目录
一、什么是依赖注入
依赖注入(Dependency Injection,简称DI),它是Spring控制反转思想的具体实现。
控制反转将对象的创建交给了Spring,但是对象中可能会依赖其他对象。比如service类中要有dao类的属性,我们称service依赖于dao。之前需要手动注入属性值,代码如下:
public interface StudentDao {
Student findById(int id);
}
public class StudentDaoImpl implements StudentDao{
@Override
public Student findById(int id) {
// 模拟根据id查询学生
return new Student(1,"程序员","北京");
}
}
public class StudentService {// service依赖dao,手动注入属性值,即手动维护依赖关系
private StudentDao studentDao = new StudentDaoImpl();
public Student findStudentById(int id){
return studentDao.findById(id);
}
}
此时,当StudentService的想要使用StudentDao的另一个实现类如StudentDaoImpl2时,则需要修改Java源码,造成代码的可维护性降低。
而使用Spring框架后,Spring管理Service对象与Dao对象,此时它能够为Service对象注入依赖的Dao属性值。这就是Spring的依赖注入。简单来说,控制反转是创建对象,依赖注入是为对象的属性赋值
二、依赖注入方式
1. Setter注入
被注入类编写属性的setter方法
public void setStudentDao(StudentDao studentDao){ this.studentDao = studentDao; } 配置文件中,给需要注入属性值的 <bean> 中设置 <property>
<bean id="studentDao" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoImpl"> </bean> <bean id="studentService" class="com.itbaizhan.service.StudentService"> <!--依赖注入--> <!--name:对象的属性名 ref:容器中对象的id值--> <property name="studentDao" ref="studentDao"></property> </bean> 测试
新增测试方法
// 测试依赖注入 @Test public void t6(){ ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml"); StudentService service = (StudentService) ac.getBean("studentService"); System.out.println(service.findStudentById(8)); }运行结果
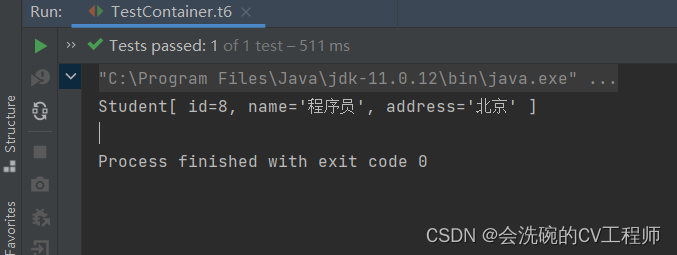
OK,确实成功测试到了
2. 构造方法注入
被注入类编写有参的构造方法
public StudentService(StudentDao studentDao){ this.studentDao = studentDao; } 给需要注入属性值的 <bean> 中设置 <constructor-arg>
<bean id="studentDao" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoImpl"></bean> <bean id="studentService" class="com.itbaizhan.service.StudentService"> <!-- 依赖注入 --> <!-- name:对象的属性名 ref:配置文件中注入对象的id值 --> <constructor-arg name="studentDao" ref="studentDao"></constructor-arg> </bean>测试结果:
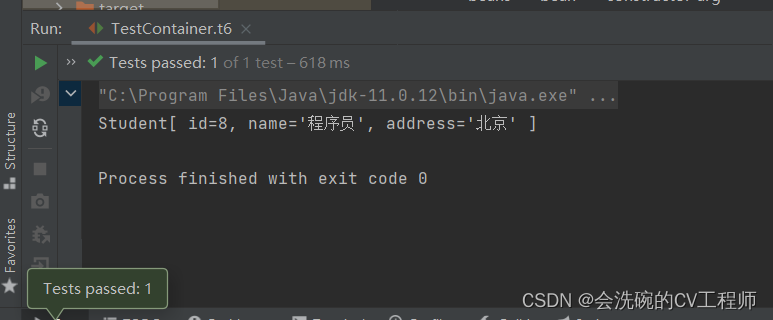
OK,确实也是可以使用的
3. 自动注入
自动注入不需要在 <bean> 标签中添加其他标签注入属性值,而是自动从容器中找到相应的bean对象设置为属性值。
自动注入有两种配置方式:
- 全局配置:在 <beans> 中设置 default-autowire 属性可以定义所有bean对象的自动注入策略。
- 局部配置:在 <bean> 中设置 autowire 属性可以定义当前bean对象的自动注入策略。
autowire的取值如下:
- no:不会进行自动注入。
- default:全局配置default相当于no,局部配置default表示使用全局配置
- byName:在Spring容器中查找id与属性名相同的bean,并进行注入。需要提供set方法。
- byType:在Spring容器中查找类型与属性类型相同的bean,并进行注入。需要提供set方法。
- constructor:在Spring容器中查找id与属性名相同的bean,并进行注入。需要提供构造方法。
三、依赖注入类型
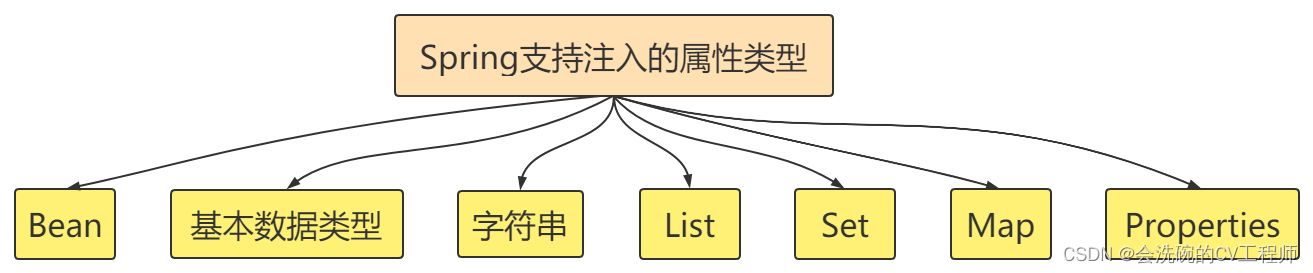
DI支持注入bean类型、基本数据类型和字符串、List集合、Set集合、Map集合、Properties对象类型等,他们的写法如下:
准备注入属性的类
package com.example.service; import com.example.dao.StudentDao; import com.example.pojo.Student; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Properties; import java.util.Set; public class StudentService { // service依赖dao,手动注入属性值,即手动维护依赖关系 //private StudentDao studentDao; // bean属性 private StudentDao studentDao; // 字符串类型 private String name; // 基本数据类型 private int count; // 字符串List集合 private List<String> students1; // 对象类型List集合 private List<Student> nameList; // 字符串类型Set集合 private Set<String> students2; // 字符串类型Map集合 private Map<String, String> students3; // 对象类型map集合 private Map<String,Student> studentMap; // Properties类型 private Properties properties; public StudentService(){} public StudentService(StudentDao studentDao){ this.studentDao = studentDao; } public Student findStudentById(int id){ return studentDao.findById(id); } public void setStudentDao(StudentDao studentDao){ this.studentDao = studentDao; } public StudentDao getStudentDao() { return studentDao; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getCount() { return count; } public void setCount(int count) { this.count = count; } public List<String> getStudents1() { return students1; } public void setStudents1(List<String> students1) { this.students1 = students1; } public Set<String> getStudents2() { return students2; } public void setStudents2(Set<String> students2) { this.students2 = students2; } public Map<String, String> getNames2() { return students3; } public void setNames2(Map<String, Student> names2) { this.studentMap = names2; } public Map<String, String> getStudents3() { return students3; } public void setStudents3(Map<String, String> students3) { this.students3 = students3; } public Properties getProperties() { return properties; } public void setProperties(Properties properties) { this.properties = properties; } public List<Student> getNameList() { return nameList; } public void setNameList(List<Student> nameList) { this.nameList = nameList; } @Override public String toString() { return "StudentService[ " + "studentDao=" + studentDao + ", name='" + name + '\'' + ", count=" + count + ", students1=" + students1 + ", nameList=" + nameList + ", students2=" + students2 + ", students3=" + students3 + ", studentMap=" + studentMap + ", properties=" + properties + " ]"; } } 准备测试方法
// 测试注入类型 @Test public void t7(){ ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml"); StudentService service = (StudentService) ac.getBean("studentService"); System.out.println(service); }1. 注入bean类型
<!-- 注入bean类型 --> <bean id="studentDao" class="com.example.dao.StudentDaoImpl1"/> <!-- 写法1 --> <bean id="studentService" class="com.example.service.StudentService"> <property name="studentDao" ref="studentDao"/> </bean> <!-- 写法2 --> <!--<bean id="studentService" class="com.example.service.StudentService"> <property name="studentDao"> <ref bean="studentDao"/> </property> </bean>-->2. 注入基本数据类型
<!-- 注入基本数据类型 --> <!-- 写法一 name:属性名 value:属性值 --> <property name="name" value="程序员"/> <!-- 写法二 name:属性名 value:属性值--> <property name="count"> <value>10</value> </property>3. 注入List集合
<!-- 注入List集合 --> <!-- 简单的数据类型List集合 name:属性名 --> <property name="students1" > <list> <value>上海</value> <value>广州</value> </list> </property> <!-- 对象类型的List集合 name:属性名 --> <property name="nameList"> <list> <bean class="com.example.pojo.Student"> <property name="id" value="1"/> <property name="name" value="几何心凉"/> <property name="address" value="北京"/> </bean> <bean class="com.example.pojo.Student"> <property name="id" value="2"/> <property name="name" value="哈士奇"/> <property name="address" value="上海"/> </bean> </list> </property>4. 注入Set集合
<!-- 注入Set集合 --> <property name="students2"> <set> <value>深圳</value> <value>北京</value> </set> </property>5. 注入Map集合
<!-- 注入Map集合 --> <property name="students3"> <map> <entry key="哈士奇" value="上海"/> <entry key="几何心凉" value="北京"/> </map> </property> <!-- 注入对象类型map类型 --> <property name="names2"> <map> <entry key="student1" value-ref="s1"/> <entry key="student2" value-ref="s2"/> </map> </property> <bean id="s1" class="com.example.pojo.Student"> <property name="id" value="1"/> <property name="name" value="几何心凉"/> <property name="address" value="北京"/> </bean> <bean id="s2" class="com.example.pojo.Student"> <property name="id" value="2"/> <property name="name" value="哈士奇"/> <property name="address" value="上海"/> </bean>上面是用到的bean对象
6. 注入Properties对象
<!-- 注入properties --> <property name="properties"> <props> <prop key="配置1">值1</prop> <prop key="配置2">值2</prop> </props> </property>运行测试方法测试一下
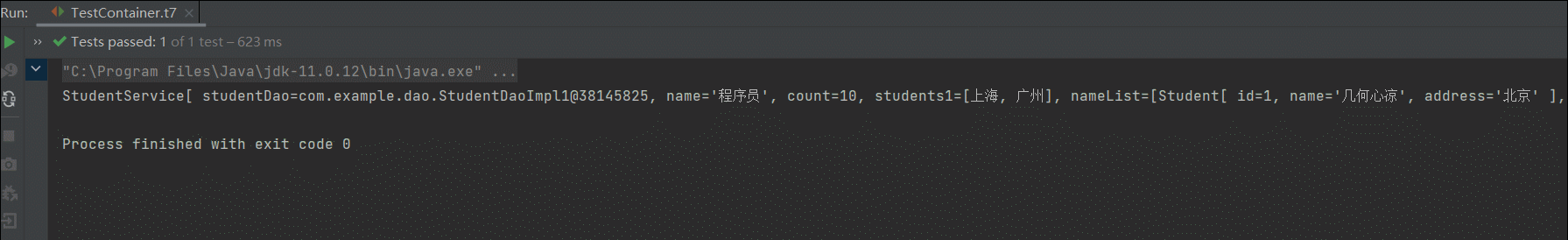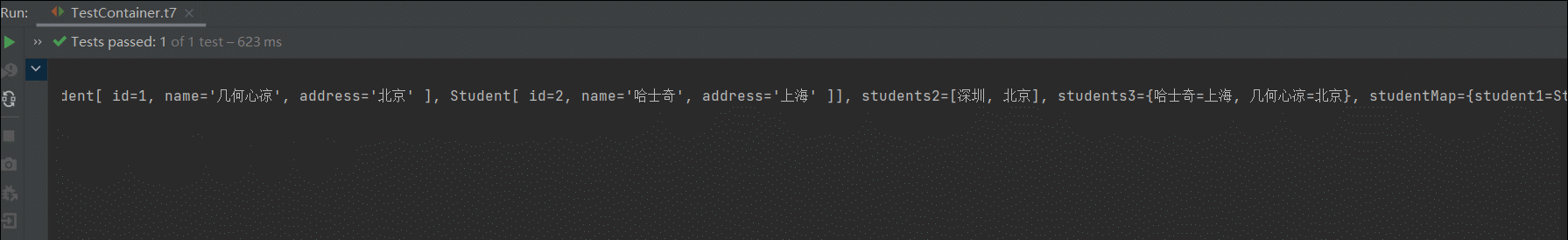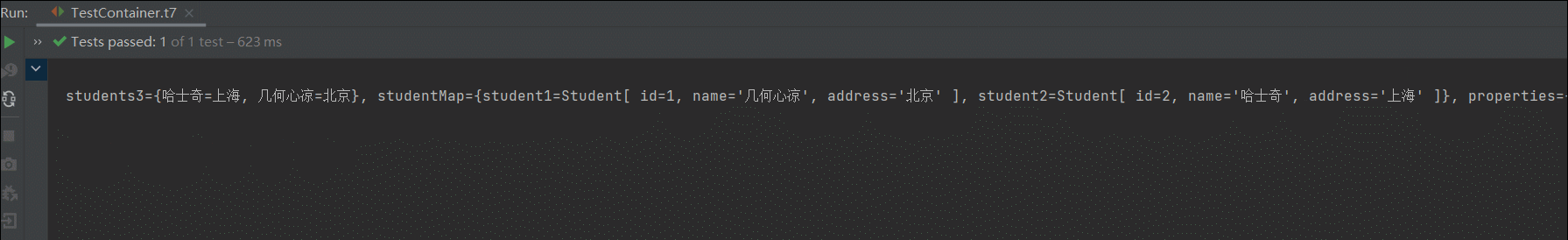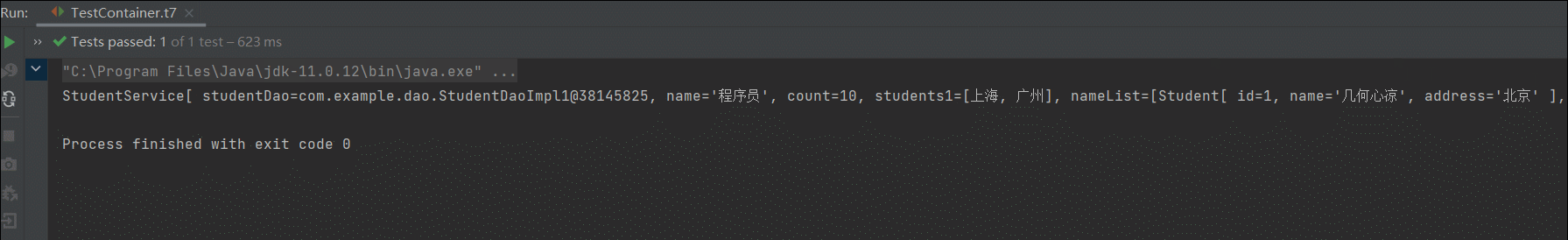
OK ,可以看到都是插入的了。
往期专栏&文章相关导读
大家如果对于本期内容有什么不了解的话也可以去看看往期的内容,下面列出了博主往期精心制作的Maven,Mybatis等专栏系列文章,走过路过不要错过哎!如果对您有所帮助的话就点点赞,收藏一下啪。其中Spring专栏有些正在更,所以无法查看,但是当博主全部更完之后就可以看啦。
1. Maven系列专栏文章
| Maven系列专栏 | Maven工程开发 |
| Maven聚合开发【实例详解---5555字】 |
