#AI夏令营 #Datawhale #夏令营
该笔记是在博主Mr.chenlex跑分后的基础上加以改进,原文连接:Datawhale AI夏令营 - 机器学习:分子性质AI预测挑战赛#ai夏令营datawhale#夏令营-CSDN博客
Baseline改进前后代码介绍
Baseline改进前后跑分结果
直接套用原博主的Baseline(需另进行库的下载以及配置,下文会进行说明)运行后的A榜分数为:0.74359

改进后的Baseline的A榜分数为:0.7619

改进思路及过程
相关库的补充下载
catboost:一个用于机器学习的库,特别是分类和回归任务。rdkit: 一个化学信息学和机器学习软件,用于处理化学结构。
在下载catboost库时,直接下载会出现权限问题:
Could not install packages due to an OSError: [Errno 13] Permission denied: '/opt/conda/envs/python35-paddle120-env/etc/jupyter/nbconfig/notebook.d/catboost-widget.json' Consider using the --user option or check the permissions.这是因为没有足够的权限来在这个路径下写入文件,我们可以使用 --user 选项来安装包,这会将包安装到你的用户目录下,而不是系统级目录。
!pip install --user catboost这样即可正常下载catboost库。
而使用同样的方式下载rdkit库时,在导入时会进行报错:
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'rdkit'此时,我们应该考虑以绝对路径的形式来进行导入,以便python解释器可以找到它,首先我们要先确定rdkit库的安装路径:
!pip show rdkit根据其显示的信息进行路径配置:

import sys sys.path.append('/home/aistudio/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages')至此,我们就完成了必用补充库的下载,接下来让我们正式开始改进。
导入模块
import numpy as np import pandas as pd from catboost import CatBoostClassifier from sklearn.model_selection import KFold from sklearn.metrics import f1_score from rdkit import Chem from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer相关库的解释与说明请移步原博主文章,在此不再赘述:Datawhale AI夏令营 - 机器学习:分子性质AI预测挑战赛#ai夏令营datawhale#夏令营-CSDN博客
这里解释一下,为什么不再引用wornings的库并且只使用KFold这一种验证方法,原文引用wornings库的目的是忽略警告,而在实际运行中,显示的这条警告意味着在训练过程中,模型会频繁地评估其性能指标,而不会按照预设的间隔进行评估,从而可能出现过拟合的情况。
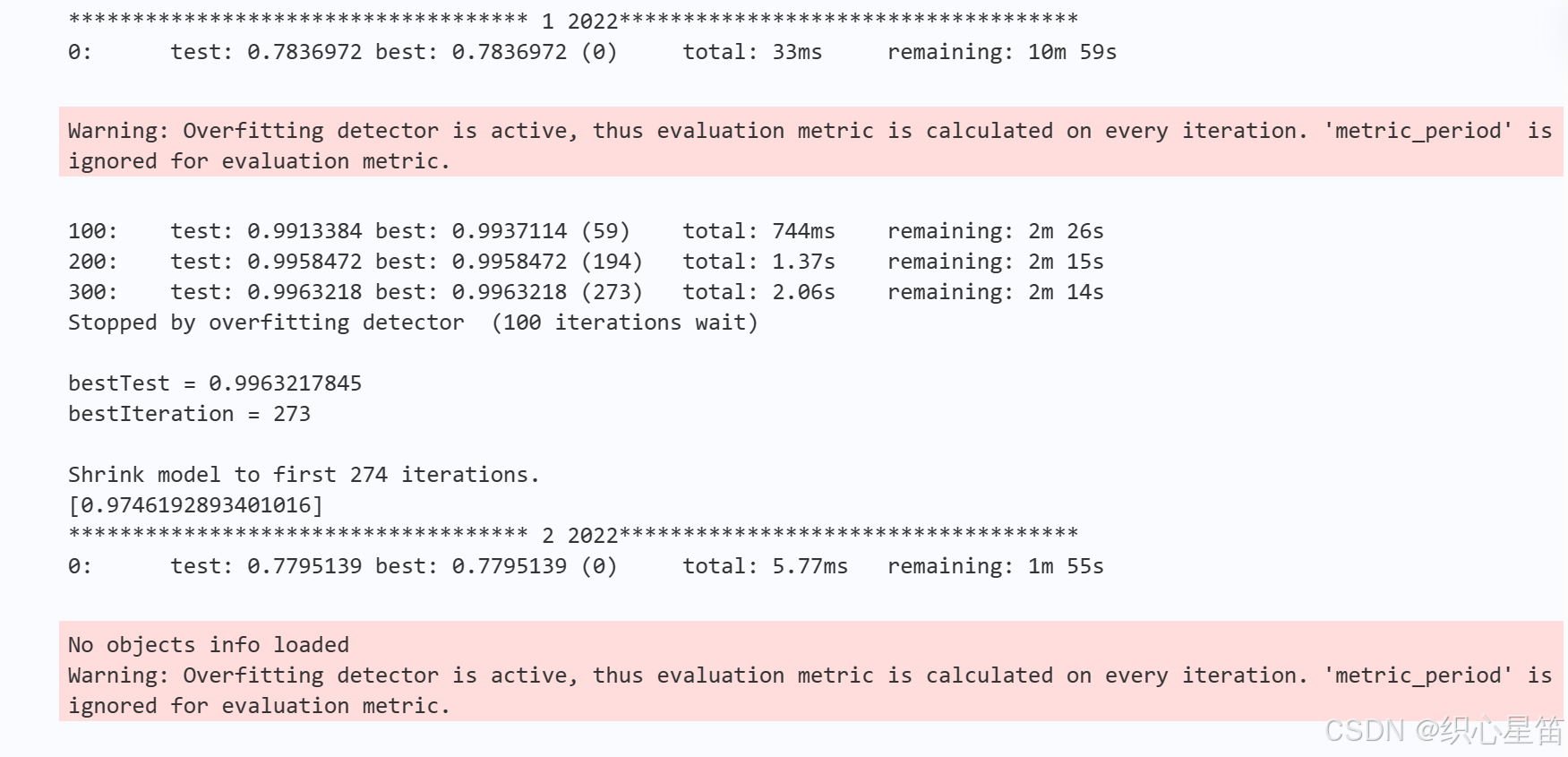
数据预处理
数据预处理部分没有实质性的改动,就是读入文件时,要根据自己的实际路径进行读入:
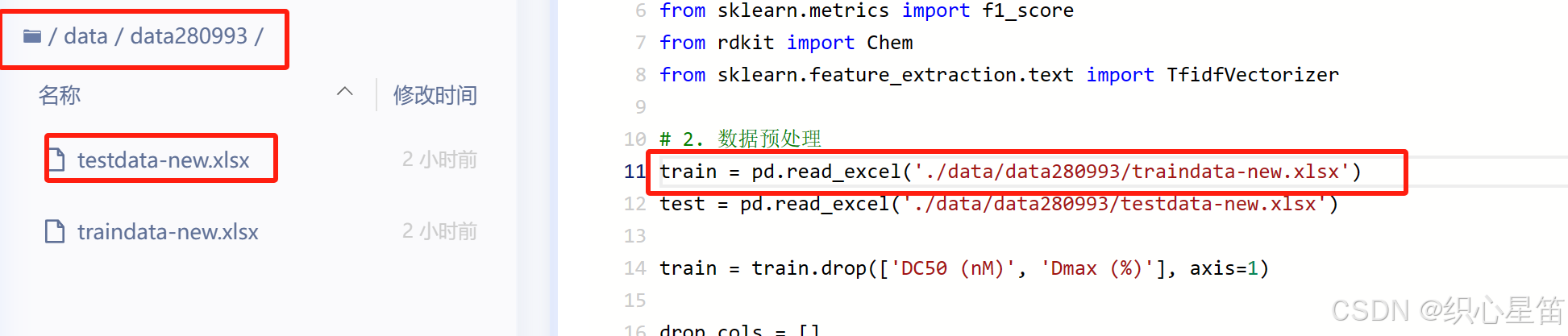
train = pd.read_excel('./data/data280993/traindata-new.xlsx') test = pd.read_excel('./data/data280993/testdata-new.xlsx') train = train.drop(['DC50 (nM)', 'Dmax (%)'], axis=1) drop_cols = [] for f in test.columns: if test[f].notnull().sum() < 10: drop_cols.append(f) train = train.drop(drop_cols, axis=1) test = test.drop(drop_cols, axis=1) data = pd.concat([train, test], axis=0, ignore_index=True)特征工程
主要是在自然数编码进行了简化:
原代码利用的是字典映射和map函数,可以自定义编码顺序并返回可读性好的标签,但需要额外的内存空间,并因其自定义的排序打乱了原本数据的顺序,会影响学习程度,丢失一定的普适性。
# 自然数编码 def label_encode(series): unique = list(series.unique()) return series.map(dict(zip( unique, range(series.nunique()) ))) 原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_51789661/article/details/140188167而简化后直接使用了pandas内置的优化方法,转换速度较快,并且category类型在内存使用上比较节省。最重要的一点是,按照默认顺序进行学习,可以增强学习的普适性。
def label_encode(series): return series.astype('category').cat.codes模型训练与预测
在此环节,只是简化了一些自定义的参数,使代码更加简洁和易读。
完整代码展示
!pip install lightgbm openpyxl !pip install --user catboost !pip install --user rdkit !pip show rdkit import sys sys.path.append('/home/aistudio/.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages') # 1. 导入需要用到的相关库 import numpy as np import pandas as pd from catboost import CatBoostClassifier from sklearn.model_selection import KFold from sklearn.metrics import f1_score from rdkit import Chem from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer # 2. 数据预处理 train = pd.read_excel('./data/data280993/traindata-new.xlsx') test = pd.read_excel('./data/data280993/testdata-new.xlsx') train = train.drop(['DC50 (nM)', 'Dmax (%)'], axis=1) drop_cols = [] for f in test.columns: if test[f].notnull().sum() < 10: drop_cols.append(f) train = train.drop(drop_cols, axis=1) test = test.drop(drop_cols, axis=1) data = pd.concat([train, test], axis=0, ignore_index=True) # 3 特征工程 data['smiles_list'] = data['Smiles'].apply(lambda x: [Chem.MolToSmiles(mol, isomericSmiles=True) for mol in [Chem.MolFromSmiles(x)]]) data['smiles_list'] = data['smiles_list'].map(lambda x: ' '.join(x)) tfidf = TfidfVectorizer(max_df=0.9, min_df=1, sublinear_tf=True) res = tfidf.fit_transform(data['smiles_list']) tfidf_df = pd.DataFrame(res.toarray(), columns=[f'smiles_tfidf_{i}' for i in range(res.shape[1])]) data = pd.concat([data, tfidf_df], axis=1) def label_encode(series): return series.astype('category').cat.codes for col in data.columns[2:]: if data[col].dtype == 'object': data[col] = label_encode(data[col]) train = data[data['Label'].notnull()].reset_index(drop=True) test = data[data['Label'].isnull()].reset_index(drop=True) features = [f for f in train.columns if f not in ['uuid', 'Label', 'smiles_list']] x_train = train[features] x_test = test[features] y_train = train['Label'].astype(int) # 4. 模型训练与预测 def cv_model(clf, train_x, train_y, test_x, clf_name, seed=2022): kf = KFold(n_splits=5, shuffle=True, random_state=seed) train_preds = np.zeros(train_x.shape[0]) test_preds = np.zeros(test_x.shape[0]) cv_scores = [] for i, (train_index, valid_index) in enumerate(kf.split(train_x)): print(f'Fold {i+1}/{kf.n_splits}') trn_x, trn_y = train_x.iloc[train_index], train_y.iloc[train_index] val_x, val_y = train_x.iloc[valid_index], train_y.iloc[valid_index] model = clf(iterations=20000, learning_rate=0.1, depth=6, l2_leaf_reg=10, bootstrap_type='Bernoulli', random_seed=seed, od_type='Iter', od_wait=100, allow_writing_files=False, task_type='CPU', eval_metric='AUC') model.fit(trn_x, trn_y, eval_set=(val_x, val_y), verbose=100, use_best_model=True) val_pred = model.predict_proba(val_x)[:, 1] test_pred = model.predict_proba(test_x)[:, 1] train_preds[valid_index] = val_pred test_preds += test_pred / kf.n_splits cv_scores.append(f1_score(val_y, np.where(val_pred > 0.5, 1, 0))) print(f"{clf_name} score list:", cv_scores) print(f"{clf_name} mean score:", np.mean(cv_scores)) print(f"{clf_name} std score:", np.std(cv_scores)) return train_preds, test_preds cat_train, cat_test = cv_model(CatBoostClassifier, x_train, y_train, x_test, "CatBoost") pd.DataFrame( { 'uuid': test['uuid'], 'Label': np.where(cat_test>0.5, 1, 0) } ).to_csv('submit.csv', index=None) 模型测试结果

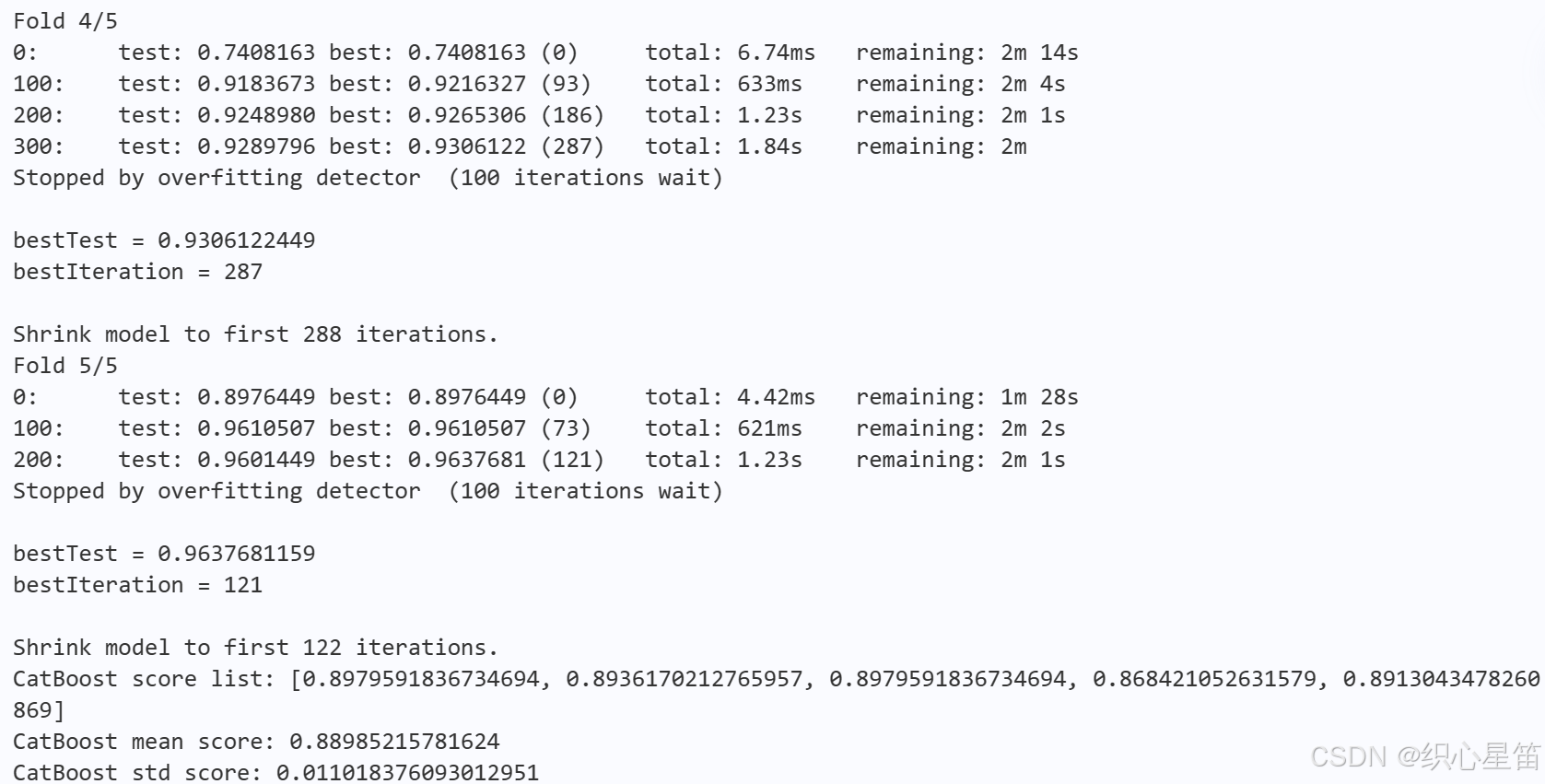
不难看出,最佳验证集表现都在0.93以上,并且得到达到最佳表现时的迭代次数都小于400,最少为38次,因为可以更快地得到最佳表现。而针对测试集,平均准确率也达到了0.89,并具有非常小的标准偏差,说明表明模型在不同折叠上的表现基本稳定且整体表现良好。
