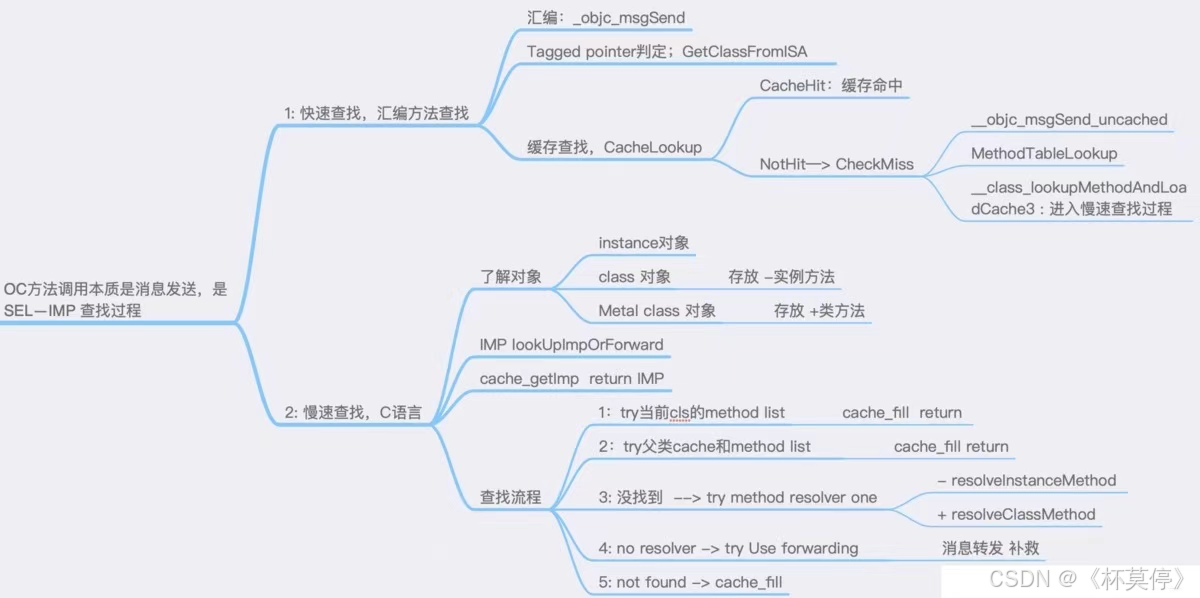
【iOS】—— 消息传递和消息转发
1. 消息传递
在iOS中,消息传递机制是基于Objective-C语言的动态性质的一种编程方式。这个概念主要涉及两个概念:发送者(消息发送的对象)和接受者(消息接收的对象)。当调用一个对象的方法的时候,实际上是向这个对象发送了一条消息。
比如下面的代码:
id returnValue = [someObject messageName: parameter]; someObject叫做接收者(receiver),messageName:叫做选择子(selector),选择子和参数合起来称为“消息”。
编译器看到此消息后,将其转换为一条标准的C语言函数调用,所调用的函数乃是消息传递机制中的核心函数叫做objc_msgSend,
编译器看到上述这条消息会转换成一条标准的 C 语言函数调用:
id returnValue = objc_msgSend(someObject, @selector(messageName:), parameter); objc_msgSend函数,这个函数将消息接收者和方法名作为主要参数,其原型如下所示:
// 不带参数 objc_msgSend(receiver, selector) // 带参数 objc_msgSend(receiver, selector, arg1, arg2,...) objc_msgSend通过以下几个步骤实现了动态绑定机制:
- 首先获取selector指向的方法实现。因为相同的方法可能会在不同的类中有不同的实现,所以要根据receiver来进行判断。
- 其次,传递对象,方法指定的参数来调用方法实现。
- 最后返回方法实现的返回值。
- 当消息传递到一个对象的时候,首先从运行时的系统缓存objc_cache中进行查找。如果找到,就执行。否则执行下一步。
- objc_msgSend通过对象的isa指针获取类的结构体,然后在结构体的methodLists中查找方法,如果没有找到,就沿着superclass找到父类,在父类的分发表methodLists中继续查找。
- 以此类推,一直沿着继承链找到NSObject类。一旦找到selector,传入相应的参数来实现具体方法,并将该方法加入到objc_cache。如果最后还没有找到,就会进入消息转发流程。
SEL选择子
SEL 是选择器(Selector)的别名,它是表示一个方法的符号名。选择器是用来表示一个方法名的,可以看作是一个指向方法的指针。
在OC中方法并不是一个单纯的函数,由两部分组成:选择器(SEL)和实现体(IMP)。
选择器是一个字符串,用来表示方法名字;实现体是一个函数指针,指向方法的实现。
每个方法在 Objective-C 运行时环境中都有一个选择器与之对应。选择器可以看作是一个内部的名称,用于在运行时识别要被调用的方法。你可以通过 @selector() 来获取一个方法的选择器。
例如,假设你有一个名为 doSomething 的方法,你可以这样获取它的选择器:
SEL selector = @selector(doSomething); 选择器主要用于以下几个方面:
- 方法的调用:可以通过 -performSelector: 方法和一些变体来间接调用一个方法。这在你需要在运行时动态决定要调用的方法时非常有用。
- 作为方法的参数:在很多 Cocoa 和 Cocoa Touch 的 API 中,你会发现有许多方法的参数是选择器,例如 NSTimer 的 +scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval:target:selector:userInfo:repeats:。
- 响应者链:在 iOS 的事件处理和图形用户界面编程中,选择器常常被用来确定哪个方法应该被调用来响应一个特定的事件,例如按钮点击等。
选择器是在编译阶段由编译器生成的。编译器会根据方法名(包括参数序列)生成一个唯一的 ID,这个 ID 就是 SEL 类型的。
其中需要注意的是:@selector等于是把方法名翻译成SEL方法名。其仅仅关心方法名和参数个数,并不关心返回值与参数类型
IMP
**IMP是一个函数指针,保存了方法地址。**它是OC方法实现代码块的地址,通过他可以直接访问任意一个方法。免去发送消息的代码,IMP声明:
typedef id (&IMP)(id,SEL,...); IMP 是一个函数指针,这个被指向的函数包含一个接收消息的对象id(self 指针),调用方法的选标SEL(方法名),以及不定个数的方法参数,并返回一个id。
IMP和SEL的区别与联系:
- SEL:类方法的指针,相当于一种编号,区别与IMP。
- IMP:函数指针,保存了方法的地址。
SEL是通过表取对应关系的IMP,进行方法的调用。可以将SEL想象成一个指向方法名的指针,但它并不直接关联方法的实现代码,而是作为查找方法实现(即IMP)的一个标记或键值。
查找 IMP方式大致分为两种:快速查找和慢速查找。
快速查找
汇编代码查找过程
首先从cmp p0,#0开始,这里p0是寄存器,存放的是消息接受者。当进入消息发送入口时,先判断消息接收者是否存在,不存在则重新执行objc_msgSend。
b.le LNilOrTagged,b是跳转到的意思。le是如果p0小于等于0,总体意思是若p0小于等于0,则跳转到LNilOrTagged,执行b.eq LReturnZero直接退出这个函数。
//进入objc_msgSend流程 ENTRY _objc_msgSend //流程开始,无需frame UNWIND _objc_msgSend, NoFrame //判断p0(消息接收者)是否存在,不存在则重新开始执行objc_msgSend cmp p0, #0 // nil check and tagged pointer check //如果支持小对象类型,返回小对象或空 #if SUPPORT_TAGGED_POINTERS //b是进行跳转,b.le是小于判断,也就是p0小于0的时候跳转到LNilOrTagged b.le LNilOrTagged // (MSB tagged pointer looks negative) #else //等于,如果不支持小对象,就跳转至LReturnZero退出 b.eq LReturnZero #endif //通过p13取isa ldr p13, [x0] // p13 = isa //通过isa取class并保存到p16寄存器中 GetClassFromIsa_p16 p13, 1, x0 // p16 = class - 如果消息接受者不为nil,汇编继续跑,到CacheLookup NORMAL,在cache中查找imp,来看一下具体的实现
//在cache中通过sel查找imp的核心流程 .macro CacheLookup Mode, Function, MissLabelDynamic, MissLabelConstant // // Restart protocol: // // As soon as we're past the LLookupStart\Function label we may have // loaded an invalid cache pointer or mask. // // When task_restartable_ranges_synchronize() is called, // (or when a signal hits us) before we're past LLookupEnd\Function, // then our PC will be reset to LLookupRecover\Function which forcefully // jumps to the cache-miss codepath which have the following // requirements: // // GETIMP: // The cache-miss is just returning NULL (setting x0 to 0) // // NORMAL and LOOKUP: // - x0 contains the receiver // - x1 contains the selector // - x16 contains the isa // - other registers are set as per calling conventions // //从x16中取出class移到x15中 mov x15, x16 // stash the original isa //开始查找 LLookupStart\Function: // p1 = SEL, p16 = isa #if CACHE_MASK_STORAGE == CACHE_MASK_STORAGE_HIGH_16_BIG_ADDRS //ldr表示将一个值存入到p10寄存器中 //x16表示p16寄存器存储的值,当前是Class //#数值 表示一个值,这里的CACHE经过全局搜索发现是2倍的指针地址,也就是16个字节 //#define CACHE (2 * __SIZEOF_POINTER__) //经计算,p10就是cache ldr p10, [x16, #CACHE] // p10 = mask|buckets lsr p11, p10, #48 // p11 = mask and p10, p10, #0xffffffffffff // p10 = buckets and w12, w1, w11 // x12 = _cmd & mask //真机64位看这个 #elif CACHE_MASK_STORAGE == CACHE_MASK_STORAGE_HIGH_16 //CACHE 16字节,也就是通过isa内存平移获取cache,然后cache的首地址就是 (bucket_t *) ldr p11, [x16, #CACHE] // p11 = mask|buckets #if CONFIG_USE_PREOPT_CACHES //获取buckets #if __has_feature(ptrauth_calls) tbnz p11, #0, LLookupPreopt\Function and p10, p11, #0x0000ffffffffffff // p10 = buckets #else //and表示与运算,将与上mask后的buckets值保存到p10寄存器 and p10, p11, #0x0000fffffffffffe // p10 = buckets //p11与#0比较,如果p11不存在,就走Function,如果存在走LLookupPreopt tbnz p11, #0, LLookupPreopt\Function #endif //按位右移7个单位,存到p12里面,p0是对象,p1是_cmd eor p12, p1, p1, LSR #7 and p12, p12, p11, LSR #48 // x12 = (_cmd ^ (_cmd >> 7)) & mask #else and p10, p11, #0x0000ffffffffffff // p10 = buckets //LSR表示逻辑向右偏移 //p11, LSR #48表示cache偏移48位,拿到前16位,也就是得到mask //这个是哈希算法,p12存储的就是搜索下标(哈希地址) //整句表示_cmd & mask并保存到p12 and p12, p1, p11, LSR #48 // x12 = _cmd & mask #endif // CONFIG_USE_PREOPT_CACHES #elif CACHE_MASK_STORAGE == CACHE_MASK_STORAGE_LOW_4 ldr p11, [x16, #CACHE] // p11 = mask|buckets and p10, p11, #~0xf // p10 = buckets and p11, p11, #0xf // p11 = maskShift mov p12, #0xffff lsr p11, p12, p11 // p11 = mask = 0xffff >> p11 and p12, p1, p11 // x12 = _cmd & mask #else #error Unsupported cache mask storage for ARM64. #endif //去除掩码后bucket的内存平移 //PTRSHIFT经全局搜索发现是3 //LSL #(1+PTRSHIFT)表示逻辑左移4位,也就是*16 //通过bucket的首地址进行左平移下标的16倍数并与p12相与得到bucket,并存入到p13中 add p13, p10, p12, LSL #(1+PTRSHIFT) // p13 = buckets + ((_cmd & mask) << (1+PTRSHIFT)) // do { //ldp表示出栈,取出bucket中的imp和sel分别存放到p17和p9 1: ldp p17, p9, [x13], #-BUCKET_SIZE // {imp, sel} = *bucket-- //cmp表示比较,对比p9和p1,如果相同就找到了对应的方法,返回对应imp,走CacheHit cmp p9, p1 // if (sel != _cmd) { //b.ne表示如果不相同则跳转到3f b.ne 3f // scan more // } else { 2: CacheHit \Mode // hit: call or return imp // } //向前查找下一个bucket,一直循环直到找到对应的方法,循环完都没有找到就调用_objc_msgSend_uncached 3: cbz p9, \MissLabelDynamic // if (sel == 0) goto Miss; //通过p13和p10来判断是否是第一个bucket cmp p13, p10 // } while (bucket >= buckets) b.hs 1b // wrap-around: // p10 = first bucket // p11 = mask (and maybe other bits on LP64) // p12 = _cmd & mask // // A full cache can happen with CACHE_ALLOW_FULL_UTILIZATION. // So stop when we circle back to the first probed bucket // rather than when hitting the first bucket again. // // Note that we might probe the initial bucket twice // when the first probed slot is the last entry. #if CACHE_MASK_STORAGE == CACHE_MASK_STORAGE_HIGH_16_BIG_ADDRS add p13, p10, w11, UXTW #(1+PTRSHIFT) // p13 = buckets + (mask << 1+PTRSHIFT) #elif CACHE_MASK_STORAGE == CACHE_MASK_STORAGE_HIGH_16 add p13, p10, p11, LSR #(48 - (1+PTRSHIFT)) // p13 = buckets + (mask << 1+PTRSHIFT) // see comment about maskZeroBits #elif CACHE_MASK_STORAGE == CACHE_MASK_STORAGE_LOW_4 add p13, p10, p11, LSL #(1+PTRSHIFT) // p13 = buckets + (mask << 1+PTRSHIFT) #else #error Unsupported cache mask storage for ARM64. #endif add p12, p10, p12, LSL #(1+PTRSHIFT) // p12 = first probed bucket // do { 4: ldp p17, p9, [x13], #-BUCKET_SIZE // {imp, sel} = *bucket-- cmp p9, p1 // if (sel == _cmd) b.eq 2b // goto hit cmp p9, #0 // } while (sel != 0 && ccmp p13, p12, #0, ne // bucket > first_probed) b.hi 4b LLookupEnd\Function: LLookupRecover\Function: b \MissLabelDynamic #if CONFIG_USE_PREOPT_CACHES #if CACHE_MASK_STORAGE != CACHE_MASK_STORAGE_HIGH_16 #error config unsupported #endif LLookupPreopt\Function: #if __has_feature(ptrauth_calls) and p10, p11, #0x007ffffffffffffe // p10 = buckets autdb x10, x16 // auth as early as possible #endif // x12 = (_cmd - first_shared_cache_sel) adrp x9, _MagicSelRef@PAGE ldr p9, [x9, _MagicSelRef@PAGEOFF] sub p12, p1, p9 // w9 = ((_cmd - first_shared_cache_sel) >> hash_shift & hash_mask) #if __has_feature(ptrauth_calls) // bits 63..60 of x11 are the number of bits in hash_mask // bits 59..55 of x11 is hash_shift lsr x17, x11, #55 // w17 = (hash_shift, ...) lsr w9, w12, w17 // >>= shift lsr x17, x11, #60 // w17 = mask_bits mov x11, #0x7fff lsr x11, x11, x17 // p11 = mask (0x7fff >> mask_bits) and x9, x9, x11 // &= mask #else // bits 63..53 of x11 is hash_mask // bits 52..48 of x11 is hash_shift lsr x17, x11, #48 // w17 = (hash_shift, hash_mask) lsr w9, w12, w17 // >>= shift and x9, x9, x11, LSR #53 // &= mask #endif // sel_offs is 26 bits because it needs to address a 64 MB buffer (~ 20 MB as of writing) // keep the remaining 38 bits for the IMP offset, which may need to reach // across the shared cache. This offset needs to be shifted << 2. We did this // to give it even more reach, given the alignment of source (the class data) // and destination (the IMP) ldr x17, [x10, x9, LSL #3] // x17 == (sel_offs << 38) | imp_offs cmp x12, x17, LSR #38 .if \Mode == GETIMP b.ne \MissLabelConstant // cache miss sbfiz x17, x17, #2, #38 // imp_offs = combined_imp_and_sel[0..37] << 2 sub x0, x16, x17 // imp = isa - imp_offs SignAsImp x0 ret .else b.ne 5f // cache miss sbfiz x17, x17, #2, #38 // imp_offs = combined_imp_and_sel[0..37] << 2 sub x17, x16, x17 // imp = isa - imp_offs .if \Mode == NORMAL br x17 .elseif \Mode == LOOKUP orr x16, x16, #3 // for instrumentation, note that we hit a constant cache SignAsImp x17 ret .else .abort unhandled mode \Mode .endif 5: ldursw x9, [x10, #-8] // offset -8 is the fallback offset add x16, x16, x9 // compute the fallback isa b LLookupStart\Function // lookup again with a new isa .endif #endif // CONFIG_USE_PREOPT_CACHES .endmacro 类对象/元类通过内存平移获得cache,获得buckets。
在缓存中找到了就直接调用,找到sel就会进入CacheHit,去return or call imp:返回或调用方法的实现(imp)。
- 如果没有找到缓存,查找下一个bucket,一直循环直到找到对应的方法,最后还没有找到的话,就调用objc_msgSend_uncached方法。
下面是上述判断跳转代码:
//LGetIsaDone是一个入口 LGetIsaDone: // calls imp or objc_msgSend_uncached //进入到缓存查找或者没有缓存查找方法的流程 CacheLookup NORMAL, _objc_msgSend, __objc_msgSend_uncached __objc_msgSend_uncached源码汇编:
STATIC_ENTRY __objc_msgSend_uncached UNWIND __objc_msgSend_uncached, FrameWithNoSaves // THIS IS NOT A CALLABLE C FUNCTION // Out-of-band p15 is the class to search MethodTableLookup TailCallFunctionPointer x17 END_ENTRY __objc_msgSend_uncached 其中调用了MethodTableLookup宏: 从方法列表中去查找方法
看一下它的结构:
.macro MethodTableLookup SAVE_REGS MSGSEND // lookUpImpOrForward(obj, sel, cls, LOOKUP_INITIALIZE | LOOKUP_RESOLVER) // receiver and selector already in x0 and x1 mov x2, x16 mov x3, #3 bl _lookUpImpOrForward // IMP in x0 mov x17, x0 RESTORE_REGS MSGSEND .endmacro 总结消息转送快速查找IMP
objc_msgSend(receiver, sel, …)
- 检查接受者是否存在,为nil则不做任何处理;
- 通过receiverdeisa指针找到对应的class类对象;
- 找到类对象之后通过内存平移找到cache;
- 从cache中获取buckets;
- 从buckets中对比sel,查看是否有同名方法;
- 如果有对应的sel,就会进入到cacheHit,调用imp;
- 如果没有对应的sel,进入objc_msgSend_uncached,然后到lookUpImpOrForward(慢速查找)。
方法缓存:
如果一个方法被调用了,那个这个方法有更大的几率被再此调用,既然如此直接维护一个缓存列表,把调用过的方法加载到缓存列表中,再次调用该方法时,先去缓存列表中去查找,如果找不到再去方法列表查询。这样避免了每次调用方法都要去方法列表去查询,大大的提高了速率。
慢速查找
NEVER_INLINE IMP lookUpImpOrForward(id inst, SEL sel, Class cls, int behavior) { const IMP forward_imp = (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache; IMP imp = nil; Class curClass; runtimeLock.assertUnlocked(); if (slowpath(!cls->isInitialized())) { ...省略部分 for (unsigned attempts = unreasonableClassCount();;) { if (curClass->cache.isConstantOptimizedCache(/* strict */true)) { #if CONFIG_USE_PREOPT_CACHES imp = cache_getImp(curClass, sel); if (imp) goto done_unlock; curClass = curClass->cache.preoptFallbackClass(); #endif } else { // curClass method list. Method meth = getMethodNoSuper_nolock(curClass, sel); if (meth) { imp = meth->imp(false); goto done; } if (slowpath((curClass = curClass->getSuperclass()) == nil)) { // No implementation found, and method resolver didn't help. // Use forwarding. imp = forward_imp; break; } } // Halt if there is a cycle in the superclass chain. if (slowpath(--attempts == 0)) { _objc_fatal("Memory corruption in class list."); } // Superclass cache. imp = cache_getImp(curClass, sel); if (slowpath(imp == forward_imp)) { // Found a forward:: entry in a superclass. // Stop searching, but don't cache yet; call method // resolver for this class first. break; } if (fastpath(imp)) { // Found the method in a superclass. Cache it in this class. goto done; } } // 未找到实现。请尝试一次方法解析器。 if (slowpath(behavior & LOOKUP_RESOLVER)) { behavior ^= LOOKUP_RESOLVER; return resolveMethod_locked(inst, sel, cls, behavior); } done: if (fastpath((behavior & LOOKUP_NOCACHE) == 0)) { #if CONFIG_USE_PREOPT_CACHES while (cls->cache.isConstantOptimizedCache(/* strict */true)) { cls = cls->cache.preoptFallbackClass(); } #endif log_and_fill_cache(cls, imp, sel, inst, curClass); } done_unlock: runtimeLock.unlock(); if (slowpath((behavior & LOOKUP_NIL) && imp == forward_imp)) { return nil; } return imp; } - 检查类是否被初始化,是否是个已知的关系,确定继承关系的准备工作。
for (unsigned attempts = unreasonableClassCount();;) { if (curClass->cache.isConstantOptimizedCache(/* strict */true)) { // 如果是常量优化缓存 // 再一次从cache查找imp // 目的:防止多线程操作时,刚好调用函数,此时缓存进来了 #if CONFIG_USE_PREOPT_CACHES // iOS操作系统且真机的情况下 imp = cache_getImp(curClass, sel); if (imp) goto done_unlock; curClass = curClass->cache.preoptFallbackClass(); #endif } else { // curClass方法列表。 method_t *meth = getMethodNoSuper_nolock(curClass, sel); if (meth) { imp = meth->imp(false); goto done; } // 每次判断都会把curClass的父类赋值给curClass if (slowpath((curClass = curClass->getSuperclass()) == nil)) { // 没有找到实现,方法解析器没有帮助。 // 使用转发。 imp = forward_imp; break; } } // 如果超类链中存在循环,则停止。 if (slowpath(--attempts == 0)) { _objc_fatal("Memory corruption in class list."); } // 超类缓存。 imp = cache_getImp(curClass, sel); if (slowpath(imp == forward_imp)) { // 在超类中找到forward::条目。 // 停止搜索,但不要缓存;调用方法 // 首先为这个类解析器。 break; } if (fastpath(imp)) { // 在超类中找到方法。在这个类中缓存它。 goto done; } } 进入循环逻辑:
- 从本类的methodList查找IMP(查找的方式是
getMethodNoSuper_nolock); - 从本类的父类的的cache中查找(
cache_getImp); - 从本类的父类demethodList查找IMP…继承链遍历…(父类->…->根父类);
- 若上面任何一个环节查找到了imp,跳出循环,缓存方法到本类的cache中;
- 直到查找到nil,指定imp为消息转发,跳出循环。
跳出循环后的逻辑:
done: if (fastpath((behavior & LOOKUP_NOCACHE) == 0)) { #if CONFIG_USE_PREOPT_CACHES // iOS操作系统且真机的情况下 while (cls->cache.isConstantOptimizedCache(/* strict */true)) { cls = cls->cache.preoptFallbackClass(); } #endif log_and_fill_cache(cls, imp, sel, inst, curClass); } done_unlock: runtimeLock.unlock(); if (slowpath((behavior & LOOKUP_NIL) && imp == forward_imp)) { return nil; } return imp; 如果找到了imp,就会把imp缓存到本类cache里(log_and_fill_cache):(注意这里不管是本类还是本类的父类找到了imp,都会缓存到本类中去)。
static void log_and_fill_cache(Class cls, IMP imp, SEL sel, id receiver, Class implementer) { #if SUPPORT_MESSAGE_LOGGING if (slowpath(objcMsgLogEnabled && implementer)) { bool cacheIt = logMessageSend(implementer->isMetaClass(), cls->nameForLogging(), implementer->nameForLogging(), sel); if (!cacheIt) return; } #endif cls->cache.insert(sel, imp, receiver); // 插入缓存 } getMethodNoSuper_nolock查找方式
tatic method_t * getMethodNoSuper_nolock(Class cls, SEL sel) { runtimeLock.assertLocked(); ASSERT(cls->isRealized()); // fixme nil cls? // fixme nil sel? auto const methods = cls->data()->methods(); for (auto mlists = methods.beginLists(), end = methods.endLists(); mlists != end; ++mlists) { // <rdar://problem/46904873> getMethodNoSuper_nolock is the hottest // caller of search_method_list, inlining it turns // getMethodNoSuper_nolock into a frame-less function and eliminates // any store from this codepath. method_t *m = search_method_list_inline(*mlists, sel); if (m) return m; } return nil; } 在search_method_list_inline里找到了method_t就会返回出去了(search_method_list_inline):
ALWAYS_INLINE static method_t * search_method_list_inline(const method_list_t *mlist, SEL sel) { int methodListIsFixedUp = mlist->isFixedUp(); int methodListHasExpectedSize = mlist->isExpectedSize(); if (fastpath(methodListIsFixedUp && methodListHasExpectedSize)) { return findMethodInSortedMethodList(sel, mlist); } else { // Linear search of unsorted method list if (auto *m = findMethodInUnsortedMethodList(sel, mlist)) return m; } #if DEBUG // sanity-check negative results if (mlist->isFixedUp()) { for (auto& meth : *mlist) { if (meth.name() == sel) { _objc_fatal("linear search worked when binary search did not"); } } } #endif return nil; } 这里就是使用findMethodInSortedMethodList和findMethodInUnsortedMethodList通过sel找到method_t的。这两个函数的区别就是:
前者是排好序的,后者是未排好序的;前者方法中的查询方式是二分查找,后者则是普通查找。
总结消息传递慢速查找IMP
IMP lookUpImpOrForward(id inst, SEL sel, Class cls, int behavior)
- 从本类的 method list (二分查找/遍历查找)查找imp
- 从本类的父类的cache查找imp(汇编)
- 从本类的父类的method list (二分查找/遍历查找)查找imp
…继承链遍历…(父类->…->根父类)里找cache和method list的imp - 若上面环节有任何一个环节查找到了imp,跳出循环,缓存方法到本类的cache,并返回imp
- 直到查找到nil,指定imp为消息转发,跳出循环,执行动态方法解析resolveMethod_locked
2. 消息转发
当一个对象无法接收某一消息时,就会启动所谓“消息转发(message forwarding)”机制。通过消息转发机制,我们可以告诉对象如何处理未知的消息。
消息转发机制大致可以分为三个步骤:
- 动态方法解析
- 备援接受者
- 完整消息转发
下图为消息转发过程的示意图: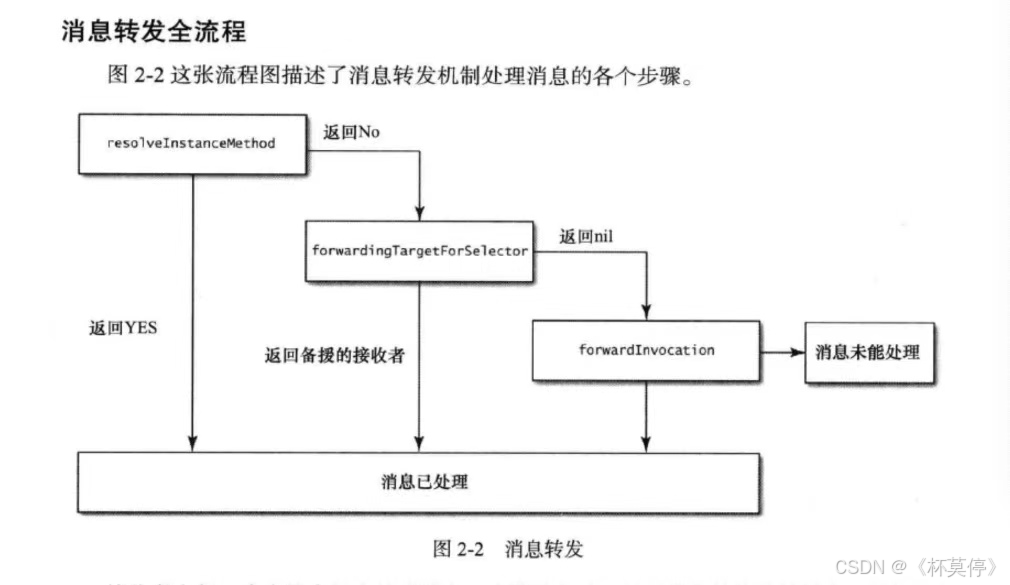
动态决议
// No implementation found. Try method resolver once. //未找到实现。尝试一次方法解析器 if (slowpath(behavior & LOOKUP_RESOLVER)) { behavior ^= LOOKUP_RESOLVER; return resolveMethod_locked(inst, sel, cls, behavior); } 通过之前的源码可以发现,如果没有找到方法则尝试调用resolveMethod_locked动态解析,只会执行一次:
/*********************************************************************** * resolveMethod_locked * Call +resolveClassMethod or +resolveInstanceMethod. * * Called with the runtimeLock held to avoid pressure in the caller * Tail calls into lookUpImpOrForward, also to avoid pressure in the callerb **********************************************************************/ static NEVER_INLINE IMP resolveMethod_locked(id inst, SEL sel, Class cls, int behavior) { lockdebug::assert_locked(&runtimeLock); ASSERT(cls->isRealized()); runtimeLock.unlock(); //判断是不是元类 if (! cls->isMetaClass()) { // try [cls resolveInstanceMethod:sel] resolveInstanceMethod(inst, sel, cls); } else { // try [nonMetaClass resolveClassMethod:sel] // and [cls resolveInstanceMethod:sel] resolveClassMethod(inst, sel, cls); if (!lookUpImpOrNilTryCache(inst, sel, cls)) { resolveInstanceMethod(inst, sel, cls); } } // chances are that calling the resolver have populated the cache // so attempt using it return lookUpImpOrForwardTryCache(inst, sel, cls, behavior); } 主要用的的方法如下:
// 类方法未找到时调起,可以在此添加方法实现 + (BOOL)resolveClassMethod:(SEL)sel; // 对象方法未找到时调起,可以在此添加方法实现 + (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel; //其中参数sel为未处理的方法 上述代码大致流程:
- 先判断进行解析的是不是元类
- 如果不是元类,则调用则调用
resolveInstanceMethod进行对象方法动态解析 - 如果是元类,则调用
resolveClassMethod进行类方法动态解析,完成类方法动态解析后,再次查询cls中的imp,如果没有找到,则进行一次对象方法动态解析。
而这两个方法resolveInstanceMethod和resolveClassMethod则称为方法的动态决议。
执行完上述代码后返回lookUpImpOrForwardTryCache:
IMP lookUpImpOrForwardTryCache(id inst, SEL sel, Class cls, int behavior) { return _lookUpImpTryCache(inst, sel, cls, behavior); } 这个方法调用的是_lookUpImpTryCache方法:
ALWAYS_INLINE static IMP _lookUpImpTryCache(id inst, SEL sel, Class cls, int behavior) { lockdebug::assert_unlocked(&runtimeLock); if (slowpath(!cls->isInitialized())) { // see comment in lookUpImpOrForward return lookUpImpOrForward(inst, sel, cls, behavior); } IMP imp = cache_getImp(cls, sel); if (imp != NULL) goto done; #if CONFIG_USE_PREOPT_CACHES if (fastpath(cls->cache.isConstantOptimizedCache(/* strict */true))) { imp = cache_getImp(cls->cache.preoptFallbackClass(), sel); } #endif if (slowpath(imp == NULL)) { return lookUpImpOrForward(inst, sel, cls, behavior); } done: if ((behavior & LOOKUP_NIL) && imp == (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache) { return nil; } return imp; } 进入_lookUpImpTryCache源码,可以看到这里有cache_getImp;也就是说在进行一次动态决议之后,还会通过cache_getImp从cache里找一遍方法的sel。
#endif if (slowpath(imp == NULL)) { return lookUpImpOrForward(inst, sel, cls, behavior); } 如果还是没找到(imp == NULL)?也就是无法通过动态添加方法的话,还会执行一次lookUpImpOrForward,这时候进lookUpImpOrForward方法,这里behavior传的值会发生变化。
第二次进入lookUpImpOrForward方法后,执行到if (slowpath(behavior & LOOKUP_RESOLVER))这个判断时:
// 这里就是消息转发机制第一层的入口 if (slowpath(behavior & LOOKUP_RESOLVER)) { behavior ^= LOOKUP_RESOLVER; return resolveMethod_locked(inst, sel, cls, behavior); } 根据变化后的behavior值和LOOKUP_RESOLVER值之间的关系导致该if语句内部只能进入第一次,因此这个判断相当于单例。解释了为什么开头说的该动态解析resolveMethod_locked为什么只执行一次。
动态解析添加方法
在动态决议阶段可以为类添加方法,以保证程序正常运行
class_addMethod(Class _Nullable cls, SEL _Nonnull name, IMP _Nonnull imp, const char * _Nullable types) @cls : 给哪个类对象添加方法 @name : SEL类型,给哪个方法名添加方法实现 @imp : IMP类型的,要把哪个方法实现添加给给定的方法名 @types : 就是表示返回值和参数类型的字符串 我们来看一个例子:
// Dog.h #import <Foundation/Foundation.h> NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_BEGIN @interface Dog : NSObject - (void)print; @end NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_END //Dog.m #import "Dog.h" #import <objc/runtime.h> #import "NiuBiDog.h" @implementation Dog @end 可以看到print方法并未实现,所以在主函数中调用程序一定会崩溃,
然后我们将代码修改为下面这样:
在.m文件中增加这个方法:
+(BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel { NSLog(@"%s, sel = %@", __func__, NSStringFromSelector(sel)); return [super resolveInstanceMethod:sel]; } 程序依然会崩溃,我们看看输出结果:
是因为找不到imp而崩溃,那么我们可以在这个方法里通过runtime的class_addMethod,给sel动态的生成imp。其中第四个参数是返回值类型,用void用字符串描述:“v@:”
+ (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel { NSLog(@"%s, sel = %@", __func__, NSStringFromSelector(sel)); if (sel == @selector(print)) { IMP imp = class_getMethodImplementation(self, @selector(add)); class_addMethod(self, sel, imp, "v@"); return YES; } return [super resolveInstanceMethod:sel]; } - (void)add { NSLog(@"12345"); } 
快速转发
当cache没有找到imp,类的继承链里的方法列表都没有找到imp,并且resolveInstanceMethod / resolveClassMethod 返回NO就会进入消息转发。也就是所以如果本类没有能力去处理这个消息,那么就转发给其他的类,让其他类去处理。
done: if ((behavior & LOOKUP_NIL) && imp == (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache) { return nil; } return imp; 从imp == (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache进入消息转发机制。
查看一下这个方法:
竟然是汇编实现的这就又印证了汇编速度更快的结论:
STATIC_ENTRY __objc_msgForward_impcache // No stret specialization. b __objc_msgForward END_ENTRY __objc_msgForward_impcache ENTRY __objc_msgForward adrp x17, __objc_forward_handler@PAGE ldr p17, [x17, __objc_forward_handler@PAGEOFF] TailCallFunctionPointer x17 END_ENTRY __objc_msgForward - Dog类中定义print方法但是不实现,利用forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector 方法进行消息快速转发。
- NiuBiDog类中定义print方法且实现:
//NiuBiDog.h #import "Dog.h" NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_BEGIN @interface NiuBiDog : Dog - (void)print; @end NS_ASSUME_NONNULL_END //NiuBiDog.m #import "NiuBiDog.h" @implementation NiuBiDog - (void)print { NSLog(@"\n%s", __func__); } @end //Dog.m #import "Dog.h" #import <objc/runtime.h> #import "NiuBiDog.h" @implementation Dog // 快速转发 - (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector { if (aSelector == @selector(print)) { return [NiuBiDog new]; } return [super forwardingTargetForSelector:aSelector]; } @end 
转发的作用在于,如果当前对象无法响应消息,就将它转发给能响应的对象。
慢速转发
如果消息的快速转发也没有找到方法;后面还有个methodSignatureForSelector方法,作用是方法有效性签名。
将刚才使用快速转发forwardingTargetForSelector方法注释后,添加上methodSignatureForSelector方法后,这个方法需要搭配forwardInvocation:
forwardInvocation方法提供了一个入参,类型是NSInvocation;它提供了target和selector用于指定目标里查找方法实现。
// 慢速转发 - (NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)aSelector { NSLog(@"%s aSelector = %@", __func__, NSStringFromSelector(aSelector)); return [NSMethodSignature signatureWithObjCTypes:"v@"]; } - (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation { NSLog(@" %s, 甘,文,崔", __func__); } 
总结
防止系统崩溃的三个救命稻草:动态解析、快速转发、慢速转发。
OC方法调用的本质就是消息发送,消息发送是SEL-IMP的查找过程。
动态决议
// 类方法未找到时调起,可以在此添加方法实现 + (BOOL)resolveClassMethod:(SEL)sel; // 对象方法未找到时调起,可以在此添加方法实现 + (BOOL)resolveInstanceMethod:(SEL)sel; //其中参数sel为未处理的方法 消息转发
消息快速转发:
- (id)forwardingTargetForSelector:(SEL)aSelector; 消息慢速转发:
// 方法签名 - (NSMethodSignature *)methodSignatureForSelector:(SEL)aSelector; // 正向调用 - (void)forwardInvocation:(NSInvocation *)anInvocation; 消息的三次拯救
- 动态方法解析
- 备援接收者
- 完整消息转发