.major_axis_line(), color=(0, 255, 0)) img.draw_line(max_blob.minor_axis_line(), color=(0, 0, 255)) # 这些值始终是稳定的。 # img.draw_rectangle(max_blob.rect()) img.draw_rectangle(160,120,35,35) img.draw_cross(cx, cy) # 注意-max_blob旋转仅限于0-180。 img.draw_keypoints( [(cx, cy, int(math.degrees(max_blob.rotation())))], size=20 ) send_data(cx,cy,cw,ch) # 发送数据 print(cx,cy,cw,ch) print(clock.fps()) 五、KEIL代码修改
5.1 串口重定义
在usart.c的最后加入重定义代码。
/* USER CODE BEGIN 1 */ int fputc(int ch, FILE *f) { HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart1, (uint8_t *)&ch, 1, 0xffff); return ch; } int fgetc(FILE *f) { uint8_t ch = 0; HAL_UART_Receive(&huart1, &ch, 1, 0xffff); return ch; } /* USER CODE END 1 */在usart.h的开头加入include。
/* USER CODE BEGIN Includes */ #include <stdio.h> /* USER CODE END Includes */5.2 串口回调函数
用到的变量初始化,大家自行放到main.c中的相应位置。
#include "string.h" #include "stdio.h" #include "stdlib.h" #define RXBUFFERSIZE 256 char RxBuffer[RXBUFFERSIZE],rx_buf[RXBUFFERSIZE]; uint8_t aRxBuffer; uint8_t Uart1_Rx_Cnt = 0; int flag=0; printf("Hello World!\r\n"); HAL_Delay(200); HAL_UART_Receive_IT(&huart2, (uint8_t *)&aRxBuffer, 1); 这段代码放在main.c中,这里为了方便确定OpenMV与STM32之间有数据传输,加入了翻转LED灯,大家可以有需要可以自己再配置一下LED,不用的话可自行删除。
/* USER CODE BEGIN 4 */ void HAL_UART_RxCpltCallback(UART_HandleTypeDef *huart) { UNUSED(huart); if(huart==&huart2){ HAL_GPIO_TogglePin(GPIOF,LED_Pin); //有数据则翻转LED灯 RxBuffer[Uart1_Rx_Cnt] = aRxBuffer; Uart1_Rx_Cnt++; if((RxBuffer[Uart1_Rx_Cnt-1] == 0xb3)&&(RxBuffer[Uart1_Rx_Cnt-2] == 0xb3)) flag=1; //帧头判定 else if((RxBuffer[Uart1_Rx_Cnt-2] == 0x0d)&&(RxBuffer[Uart1_Rx_Cnt-1] == 0x0a)) flag=2; //帧尾判定 else flag=0; switch (flag) { case 1: Uart1_Rx_Cnt = 0; memset(RxBuffer,0x00,sizeof(RxBuffer)); break; case 2: RxBuffer[Uart1_Rx_Cnt-1] = '\0'; RxBuffer[Uart1_Rx_Cnt-2] = '\0'; strcpy(rx_buf,RxBuffer); printf("%s\r\n",rx_buf); while(HAL_UART_GetState(&huart2) == HAL_UART_STATE_BUSY_TX); Uart1_Rx_Cnt = 0; memset(RxBuffer,0x00,sizeof(RxBuffer)); break; default:break; } HAL_UART_Receive_IT(&huart2, (uint8_t *)&aRxBuffer, 1); } } /* USER CODE END 4 */5.3 加入pid控制文件
5.3.1 pid.c
由于两个舵机分别控制横向和纵向的移动,所以此处定义了两个句柄和两个pid函数,分别对应两个舵机,大家可以自行调试其中Kp,Ki,Kd的值。
#include "pid.h" pid_typedef pid1; pid_typedef pid2; void PID_init(void) { pid1.SetPosition=0; pid1.ActualPosition=0.0; pid1.err=0.0; pid1.err_last=0.0; pid1.out=0.0; pid1.integral=0.0; pid1.Kp=0.025; pid1.Ki=0; pid1.Kd=0.017; pid2.SetPosition=0; pid2.ActualPosition=0.0; pid2.err=0.0; pid2.err_last=0.0; pid2.out=0.0; pid2.integral=0.0; pid2.Kp=0.025; pid2.Ki=0; pid2.Kd=0.017; } float PIDx_realize(float ActualPosition,float SetPosition) { pid1.ActualPosition=ActualPosition; pid1.SetPosition=SetPosition; pid1.err=pid1.SetPosition-pid1.ActualPosition; pid1.integral+=pid1.err; pid1.out=pid1.Kp*pid1.err+pid1.Ki*pid1.integral+pid1.Kd*(pid1.err-pid1.err_last); pid1.err_last=pid1.err; return pid1.out; } float PIDy_realize(float ActualPosition,float SetPosition) { pid2.ActualPosition=ActualPosition; pid2.SetPosition=SetPosition; pid2.err=pid2.ActualPosition-pid2.SetPosition; pid2.integral+=pid2.err; pid2.out=pid2.Kp*pid2.err+pid2.Ki*pid2.integral+pid2.Kd*(pid2.err-pid2.err_last); pid2.err_last=pid2.err; return pid2.out; } 5.3.2 pid.h
#ifndef __PID_H #define __PID_H #include "stm32f4xx.h" typedef struct { float SetPosition;//设定值 float ActualPosition;//实际值 float err; float err_last; float Kp; float Ki; float Kd; float out;//执行器的变量 float integral;//积分值 }pid_typedef; void PID_init(void); float PIDx_realize(float ActualPosition,float SetPosition); float PIDy_realize(float ActualPosition,float SetPosition); #endif 添加好文件之后不要忘记添加pid.h的目录 。
5.4 实现对PWM波占空比的控制
放置在前面的初始化代码。
#include "pid.h" double motor1=25; double motor2=35; int cx,cy; PID_init(); HAL_Delay(100) ; HAL_TIM_PWM_Start(&htim3, TIM_CHANNEL_1);//开启PWM波 HAL_TIM_PWM_Start(&htim4, TIM_CHANNEL_1); __HAL_TIM_SET_COMPARE(&htim3, TIM_CHANNEL_1, motor1);//占空比初始化,为25\1000=2.5% __HAL_TIM_SET_COMPARE(&htim4, TIM_CHANNEL_1, motor2);放在中断回调函数中的代码,可以选择放在case2中的printf下面,因为在OpenMV中设定的QVGA的中心坐标为160,120,所以下列的设定横纵坐标分别为160和120。其中舵机2我设定的占空比在3.5%和6%之间是因为我的装置结构问题,如果上面的电机往下太多会导致数据线与底座接触,造成电机卡住,大家可以根据自己的装配情况自行更改占空比的上下范围。
sscanf(rx_buf, "%d %d", &cx, &cy);//提取rx_buf中的前两个数字,即为横纵坐标 //对下面对应横坐标的舵机进行控制 motor1=motor1+PIDx_realize(cx,160);//第一参数为实际坐标,第二个参数为设定坐标 if(motor1<25)motor1=25;//防止超过舵机的工作范围内的占空比 if(motor1>125)motor1=125; TIM3->CCR1=motor1; //对上面对应纵坐标的舵机进行控制 motor2=motor2+PIDy_realize(cy,120); if(motor2<35)motor2=35; if(motor2>60)motor2=60; TIM4->CCR1=motor2;六、成果展示
由于实验室器材有限,无奈拿了一个开学典礼的灯作为底座,所以在舵机运行起来时会不稳,建议大家把舵机固定在重一点且高一点的东西上,可以避免OpenMV的线被卡住。总体来说,摄像头的跟踪效果还是不错的。
色块跟踪
七、结语
大家如果想要购买我的同款舵机,可以私信我,但是这个舵机的装配比较麻烦,需要自己用工具把材料修剪到合适的大小。然后这是我写的第一份博客,内容可能有不足的地方,大家都可以指出,最后为大家分享几篇我在做的过程中参考的文章,其中第一篇来自我同实验室的同学。