游戏服务器的热更新是一种常见的需求,skynet可以通过inject的方式,来修改一个服务的消息处理函数,达到热更新的效果。
skynet内置服务debug_console
skynet自带了一个调试控制台服务。inject注入代码需要先启动这个服务。
skynet.newservice("debug_console", "127.0.0.1", "9666") 启动之后,我们可以用telnet或者nc等指令来登录调试控制台。
> nc 127.0.0.1 9666 输入list指令,可以得到当前系统中所有服务的地址:
list :00000004 snlua cdummy :00000006 snlua datacenterd :00000007 snlua service_mgr :00000008 snlua main :00000009 snlua debug_console 127.0.0.1 9666 :0000000a snlua serviceA <CMD OK> 输入inject指令,我们可以将某个代码文件,注入到指定的服务中:
inject :0000000a service/hotfix.lua <CMD OK> 更多的debug_console指令可以参考这里
inject实例
我们在系统启动时,打开debug_console,然后启动服务serviceA,接着设置每隔5秒给serviceA发送两个lua消息,一个参数bar,一个参数foo,代码如下:
--main.lua local skynet = require "skynet" skynet.start(function() skynet.newservice("debug_console", "127.0.0.1", "9666") local addr = skynet.newservice("serviceA") local function tick() skynet.send(addr, "lua", "foo") skynet.send(addr, "lua", "bar") skynet.timeout(500, tick) end skynet.timeout(500, tick) end) 在服务serverA中,我们根据参数,调用不同的处理函数:
--serviceA.lua local skynet = require "skynet" local handles = {} handles.foo = function() print("foo") end skynet.start(function() skynet.dispatch("lua", function(session, source, cmd, ...) local handle = handles[cmd] if handle then handle() else print("cmd not found", cmd) end end) end) 现在我们启动skynet,可以看到每隔5秒输出:
foo cmd not found bar 现在我们新建一个文件hotfix.lua:
--hotfix.lua local handles = _P.lua.handles local print = _G.print handles.foo = function() print("foo after hotfix") end handles.bar = function() print("bar after hotfix") end 接下来连接到控制台,并输入inject指令:
echo 'inject :0000000a services/hotfix.lua' | nc 127.0.0.1 9666 等到下次输出的时候,我们看到的就是:
foo after hotfix bar after hotfix 更新完成,修改了foo函数,新增了bar函数。
使用
inject调用hotfix.lua时,debug_console的返回输出函数,所以如果要用到print的话,需要使用全局变量_G.print
对upValue的处理
如果我们的serviceA是这样的:
--serviceA.lua local skynet = require "skynet" local handles = {} local N = 1 local T = { count = 0, } handles.foo = function() N = N + 2 T.count = T.count + 1 print("foo", N, T.count) end handles.bar = function() N = N - 1 print("bar", N) end skynet.start(function() skynet.dispatch("lua", function(session, source, cmd, ...) local handle = handles[cmd] if handle then handle() else print("cmd not found", cmd) end end) end) foo函数带有两个upValue: N和T,bar函数带有一个upValue: N 如果hotfix.lua文件没有做特殊处理,直接覆盖函数的话,那么就会丢失这些upValue。那么,要怎么处理这些upValue呢?这里需要用到lua的debug库,主要是两个函数:
debug.getupvalue(f, i): 获取函数f中的第i个upValue的变量名和值。debug.upvaluejoin(f1, i, f2, j):让函数f1的第i个upValue引用f2中的第j个upValue。
热更新带有upValue的函数,我们的hotfix.lua分三步走:
- 定义一个函数
get_up,来获取原有的函数的upValue列表。 - 定义新的处理函数。
- 定义一个函数
uv_join,将新函数的upValue和旧函数的upValue绑定起来。
完整代码如下:
local handles = _P.lua.handles local print = _G.print local function get_up(f) local u = {} if not f then return u end local i = 1 while true do local name = debug.getupvalue(f, i) if name == nil then return u end u[name] = i i = i + 1 end return u end local function uv_join(f, old_f, old_uv) local i = 1 while true do local name = debug.getupvalue(f, i) if not name then break end if old_uv[name] then debug.upvaluejoin(f, i, old_f, old_uv[name]) end i = i + 1 end end local foo = handles.foo local up = get_up(foo) local N, T --定义两个upValue,否则函数里会变成全局变量 handles.foo = function() N = N + 200 T.count = T.count + 100 print("foo", N, T.count) end uv_join(handles.foo, foo, up) 这里的
get_up函数只取了传入函数的upValue,如果要嵌套处理函数中的函数,可以参考lualib/skynet/inject.lua中的getupvaluetable函数。
inject实现原理
debug_console服务的代码位于service/debug_console.lua文件中,其对inject指令的处理,其实就是发送一条debug类型的消息到目标服务:
--debug_console.lua function COMMAND.inject(address, filename, ...) address = adjust_address(address) local f = io.open(filename, "rb") if not f then return "Can't open " .. filename end local source = f:read "*a" f:close() local ok, output = skynet.call(address, "debug", "RUN", source, filename, ...) if ok == false then error(output) end return output end 在我们的服务中,当我们require 'skynet'的时候,会自动注册debug消息类型的处理:
--lualib/skynet.lua -- Inject internal debug framework local debug = require "skynet.debug" debug.init(skynet, { dispatch = skynet.dispatch_message, suspend = suspend, resume = coroutine_resume, }) --lualib/skynet/debug.lua skynet.register_protocol { name = "debug", id = assert(skynet.PTYPE_DEBUG), pack = assert(skynet.pack), unpack = assert(skynet.unpack), dispatch = _debug_dispatch, } 其中,参数RUN是这样处理的
--lualib/skynet/debug.lua function dbgcmd.RUN(source, filename, ...) local inject = require "skynet.inject" local args = table.pack(...) local ok, output = inject(skynet, source, filename, args, export.dispatch, skynet.register_protocol) collectgarbage "collect" skynet.ret(skynet.pack(ok, table.concat(output, "\n"))) end 追溯代码,来到最终的inject函数: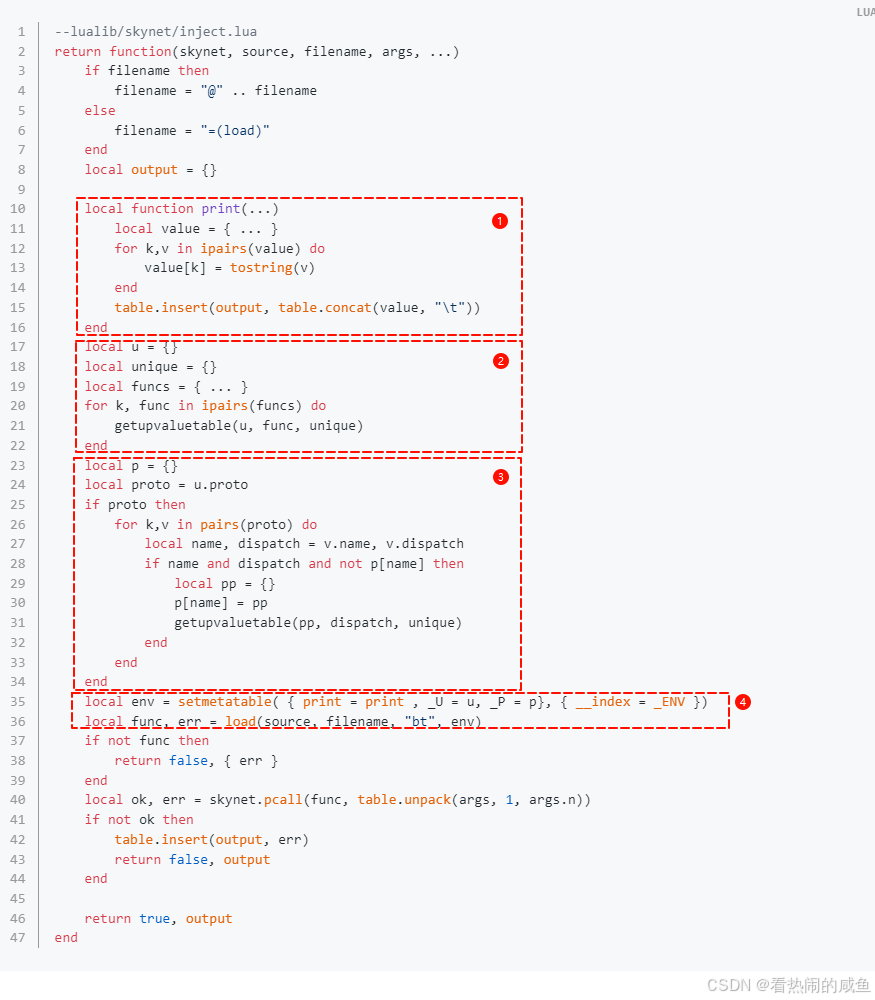
- 修改
print函数,可以返回输出内容给debug_console服务。 - 在上一层调用的时候,传进来的
...实际上两个函数skynet.dispatch_message和skynet.register_protocol,这里将这两个函数,以及函数中包含的子函数,所用到的upVluae都收集起来,存入表u中。 proto是skynet.register_protocol中用到的一个upValue,存放着当前服务所注册的消息类型。遍历proto,将每个消息的处理函数用到的upValue收集起来,存放到表p中。- 设置环境,调用传入的热更新文件。现在我们知道,在上面的例子中的
hotfix.lua,用到的_P,就是存放各种消息类型的处理函数的upValue表。
在控制台调用inject指令时,还可以传入额外的参数,例如:
inject :0000000a services/hotfix.lua xxx yyy,最终这两个参数,就是这里的inject函数中的第四个参数args,可以在hotfix.lua中直接使用这两个参数。
