run方法核心流程
我们在启动SpringBoot的时候调用的是SpringApplication类的静态run方法。其核心流程如下图所示: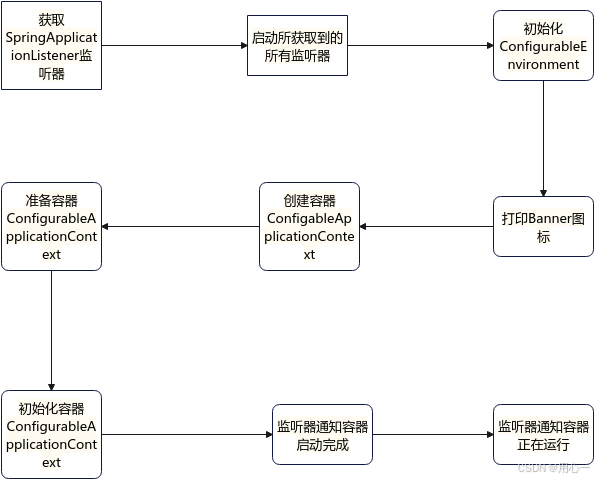
在run方法内完成了SpringApplication的声明周期。,这个过程涉及的几个核心类如下:
SpringApplicationRunListeners:这个接口会在run方法执行的过程中被调用,也就是可以看做SpringApplication的生命周期回调函数,比如ApplicationCntext创建好了可以调用contextPrepared方法,该方法传入的参数是ConfigurableApplicationContext,也就是spring的容器,如果我们有某些业务要在应用启动前进行处理都可以在这个接口的回调中实现。
较新版本的run方法源码如下:
/** * Run the Spring application, creating and refreshing a new * {@link ApplicationContext}. * @param args the application arguments (usually passed from a Java main method) * @return a running {@link ApplicationContext} */ public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) { Startup startup = Startup.create(); if (this.registerShutdownHook) { SpringApplication.shutdownHook.enableShutdownHookAddition(); } DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext(); ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null; configureHeadlessProperty(); //从META-INF/spring.factories配置文件中加载Listeners SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args); //启动listeners的starting回调方法 listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass); try { ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args); //创建环境变量管理类, ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments); //打印Springboot的启动画面 Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment); //创建spring容器 context = createApplicationContext(); context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup); //准备spring容器,也就是把环境啥的给spring容器,完成bean定义的加载等功能 prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner); //刷新spring容器,即开启bean的创建过程(主要是单例bean?) refreshContext(context); //这个函数目前实现为空,留作后面扩展 afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments); startup.started(); if (this.logStartupInfo) { new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), startup); } //调用listeners的started回调函数 listeners.started(context, startup.timeTakenToStarted()); //调用Runners的实现类,就是在springboot启动后可以实现一些业务处理,比如你的应用可能要升级,做一些升级操作都可以在Runners实现类中完成 callRunners(context, applicationArguments); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw handleRunFailure(context, ex, listeners); } try { if (context.isRunning()) { listeners.ready(context, startup.ready()); } } catch (Throwable ex) { throw handleRunFailure(context, ex, null); } return context; } SpringApplicationRunListener监听器
如上所述,这个监听器就是在run方法的执行过程中,会被调用其回调函数的,SpringBoot官方只注册了一个Listener,即EventPublishingRunListener,Listeners都是配置到META-INF/spring.factories配置文件中的。
SpringApplicationRunListener源码
public interface SpringApplicationListener { //在上面的run方法里已看到过有调用,在比较前的位置就调用了 default void starting(){}; /** environment准备完成,在ApplicationContext创建之前,该方法被调用 * Called once the environment has been prepared, but before the * {@link ApplicationContext} has been created. * @param bootstrapContext the bootstrap context * @param environment the environment */ default void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ConfigurableEnvironment environment) { } /** * Called once the {@link ApplicationContext} has been created and prepared, but * before sources have been loaded. * @param context the application context */ default void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { } /** * Called once the application context has been loaded but before it has been * refreshed. * @param context the application context */ default void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { } /** * The context has been refreshed and the application has started but * {@link CommandLineRunner CommandLineRunners} and {@link ApplicationRunner * ApplicationRunners} have not been called. * @param context the application context. * @param timeTaken the time taken to start the application or {@code null} if unknown * @since 2.6.0 */ default void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Duration timeTaken) { } /** * Called immediately before the run method finishes, when the application context has * been refreshed and all {@link CommandLineRunner CommandLineRunners} and * {@link ApplicationRunner ApplicationRunners} have been called. * @param context the application context. * @param timeTaken the time taken for the application to be ready or {@code null} if * unknown * @since 2.6.0 */ default void ready(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Duration timeTaken) { } /** * Called when a failure occurs when running the application. * @param context the application context or {@code null} if a failure occurred before * the context was created * @param exception the failure * @since 2.0.0 */ default void failed(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception) { } } 官方代码的注释已比较清楚了。总结如下图: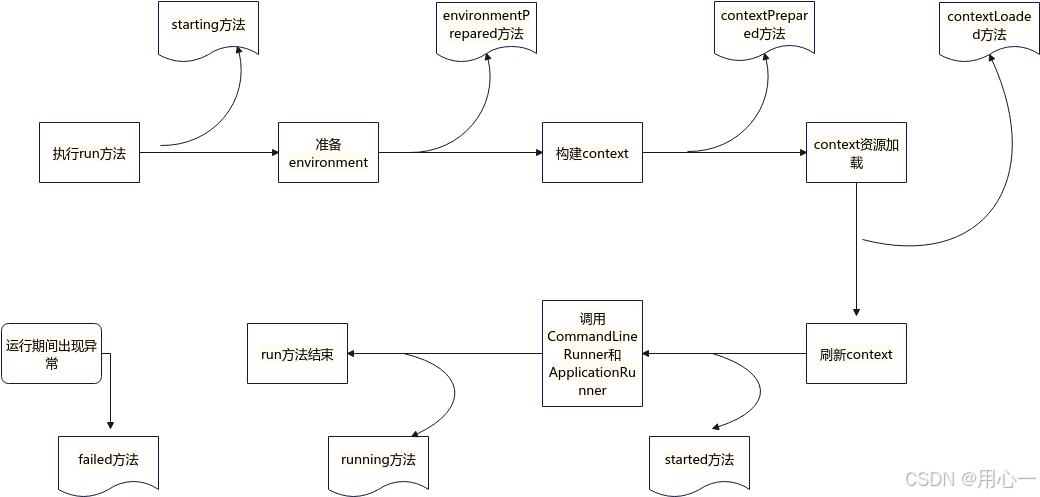
我们可以自定义SpringApplicationRunListener以实现一些在spring应用启动过程中需要完成的业务逻辑。
初始化ApplicationArguments
这个对象主要用来封装main方法的参数args
初始化ConfigurableEnvironment
ConfiguraableEnvironment接口继承自Environment接口和ConfigurablePropertyResolver接口,主要作用是提供当前运行环境的公开接口,比如配置文件profiles各类系统属性和变量的设置、添加、读取、合并等功能。
源码如下:
public interface ConfigurableEnvironment extends Environment, ConfigurablePropertyResolver { //设置激活的组集合 void setActiveProfiles(String... profiles); //向当前激活的组集合中添加一个profile void addActiveProfile(String profile); //设置默认激活的组集合,激活的组集合为空时会使用默认的组集合 void setDefaultProfiles(String... profiles); //获取当前环境对象中的属性源集合 MutablePropertySources getPropertySources(); //获取虚拟机环境变量,该方法提供了直接配置虚拟机环境变量的入口 Map<String, Object> getSystemProperties(); //获取操作系统的环境变量 Map<String, Object> getSystemEnvironment(); //合并指定环境中的配置到当前环境中 void merge(ConfigurableEnvironment parent); } 打印Banner
就是在控制台打印Banner,可以自定义自己要打印的Logo。
Spring应用上下文的创建
应用上下文的创建会根据推断出来的web应用类型,创建不同的应用上下文。springboot中使用如下默认的应用程序上下文工厂创建:
/* * Copyright 2012-2022 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.boot; import java.util.function.BiFunction; import java.util.function.Supplier; import org.springframework.aot.AotDetector; import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.GenericApplicationContext; import org.springframework.core.env.ConfigurableEnvironment; import org.springframework.core.io.support.SpringFactoriesLoader; /** * Default {@link ApplicationContextFactory} implementation that will create an * appropriate context for the {@link WebApplicationType}. * * @author Phillip Webb */ class DefaultApplicationContextFactory implements ApplicationContextFactory { @Override public Class<? extends ConfigurableEnvironment> getEnvironmentType(WebApplicationType webApplicationType) { return getFromSpringFactories(webApplicationType, ApplicationContextFactory::getEnvironmentType, null); } @Override public ConfigurableEnvironment createEnvironment(WebApplicationType webApplicationType) { return getFromSpringFactories(webApplicationType, ApplicationContextFactory::createEnvironment, null); } @Override public ConfigurableApplicationContext create(WebApplicationType webApplicationType) { try { return getFromSpringFactories(webApplicationType, ApplicationContextFactory::create, this::createDefaultApplicationContext); } catch (Exception ex) { throw new IllegalStateException("Unable create a default ApplicationContext instance, " + "you may need a custom ApplicationContextFactory", ex); } } private ConfigurableApplicationContext createDefaultApplicationContext() { if (!AotDetector.useGeneratedArtifacts()) { return new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(); } return new GenericApplicationContext(); } private <T> T getFromSpringFactories(WebApplicationType webApplicationType, BiFunction<ApplicationContextFactory, WebApplicationType, T> action, Supplier<T> defaultResult) { for (ApplicationContextFactory candidate : SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactories(ApplicationContextFactory.class, getClass().getClassLoader())) { T result = action.apply(candidate, webApplicationType); if (result != null) { return result; } } return (defaultResult != null) ? defaultResult.get() : null; } } 由源码可以看到需要根据推断出来的应用类型创建上下文对象。
Spring应用上下文的准备
应用上下文准备阶段
主要由三步:
对context设置environment,在AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext中的实现如下:
/** * {@inheritDoc} * <p> * Delegates given environment to underlying {@link AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader} and * {@link ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner} members. */ @Override public void setEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) { super.setEnvironment(environment); this.reader.setEnvironment(environment); this.scanner.setEnvironment(environment); } 主要是将环境对象设置给reader和scanner
应用上下文后置处理器:
给上下文对象持有的beanFactory容器设置beanNameGenerator,设置资源加载器和类加载器。ConversionService的设置。
ApplicationContextInitializer初始化context操作:ApplicationContextInitializer接口允许在应用上下文初始化之前(还没有调用refresh刷新应用上下文)执行一些自定义逻辑,需要实现其initialize方法,在这一步会被调用。
应用上下文加载阶段
主要实现对bean定义的加载,在以下方法内:
private void prepareContext(DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) { context.setEnvironment(environment); postProcessApplicationContext(context); addAotGeneratedInitializerIfNecessary(this.initializers); applyInitializers(context); listeners.contextPrepared(context); bootstrapContext.close(context); if (this.logStartupInfo) { logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null); logStartupProfileInfo(context); } // Add boot specific singleton beans ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory(); beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments); if (printedBanner != null) { beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner); } if (beanFactory instanceof AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory autowireCapableBeanFactory) { autowireCapableBeanFactory.setAllowCircularReferences(this.allowCircularReferences); if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory listableBeanFactory) { listableBeanFactory.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding); } } if (this.lazyInitialization) { context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new LazyInitializationBeanFactoryPostProcessor()); } if (this.keepAlive) { context.addApplicationListener(new KeepAlive()); } context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new PropertySourceOrderingBeanFactoryPostProcessor(context)); if (!AotDetector.useGeneratedArtifacts()) { // Load the sources 加载所有配资源 Set<Object> sources = getAllSources(); Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty"); //调用加载bean定义的方法 load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0])); } listeners.contextLoaded(context); } 这个加载bean定义的核心逻辑在spring源码中,核心实现是在BeanDefinitionLoader中
其构造函数如下:
/** * Create a new {@link BeanDefinitionLoader} that will load beans into the specified * {@link BeanDefinitionRegistry}. * @param registry the bean definition registry that will contain the loaded beans * @param sources the bean sources */ BeanDefinitionLoader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object... sources) { Assert.notNull(registry, "Registry must not be null"); Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty"); this.sources = sources; this.annotatedReader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(registry); this.xmlReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(registry); this.groovyReader = (isGroovyPresent() ? new GroovyBeanDefinitionReader(registry) : null); this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(registry); this.scanner.addExcludeFilter(new ClassExcludeFilter(sources)); } 由构造函数可知,这个加载bean定义的类支持多种加载方法,由于目前的sources来源是primarySources配置源和sources配置源,这两个变量的类型分别为Class和String,所以实际上只加载类和字符配置源。我们经常用到的应该是基于java类的注解配置,所以一般是调用下面这个方法:
private void load(Class<?> source) { if (isGroovyPresent() && GroovyBeanDefinitionSource.class.isAssignableFrom(source)) { // Any GroovyLoaders added in beans{} DSL can contribute beans here GroovyBeanDefinitionSource loader = BeanUtils.instantiateClass(source, GroovyBeanDefinitionSource.class); ((GroovyBeanDefinitionReader) this.groovyReader).beans(loader.getBeans()); } if (isEligible(source)) { this.annotatedReader.register(source); } } 即基于注解的配置类加载过程。
Spring应用上下文的刷新
即调用AbstractApplicationContext的refresh方法,这是spring的功能,在spring-context包内,属于初始化SpringIOC容器的过程。简要代码如下:
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException{ prepareRefresh(); //通知子类刷新内部bean工厂 ConfigurableListableBeanFDactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); //为当前context准备bean工厂 prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { //允许context的子类对bean工厂进行后置处理 postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); //调用context中注册为bean的工厂处理器 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); //注册bean处理器(beanPostProcessors) registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); //初始化context的信息源,和国际化有关 initMessageSource(); //初始化context的事件传播器 initApplicationEventMulticaster(); //初始化其他特殊的bean onRefresh(); //检查并注册事件监听器 registerListeners(); //实例化所有非懒加载单例 finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); //最后一步:发布对应事件 finishRefresh(); } catch (BeanException e ) { } finally { } } 调用ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner
即获取上一步中注册在spring容器内的ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner实现,对他们进行排序(基于@Order控制执行顺序),然后一个一个调用。所以这两个接口可以在SpringBoot初始化完成之后执行一些处理逻辑。
