目录

1 -> 红黑树
1.1 -> 红黑树的概念
红黑树,是一种二叉搜索树,但在每个节点上增加了一个存储位表示节点的颜色,可以是Red或Black。通过对任何一条从根到叶子的路径上各个节点着色方式的限制,红黑树确保没有一条路径会比其他路径长出两倍,因而是接近平衡的。
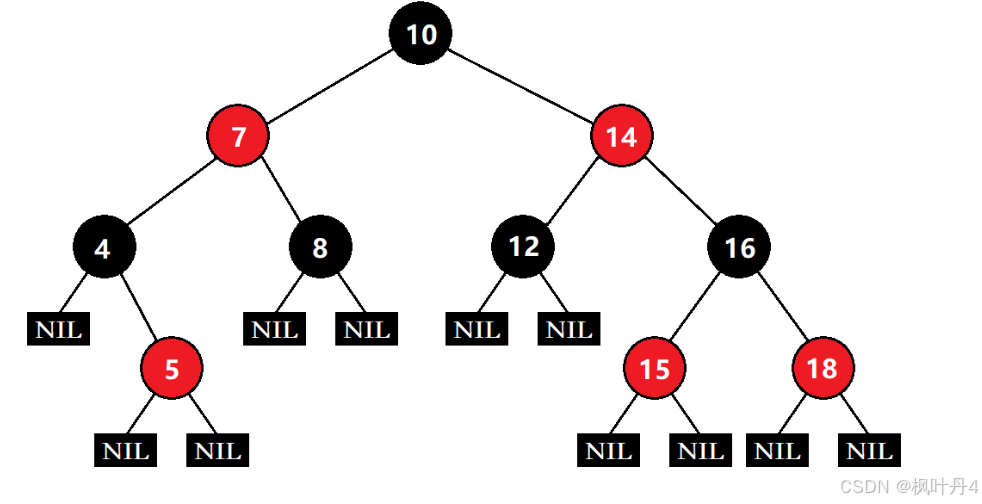
1.2 -> 红黑树的性质
- 每个节点不是红色就是黑色。
- 根节点是黑色的。
- 如果一个节点是红色的,则它的两个孩子节点是黑色的。
- 对于每个节点,从该节点到其所有后代叶节点的简单路径上,均包含相同数目的黑色节点。
- 每个叶子节点都是黑色的(此处的叶子节点指空节点)。
1.3 -> 红黑树节点的定义
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1 #include <iostream> using namespace std; // 节点的颜色 enum Color { RED, BLACK }; // 红黑树节点的定义 template<class ValueType> struct RBTreeNode { RBTreeNode(const ValueType& data = ValueType(),Color color = RED) : _pLeft(nullptr), _pRight(nullptr), _pParent(nullptr) , _data(data), _color(color) {} RBTreeNode<ValueType>* _pLeft; // 节点的左孩子 RBTreeNode<ValueType>* _pRight; // 节点的右孩子 RBTreeNode<ValueType>* _pParent; // 节点的双亲(红黑树需要旋转,为了实现简单给出该字段) ValueType _data; // 节点的值域 Color _color; // 节点的颜色 };1.4 -> 红黑树的结构
为了后续实现关联式容器更加简单,红黑树的实现中增加一个头节点,因为根节点必须是黑色的,为了与根节点区分开,将头节点给成黑色,并且让头节点的pParent域指向红黑树的根节点,pLeft域指向红黑树中最小的节点,_pRight域指向红黑树中最大的节点。
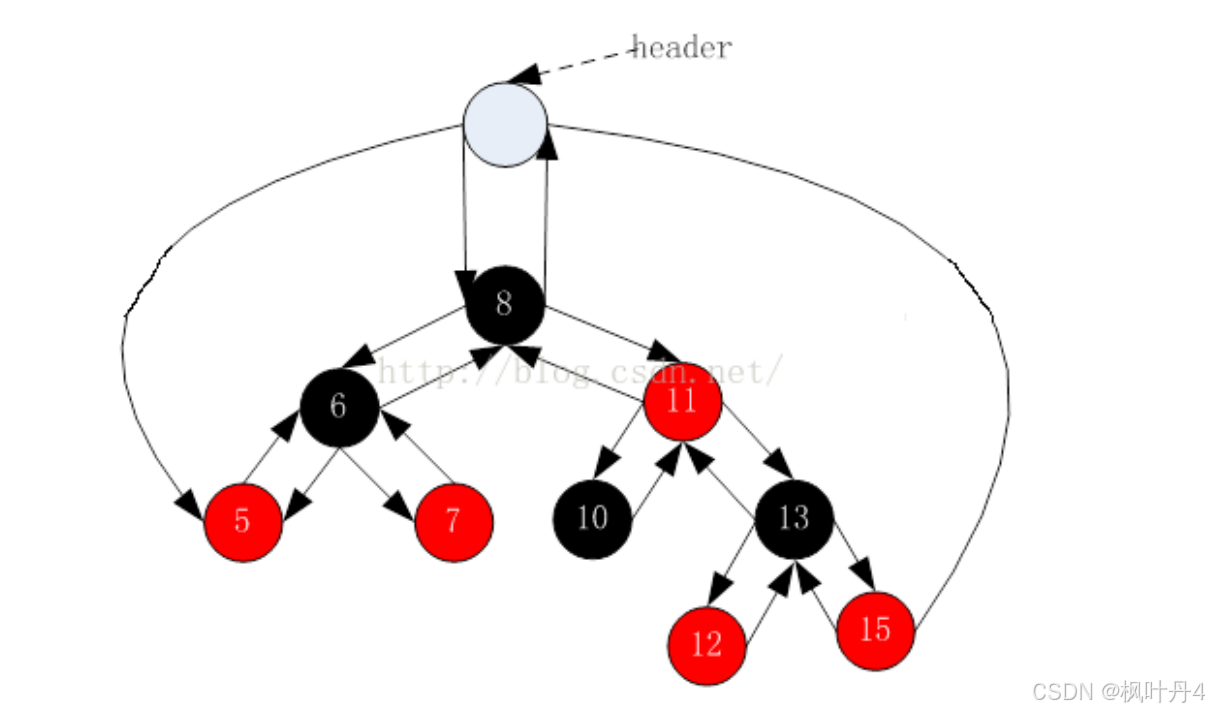
1.5 -> 红黑树的插入操作
红黑树是在二叉搜索树的基础上加上其平衡限制条件,因此红黑树的插入可以分为两步:
1. 按照二叉搜索树的树规则插入新节点。
template<class ValueType> struct RBTree { bool Insert(const ValueType& data) { PNode& pRoot = GetRoot(); if (nullptr == pRoot) { pRoot = new Node(data, BLACK); // 根的双亲为头节点 pRoot->_pParent = _pHead; _pHead->_pParent = pRoot; } else { // 1. 按照二叉搜索的树方式插入新节点 // 2. 检测新节点插入后,红黑树的性质是否造到破坏, // 若满足直接退出,否则对红黑树进行旋转着色处理 } // 根节点的颜色可能被修改,将其改回黑色 pRoot->_color = BLACK; _pHead->_pLeft = LeftMost(); _pHead->_pRight = RightMost(); return true; } private: PNode& GetRoot() { return _pHead->_pParent; } // 获取红黑树中最小节点,即最左侧节点 PNode LeftMost(); // 获取红黑树中最大节点,即最右侧节点 PNode RightMost(); private: PNode _pHead; }2. 检测新节点插入后,红黑树的性质是否遭到破坏。
因为新节点的默认颜色为红色,因此:如果其双亲节点的颜色是黑色,没有违反红黑树的任何性质,则不需要调整;但当新插入节点的双亲节点颜色为红色时,就违反了性质三,即不能有连在一起的红色节点,此时需要对红黑树分情况来讨论:
- 情况一:cur为红,p为红,g为黑,u存在且为红。
注意:此处看到的树可能是一棵完整的树,也可能是一棵子树。
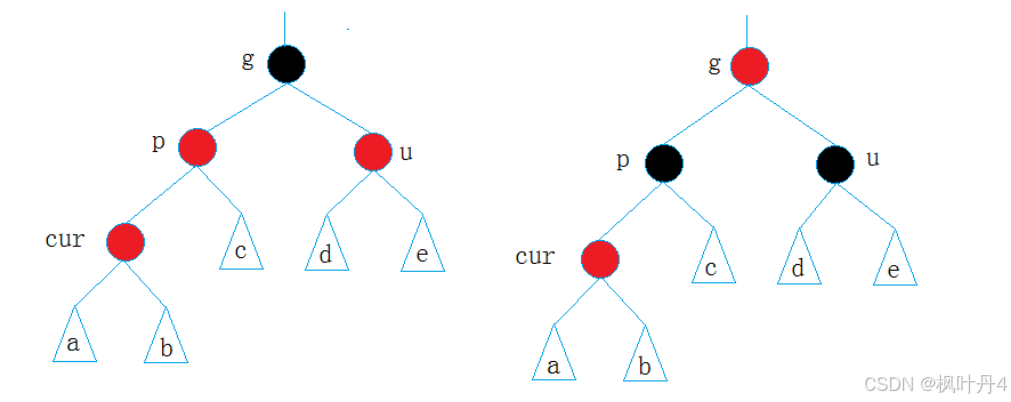
如果g是根节点,调整完成后,需要将g改为黑色。
如果g是子树,g一定有双亲,且g的双亲如果是红色,就需要继续向上调整。
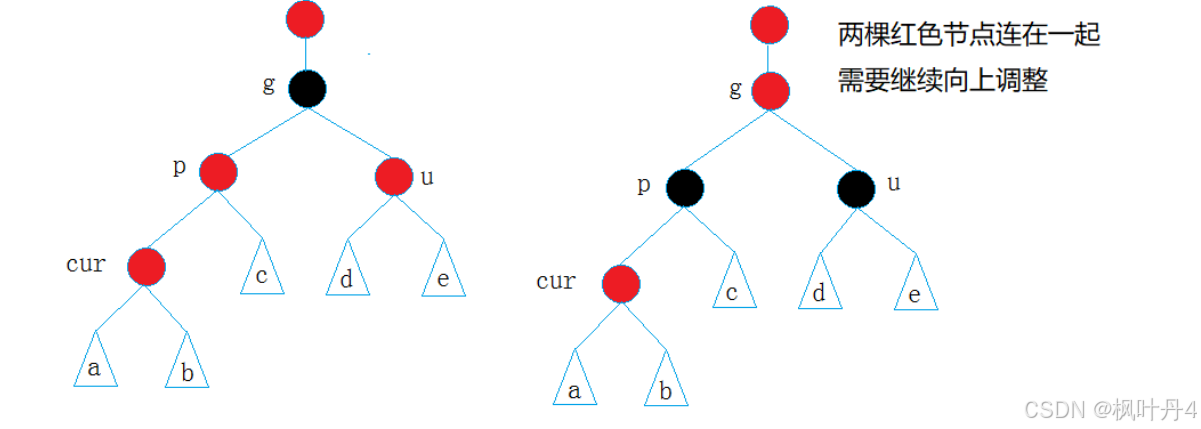
cur和p均为红,违反了性质三。
解决方法:将p、u改为黑,g改为红,然后把g当成cur,继续向上调整。
- 情况二:cur为红,p为红,g为黑,u不存在/u存在且为黑。
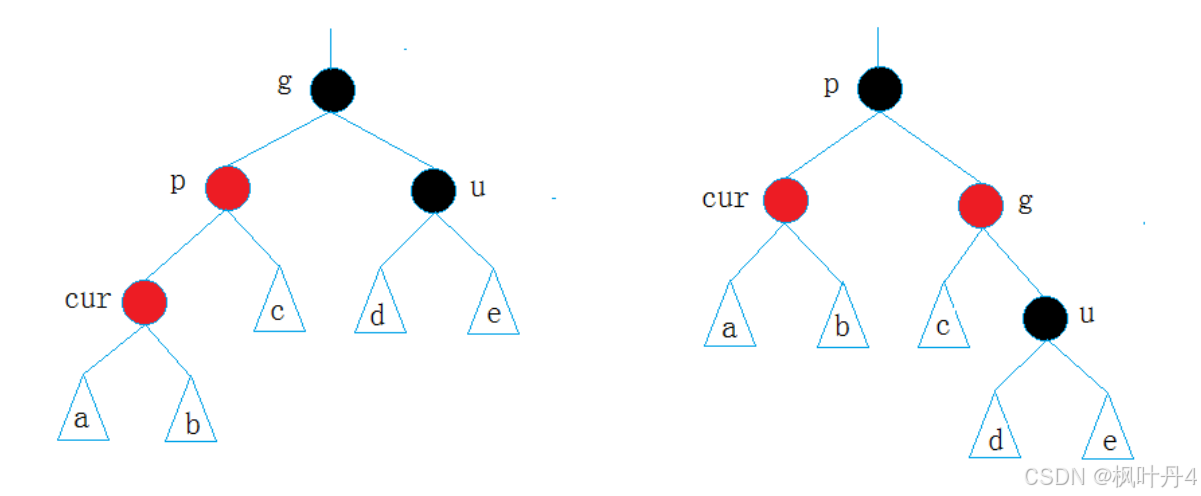
说明:
- 如果u节点不存在,则cur一定是新插入节点,因为如果cur不是新插入节点,则cur和p一定有一个节点的颜色是黑色,就不满足性质4:每条路径黑色节点个数相同。
- 如果u节点存在,则其一定是黑色的,那么cur节点原来的颜色一定是黑色的,现在看到其是红色的原因是因为cur的子树在调整的过程中将cur节点的颜色由黑色改成了红色。
p为g的左孩子,cur为p的左孩子,则进行右单旋转。
p为g的右孩子,cur为p的右孩子,则进行左单旋转。
p、g变色——p变黑,g变红。
- 情况三:cur为红,p为红,g为黑,u不存在/u存在且为黑。
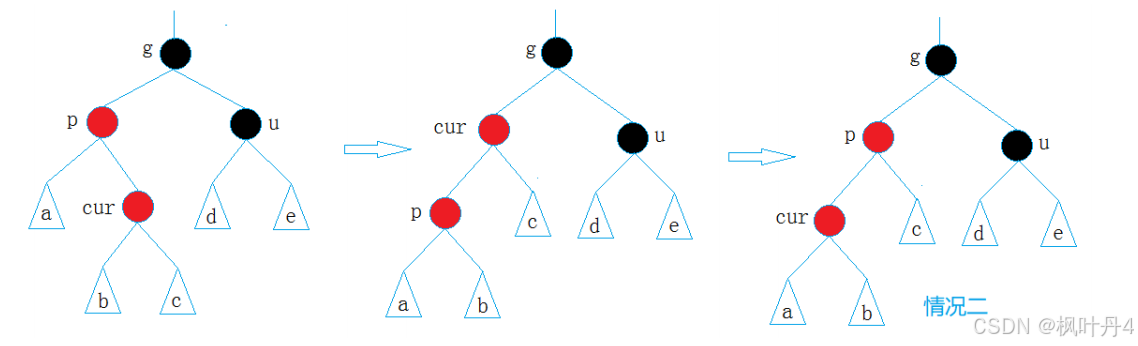
p为g的左孩子,cur为p的右孩子,则针对p进行左单旋转。
p为g的右孩子,cur为p的左孩子,则针对p进行右单旋转。
则转换成情况二。
针对每种情况进行相应的处理即可。
bool Insert(const ValueType& data) { // ... // 新节点插入后,如果其双亲节点的颜色为空色,则违反性质3:不能有连在一起的红色结点 while (pParent && RED == pParent->_color) { // 注意:grandFather一定存在 // 因为pParent存在,且不是黑色节点,则pParent一定不是根,则其一定有双亲 PNode grandFather = pParent->_pParent; // 先讨论左侧情况 if (pParent == grandFather->_pLeft) { PNode unclue = grandFather->_pRight; // 情况三:叔叔节点存在,且为红 if (unclue && RED == unclue->_color) { pParent->_color = BLACK; unclue->_color = BLACK; grandFather->_color = RED; pCur = grandFather; pParent = pCur->_pParent; } else { // 情况五:叔叔节点不存在,或者叔叔节点存在且为黑 if (pCur == pParent->_pRight) { _RotateLeft(pParent); swap(pParent, pCur); } // 情况五最后转化成情况四 grandFather->_color = RED; pParent->_color = BLACK; _RotateRight(grandFather); } } else { // … } } // ... }1.6 -> 红黑树的验证
红黑树的检测分为两步:
- 检测其是否满足二叉搜索树(中序遍历是否为有序序列)。
- 检测其是否满足红黑树的性质。
bool IsValidRBTree() { PNode pRoot = GetRoot(); // 空树也是红黑树 if (nullptr == pRoot) return true; // 检测根节点是否满足情况 if (BLACK != pRoot->_color) { cout << "违反红黑树性质二:根节点必须为黑色" << endl; return false; } // 获取任意一条路径中黑色节点的个数 size_t blackCount = 0; PNode pCur = pRoot; while (pCur) { if (BLACK == pCur->_color) blackCount++; pCur = pCur->_pLeft; } // 检测是否满足红黑树的性质,k用来记录路径中黑色节点的个数 size_t k = 0; return _IsValidRBTree(pRoot, k, blackCount); } bool _IsValidRBTree(PNode pRoot, size_t k, const size_t blackCount) { //走到null之后,判断k和black是否相等 if (nullptr == pRoot) { if (k != blackCount) { cout << "违反性质四:每条路径中黑色节点的个数必须相同" << endl; return false; } return true; } // 统计黑色节点的个数 if (BLACK == pRoot->_color) k++; // 检测当前节点与其双亲是否都为红色 PNode pParent = pRoot->_pParent; if (pParent && RED == pParent->_color && RED == pRoot->_color) { cout << "违反性质三:没有连在一起的红色节点" << endl; return false; } return _IsValidRBTree(pRoot->_pLeft, k, blackCount) && _IsValidRBTree(pRoot->_pRight, k, blackCount); }1.8 -> 红黑树与AVL树的比较
红黑树和AVL树都是高效的平衡二叉树,增删改查的时间复杂度都是O(n),红黑树不追求绝对平衡,其只需保证最长路径不超过最短路径的2倍,相对而言,降低了插入和旋转的次数,所以在经常进行增删的结构中性能比AVL树更优,而且红黑树实现比较简单,所以在实际运用中红黑树更多。
2 -> 红黑树模拟实现STL中的map与set
2.1 -> 红黑树的迭代器
迭代器的好处是可以方便遍历,是数据结构的底层实现与用户透明。如果想要给红黑树增加迭代器,需要考虑以下问题:
- begin()和end()
STL明确规定,begin()与end()代表的是一段前闭后开的区间,而对红黑树进行中序遍历后,可以得到一个有序的序列,因此:begin()可以放在红黑树中最小节点(即最左侧节点)的位置,end()放在最大节点(最右侧节点)的下一个位置,关键是最大节点的下一个位置在哪里呢?能否给成nullptr呢?
答案是行不通的,因为对end()位置的迭代器进行--操作,必须要能找到最后一个元素,此处就不行,因此最好的方式是将end()放在头节点的位置:
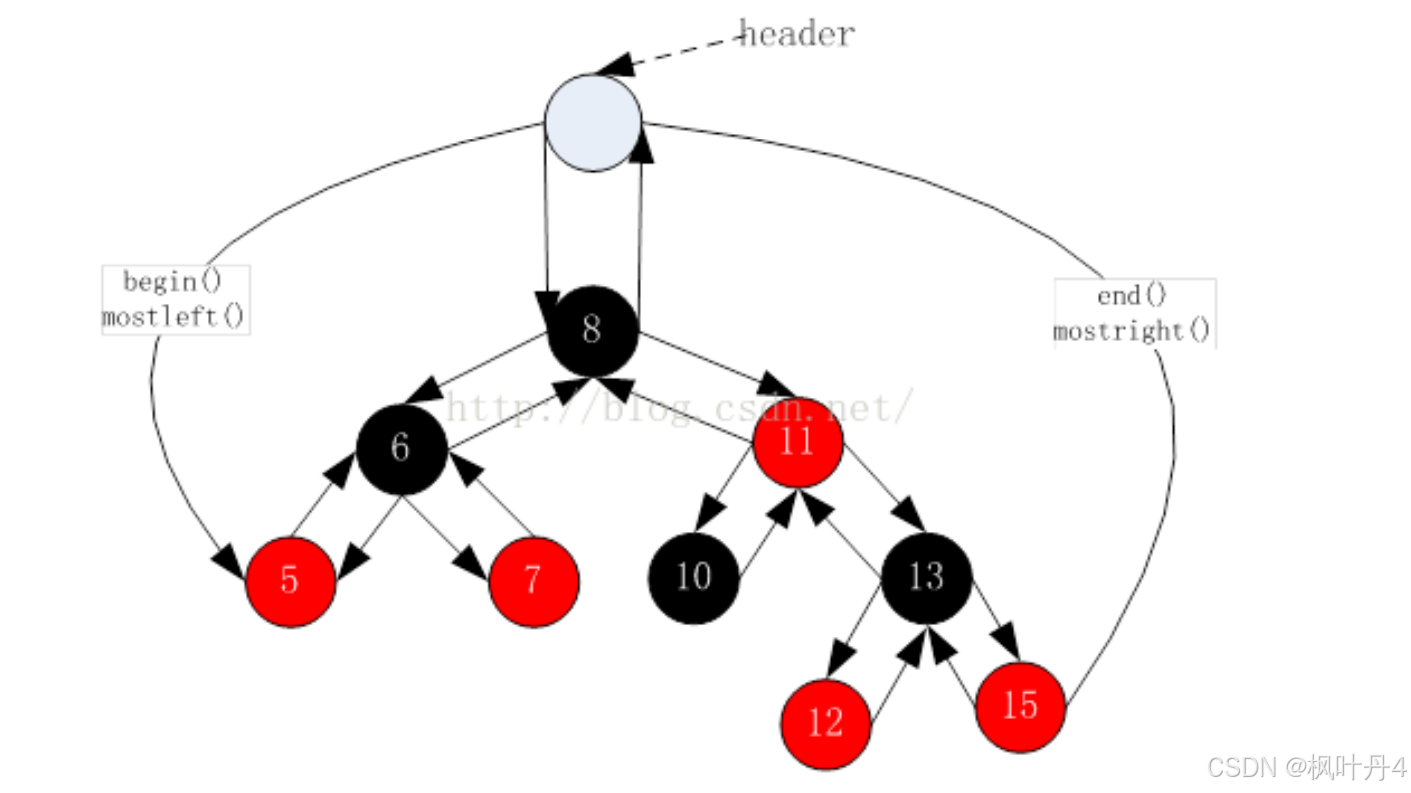
- operator++()与operator--()
// 找迭代器的下一个节点,下一个节点肯定比其大 void Increasement() { //分两种情况讨论:_pNode的右子树存在和不存在 // 右子树存在 if (_pNode->_pRight) { // 右子树中最小的节点,即右子树中最左侧节点 _pNode = _pNode->_pRight; while (_pNode->_pLeft) _pNode = _pNode->_pLeft; } else { // 右子树不存在,向上查找,直到_pNode != pParent->right PNode pParent = _pNode->_pParent; while (pParent->_pRight == _pNode) { _pNode = pParent; pParent = _pNode->_pParent; } // 特殊情况:根节点没有右子树 if (_pNode->_pRight != pParent) _pNode = pParent; } } // 获取迭代器指向节点的前一个节点 void Decreasement() { //分三种情况讨论:_pNode 在head的位置,_pNode 左子树存在,_pNode 左子树不 存在 // 1. _pNode 在head的位置,--应该将_pNode放在红黑树中最大节点的位置 if (_pNode->_pParent->_pParent == _pNode && _pNode->_color == RED) _pNode = _pNode->_pRight; else if (_pNode->_pLeft) { // 2. _pNode的左子树存在,在左子树中找最大的节点,即左子树中最右侧节点 _pNode = _pNode->_pLeft; while (_pNode->_pRight) _pNode = _pNode->_pRight; } else { // _pNode的左子树不存在,只能向上找 PNode pParent = _pNode->_pParent; while (_pNode == pParent->_pLeft) { _pNode = pParent; pParent = _pNode->_pParent; } _pNode = pParent; } }2.2 -> 改造红黑树
#pragma once // set ->key // map ->key/value enum Colour { RED, BLACK }; template<class T> struct RBTreeNode { RBTreeNode<T>* _left; RBTreeNode<T>* _right; RBTreeNode<T>* _parent; T _data; Colour _col; RBTreeNode(const T& data) :_left(nullptr) , _right(nullptr) , _parent(nullptr) , _data(data) , _col(RED) {} }; template<class T> struct __TreeIterator { typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node; typedef __TreeIterator<T> Self; Node* _node; __TreeIterator(Node* node) :_node(node) {} T& operator*() { return _node->_data; } T* operator->() { return &_node->_data; } Self& operator--(); Self& operator++() { if (_node->_right) { // 下一个就是右子树的最左节点 Node* cur = _node->_right; while (cur->_left) { cur = cur->_left; } _node = cur; } else { // 左子树 根 右子树 // 右为空,找孩子是父亲左的那个祖先 Node* cur = _node; Node* parent = cur->_parent; while (parent && cur == parent->_right) { cur = parent; parent = parent->_parent; } _node = parent; } return *this; } bool operator!=(const Self& s) { return _node != s._node; } bool operator==(const Self& s) { return _node == s._node; } }; // set->RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t; // map->RBTree<K, pair<K, T>, MapKeyOfT> _t; template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT> class RBTree { typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node; public: typedef __TreeIterator<T> iterator; iterator begin() { Node* cur = _root; while (cur && cur->_left) { cur = cur->_left; } return iterator(cur); } iterator end() { return iterator(nullptr); } pair<iterator, bool> Insert(const T& data) { if (_root == nullptr) { _root = new Node(data); _root->_col = BLACK; return make_pair(iterator(_root), true); } Node* parent = nullptr; Node* cur = _root; KeyOfT kot; while (cur) { if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data)) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_right; } else if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data)) { parent = cur; cur = cur->_left; } else { return make_pair(iterator(cur), false); } } // 新增节点给红色 cur = new Node(data); Node* newnode = cur; cur->_col = RED; if (kot(parent->_data) < kot(data)) { parent->_right = cur; cur->_parent = parent; } else { parent->_left = cur; cur->_parent = parent; } while (parent && parent->_col == RED) { Node* grandfather = parent->_parent; if (parent == grandfather->_left) { // g // p u // c Node* uncle = grandfather->_right; if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED) { // 变色 parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK; grandfather->_col = RED; // 继续往上更新处理 cur = grandfather; parent = cur->_parent; } else { if (cur == parent->_left) { // 单旋 // g // p // c RotateR(grandfather); parent->_col = BLACK; grandfather->_col = RED; } else { // 双旋 // g // p // c RotateL(parent); RotateR(grandfather); cur->_col = BLACK; grandfather->_col = RED; } break; } } else // parent == grandfather->_right { // g // u p // c // Node* uncle = grandfather->_left; if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED) { // 变色 parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK; grandfather->_col = RED; // 继续往上处理 cur = grandfather; parent = cur->_parent; } else { if (cur == parent->_right) { RotateL(grandfather); parent->_col = BLACK; grandfather->_col = RED; } else { // g // u p // c // RotateR(parent); RotateL(grandfather); cur->_col = BLACK; grandfather->_col = RED; } break; } } } _root->_col = BLACK; return make_pair(iterator(newnode), true); } void RotateL(Node* parent) { Node* subR = parent->_right; Node* subRL = subR->_left; parent->_right = subRL; subR->_left = parent; Node* parentParent = parent->_parent; parent->_parent = subR; if (subRL) subRL->_parent = parent; if (_root == parent) { _root = subR; subR->_parent = nullptr; } else { if (parentParent->_left == parent) { parentParent->_left = subR; } else { parentParent->_right = subR; } subR->_parent = parentParent; } } void RotateR(Node* parent) { Node* subL = parent->_left; Node* subLR = subL->_right; parent->_left = subLR; if (subLR) subLR->_parent = parent; Node* parentParent = parent->_parent; subL->_right = parent; parent->_parent = subL; if (_root == parent) { _root = subL; subL->_parent = nullptr; } else { if (parentParent->_left == parent) { parentParent->_left = subL; } else { parentParent->_right = subL; } subL->_parent = parentParent; } } void InOrder() { _InOrder(_root); cout << endl; } void _InOrder(Node* root) { if (root == nullptr) return; _InOrder(root->_left); cout << root->_kv.first << " "; _InOrder(root->_right); } // 根节点->当前节点这条路径的黑色节点的数量 bool Check(Node* root, int blacknum, const int refVal) { if (root == nullptr) { //cout << balcknum << endl; if (blacknum != refVal) { cout << "存在黑色节点数量不相等的路径" << endl; return false; } return true; } if (root->_col == RED && root->_parent->_col == RED) { cout << "有连续的红色节点" << endl; return false; } if (root->_col == BLACK) { ++blacknum; } return Check(root->_left, blacknum, refVal) && Check(root->_right, blacknum, refVal); } bool IsBalance() { if (_root == nullptr) return true; if (_root->_col == RED) return false; //参考值 int refVal = 0; Node* cur = _root; while (cur) { if (cur->_col == BLACK) { ++refVal; } cur = cur->_left; } int blacknum = 0; return Check(_root, blacknum, refVal); } int Height() { return _Height(_root); } int _Height(Node* root) { if (root == nullptr) return 0; int leftHeight = _Height(root->_left); int rightHeight = _Height(root->_right); return leftHeight > rightHeight ? leftHeight + 1 : rightHeight + 1; } size_t Size() { return _Size(_root); } size_t _Size(Node* root) { if (root == NULL) return 0; return _Size(root->_left) + _Size(root->_right) + 1; } Node* Find(const K& key) { Node* cur = _root; while (cur) { if (cur->_kv.first < key) { cur = cur->_right; } else if (cur->_kv.first > key) { cur = cur->_left; } else { return cur; } } return NULL; } private: Node* _root = nullptr; }; 2.3 -> map的模拟实现
map的底层结构就是红黑树,因此在map中直接封装一棵红黑树,然后将其接口包装下即可。
#pragma once #include"RBTree.h" namespace fyd { template<class K, class V> class map { public: struct MapKeyOfT { const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv) { return kv.first; } }; // 对类模板取内嵌类型,加typename告诉编译器这里是类型 typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator; iterator begin() { return _t.begin(); } iterator end() { return _t.end(); } V& operator[](const K& key) { pair<iterator, bool> ret = insert(make_pair(key, V())); return ret.first->second; } pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K, V>& kv) { return _t.Insert(kv); } private: RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t; }; } 2.4 -> set的模拟实现
set的底层为红黑树,因此只需在set内部封装一棵红黑树,即可将该容器实现出来。
#pragma once #include"RBTree.h" namespace fyd { template<class K> class set { public: struct SetKeyOfT { const K& operator()(const K& key) { return key; } }; typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::iterator iterator; iterator begin() { return _t.begin(); } iterator end() { return _t.end(); } pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key) { return _t.Insert(key); } private: RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t; }; } 感谢各位大佬支持!!!
互三啦!!!
