文章目录
案例说明
本案例我们希望使用三种方式查询数据库某张表下所有数据:
- 单线程+分页查询获取所有数据
- 单线程+直接查询获取所有数据
- 多线程+分页查询获取所有数据
测试结论
在比较这三种方式的效率时,我们需要考虑几个关键因素:数据量的大小、查询操作的复杂性、以及并行处理的能力。
首先,我们来看 list() 方法。这个方法直接调用 deviceTestOneService.list() 来获取表中的所有数据。如果数据量非常大,那么这种方法可能会导致内存溢出,因为它会一次性加载所有数据到内存中。此外,由于它是同步执行的,没有利用并行处理的能力,所以在处理大量数据时可能会比较慢。
接下来是 getPageAll() 方法。这个方法采用了分页查询的方式,每次只获取一部分数据,从而避免了内存溢出的问题。然而,它也是同步执行的,没有利用多线程或并行处理的能力。如果每次分页查询的数据量仍然很大,或者需要查询的轮数很多,那么这种方法的效率可能仍然会受到限制。
最后是 multithreading() 方法。这个方法利用了多线程并行处理的能力,将查询任务分配给多个线程同时执行。这样,可以同时从数据库中获取多个数据块,从而提高了整体的查询效率。当然,多线程也带来了一定的复杂性和开销,比如线程创建、管理和同步等。但是,在数据量较大且服务器资源足够的情况下,多线程方法通常能够显著提高查询效率。
综上所述,从效率角度来看,我们可以将这三种方式按以下顺序排序(从高到低):
- multithreading():利用多线程并行处理,能够同时执行多个查询任务,提高了整体的查询效率。
- getPageAll():采用分页查询的方式,避免了内存溢出的问题,但仍然是同步执行的。
- list():直接加载所有数据到内存中,可能导致内存溢出,且没有利用并行处理的能力,效率较低。
需要注意的是,这个排序是基于一般情况下的假设。在实际应用中,效率还受到其他因素的影响,如数据库的性能、网络延迟、服务器资源等。因此,在选择使用哪种方式时,还需要根据具体的场景和需求进行评估和测试。
Controller层核心代码
package com.interviewbar.system.controller; import com.interviewbar.common.vo.Result; import com.interviewbar.system.entity.DeviceTestOne; import com.interviewbar.system.service.DeviceTestOneService; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.concurrent.*; /** * @author FangGL */ @RestController @RequestMapping("/deviceTestOne") public class DeviceTestOneController { private final DeviceTestOneService deviceTestOneService; public DeviceTestOneController(DeviceTestOneService deviceTestOneService) { this.deviceTestOneService = deviceTestOneService; } /** * 查询表中所有数据 * @return */ @GetMapping("/list") public Result list() { List<DeviceTestOne> list = deviceTestOneService.list(); return Result.success(list); } /** * 查询表中所有数据 * @return */ @GetMapping("/getPageAll") public Result getPageAll() { List<DeviceTestOne> list = new ArrayList<>(); int limit = 50000; long count = deviceTestOneService.count(); //循环次数 long cycles = count / limit+1; for (int i = 0; i < cycles; i++) { long startIdx = i * limit; long endIdx = (i + 1) * limit; if (endIdx > count){ endIdx = count; } List<DeviceTestOne> list1 = deviceTestOneService.getPageAll(startIdx, endIdx); list.addAll(list1); } return Result.success(list); } @GetMapping("/multithreading") public Result multithreading() { List<DeviceTestOne> list = new ArrayList<>(); int limit = 50000; long count = deviceTestOneService.count(); //循环次数 long cycles = count / limit+1; CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(7); ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(7); for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) { final int currentIndex = i; executorService.submit(() -> { long startIdx = currentIndex * limit; long endIdx = (currentIndex + 1) * limit; if (endIdx > count) { endIdx = count; } List<DeviceTestOne> list1 = deviceTestOneService.getPageAll(startIdx, endIdx); list.addAll(list1); latch.countDown(); // 通知完成 }); } try { // 等待所有任务完成 latch.await(); // 没有异常发生,开始关闭线程池 executorService.shutdown(); // 等待线程池关闭完成,或者达到超时时间 if (!executorService.awaitTermination(60, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) { // 如果超时,强制关闭线程池 executorService.shutdownNow(); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { // 发生中断异常,重新设置中断状态 Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); // 尝试关闭线程池 executorService.shutdownNow(); } return Result.success(list); } } 测试数据生成
建表语句
CREATE TABLE `x_device_test_one` ( `line_id` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL, `device_id` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL, `date_partition` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL, `status` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL, `card_swipes_count` bigint(20) DEFAULT NULL, `station_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, `id` int(255) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=340004 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 ROW_FORMAT=DYNAMIC; 数据生成根据自己需求生成适合数据量即可 第一步:运行下面语句 DELIMITER // CREATE PROCEDURE InsertTestData() BEGIN DECLARE i INT DEFAULT 0; WHILE i < 300000 DO INSERT INTO x_device_test_one (line_id, device_id, date_partition, status, card_swipes_count, station_id) VALUES ( CONCAT('line_', FLOOR(RAND() * 1000000)), -- 假设line_id是一个随机生成的字符串 CONCAT('device_', FLOOR(RAND() * 1000000)), -- 假设device_id是一个随机生成的字符串 DATE_FORMAT(NOW() - INTERVAL FLOOR(RAND() * 3650) DAY, '%Y-%m-%d'), -- 假设date_partition是过去3650天内的随机日期 CONCAT('status_', FLOOR(RAND() * 5) + 1), -- 假设有5种状态,编号从1到5 FLOOR(RAND() * 10000), -- 假设card_swipes_count是一个0到9999之间的随机数 FLOOR(RAND() * 1000) -- 假设station_id是一个0到999之间的随机数 ); SET i = i + 1; END WHILE; END // DELIMITER ; 第二步:运行下面语句 -- 调用存储过程以插入数据 CALL InsertTestData(); 注意:如果你不再需要它,才执行这一条 -- 删除存储过程 DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS InsertTestData; 测试报告
单线程+分页查询获取所有数据-测试报告
平均耗时4.15秒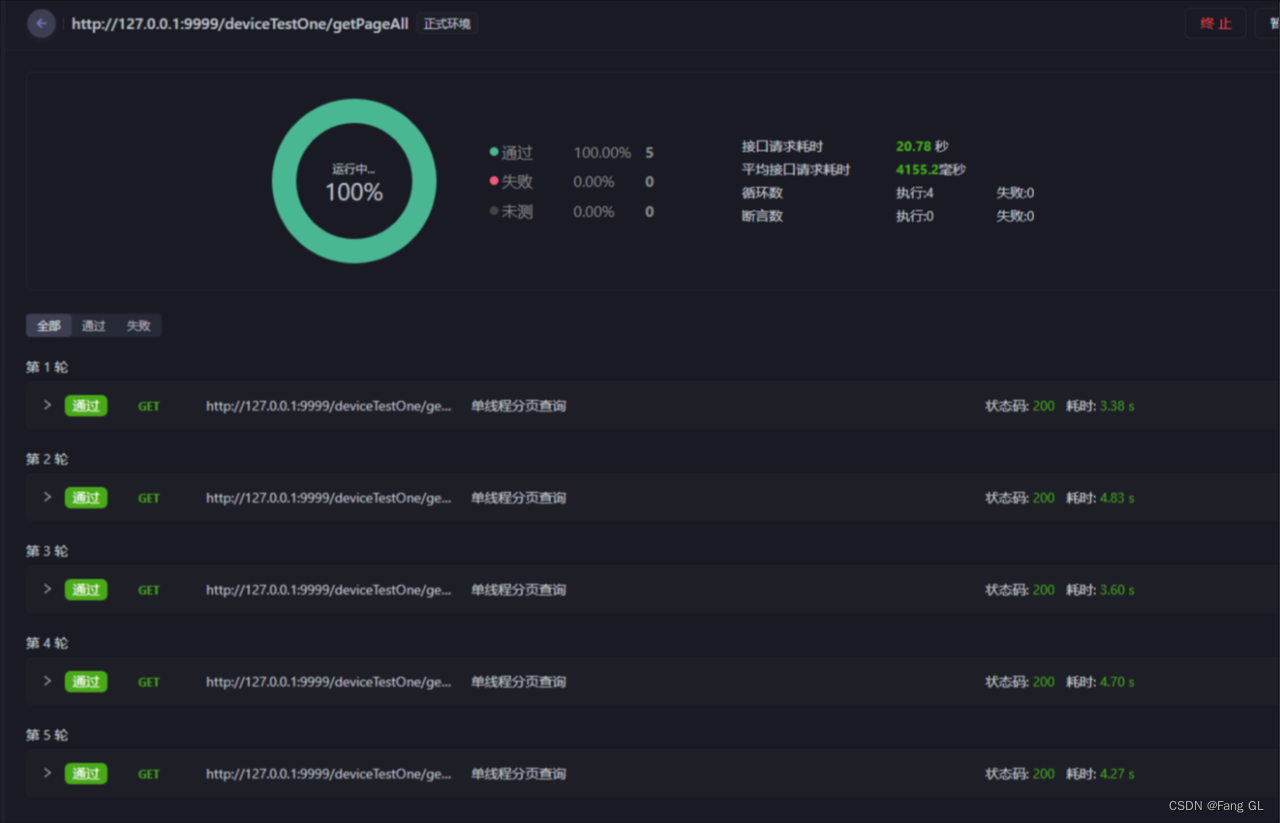
单线程+直接查询获取所有数据-测试报告
平均耗时3.14秒
虽然单线程直接查询库中所有数据要比单线程分页快,但是存在极大风险。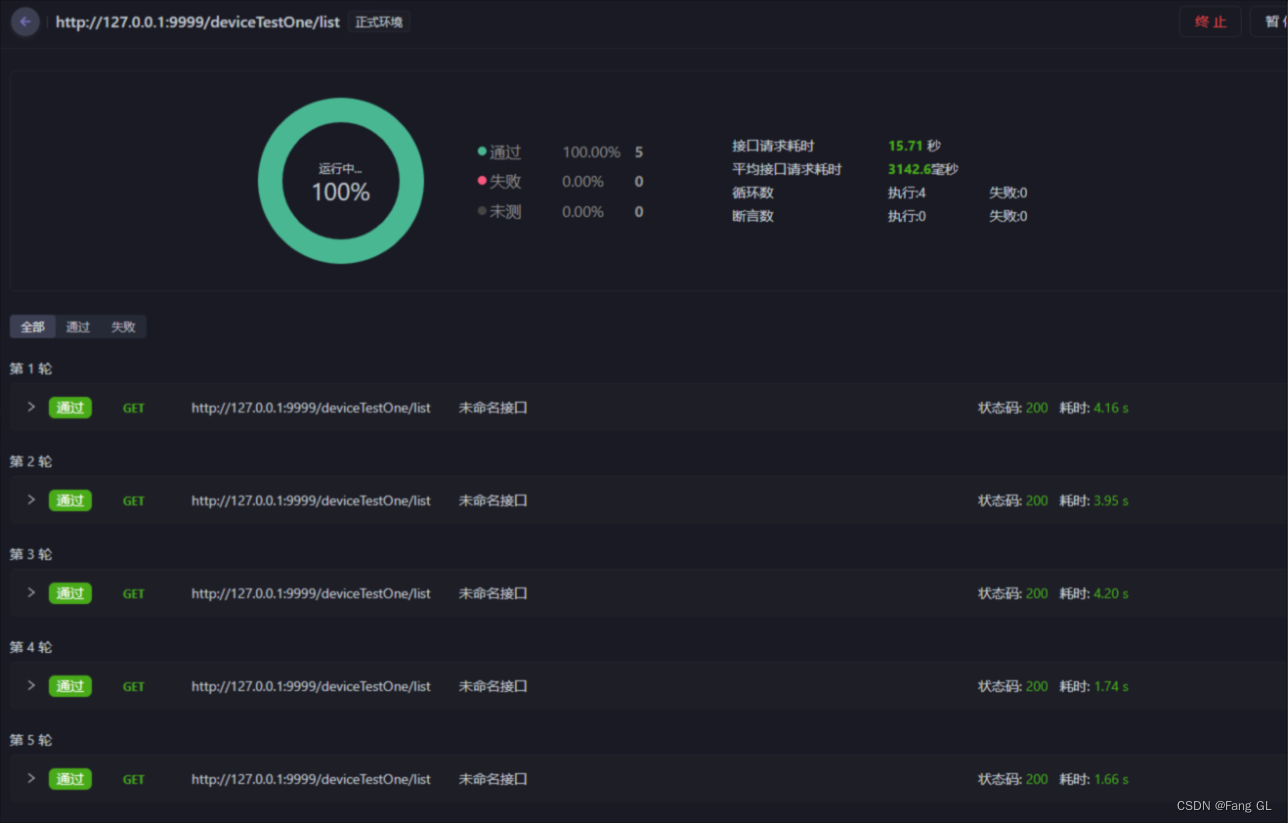
多线程+分页查询获取所有数据-测试报告
平均耗时1秒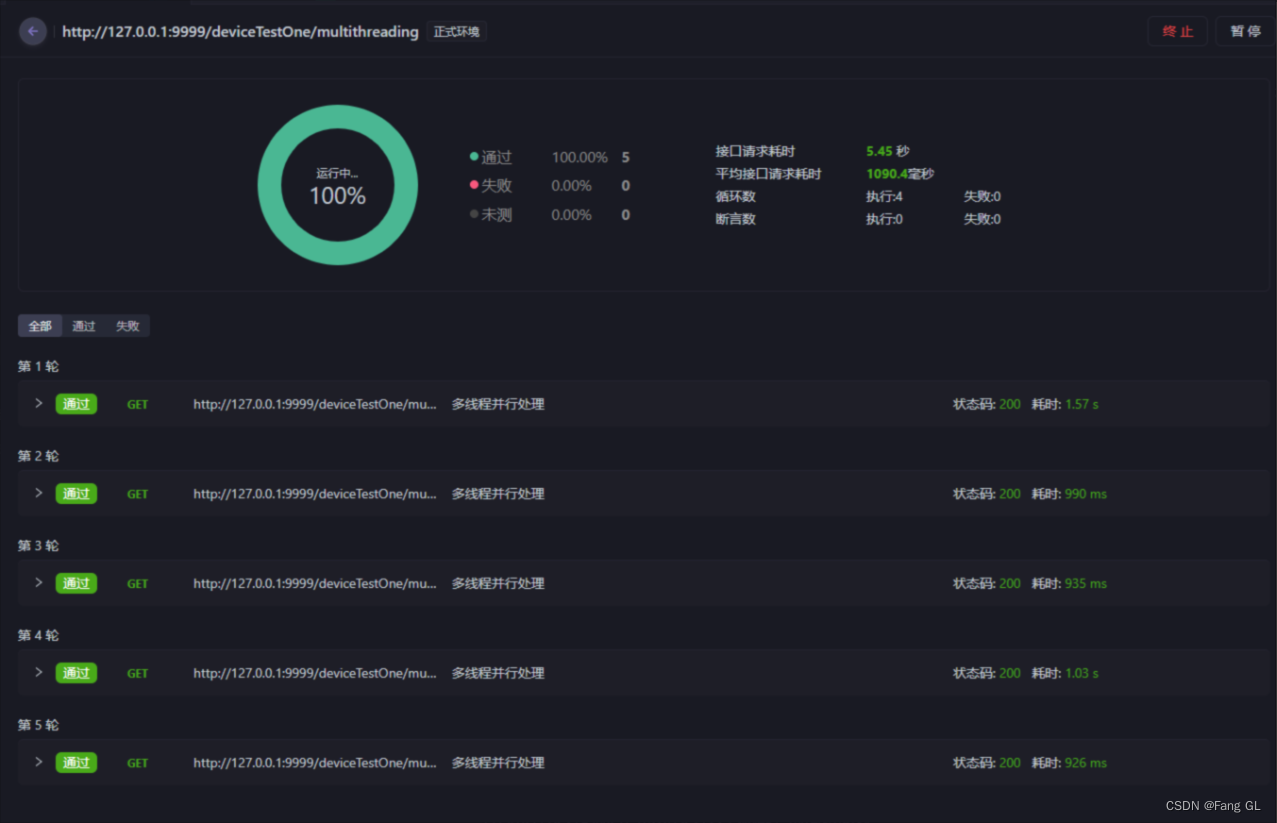
参考文档:https://www.cnblogs.com/iamamg97/p/15579233.html
源码获取
在笔者的代码仓库中已存放本次测试的代码及数据库,欢迎下载并start🤖
https://gitee.com/fanggaolei/multithreading-project
