阅读量:0
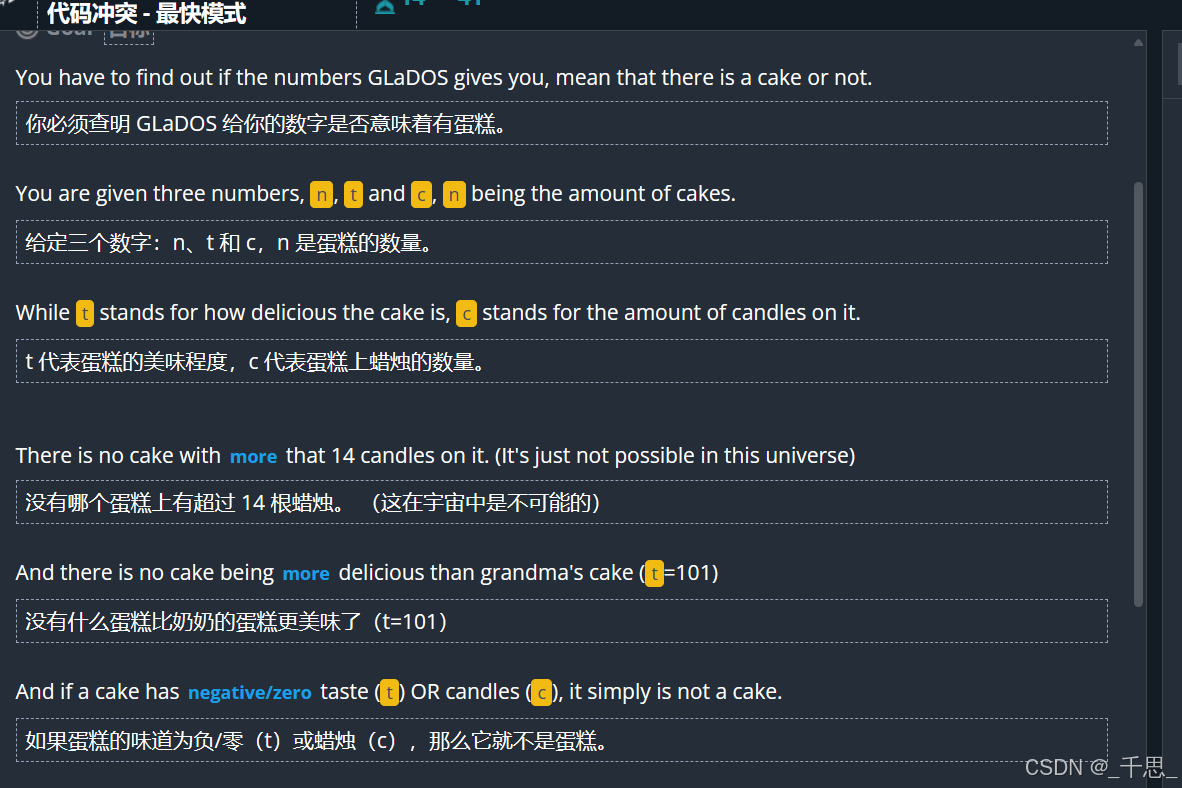
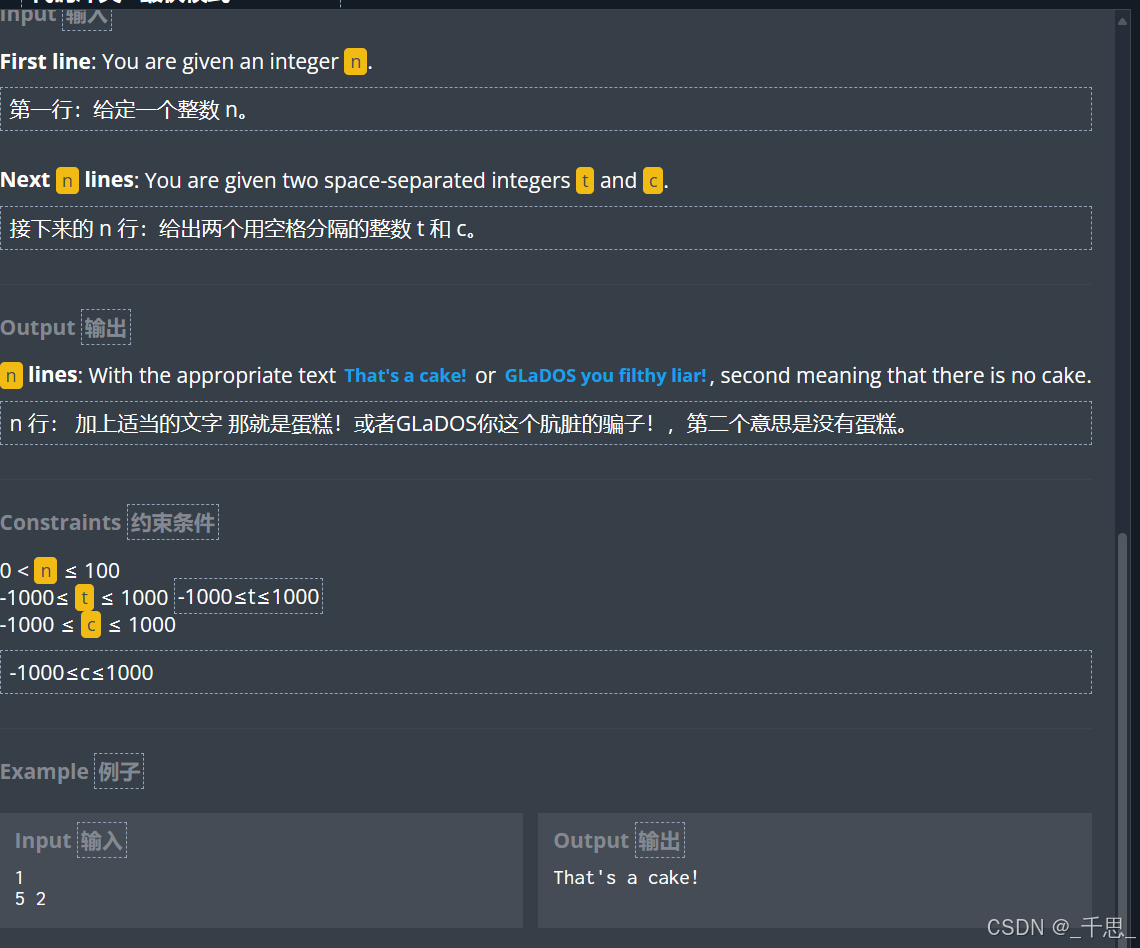
import sys import math # Auto-generated code below aims at helping you parse # the standard input according to the problem statement. n = int(input()) for i in range(n): t, c = [int(j) for j in input().split()] if c>14 or t<=0 or t>101: print("GLaDOS you filthy liar!") else: print("That's a cake!") # print("That's a cake! or GLaDOS you filthy liar!") 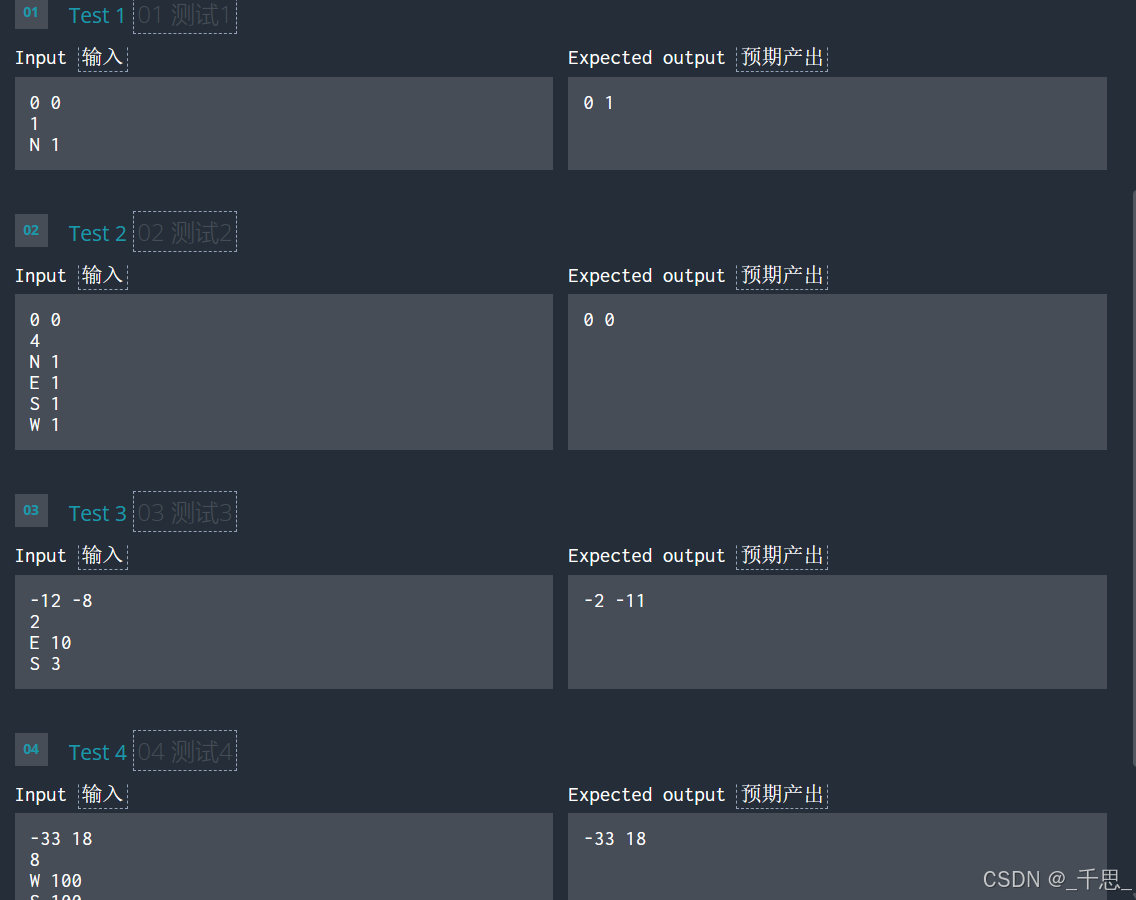
import sys import math # Auto-generated code below aims at helping you parse # the standard input according to the problem statement. x, y = [int(i) for i in input().split()] n = int(input()) for i in range(n): inputs = input().split() _dir = inputs[0] dist = int(inputs[1]) if _dir == 'N': y += dist elif _dir == 'S': y -= dist elif _dir == 'E': x += dist elif _dir == 'W': x -= dist print(x,y) 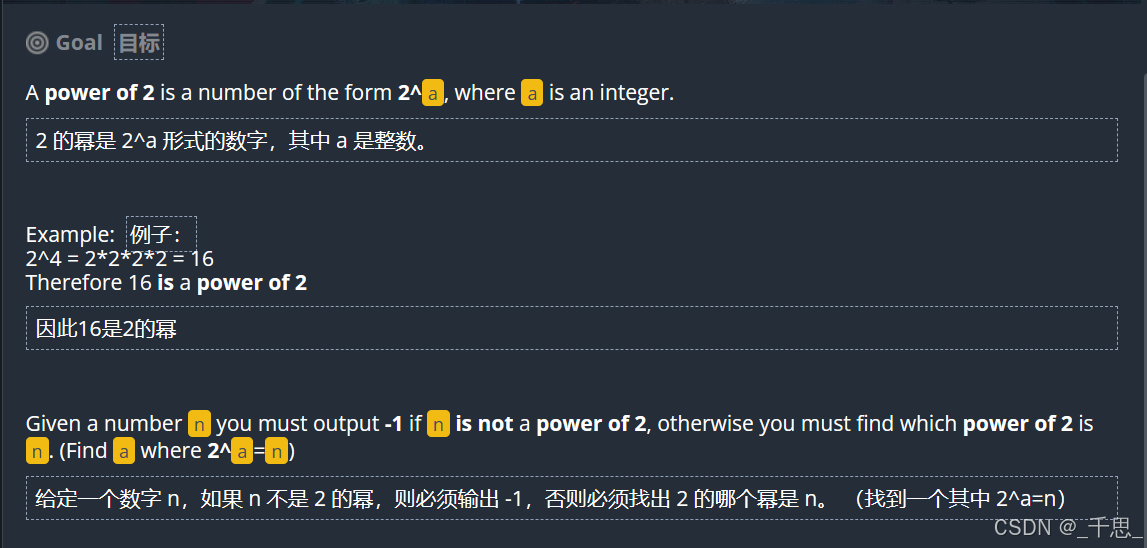
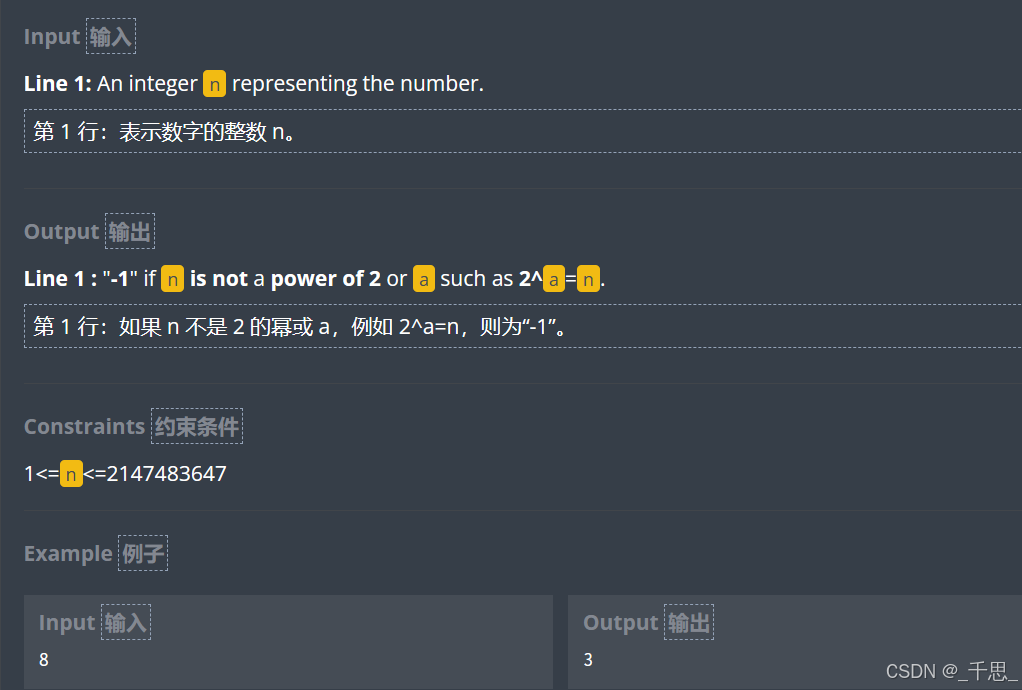
import sys import math from math import log2 # Auto-generated code below aims at helping you parse # the standard input according to the problem statement. n = int(input()) if log2(n) == int(log2(n)): print(int(log2(n))) else: print(-1) 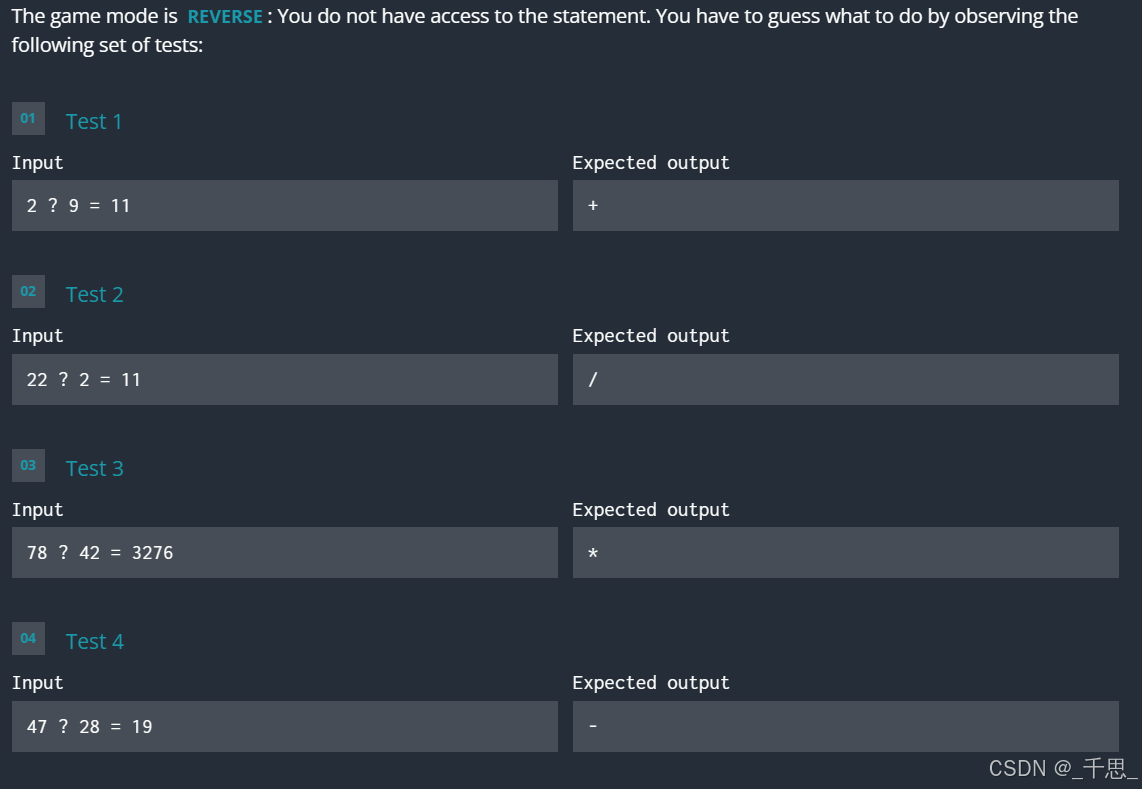
import sys import math # Auto-generated code below aims at helping you parse # the standard input according to the problem statement. problem = input() if eval(problem.replace('?', '+').replace('=', '==')): print("+") if eval(problem.replace('?', '-').replace('=', '==')): print("-") if eval(problem.replace('?', '*').replace('=', '==')): print("*") if eval(problem.replace('?', '/').replace('=', '==')): print("/") eval不安全,看情况使用
