这节课开始讲链表相关的题目, 在面试中经常会被考到。
掌握了基本套路之外,还有画画图,看看这些指针在哪里, 无他,唯手熟尔!
性质:
反转结束后,从原来的链表上看:
pre 指向反转这一段的未尾
cur 指向反转这一段后续的下一个节点
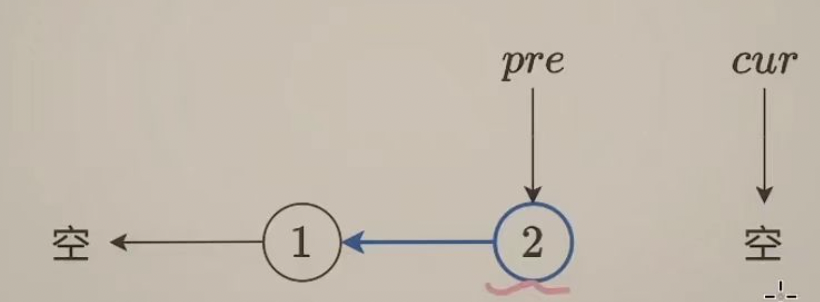
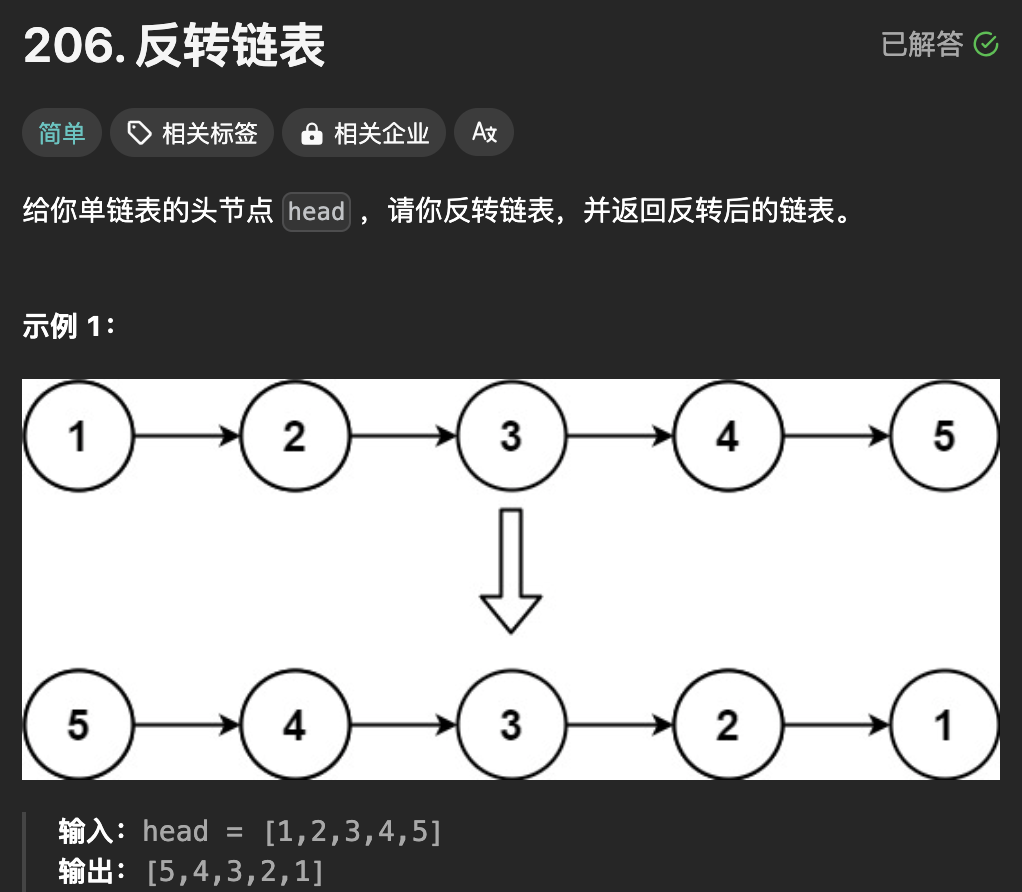
反转链表是经典题,背也得背熟(开玩笑) ,还是理解原理比较好。
做链表题还是要画画,指针的方向怎么变化很容易
我懒得画图了
解法:
1️⃣ 迭代法
1 -> 2 - > 3 -> None 为例
变化的步骤 :
None <- 1 2 -> 3 -> None
None <- 1 <- 2 3 -> None
None <- 1 <-2 <-3
返回第一个最后一个节点 。
需要使用三个指针, pre, cur, nxt 。 nxt 指针需要保存当前遍历节点的下一个指针,当操作了当前节点的next 之后,这个节点就找不到了,需要记录下来。
代码:
# Definition for singly-linked list. class ListNode(object): def __init__(self, val=0, next=None): self.val = val self.next = next class Solution(object): def reverseList(self, head): """ :type head: ListNode :rtype: ListNode """ pre = None cur = head while cur : nxt = cur.next cur.next = pre pre = cur cur = nxt return pre def print_linked_list(self, head): current = head while current: print(current.val, end=" -> ") current = current.next print("None") def convert_list_to_link_list(self, array): dummy = ListNode(-1) cur = dummy for val in array: cur.next = ListNode(val) cur = cur.next return dummy.next s = Solution() a = [1,2,3] a_head = s.convert_list_to_link_list(a) res = s.reverseList(a_head) s.print_linked_list(res) 2️⃣ 递归
递归的写法,
1 -> 2 -> 3 -> None
当自身当成一个对递归函数,
终止条件: 如果 空链表或者只有一个节点,返回本身。
拆解问题: 反转 2-> 3 -> None ,得到 3-> 2 ->None ,这就是子问题,是个“递”的过程。
归的过程: 把 子问题返回的结果,返回给上一层。 从 : 3 -> 2 <-1 , ==> 3 -> 2 -> 1 -> None
返回结果。
代码:
class ListNode(object): def __init__(self, val=0, next=None): self.val = val self.next = next class Solution(object): def reverseList01(self, head): """ :type head: ListNode :rtype: ListNode """ if not head or not head.next : return head node = self.reverseList01(head.next) head.next.next = head head.next = None return node 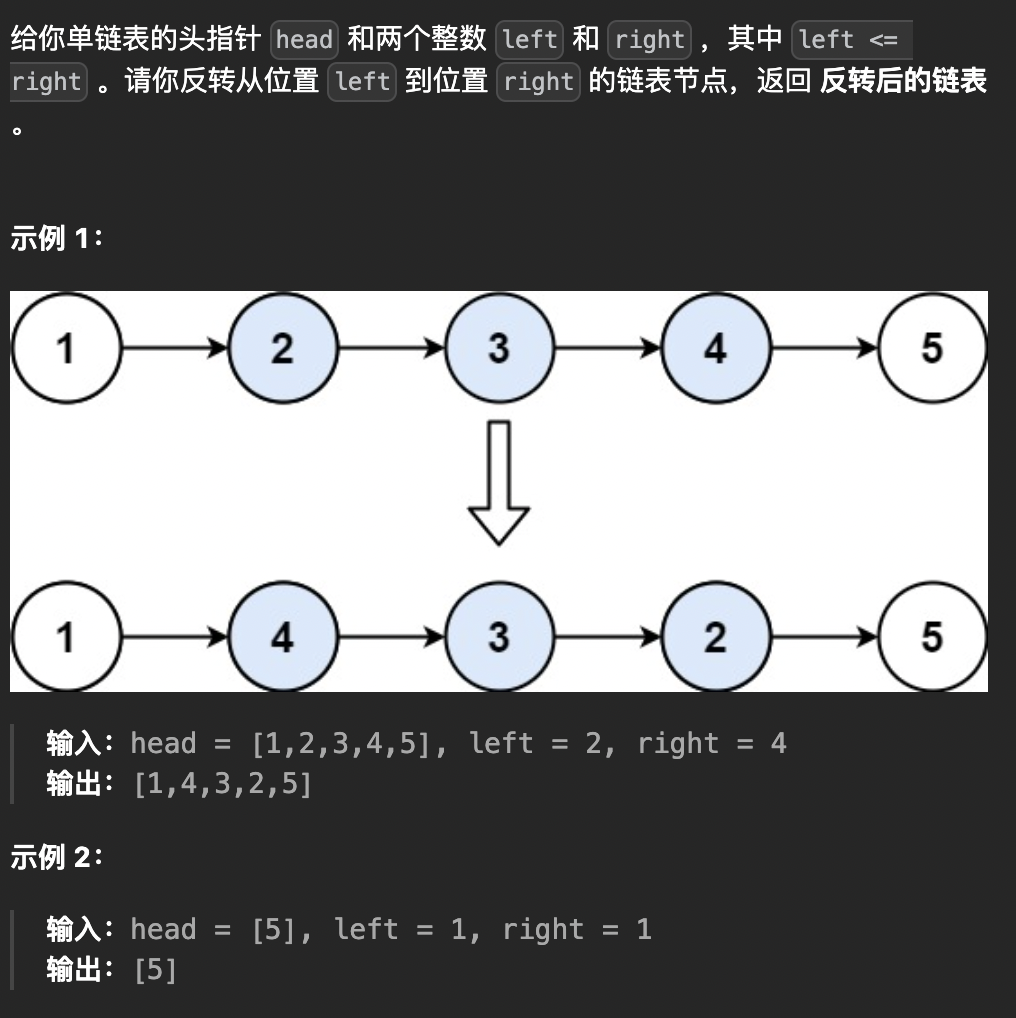
升级下问题 ,给定一个链表,反转其中的一段。
迭代法解决
1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> None , left = 2, right = 4
一样的,我们设置三个指针 , cur , pre = None, nxt
但是, 我们需要设置一个指针,记录需要反转的前一个节点。
cur 走到 2时开始迭代, 按照上题的方法迭代。
1 -> 2 <-3 <- 4 5 -> None
此时 pre 指向了 4, cur 指向了 5
接下来需要吧整个链表链接起来。
需要反转的前一个指针 指向 4 , 1 -> 4 : 1-> 4 -> 3-> 2 5 ->None
2 指向 5 ,1-> 4 -> 3-> 2 5 ->None
那这种情况下,我们返回head 就可以了吧。
但是有一种特殊情况,left = 1 , 上面返回head 指针就不行了。
我们需要在前面加个哨兵指针。
代码
# Definition for singly-linked list. class ListNode(object): def __init__(self, val=0, next=None): self.val = val self.next = next class Solution(object): def reverseBetween(self, head, left, right): """ :type head: ListNode :type left: int :type right: int :rtype: ListNode """ # 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 dummy = ListNode(next=head) p = dummy cur = head for _ in range(left-1): cur = cur.next p = p.next # cur -> 2, p -> 1 pre = None for _ in range(right - left + 1): nxt = cur.next cur.next = pre pre = cur cur = nxt # cur -> 5, pre -> 4, p -> 1 p.next.next = cur p.next = pre return dummy.next def print_linked_list(self, head): current = head while current: print(current.val, end=" -> ") current = current.next print("None") def convert_list_to_link_list(self, array): dummy = ListNode(-1) cur = dummy for val in array: cur.next = ListNode(val) cur = cur.next return dummy.next s = Solution() a = [1,2,3,4,5] a_head = s.convert_list_to_link_list(a) left = 1 right = 4 res =s.reverseBetween(a_head, left, right) s.print_linked_list(res) 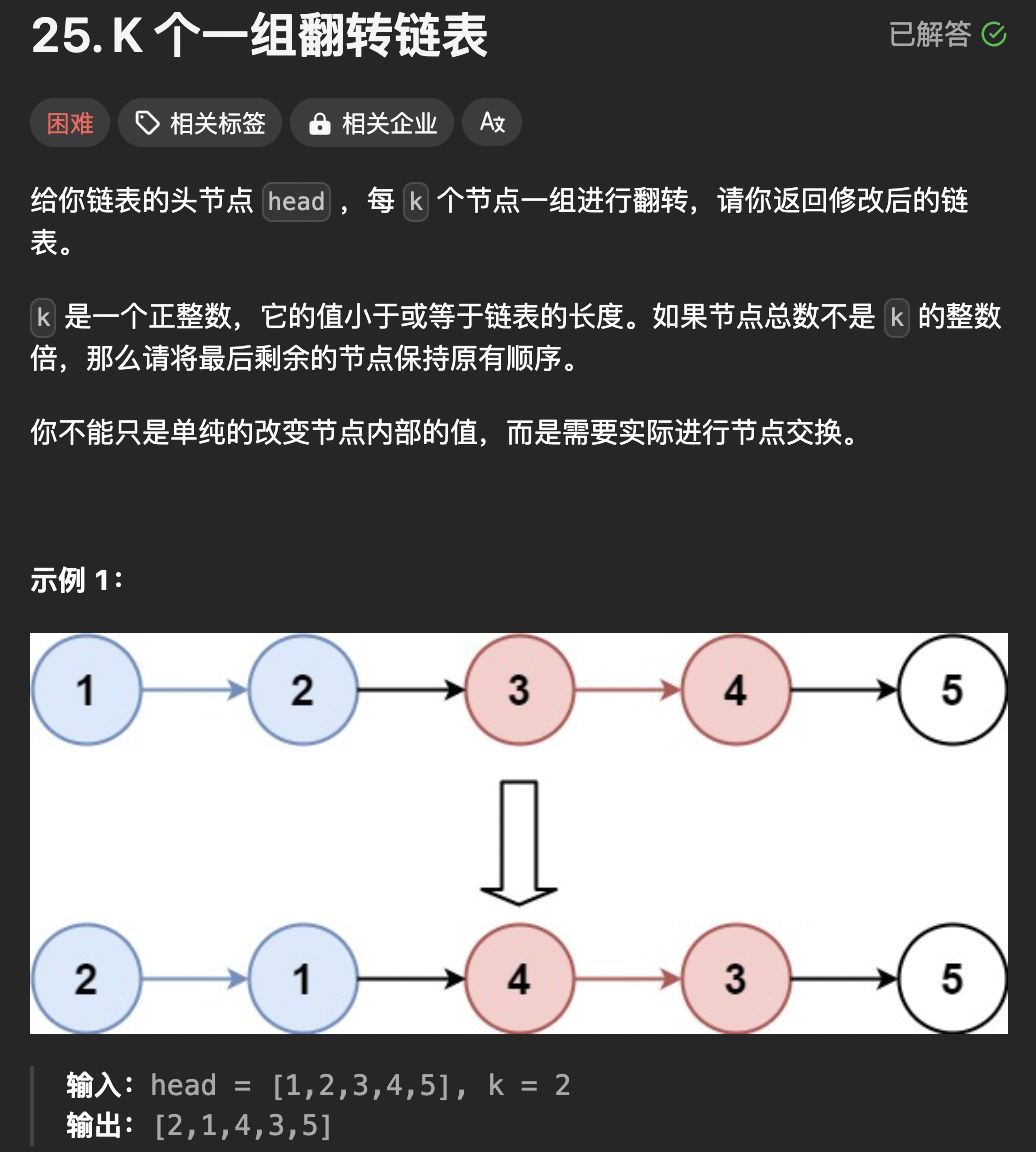
再升级一下难度,从一部分变成了多个分组。 这题在面试中也经常遇到。
解题思路:
如果不足K ,不反转。
- 先计算链表的长度 n。
举个例子吧:
1 2 3 4 5 k = 2
n = 5
设置 哨兵节点,指向head 0 -> 1 -> 2 ->3 -> 4 -> 5 -> None
第一组为例, 其实就是和上一题一样
p -> 0 ,
第一步: 反转完 0 -> 1 <- 2 3 -> 4 -> 5 -> None # 此时 pre-> 2 cur -> 3
第二部: 把 1 这个节点存一下, 然后把链表连起来, p 指向 2, 1 指向3 ,然后让 p 走到下一组要反转前一个位置。
代码:
# Definition for singly-linked list. class ListNode(object): def __init__(self, val=0, next=None): self.val = val self.next = next class Solution(object): def reverseKGroup(self, head, k): """ :type head: ListNode :type k: int :rtype: ListNode """ cur = head n = 0 while cur : n += 1 cur = cur.next pre = None cur = head dummy = ListNode(next=head) p = dummy while n >= k: # 链表还包含K个元素就反转。 n -= k for _ in range(k): nxt = cur.next cur.next = pre pre = cur cur = nxt nxt = p.next nxt.next = cur p.next = pre p = nxt return dummy.next def print_linked_list(self, head): current = head while current: print(current.val, end=" -> ") current = current.next print("None") def convert_list_to_link_list(self, array): dummy = ListNode(-1) cur = dummy for val in array: cur.next = ListNode(val) cur = cur.next return dummy.next s = Solution() a = [1,2,3,4,5] a_head = s.convert_list_to_link_list(a) res =s.reverseKGroup(a_head, 2) s.print_linked_list(res) K = 2 的情况, 可以完全写上面的代码
另外这题也可以用递归的方式来解决。
也很简单,1. 递 2. 贵, 也很简单。
# Definition for singly-linked list. class ListNode(object): def __init__(self, val=0, next=None): self.val = val self.next = next class Solution(object): def swapPairs(self, head): """ :type head: ListNode :rtype: ListNode """ # 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 # 上面使用了的迭代法来 # 现在用递归来解决此问题。 if not head or not head.next : # 不足两个,直接返回 return head # 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 node1 = head node2 = head.next node3 = node2.next node1.next = self.swapPairs(node3) node2.next = node1 return node2 def print_linked_list(self, head): current = head while current: print(current.val, end=" -> ") current = current.next print("None") def convert_list_to_link_list(self, array): dummy = ListNode(-1) cur = dummy for val in array: cur.next = ListNode(val) cur = cur.next return dummy.next s = Solution() a = [1,2,3,4,5] a_head = s.convert_list_to_link_list(a) res = s.swapPairs(a_head) s.print_linked_list(res) 