阅读量:2
目录
前言
先来看看下面这段代码:
Person* person = [Person alloc]; Person* person1 = [person init]; Person* person2 = [person init]; NSLog(@"person = %@ ** %p ** %p", person, person, &person); NSLog(@"person1 = %@ ** %p ** %p", person1, person1, &person1); NSLog(@"person2 = %@ ** %p ** %p", person2, person2, &person2); 运行结果:
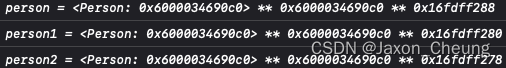
可以看出person、person1以及person2的指针变量是不同的,但却指向了同一个内存地址,所以内存的申请开辟是在alloc方法里实现的,init方法只是生成对象指针并初始化一些信息,并没有对内存空间做任何处理
alloc方法源码探索
1. alloc方法:
+ (id)alloc { return _objc_rootAlloc(self); } 2. _objc_rootAlloc()方法:
// Base class implementation of +alloc. cls is not nil. // Calls [cls allocWithZone:nil]. 从OC视角来看,alloc 实际会调用 allocWithZone: id _objc_rootAlloc(Class cls) { return callAlloc(cls, false/*checkNil*/, true/*allocWithZone*/); } 3. callAlloc()方法:
// Call [cls alloc] or [cls allocWithZone:nil], with appropriate // shortcutting optimizations. static ALWAYS_INLINE id callAlloc(Class cls, bool checkNil, bool allocWithZone=false) { if (slowpath(checkNil && !cls)) return nil; // 判断该类是否实现了自定义的 +allocWithZone:,没有则进入 if 条件语句 if (fastpath(!cls->ISA()->hasCustomAWZ())) { return _objc_rootAllocWithZone(cls, nil); } // No shortcuts available. if (allocWithZone) { return ((id(*)(id, SEL, struct _NSZone *))objc_msgSend)(cls, @selector(allocWithZone:), nil); } return ((id(*)(id, SEL))objc_msgSend)(cls, @selector(alloc)); } 4. 里面有个_objc_rootAllocWithZone()方法:
id _objc_rootAllocWithZone(Class cls, objc_zone_t) { // allocWithZone under __OBJC2__ ignores the zone parameter return _class_createInstance(cls, 0, OBJECT_CONSTRUCT_CALL_BADALLOC); } 5. _class_createInstance()方法:
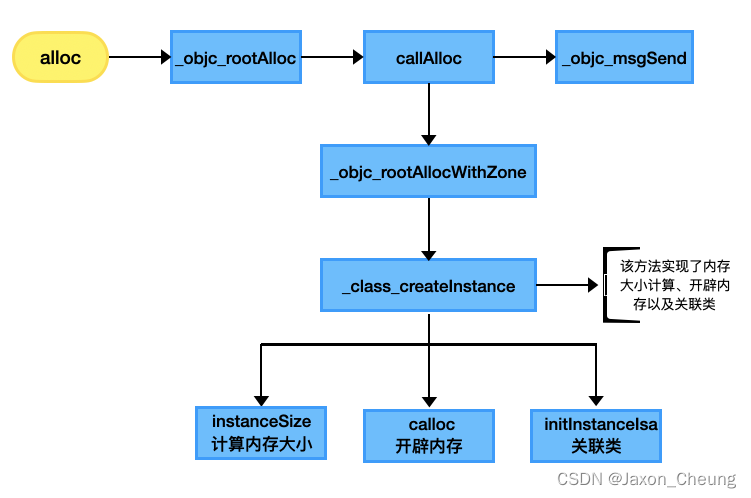
static ALWAYS_INLINE id _class_createInstance(Class cls, size_t extraBytes, int construct_flags = OBJECT_CONSTRUCT_NONE, bool cxxConstruct = true, size_t *outAllocatedSize = nil) { ASSERT(cls->isRealized()); // Read class's info bits all at once for performance bool hasCxxCtor = cxxConstruct && cls->hasCxxCtor(); bool hasCxxDtor = cls->hasCxxDtor(); bool fast = cls->canAllocNonpointer(); size_t size; size = cls->instanceSize(extraBytes); //计算开辟内存大小 if (outAllocatedSize) *outAllocatedSize = size; id obj = objc::malloc_instance(size, cls); //申请内存 if (slowpath(!obj)) { if (construct_flags & OBJECT_CONSTRUCT_CALL_BADALLOC) { return _objc_callBadAllocHandler(cls); } return nil; } if (fast) { obj->initInstanceIsa(cls, hasCxxDtor); //关联当前类的 isa } else { // Use raw pointer isa on the assumption that they might be // doing something weird with the zone or RR. // 使用原始指针 isa,假设它们可能在处理区域(zone)或资源记录(RR)时做了一些特殊操作。 obj->initIsa(cls); } if (fastpath(!hasCxxCtor)) { return obj; } construct_flags |= OBJECT_CONSTRUCT_FREE_ONFAILURE; return object_cxxConstructFromClass(obj, cls, construct_flags); } 这个方法真正开辟了内存,3个关键步骤:instanceSize()计算开辟内存大小、objc::malloc_instance()开辟内存、initInstanceIsa()关联当前类的 isa
上面第 1 个方法提到alloc实际上调用的是allocWithZone:(struct _NSZone *)zone方法,查allocWithZone:的源码同样的能寻到上述后续步骤的方法
instanceSize()方法
inline size_t instanceSize(size_t extraBytes) const { // 快速计算内存大小 if (fastpath(cache.hasFastInstanceSize(extraBytes))) { return cache.fastInstanceSize(extraBytes); } //计算类中所有变量需要的内存大小 extraBytes额外字节数一般是0 size_t size = alignedInstanceSize() + extraBytes; // CF requires all objects be at least 16 bytes. if (size < 16) size = 16; return size; } fastInstanceSize()方法
size_t fastInstanceSize(size_t extra) const { ASSERT(hasFastInstanceSize(extra)); if (__builtin_constant_p(extra) && extra == 0) { return _flags & FAST_CACHE_ALLOC_MASK16; } else { size_t size = _flags & FAST_CACHE_ALLOC_MASK; // remove the FAST_CACHE_ALLOC_DELTA16 that was added // by setFastInstanceSize return align16(size + extra - FAST_CACHE_ALLOC_DELTA16); } } align16()方法(16 字节对齐)
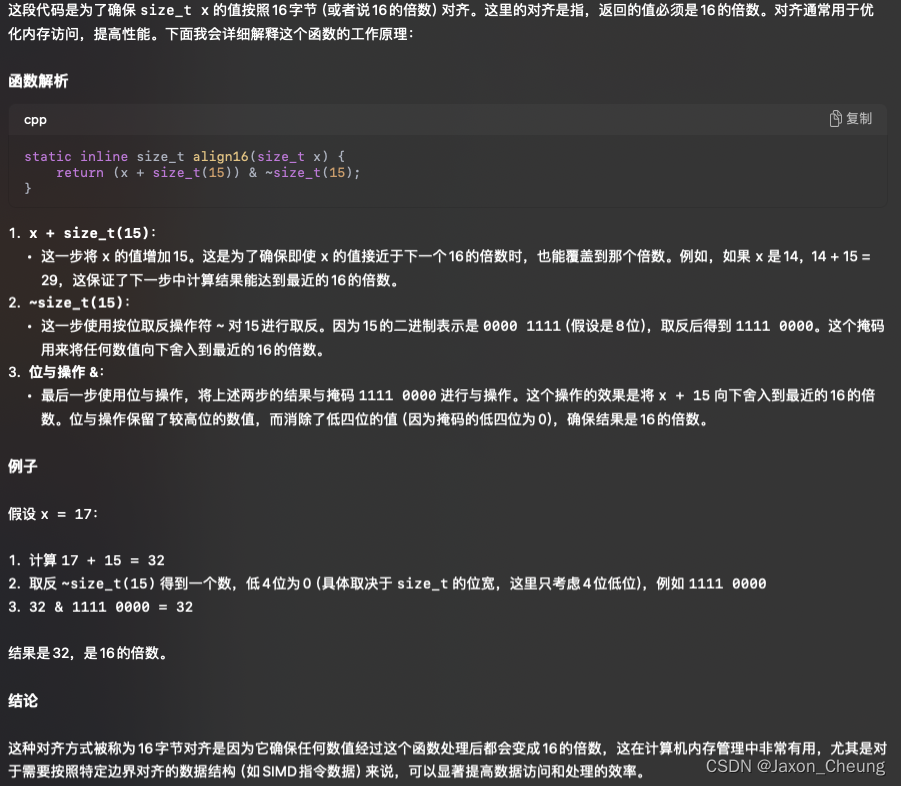
static inline size_t align16(size_t x) { return (x + size_t(15)) & ~size_t(15); } 这个函数是为了确保,传进去的
x值按照 16 字节对齐,也就是返回值必须是 16 的倍数。
因为掩码的最低4位为0,对 x + 15 的结果进行 & 操作后,会把结果中的最低4位清零,这意味着结果必定是16的倍数。原因是二进制中的数如果最后四位是0,则该数可以被16整除。
malloc_instance方法
static inline id malloc_instance(size_t size, Class cls __unused) { #if _MALLOC_TYPE_ENABLED malloc_type_descriptor_t desc = {}; desc.summary.type_kind = MALLOC_TYPE_KIND_OBJC; return (id)malloc_type_calloc(1, size, desc.type_id); #else return (id)calloc(1, size); #endif } 实际是调用calloc函数开辟内存
initInstanceIsa方法
inline void objc_object::initInstanceIsa(Class cls, bool hasCxxDtor) { ASSERT(!cls->instancesRequireRawIsa()); ASSERT(hasCxxDtor == cls->hasCxxDtor()); initIsa(cls, true, hasCxxDtor); } 初始化 isa 指针,和类关联起来
alloc流程总结
init方法
- (id)init { return _objc_rootInit(self); } id _objc_rootInit(id obj) { // In practice, it will be hard to rely on this function. // Many classes do not properly chain -init calls. return obj; } init方法返回的是对象本身,类似工厂模式,init方法的意义除了初始化内存,还可以扩展更多的初始化方法
new方法
+ (id)new { return [callAlloc(self, false/*checkNil*/) init]; } new方法的底层实现就是调用alloc流程 + init方法
