client-go 是一个库,提供了与 Kubernetes API 服务器交互的基础设施。它提供了诸如 Informer、Lister、ClientSet 等工具,用于监听、缓存和操作 Kubernetes 资源。而自定义控制器则利用这些工具来实现特定的业务逻辑和自动化任务。业务逻辑实现:client-go 不包含特定的业务逻辑。自定义控制器允许实现特定于您的应用程序或需求的逻辑。扩展 Kubernetes:通过自定义控制器,可以扩展 Kubernetes 的功能,处理自定义资源或实现特定的自动化任务。响应资源变化:自定义控制器可以监听特定资源的变化,并据此执行相应的操作。
而这里的workqueue是costromer Controller的一部分:
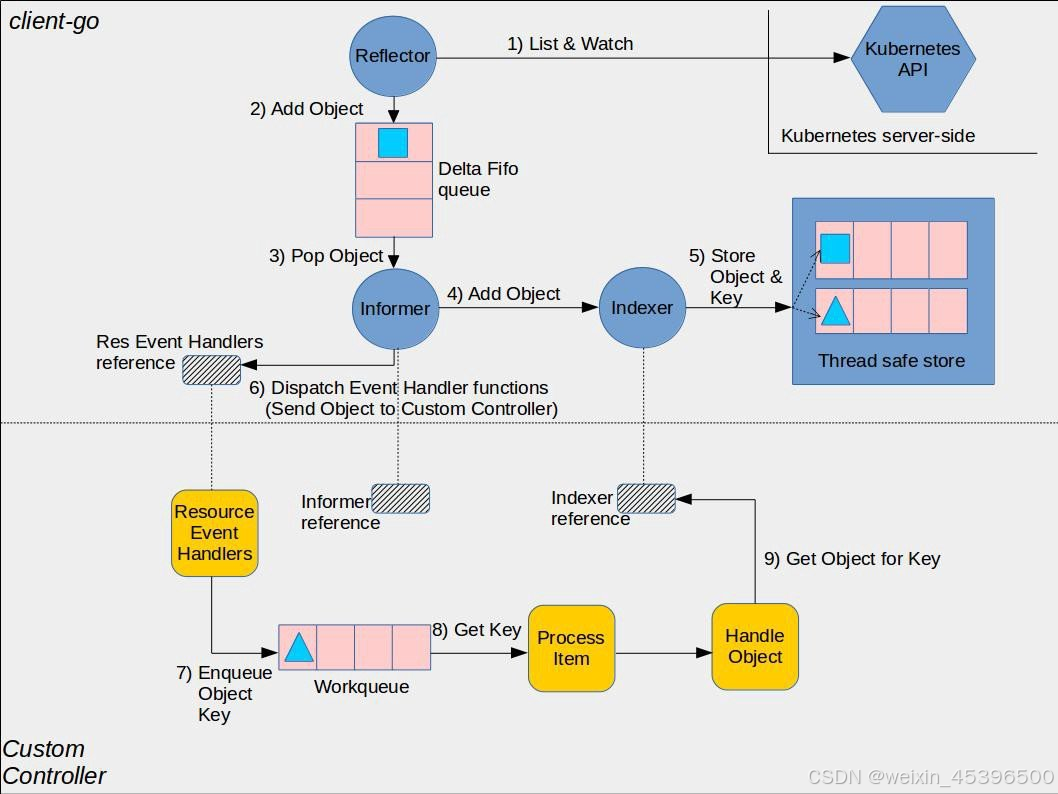
逻辑
当我们创建一个workqueue的时候,到底发生了什么
queue := workqueue.New()该方法调用的new方法又调用了NewWithConfig()以及newQueueWithConfig().可以看到逐级返回以后,返回的是一个type类型的数据。
func New() *Type { return NewWithConfig(QueueConfig{ Name: "", }) } func NewTyped[T comparable]() *Typed[T] { return NewTypedWithConfig(TypedQueueConfig[T]{ Name: "", }) } func NewWithConfig(config QueueConfig) *Type { return NewTypedWithConfig(config) } func NewTypedWithConfig[T comparable](config TypedQueueConfig[T]) *Typed[T] { return newQueueWithConfig(config, defaultUnfinishedWorkUpdatePeriod) } // newQueueWithConfig constructs a new named workqueue // with the ability to customize different properties for testing purposes func newQueueWithConfig[T comparable](config TypedQueueConfig[T], updatePeriod time.Duration) *Typed[T] { var metricsFactory *queueMetricsFactory if config.MetricsProvider != nil { metricsFactory = &queueMetricsFactory{ metricsProvider: config.MetricsProvider, } } else { metricsFactory = &globalMetricsFactory } if config.Clock == nil { config.Clock = clock.RealClock{} } if config.Queue == nil { config.Queue = DefaultQueue[T]() } return newQueue( config.Clock, config.Queue, metricsFactory.newQueueMetrics(config.Name, config.Clock), updatePeriod, ) } TypedInterface
Interface 被标记为废弃(Deprecated),并建议使用 TypedInterface 代替。这种变化主要是因为 Go 语言引入了泛型特性。TypedInterface[T comparable] 使用了泛型,T 是一个类型参数,它必须是可比较的(comparable)。泛型允许在编译时进行类型检查,提供了更好的类型安全性。使用 TypedInterface[T] 可以在编译时捕获类型错误,而不是在运行时。
这里最后返回了一个newQueue,而它的定义如下:
func newQueue[T comparable](c clock.WithTicker, queue Queue[T], metrics queueMetrics, updatePeriod time.Duration) *Typed[T] { t := &Typed[T]{ clock: c, queue: queue, dirty: set[T]{}, processing: set[T]{}, cond: sync.NewCond(&sync.Mutex{}), metrics: metrics, unfinishedWorkUpdatePeriod: updatePeriod, } // Don't start the goroutine for a type of noMetrics so we don't consume // resources unnecessarily if _, ok := metrics.(noMetrics); !ok { go t.updateUnfinishedWorkLoop() } return t }那么Type类型到底是什么:Type 是 Typed[any] 的一个别名。这意味着 Type 可以在任何使用 Typed[any] 的地方使用,它们是完全等价的。
type Type = Typed[any] type Typed[t comparable] struct { queue Queue[t] // dirty defines all of the items that need to be processed. dirty set[t] // Things that are currently being processed are in the processing set. // These things may be simultaneously in the dirty set. When we finish // processing something and remove it from this set, we'll check if // it's in the dirty set, and if so, add it to the queue. processing set[t] cond *sync.Cond shuttingDown bool drain bool metrics queueMetrics unfinishedWorkUpdatePeriod time.Duration clock clock.WithTicker } type empty struct{} type t interface{} type set[t comparable] map[t]empty这里有两个set,一个是process一个是dirty,一个项目可能同时存在于这两个集合中。这是因为一个正在处理的项目(在 processing 中)可能在处理过程中被标记为需要重新处理(因此也在 dirty 中)。如果它在 dirty 集合中,说明在处理过程中它被标记为需要重新处理。这时,系统会将它重新加入到处理队列中。
这里的t是一个空接口,允许存储任何形式的kubernetes资源。
这里还定义了接口,而Type实现了这个接口。
type Interface interface { Add(item interface{}) Len() int Get() (item interface{}, shutdown bool) Done(item interface{}) ShutDown() ShutDownWithDrain() ShuttingDown() bool }dirty队列
添加任务:当有新任务时,首先检查它是否已经在 dirty 中。如果不在,就添加进去。开始处理:当开始处理一个任务时,将它从 dirty 中移除。重新添加:如果一个正在处理的任务需要重新处理,就把它再次加入 dirty。dirty 帮助工作队列系统更高效地管理需要处理的任务,避免重复工作,并能快速决定是否需要添加新任务到处理队列中。
各种类型的queue
在k8s.io/client-go/util/workqueue中查看。
从上面的例子可以看到,一个queue是有很多参数的,如果只是简单的通过new来创建,很多参数都是默认的参数。
限速队列
k8s.io/client-go/util/workqueue/default-rate-limiters.go
限速队列应用得非常广泛,比如在我们做一些操作失败后希望重试几次,但是立刻重试很有可能还是会失败,这个时候我们可以延迟一段时间再重试,而且失败次数越多延迟时间越长,这个其实就是限速。首先我们需要来了解下限速器。
type RateLimiter TypedRateLimiter[any] type TypedRateLimiter[T comparable] interface { // When gets an item and gets to decide how long that item should wait When(item T) time.Duration // Forget indicates that an item is finished being retried. Doesn't matter whether it's for failing // or for success, we'll stop tracking it Forget(item T) // NumRequeues returns back how many failures the item has had NumRequeues(item T) int }TypedBucketRateLimiter (令牌桶限速器)
这个限速器基于令牌桶算法。想象一个固定容量的桶,桶里装着令牌。令牌以固定的速率被加入到桶中。当一个请求(或任务)到来时,它需要从桶中获取一个令牌。如果桶中有令牌,请求可以立即处理。如果桶是空的,请求必须等待直到新的令牌被加入。这种方法可以很好地控制平均处理速率,同时允许短时间的突发流量。
TypedItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter (指数退避限速器)
这个限速器根据失败次数增加等待时间:每次失败,等待时间会指数增加(基础延迟 * 2^失败次数)。有一个最大延迟时间,防止等待时间无限增长。
TypedItemFastSlowRateLimiter (快慢双速限速器)
这个限速器有两种速率:快速和慢速:在最初的几次尝试中使用快速延迟。超过设定的尝试次数后,切换到慢速延迟。适用于需要快速重试几次,然后如果仍然失败就减慢重试频率的场景。
TypedMaxOfRateLimiter (最大值限速器)
这个限速器组合了多个其他限速器:
它包含一个限速器的列表。当需要决定延迟时间时,它会询问所有的限速器。然后返回所有限速器中最长的延迟时间。这允许你组合多种限速策略,总是使用最保守(最慢)的那个。
TypedWithMaxWaitRateLimiter (最大等待时间限速器)
从代码中可以看到,有一个基础的RateLimiter的接口interface,然后其余的结构体都是这个端口的实现:
type TypedBucketRateLimiter[T comparable] struct { *rate.Limiter } ype TypedItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter[T comparable] struct { failuresLock sync.Mutex failures map[T]int baseDelay time.Duration maxDelay time.Duration } type TypedItemFastSlowRateLimiter[T comparable] struct { failuresLock sync.Mutex failures map[T]int maxFastAttempts int fastDelay time.Duration slowDelay time.Duration } type TypedMaxOfRateLimiter[T comparable] struct { limiters []TypedRateLimiter[T] } type TypedWithMaxWaitRateLimiter[T comparable] struct { limiter TypedRateLimiter[T] maxDelay time.Duration }他们的new函数(部分)
func NewWithMaxWaitRateLimiter(limiter RateLimiter, maxDelay time.Duration) RateLimiter { return NewTypedWithMaxWaitRateLimiter[any](limiter, maxDelay) } func NewTypedWithMaxWaitRateLimiter[T comparable](limiter TypedRateLimiter[T], maxDelay time.Duration) TypedRateLimiter[T] { return &TypedWithMaxWaitRateLimiter[T]{limiter: limiter, maxDelay: maxDelay} }接口实现:
func (w TypedWithMaxWaitRateLimiter[T]) When(item T) time.Duration { delay := w.limiter.When(item) if delay > w.maxDelay { return w.maxDelay } return delay } func (w TypedWithMaxWaitRateLimiter[T]) Forget(item T) { w.limiter.Forget(item) } func (w TypedWithMaxWaitRateLimiter[T]) NumRequeues(item T) int { return w.limiter.NumRequeues(item) }我们可以看到有的限速器需要一个基础限速器:NewTypedWithMaxWaitRateLimiter是从多个限速器中取得最大的限速时间。(这里函数名称不同,源代码里是NewTypedWithMaxWaitRateLimiter而实际演示代码是NewWithMaxWaitRateLimiter,这是因为源码读的是最新版,而实际安装的go是1.22,所以不一样,但是只有增加和缺少Type的区别)
baseRateLimiter := workqueue.NewItemExponentialFailureRateLimiter(100*time.Millisecond, 10*time.Second) ratelimiter :=workqueue.NewWithMaxWaitRateLimiter(baseRateLimiter,10*time.Second) ratelimitedQueue := workqueue.NewRateLimitingQueue(ratelimiter)延迟队列
type DelayingInterface interface { Interface // AddAfter adds an item to the workqueue after the indicated duration has passed AddAfter(item interface{}, duration time.Duration) } type delayingType struct { Interface // clock tracks time for delayed firing clock clock.Clock // stopCh lets us signal a shutdown to the waiting loop stopCh chan struct{} // stopOnce guarantees we only signal shutdown a single time stopOnce sync.Once // heartbeat ensures we wait no more than maxWait before firing heartbeat clock.Ticker // waitingForAddCh is a buffered channel that feeds waitingForAdd waitingForAddCh chan *waitFor // metrics counts the number of retries metrics retryMetrics } func NewDelayingQueue() DelayingInterface { return NewDelayingQueueWithConfig(DelayingQueueConfig{}) }具体实现:可以看到NewDelayingQueue()->NewDelayingQueueWithConfig{return newDelayingQueue(config.Clock, config.Queue, config.Name, config.MetricsProvider)},然后有一个newDelayingQueue但是带有参数的方法,这里的new的n是小写的,代表这是一个私有的方法,可以看到最后返回的是一个delayingType。而NewDelayingQueue()返回的是一个interface。
func NewDelayingQueue() DelayingInterface { return NewDelayingQueueWithConfig(DelayingQueueConfig{}) } func NewDelayingQueueWithConfig(config DelayingQueueConfig) DelayingInterface { if config.Clock == nil { config.Clock = clock.RealClock{} } if config.Queue == nil { config.Queue = NewWithConfig(QueueConfig{ Name: config.Name, MetricsProvider: config.MetricsProvider, Clock: config.Clock, }) } return newDelayingQueue(config.Clock, config.Queue, config.Name, config.MetricsProvider) } func newDelayingQueue(clock clock.WithTicker, q Interface, name string, provider MetricsProvider) *delayingType { ret := &delayingType{ Interface: q, clock: clock, heartbeat: clock.NewTicker(maxWait), stopCh: make(chan struct{}), waitingForAddCh: make(chan *waitFor, 1000), metrics: newRetryMetrics(name, provider), } go ret.waitingLoop() return ret } func (q *delayingType) AddAfter(item interface{}, duration time.Duration) { // don't add if we're already shutting down if q.ShuttingDown() { return } q.metrics.retry() // immediately add things with no delay if duration <= 0 { q.Add(item) return } select { case <-q.stopCh: // unblock if ShutDown() is called case q.waitingForAddCh <- &waitFor{data: item, readyAt: q.clock.Now().Add(duration)}: } }可以看到还有很多变种,但是最后都会调用 NewDelayingQueue但是带有参数的方法。
// NewDelayingQueueWithCustomQueue constructs a new workqueue with ability to // inject custom queue Interface instead of the default one // Deprecated: Use NewDelayingQueueWithConfig instead. func NewDelayingQueueWithCustomQueue(q Interface, name string) DelayingInterface { return NewDelayingQueueWithConfig(DelayingQueueConfig{ Name: name, Queue: q, }) } // NewNamedDelayingQueue constructs a new named workqueue with delayed queuing ability. // Deprecated: Use NewDelayingQueueWithConfig instead. func NewNamedDelayingQueue(name string) DelayingInterface { return NewDelayingQueueWithConfig(DelayingQueueConfig{Name: name}) } // NewDelayingQueueWithCustomClock constructs a new named workqueue // with ability to inject real or fake clock for testing purposes. // Deprecated: Use NewDelayingQueueWithConfig instead. func NewDelayingQueueWithCustomClock(clock clock.WithTicker, name string) DelayingInterface { return NewDelayingQueueWithConfig(DelayingQueueConfig{ Name: name, Clock: clock, }) }为什么newDelayingQueue返回的是type类型,而他的上级返回的是interface类型呢?以下面的代码为例:advancedAnimal实现的结构体包含一个interface:animal,和一个trick。这个trick字段是为了实现PerformTrick方法。
func (a *advancedAnimalType) PerformTrick() string {
return a.trick
}
这个接收advancedAnimal的函数实现了PerformTrick(),所以可以看作是advancedAnimal实现了AdvancedAnimal的interface。 所以在下面的New函数中,虽然返回的是advancedAnimalType,但是最后NewAdvancedAnimal返回的是interface类型。
func NewAdvancedAnimal(config AdvancedAnimalConfig) AdvancedAnimal {
if config.Animal == nil {
config.Animal = NewAnimal(config.Species, config.Sound, config.Movement)
}return &advancedAnimalType{
Animal: config.Animal,
trick: config.Trick,
}
}
type Animal interface { Speak() string Move() string } // 扩展的 AdvancedAnimal 接口 type AdvancedAnimal interface { Animal PerformTrick() string } // 基本的动物实现 type basicAnimal struct { species string sound string movement string } func (a *basicAnimal) Speak() string { return a.sound } func (a *basicAnimal) Move() string { return a.movement } // 高级动物实现 type advancedAnimalType struct { Animal trick string } func (a *advancedAnimalType) PerformTrick() string { return a.trick } // 创建基本动物的函数 func NewAnimal(species, sound, movement string) Animal { return &basicAnimal{ species: species, sound: sound, movement: movement, } } // 创建高级动物的函数 func NewAdvancedAnimal(config AdvancedAnimalConfig) AdvancedAnimal { if config.Animal == nil { config.Animal = NewAnimal(config.Species, config.Sound, config.Movement) } return &advancedAnimalType{ Animal: config.Animal, trick: config.Trick, } } // 配置结构体 type AdvancedAnimalConfig struct { Animal Animal Species string Sound string Movement string Trick string }
