前端数据展示(数据可视化、数据大屏等)可使用的工具比较多,很多第三方都提供了在线平台,比如阿里云,只需数据接口,在线配置一下界面即可使用。
- 阿里云的使用:利用阿里云物联网平台(IoT)实现WEB数据可视化
- 第三方平台对比:有哪些免费简单的数据展示(数据可视化)网站
也可以使用开源代码自己开发前端,本文所介绍的就是
ECharts的开发,这是一款基于JavaScript 的开源可视化图表库,可以流畅的运行在 PC 和移动设备上,兼容当前绝大部分浏览器(IE9/10/11,Chrome,Firefox,Safari等),底层依赖矢量图形库 ZRender,提供直观,交互丰富,可高度个性化定制的数据可视化图表。
注意,本文是在Vue3版本下的Element-UI中使用,ECharts官网打开较慢,可尝试翻越。
安装
npm install echarts --save 调用
创建一个*.vue页面,实现方法如下三种。
1. 本页数据
修改官方代码:https://echarts.apache.org/handbook/zh/basics/import
<template> <div id="main" style="width: 600px;height:400px;"></div> </template> <script setup> import * as echarts from 'echarts' </script> <script> export default { data() { return {} }, created() {}, // DOM 渲染完成触发 mounted() { // 基于准备好的dom,初始化echarts实例 var myChart = echarts.init(document.getElementById('main')) // 绘制图表 myChart.setOption({ title: { text: 'ECharts 入门示例' }, tooltip: {}, xAxis: { data: ['衬衫', '羊毛衫', '雪纺衫', '裤子', '高跟鞋', '袜子'] }, yAxis: {}, series: [ { name: '销量', type: 'bar', data: [5, 20, 36, 10, 10, 20] } ] }); } } </script> 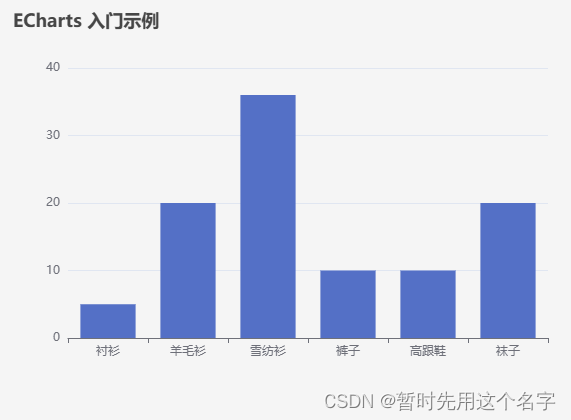
2. 调用数据
修改官方的线性图示例图代码,修改为线性和柱状混合展示图
https://echarts.apache.org/examples/zh/editor.html?c=data-transform-filter&lang=js
另需准备一个json文件,下载自官网:https://echarts.apache.org/examples/data/asset/data/life-expectancy-table.json
本例中将文件放于根目录,本例中路径为:http://localhost/life-expectancy-table.json
<template> <div id="main" style="width: 600px;height:400px;"></div> </template> <script setup> import * as echarts from 'echarts' import axios from 'axios' import { nextTick } from 'vue' </script> <script> export default { data() { return {} }, created() {}, // DOM 渲染完成触发 mounted() { // 数据来源,注意自行修改 var url = 'http://localhost/life-expectancy-table.json'; // 基于准备好的dom,初始化echarts实例 var myChart = echarts.init(document.getElementById('main')) // 每隔三秒发起请求,获取数据并绘制图表 nextTick(() => { setInterval(() => { // 执行 this.run(url, myChart); }, 3000) }) }, methods: { // 执行 run (url, obj){ // 调用json axios.get(url).then(res => { let option = { dataset: [ { id: 'dataset_raw', source: res.data }, { id: 'dataset_since_1950_of_germany', fromDatasetId: 'dataset_raw', transform: { type: 'filter', config: { and: [ { dimension: 'Year', gte: 1950 }, { dimension: 'Country', '=': 'Germany' } ] } } }, { id: 'dataset_since_1950_of_france', fromDatasetId: 'dataset_raw', transform: { type: 'filter', config: { and: [ { dimension: 'Year', gte: 1950 }, { dimension: 'Country', '=': 'France' } ] } } } ], title: { text: 'Income of Germany and France since 1950' }, tooltip: { trigger: 'axis' }, xAxis: { type: 'category', nameLocation: 'middle' }, yAxis: { name: 'Income' }, series: [ { type: 'line', datasetId: 'dataset_since_1950_of_germany', showSymbol: false, encode: { x: 'Year', y: 'Income', itemName: 'Year', tooltip: ['Income'] } }, { type: 'bar', datasetId: 'dataset_since_1950_of_france', showSymbol: false, encode: { x: 'Year', y: 'Income', itemName: 'Year', tooltip: ['Income'] } } ] }; obj.setOption(option); }) } } } </script> 展示图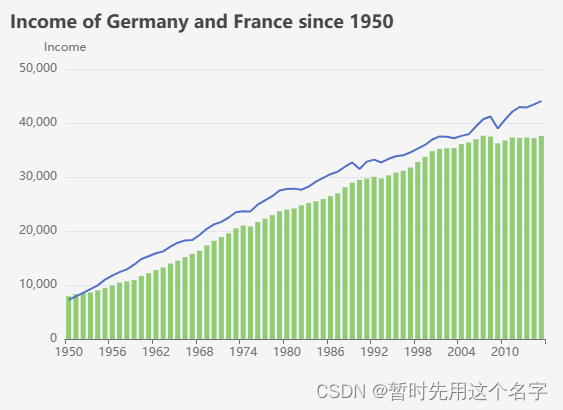
- 可以顺便学习一下vue3中 nextTick 的具体用法。
3. 异步调用
还是上面的例子(实现略有不同),setInterval()中原有的run()函数改为了getOpt()函数,主要用来学习axios如何返回值~~
学习:获取axios的return值
<template> <div id="main" style="width: 600px;height:400px;"></div> </template> <script setup> import * as echarts from 'echarts' import axios from 'axios' import { nextTick } from 'vue' </script> <script> export default { data() { return {} }, created() {}, // DOM 渲染完成触发 mounted() { // 数据来源,注意自行修改 var url = 'http://localhost/life-expectancy-table.json'; // 基于准备好的dom,初始化echarts实例 var myChart = echarts.init(document.getElementById('main')) // 每隔三秒发起请求,获取数据并绘制图表 nextTick(() => { setInterval(() => { // 与上面不同的实现方式 this.getOpt(url).then(opt=>{ myChart.setOption(opt); }); }, 3000) }) }, methods: { // 获取 async getOpt (url){ let option; // 调用json await axios.get(url).then(res => { option = { dataset: [ { id: 'dataset_raw', source: res.data }, { id: 'dataset_since_1950_of_germany', fromDatasetId: 'dataset_raw', transform: { type: 'filter', config: { and: [ { dimension: 'Year', gte: 1950 }, { dimension: 'Country', '=': 'Germany' } ] } } }, { id: 'dataset_since_1950_of_france', fromDatasetId: 'dataset_raw', transform: { type: 'filter', config: { and: [ { dimension: 'Year', gte: 1950 }, { dimension: 'Country', '=': 'France' } ] } } } ], title: { text: 'Income of Germany and France since 1950' }, tooltip: { trigger: 'axis' }, xAxis: { type: 'category', nameLocation: 'middle' }, yAxis: { name: 'Income' }, series: [ { type: 'line', datasetId: 'dataset_since_1950_of_germany', showSymbol: false, encode: { x: 'Year', y: 'Income', itemName: 'Year', tooltip: ['Income'] } }, { type: 'bar', datasetId: 'dataset_since_1950_of_france', showSymbol: false, encode: { x: 'Year', y: 'Income', itemName: 'Year', tooltip: ['Income'] } } ] }; }) return option; } } } </script> 4. 多表同时
结合两种不同的图标放在一个页面,其中新增一种表为:
https://echarts.apache.org/examples/zh/editor.html?c=gauge-ring
<template> <div id="main" style="width: 600px;height:400px;float:left"></div> <div id="sub" style="width: 600px;height:400px;float:left;"></div> </template> <script setup> import * as echarts from 'echarts' import axios from 'axios' import { nextTick } from 'vue' </script> <script> export default { data() { return {} }, created() {}, // DOM 渲染完成触发 mounted() { // 数据来源,注意自行修改 var url = 'http://localhost/life-expectancy-table.json'; // 基于准备好的dom,初始化echarts实例 var myMain = echarts.init(document.getElementById('main')) var mySub = echarts.init(document.getElementById('sub')) var option; const gaugeData = [ { value: 20, name: 'Perfect', title: { offsetCenter: ['0%', '-30%'] }, detail: { valueAnimation: true, offsetCenter: ['0%', '-20%'] } }, { value: 40, name: 'Good', title: { offsetCenter: ['0%', '0%'] }, detail: { valueAnimation: true, offsetCenter: ['0%', '10%'] } }, { value: 60, name: 'Commonly', title: { offsetCenter: ['0%', '30%'] }, detail: { valueAnimation: true, offsetCenter: ['0%', '40%'] } } ]; option = { series: [ { type: 'gauge', startAngle: 90, endAngle: -270, pointer: { show: false }, progress: { show: true, overlap: false, roundCap: true, clip: false, itemStyle: { borderWidth: 1, borderColor: '#464646' } }, axisLine: { lineStyle: { width: 40 } }, splitLine: { show: false, distance: 0, length: 10 }, axisTick: { show: false }, axisLabel: { show: false, distance: 50 }, data: gaugeData, title: { fontSize: 14 }, detail: { width: 50, height: 14, fontSize: 14, color: 'inherit', borderColor: 'inherit', borderRadius: 20, borderWidth: 1, formatter: '{value}%' } } ] }; // 每隔三秒发起请求,获取数据并绘制图表 nextTick(() => { setInterval(() => { // main部分 this.getOptMain(url).then(opt=>{ myMain.setOption(opt); }); // sub部分 gaugeData[0].value = +(Math.random() * 100).toFixed(2); gaugeData[1].value = +(Math.random() * 100).toFixed(2); gaugeData[2].value = +(Math.random() * 100).toFixed(2); mySub.setOption({ series: [ { data: gaugeData, pointer: { show: false } } ] }); }, 3000) }) option && mySub.setOption(option); }, methods: { // 获取 async getOptMain (url){ let option; // 调用json await axios.get(url).then(res => { option = { dataset: [ { id: 'dataset_raw', source: res.data }, { id: 'dataset_since_1950_of_germany', fromDatasetId: 'dataset_raw', transform: { type: 'filter', config: { and: [ { dimension: 'Year', gte: 1950 }, { dimension: 'Country', '=': 'Germany' } ] } } }, { id: 'dataset_since_1950_of_france', fromDatasetId: 'dataset_raw', transform: { type: 'filter', config: { and: [ { dimension: 'Year', gte: 1950 }, { dimension: 'Country', '=': 'France' } ] } } } ], title: { text: 'Income of Germany and France since 1950' }, tooltip: { trigger: 'axis' }, xAxis: { type: 'category', nameLocation: 'middle' }, yAxis: { name: 'Income' }, series: [ { type: 'line', datasetId: 'dataset_since_1950_of_germany', showSymbol: false, encode: { x: 'Year', y: 'Income', itemName: 'Year', tooltip: ['Income'] } }, { type: 'bar', datasetId: 'dataset_since_1950_of_france', showSymbol: false, encode: { x: 'Year', y: 'Income', itemName: 'Year', tooltip: ['Income'] } } ] }; }) return option; } } } </script> 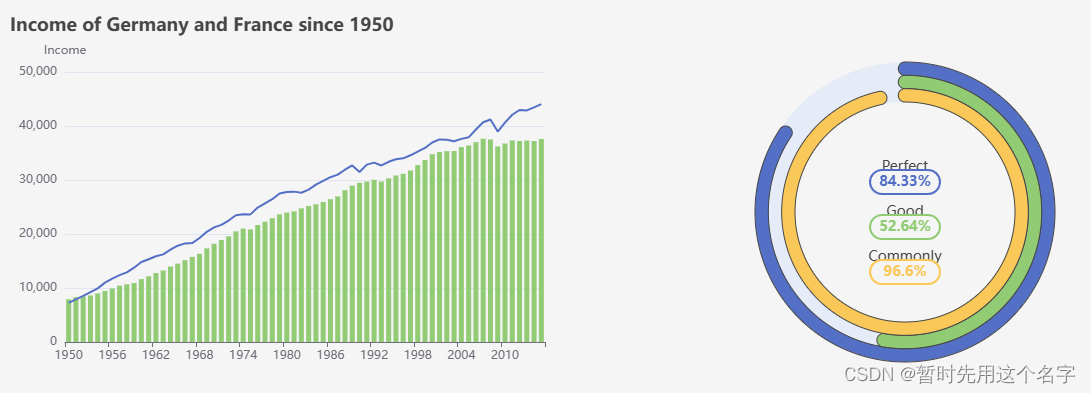
参考:
Vue Element UI 之ECharts图表
Echarts 在vue3x中使用(包括动态数据变化)
优化了三年经验者的Echarts卡顿
关于vue+elementui 访问本地json和跨域访问API问题
Vue3+ElementPlus+Axios实现从后端请求数据并渲染
Vue3中的Methods用法介绍
Vue3中你应该知道的setup!

