gitee源码获取链接:
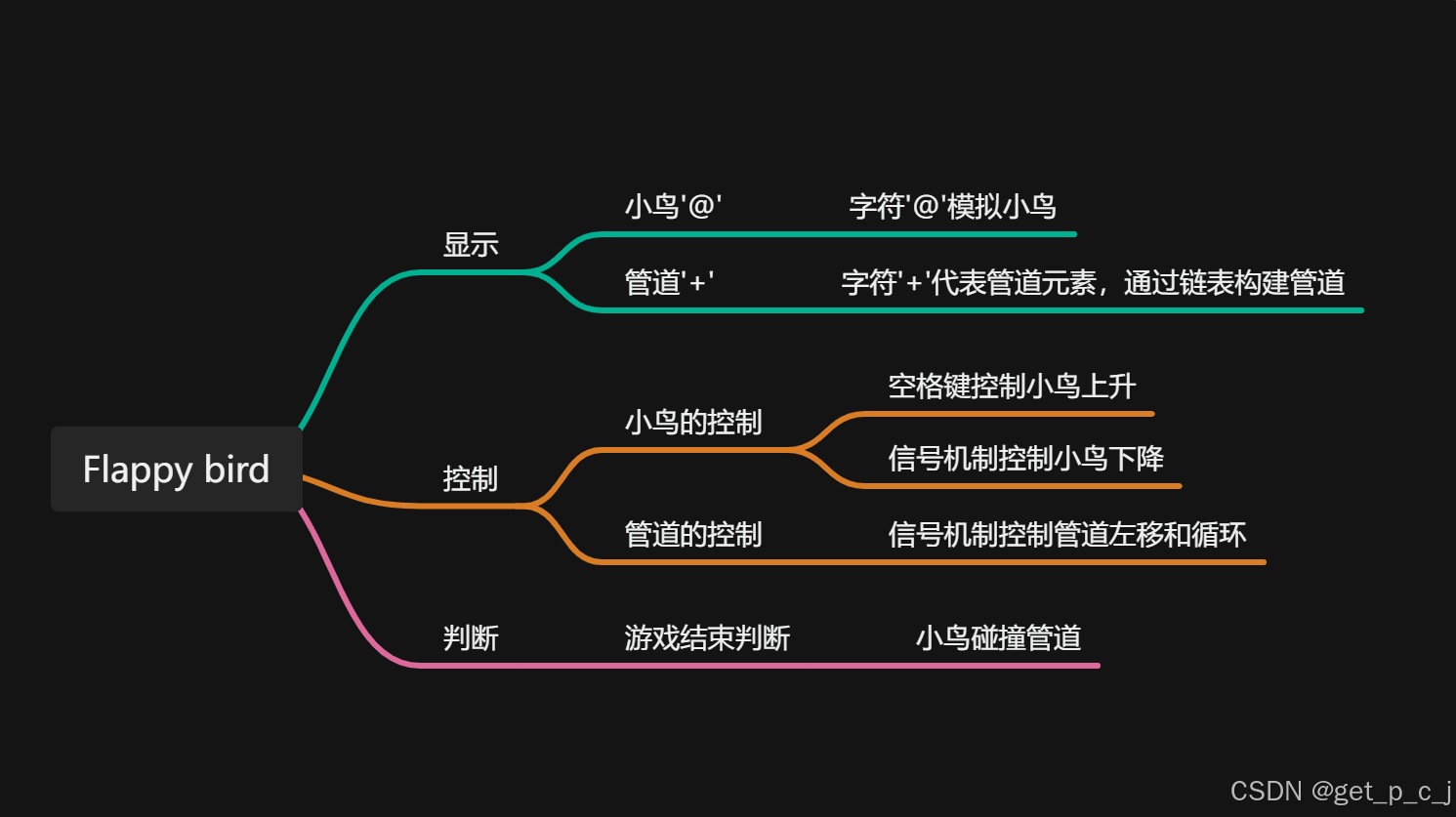
一、项目功能
- 按下空格键小鸟上升,不按空格键小鸟下降。
- 搭建小鸟需要穿过的管道。
- 管道自动左移和创建。
- 小鸟与管道碰撞游戏结束。
二、知识储备
- C语言。
- 数据结构——链表。
- Ncurses库。
- 信号机制。
三、项目框图
四、Ncurses 库
问题引入?
- 如何显示游戏界面?
- 如何实现空格键控制小鸟上升?
4.1 Ncurses 库介绍
Ncurses是最早的System V Release 4.0 (SVr4)中 curses的一个克隆和升级。这是一个可自由配置的库,完全兼容旧版本curses。
Ncurses构成了一个工作在底层终端代码之上的封装,并向用户提供了一个灵活高效的API(Application Programming Interface 应用程序接口)。它提供了创建窗口界面,移动光标,产生颜色,处理键盘按键等功能。使程序员编写应用程序不需要关心那些底层的终端操作。
简而言之,它是一个管理应用程序在字符终端显示的函数库。
4.2 Ncurses 库函数
注:
- 只介绍需要用到的库函数,其他的如果有兴趣可以自行了解。
- 为了能够使用Ncurses库,必须在源程序中将#include<curses.h>包括进来,而且在编译的需 要与它链接起来。
- 在gcc中可以使用参数-lncurses进行编译.
函数介绍:
1. initscr(void); 是curses模式的入口。将终端屏幕初始化为curses模式,为当前屏幕和相关的数据结构分配内存。 2. int endwin(void); 是curses模式的出口,退出curses模式,释放curses子系统和相关数据结构占用的内存。 3. int curs_set(int visibility); 设置光标是否可见,visibility:0(不可见),1(可见) 4. int move(int new_y, int new_x); 将光标移动到new_y所指定的行和new_x所指定的列 5. int addch(const chtype char); 在当前光标位置添加字符 6. int refresh(void); 刷新物理屏幕。将获取的内容显示到显示器上。 7. int keypad(WINDOW *window_ptr, bool key_on); 允许使用功能键。exp:keypad(stdscr,1);//允许使用功能按键 8. int getch(void); 读取键盘输入的一个字符 9. chtype inch(void); 获取当前光标位置的字符。 注:curses有自己的字符类型chtype,使用时强制类型转换为char 10. int start_color(void); 启动color机制,初始化当前终端支持的所有颜色 11. int init_pair(short pair_number, short foreground, short background); 配置颜色对 COLOR_BLACK 黑色 COLOR_MAGENTA 品红色 COLOR_RED 红色 COLOR_CYAN 青色 COLOR_GREEN 绿色 COLOR_WHITE 白色 COLOR_YELLOW 黄色 COLOR_BLUE 蓝色 12. int COLOR_PAIR(int pair_number); 设置颜色属性,设置完颜色对,可以通过COLOR_PAIR实现 13. int attron(chtype attribute); 启用属性设置 14. int attroff(chtype attribute); 关闭属性设置4.3 Ncurses 库安装
安装命令:sudo apt-get install libncurses5-dev
五、信号机制
问题引入?
- getch()阻塞获取键盘按键输入,怎么操作才能不影响小鸟下落和管道移动?
5.1 信号
在Linux中,软中断信号(signal,简称为信号)是在软件层次上对中断的一种模拟,用来通知进程发生了异步事件。内核可以因为内部事件而给进程发送信号,通知进程发生了某个事件。
信号响应的方式:
- 忽略信号,即对信号不做任何处理;
- 捕捉信号,即信号发生时执行用户自定义的信号处理函数。
- 执行缺省操作,Linux对每种信号都规定了默认操作。
在linux中查看信号可通过命令:kill -l
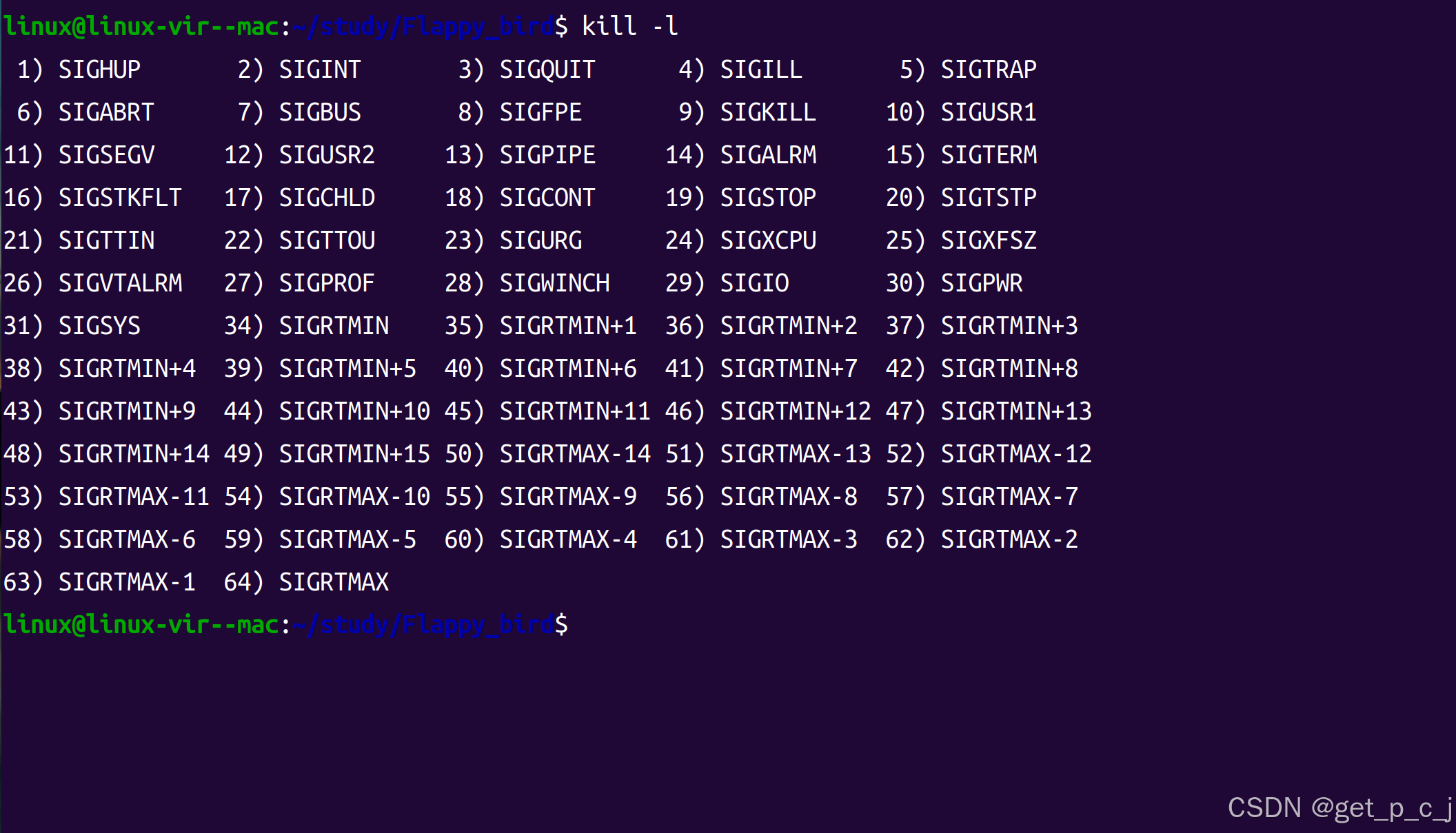
一共62个信号,因为31~34中间缺了两个。
这里介绍两个信号:
- SIGINT:通知终端结束当前终端的所有进程。
- SIGALRM:通知进程定时器时间已到。
5.2 信号的检测与处理流程
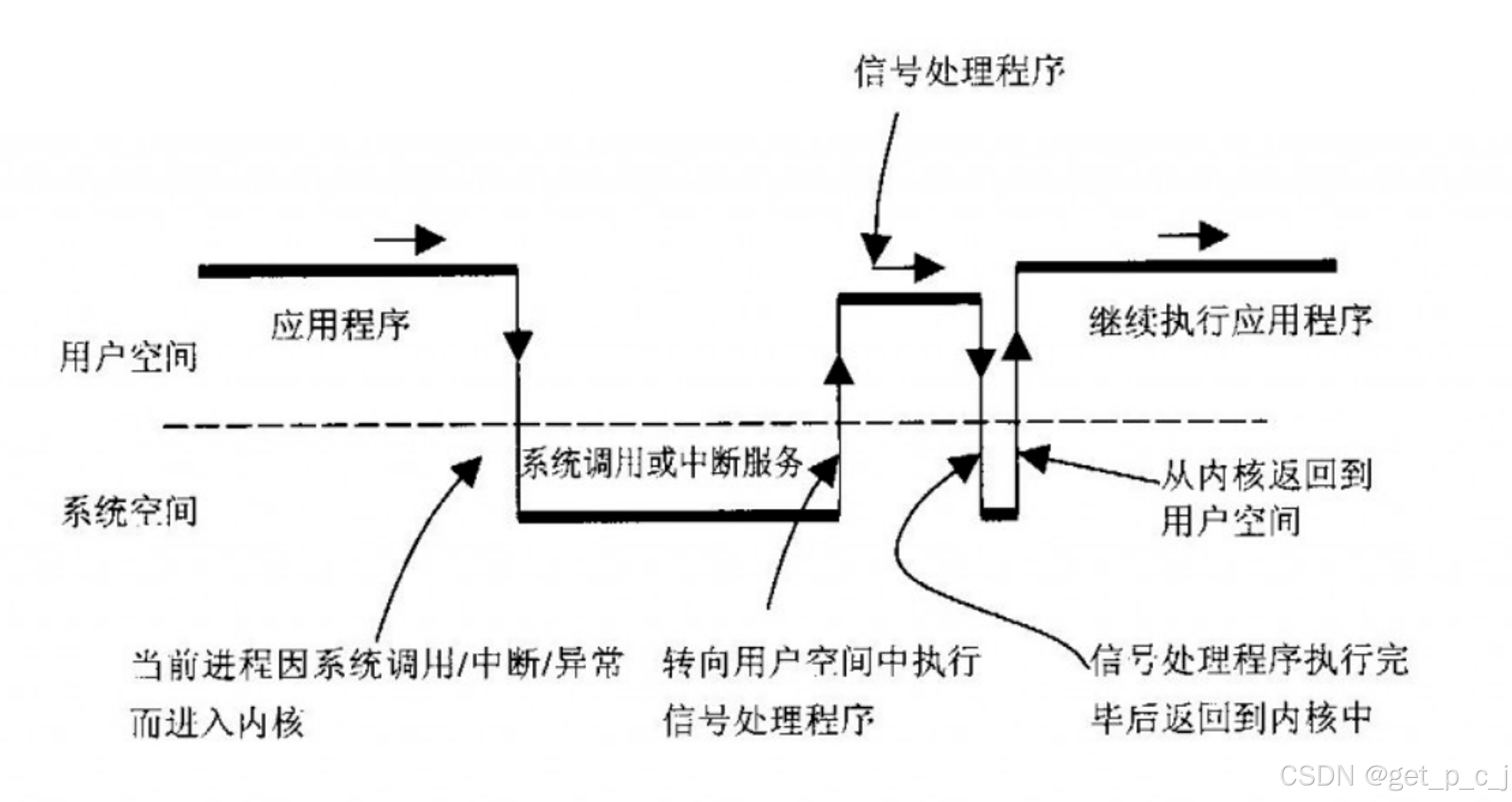
当我们的代码在执行过程中,一旦遇到系统调用或中断服务,就会进入到内核中,检测是不是有信号产生,如果有信号产生,就会执行信号处理函数,在信号处理函数执行完后会返回到内核中,找到进入内核的断点,从断点回到应用程序继续执行。
我们的项目在应用程序中设定好定时时间和信号处理函数,当定时时间到达时,会进入内核,在内核中调用信号处理函数,执行处理函数后回到应用程序继续执行。那么从进入内核到返回应用程序这中间的过程都是由内核来调度的,所以我们可以把小鸟的下落,管道的移动都放在信号处理程序中,由内核来调度。这样就与getch()阻塞获取键盘按键输入没有关系了。信号机制就是用来解决这一问题。
5.3 定时功能实现。
1、 设置信号响应方式——signal
#include <unistd.h> #include <signal.h> typedef void (*sighandler_t)(int); sighandler_t signal(int signum, sighandler_t handler); 成功时返回原先的信号处理函数,失败时返回SIG_ERR signum:指明了所要处理的信号类型 handler:描述了与信号关联的动作 SIG_DFL代表缺省方式; SIG_IGN 代表忽略信号; 指定的信号处理函数代表捕捉方式 2、设置定时器
struct itimerval { struct timeval it_interval; /* 计时器重新启动的间歇值 */ struct timeval it_value; /* 计时器安装后首次启动的初 }; 始值,之后就没有用 */ struct timeval { long tv_sec; /* 秒 */ long tv_usec; /* 微妙*/ }; 3、启动定时器
int setitimer(int which, const struct itimerval *value, struct itimerval *ovalue) 参数: which:间歇计时器类型, ITIMER_REAL //数值为0,发送的信号是SIGALRM。 struct itimerval *value:将value指向的结构体设为计时器的当前值, struct itimerval *ovalue:保存计时器原有值。一般设置为NULL。 返回值: 成功返回0。失败返回-1。 4、功能实现
#include <stdio.h> #include <sys/time.h> #include <signal.h> void handler(int sig){ printf("time starts\n"); } int main() { signal(SIGALRM, handler); /*设置定时时间*/ struct itimerval timer; timer.it_value.tv_sec = 3; // 首次启动定时时间 timer.it_value.tv_usec = 0; timer.it_interval.tv_sec = 1; // 之后每次定时时间 timer.it_interval.tv_usec = 0; /*启动定时*/ setitimer(ITIMER_REAL, &timer, NULL); while(1); return 0; } 六、项目功能实现
项目安排
阶段1:初始化工作,小鸟功能实现。
阶段2:管道功能实现。
阶段3:完善代码,进行项目总结。
6.1 阶段一
1、初始化NCurses库
2、设置定时时间
3、实现小鸟功能
- 显示小鸟
- 清除小鸟
- 移动小鸟
#include <stdio.h> #include <curses.h> #include <signal.h> #include <sys/time.h> #define BIRD '@' #define BLACK ' ' int bird_x, bird_y; // 代表小鸟坐标 void show_bird(); // 显示小鸟 void clear_bird(); // 清除小鸟 void move_bird(); // 移动小鸟 void init_curses(); // curses库初始化 int set_timer(int ms_t); // 设置定时时间 --ms void handler(int sig); // 信号处理函数 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { bird_y = 15; // 行 bird_x = 10; // 列 init_curses(); signal(SIGALRM, handler); set_timer(500); // 500ms show_bird(); move_bird(); return 0; } void init_curses(){ initscr(); // 进入curses模式 curs_set(0); // 禁止光标显示 noecho(); // 禁止输入字符显示 keypad(stdscr, 1); // 启动功能按键 start_color(); // 启动颜色机制 } int set_timer(int ms_t){ struct itimerval timer; long t_sec, t_usec; int ret; t_sec = ms_t / 1000; // s t_usec = (ms_t % 1000) * 1000; // us timer.it_value.tv_sec = t_sec; timer.it_value.tv_usec = t_usec; // 首次启动定时值 timer.it_interval.tv_sec = t_sec; timer.it_interval.tv_usec = t_usec; // 定时时间间隔 ret = setitimer(ITIMER_REAL, &timer, NULL); return ret; } void handler(int sig){ clear_bird(); bird_y++; show_bird(); } void show_bird(){ move(bird_y, bird_x); addch(BIRD); refresh(); } void clear_bird(){ move(bird_y, bird_x); addch(BLACK); refresh(); } void move_bird(){ char key; while(1){ key = getch(); if(key == BLACK){ clear_bird(); bird_y--; show_bird(); } } } 6.2 阶段二
- 创建链表
- 显示管道
- 清除管道
- 移动管道
/*定义关于管道的结构体*/ typedef struct Pipe{ int x; // 列坐标 int y; // 横坐标 struct Pipe *next; }Pipe_node, *Pipe_list; Pipe_list head, tail; void creat_list(); // 创建链表 void show_pipe(); // 显示管道 void clear_pipe(); // 清除管道 void move_pipe(); // 移动管道 // 创建链表,每个节点表示一个管道 void creat_list(){ int i; Pipe_list p, new; // 分配头节点并初始化 head = (Pipe_list)malloc(sizeof(Pipe_node)); head->next = NULL; p = head; // p用于遍历链表 for(i = 0; i < 5; i++){ new = (Pipe_list)malloc(sizeof(Pipe_node)); // 分配新节点 new->x = (i + 1) * 20; // 设置管道的水平位置 new->y = rand() % 11 + 5; // 设置管道的垂直位置(5-15行) new->next = NULL; p->next = new; // 将新节点添加到链表 p = new; // 移动p到链表的末尾 } tail = p; // tail指向链表的最后一个节点 } // 显示链表中的所有管道 void show_pipe(){ Pipe_list p; int i, j; p = head->next; // 跳过头节点 while(p){ for(i = p->x; i < p->x+10; i++){ // 遍历管道的每个水平位置 // 绘制管道的上半部分 for(j = 0; j < p->y; j++){ move(j, i); addch(PIPE); // 假设PIPE是一个宏或常量,表示管道字符 } // 绘制管道的下半部分(假设管道高度固定为5) for(j = p->y+5; j < 25; j++){ move(j, i); addch(PIPE); } } refresh(); // 刷新屏幕以显示管道 p = p->next; } } // 清除链表中的所有管道 void clear_pipe(){ // 类似于show_pipe,但用BLACK字符替换PIPE // ... (省略了与show_pipe相同的循环结构,但将addch(PIPE)替换为addch(BLACK)) } // 将所有管道向左移动一个单位 void move_pipe(){ Pipe_list p; p = head->next; while(p){ p->x--; // 将每个管道的x坐标减一 p = p->next; } // 注意:这里没有处理管道移出屏幕的情况 }
6.3 阶段三
- 判断游戏结束:小鸟与管道碰撞
- 循环创建管道
- 为管道和小鸟添加色彩
/*游戏结束判断*/ if((char)inch() == PIPE){ set_timer(0); endwin(); exit(0); } /*循环管道创建*/ int i, j; p = head->next; if(p->x == 0){ head->next = p->next; for(i = p->x; i < p->x+10; i++){ /*清除上半部分管道*/ for(j = 0; j < p->y; j++){ move(j, i); addch(BLACK); } /*清除部分管道创建*/ for(j = p->y+5; j < 25; j++){ move(j, i); addch(BLACK); } refresh(); } free(p); new = (Pipe_list)malloc(sizeof(Pipe_list)); new->x = tail->x + 20; new->y = rand() % 11 + 5; new->next = NULL; tail->next = new; tail = new; } init_pair(1, COLOR_WHITE, COLOR_RED); //小鸟颜色设置 init_pair(2, COLOR_WHITE, COLOR_GREEN); //管道颜色设置 七、完整项目源码
#include <stdio.h> #include <curses.h> #include <signal.h> #include <sys/time.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <time.h> #define BIRD '@' #define BLACK ' ' #define PIPE '+' /*定义关于管道的结构体*/ typedef struct Pipe{ int x; // 列坐标 int y; // 横坐标 struct Pipe *next; }Pipe_node, *Pipe_list; Pipe_list head, tail; void creat_list(); // 创建链表 void show_pipe(); // 显示管道 void clear_pipe(); // 清除管道 void move_pipe(); // 移动管道 int bird_x, bird_y; // 代表小鸟坐标 void show_bird(); // 显示小鸟 void clear_bird(); // 清除小鸟 void move_bird(); // 移动小鸟 void init_curses(); // curses库初始化 int set_timer(int ms_t); // 设置定时时间 --ms void handler(int sig); // 信号处理函数 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { bird_y = 15; // 行 bird_x = 13; // 列 init_curses(); signal(SIGALRM, handler); set_timer(500); // 500ms srand(time(0)); // 随机种子 creat_list(); show_pipe(); show_bird(); move_bird(); return 0; } void init_curses(){ initscr(); // 进入curses模式 curs_set(0); // 禁止光标显示 noecho(); // 禁止输入字符显示 keypad(stdscr, 1); // 启动功能按键 start_color(); // 启动颜色机制 init_pair(1, COLOR_WHITE, COLOR_RED); //小鸟颜色设置 init_pair(2, COLOR_WHITE, COLOR_GREEN); //管道颜色设置 } int set_timer(int ms_t){ struct itimerval timer; long t_sec, t_usec; int ret; t_sec = ms_t / 1000; // s t_usec = (ms_t % 1000) * 1000; // us timer.it_value.tv_sec = t_sec; timer.it_value.tv_usec = t_usec; // 首次启动定时值 timer.it_interval.tv_sec = t_sec; timer.it_interval.tv_usec = t_usec; // 定时时间间隔 ret = setitimer(ITIMER_REAL, &timer, NULL); return ret; } void handler(int sig){ Pipe_list p, new; int i, j; /*小鸟下落*/ clear_bird(); bird_y++; show_bird(); /*游戏结束判断*/ if((char)inch() == PIPE){ set_timer(0); endwin(); exit(0); } p = head->next; if(p->x == 0){ head->next = p->next; for(i = p->x; i < p->x+10; i++){ /*清除上半部分管道*/ for(j = 0; j < p->y; j++){ move(j, i); addch(BLACK); } /*清除部分管道创建*/ for(j = p->y+5; j < 25; j++){ move(j, i); addch(BLACK); } refresh(); } free(p); new = (Pipe_list)malloc(sizeof(Pipe_list)); new->x = tail->x + 20; new->y = rand() % 11 + 5; new->next = NULL; tail->next = new; tail = new; } /*管道移动*/ clear_pipe(); move_pipe(); show_pipe(); } void show_bird(){ attron(COLOR_PAIR(1)); move(bird_y, bird_x); addch(BIRD); refresh(); attroff(COLOR_PAIR(1)); } void clear_bird(){ move(bird_y, bird_x); addch(BLACK); refresh(); } void move_bird(){ char key; while(1){ key = getch(); if(key == BLACK){ clear_bird(); bird_y--; show_bird(); /*游戏结束判断*/ if((char)inch() == PIPE){ set_timer(0); endwin(); exit(0); } } } } void creat_list(){ int i; Pipe_list p, new; head = (Pipe_list)malloc(sizeof(Pipe_node)); head->next = NULL; p = head; for(i = 0; i < 5; i++){ new = (Pipe_list)malloc(sizeof(Pipe_node)); new->x = (i + 1) * 20; new->y = rand() % 11 + 5; // 5-15行 new->next = NULL; p->next = new; p = new; } tail = p; } void show_pipe(){ Pipe_list p; int i, j; p = head->next; attron(COLOR_PAIR(2)); while(p){ for(i = p->x; i < p->x+10; i++){ /*创建上半部分管道*/ for(j = 0; j < p->y; j++){ move(j, i); addch(PIPE); } /*下半部分管道创建*/ for(j = p->y+5; j < 25; j++){ move(j, i); addch(PIPE); } } refresh(); p = p->next; } attroff(COLOR_PAIR(2)); } void clear_pipe(){ Pipe_list p; int i, j; p = head->next; while(p){ for(i = p->x; i < p->x+10; i++){ /*创建上半部分管道*/ for(j = 0; j < p->y; j++){ move(j, i); addch(BLACK); } /*下半部分管道创建*/ for(j = p->y+5; j < 25; j++){ move(j, i); addch(BLACK); } } refresh(); p = p->next; } } void move_pipe(){ Pipe_list p; p = head->next; while(p){ p->x--; p = p->next; } }