我们今天的主角是Gateway网关,一听名字就知道它基本的任务就是去分发路由。根据不同的指定名称去请求各个服务,下面是Gateway官方的解释:
Spring Cloud Gateway,其他的博主就不多说了,大家多去官网看看,只有官方的才是最正确的,回归主题,我们的过滤器与断言如何加载进来的,并且是如何进行对请求进行过滤的。
大家如果对SpringBoot自动加载的熟悉的话,一定知道要看一个代码的源码,要找到META-INF下的spring.factories,具体为啥的博主就不多说了,网上也有很多讲解自动加载的源码分析,今天就讲解Gateway,所有项目三板斧:加依赖、写注解、弄配置
依赖:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId> </dependency>
注解:启动类上需要添加@EnableDiscoveryClient,启动服务发现
配置:
spring: cloud: gateway: routes: - id: after-route #id必须要唯一 uri: lb://product-center predicates: - After=2030-12-16T15:53:22.999+08:00[Asia/Shanghai] filters: - PrefixPath=/product-api
大家看到这个配置的时候,为什么我们写After断言与PrefixPath过滤器,gateway就会自动识别呢,那我们有没有那一个地方可以看到所有的自带的属性呢?当然有,而且我们本篇就主要讲解为什么gateway会自动识别,并且我们要自己实现并且添加自定义属性。开始源码解析第一步,找到自动加载的类一探究竟;
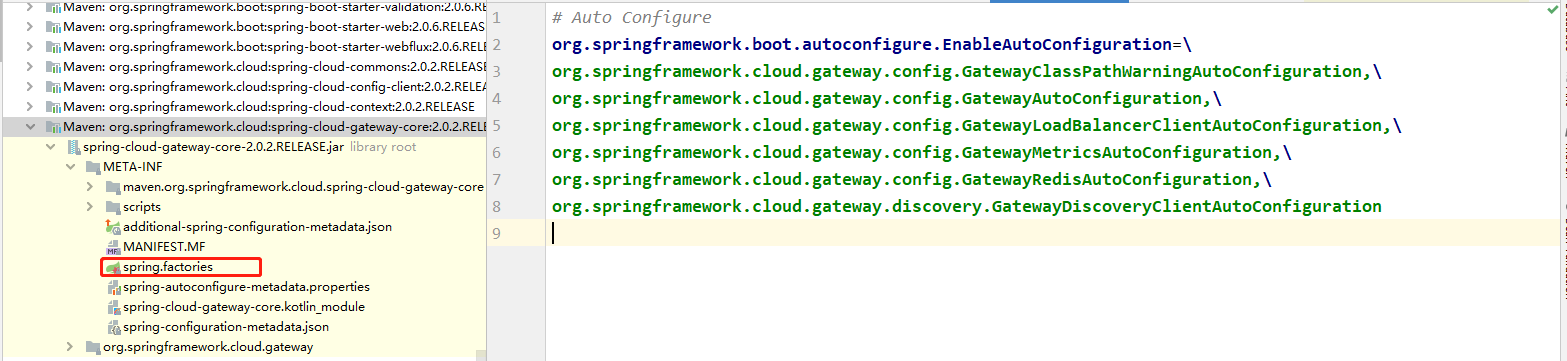
看到这里的时候,第一步就成功了,剩下的就是找到org.springframework.cloud.gateway.config.GatewayAutoConfiguration这个关键类,我们主要看看里面的两个类
@Bean public RouteLocator routeDefinitionRouteLocator(GatewayProperties properties, List<GatewayFilterFactory> GatewayFilters, List<RoutePredicateFactory> predicates, RouteDefinitionLocator routeDefinitionLocator) { return new RouteDefinitionRouteLocator(routeDefinitionLocator, predicates, GatewayFilters, properties); } @Bean @Primary //TODO: property to disable composite? public RouteLocator cachedCompositeRouteLocator(List<RouteLocator> routeLocators) { return new CachingRouteLocator(new CompositeRouteLocator(Flux.fromIterable(routeLocators))); } 这俩个类配置,大家可能非常熟悉,大家上手一个新知识点的时候,肯定会找一些快速入门的文章看看,博主还是习惯直接找官方的quick start来看,大家可以看看这些快速上手项目:Getting Started | Building a Gateway
所以博主直接就找到了RouteLocator这个类配置,果不其然,我们找到了断言与过滤器的注入,虽然实在方法体内作为参数传入,但是会被spring解析到,直接去工厂里拿到,具体怎么拿呢?我们再来看看:
1 public BeanWrapper instantiateUsingFactoryMethod( 2 String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] explicitArgs) { 3 4 ..... 5 6 for (Method candidate : candidates) { 7 Class<?>[] paramTypes = candidate.getParameterTypes(); 8 9 if (paramTypes.length >= minNrOfArgs) { 10 ArgumentsHolder argsHolder; 11 12 if (explicitArgs != null) { 13 // Explicit arguments given -> arguments length must match exactly. 14 if (paramTypes.length != explicitArgs.length) { 15 continue; 16 } 17 argsHolder = new ArgumentsHolder(explicitArgs); 18 } 19 else { 20 // Resolved constructor arguments: type conversion and/or autowiring necessary. 21 try { 22 String[] paramNames = null; 23 ParameterNameDiscoverer pnd = this.beanFactory.getParameterNameDiscoverer(); 24 if (pnd != null) { 25 paramNames = pnd.getParameterNames(candidate); 26 } 27 //主要就是会进入到这里去解析每一个参数类型 28 argsHolder = createArgumentArray(beanName, mbd, resolvedValues, bw, 29 paramTypes, paramNames, candidate, autowiring, candidates.length == 1); 30 } 31 catch (UnsatisfiedDependencyException ex) { 32 if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { 33 logger.trace("Ignoring factory method [" + candidate + "] of bean '" + beanName + "': " + ex); 34 } 35 // Swallow and try next overloaded factory method. 36 if (causes == null) { 37 causes = new LinkedList<>(); 38 } 39 causes.add(ex); 40 continue; 41 } 42 } 43 44 int typeDiffWeight = (mbd.isLenientConstructorResolution() ? 45 argsHolder.getTypeDifferenceWeight(paramTypes) : argsHolder.getAssignabilityWeight(paramTypes)); 46 // Choose this factory method if it represents the closest match. 47 if (typeDiffWeight < minTypeDiffWeight) { 48 factoryMethodToUse = candidate; 49 argsHolderToUse = argsHolder; 50 argsToUse = argsHolder.arguments; 51 minTypeDiffWeight = typeDiffWeight; 52 ambiguousFactoryMethods = null; 53 } 54 // Find out about ambiguity: In case of the same type difference weight 55 // for methods with the same number of parameters, collect such candidates 56 // and eventually raise an ambiguity exception. 57 // However, only perform that check in non-lenient constructor resolution mode, 58 // and explicitly ignore overridden methods (with the same parameter signature). 59 else if (factoryMethodToUse != null && typeDiffWeight == minTypeDiffWeight && 60 !mbd.isLenientConstructorResolution() && 61 paramTypes.length == factoryMethodToUse.getParameterCount() && 62 !Arrays.equals(paramTypes, factoryMethodToUse.getParameterTypes())) { 63 if (ambiguousFactoryMethods == null) { 64 ambiguousFactoryMethods = new LinkedHashSet<>(); 65 ambiguousFactoryMethods.add(factoryMethodToUse); 66 } 67 ambiguousFactoryMethods.add(candidate); 68 } 69 } 70 } 71 72 ..... 73 return bw; 74 } 每一个参数都需要解析,但是看这里不像没关系,继续往下走:就会看到
private ArgumentsHolder createArgumentArray( String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable ConstructorArgumentValues resolvedValues, BeanWrapper bw, Class<?>[] paramTypes, @Nullable String[] paramNames, Executable executable, boolean autowiring, boolean fallback) throws UnsatisfiedDependencyException { .... //这下就是了,每个参数都被进行解析 for (int paramIndex = 0; paramIndex < paramTypes.length; paramIndex++) { .... try { //我们的参数就是在这里被进行解析的--resolveAutowiredArgument Object autowiredArgument = resolveAutowiredArgument( methodParam, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, converter, fallback); args.rawArguments[paramIndex] = autowiredArgument; args.arguments[paramIndex] = autowiredArgument; args.preparedArguments[paramIndex] = new AutowiredArgumentMarker(); args.resolveNecessary = true; } catch (BeansException ex) { throw new UnsatisfiedDependencyException( mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, new InjectionPoint(methodParam), ex); } } } //其他不重要的,直接忽略掉 ... return args; } 开始解析的时看到了,我们需要把断言和过滤器列表都加在进来,那spring是如何加载的呢?是根据方法体内传入的类型找到所有实现了断言和过滤器工厂接口的类并且进行获取实例,我们仔细这些工厂的实现类,就会找到我们的使用的一些属性,比如我们例子中的PrefixPath过滤器和Path断言;
protected Map<String, Object> findAutowireCandidates( @Nullable String beanName, Class<?> requiredType, DependencyDescriptor descriptor) { //主要的就是这个,beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors方法,该方法就是从bean工厂中获取所有当前类的实现实例名称, String[] candidateNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors( this, requiredType, true, descriptor.isEager()); Map<String, Object> result = new LinkedHashMap<>(candidateNames.length); ... //遍历名称,进行实例化 for (String candidate : candidateNames) { if (!isSelfReference(beanName, candidate) && isAutowireCandidate(candidate, descriptor)) { addCandidateEntry(result, candidate, descriptor, requiredType); } } ..... return result; } 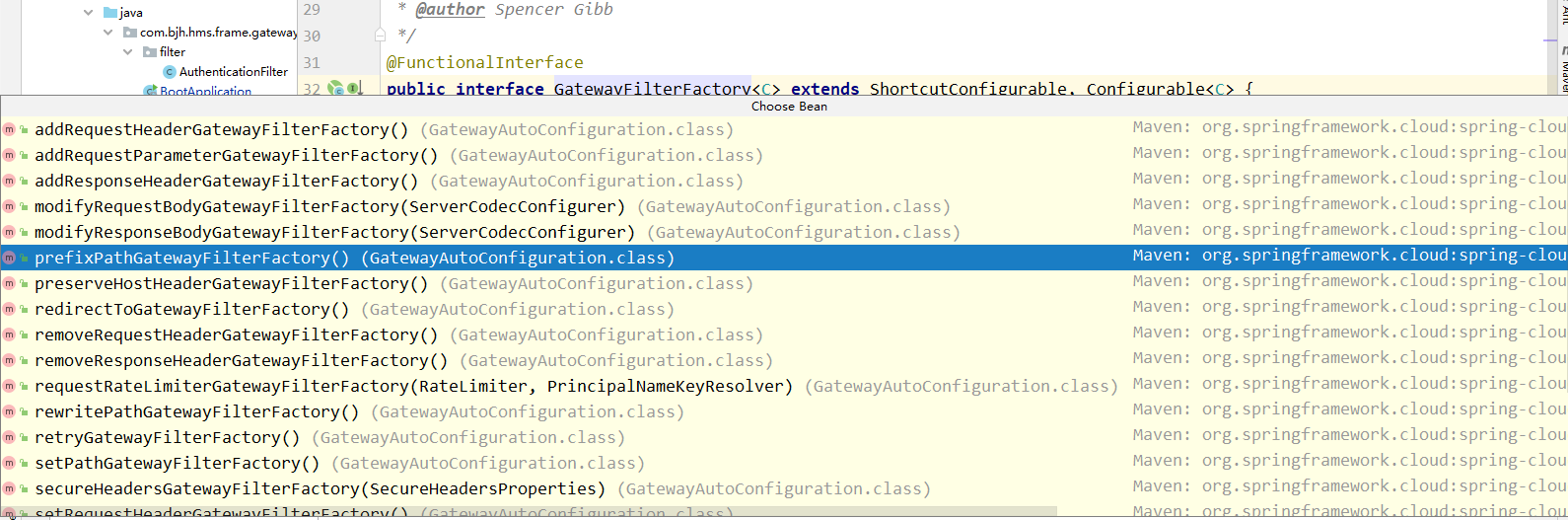
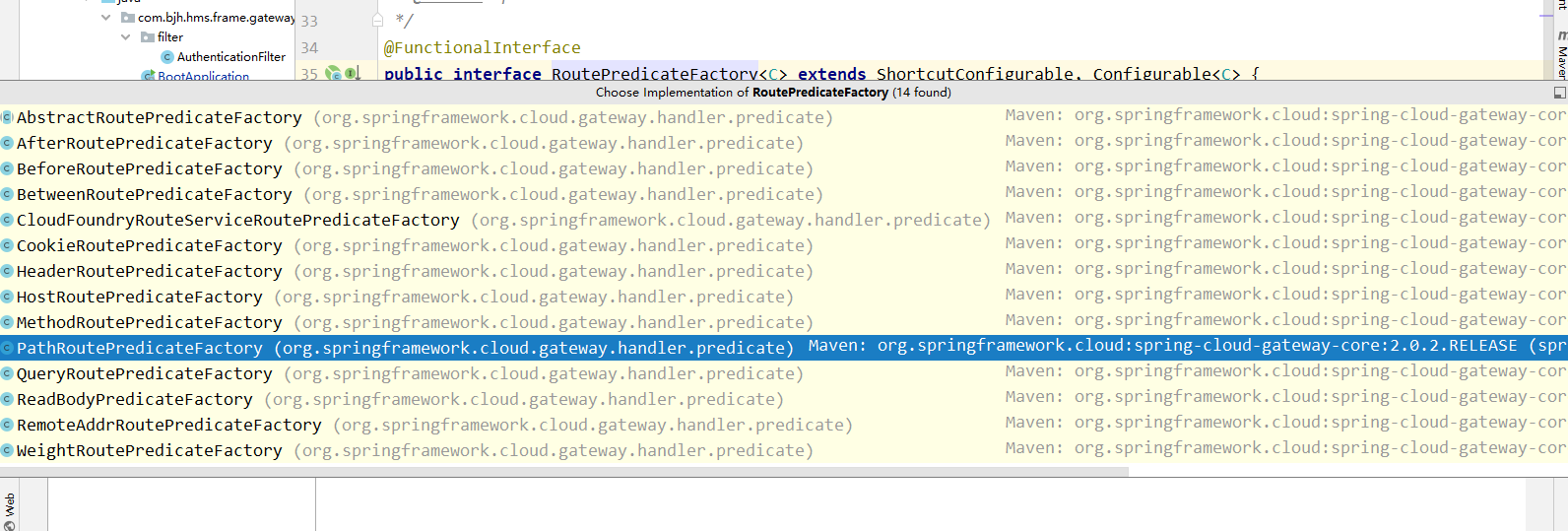
这下我们知道了,系统配置的断言和过滤器是如何被加载 的了,那我们还有一个问题,如果我自定义一个,如何被系统识别呢?并且怎么进行配置呢?不难发现我们之前看源码时,他是被spring通过找工厂实现类找到并且加载进来的,那我们自己实现工厂接口并且使用@Component注解,让spring加载进来不就的了吗?但是你会发现系统自定义的属性断言或者过滤器都有工厂名字的后缀,这是为什么呢?影响我们自定义 的类被加载到gateway中且生效吗?事实是会影响,那为什么影响呢?我们还是看源码。因为我们之前的类加载还没有看完,我们最开始的时候就找到了两个@bean 的自动加载,那这两个类实例化的时候都做了哪些工作,我们还没有细看;
public RouteDefinitionRouteLocator(RouteDefinitionLocator routeDefinitionLocator, List<RoutePredicateFactory> predicates, List<GatewayFilterFactory> gatewayFilterFactories, GatewayProperties gatewayProperties) { this.routeDefinitionLocator = routeDefinitionLocator; initFactories(predicates); gatewayFilterFactories.forEach(factory -> this.gatewayFilterFactories.put(factory.name(), factory)); this.gatewayProperties = gatewayProperties; } initFactories(predicates):这段代码主要是进行解析断言工厂实现类;并且放入一个Map中,
gatewayFilterFactories.forEach(factory -> this.gatewayFilterFactories.put(factory.name(), factory)):跟断言的代码几乎一样,因为没有其他多余的逻辑,所以没有封装到方法中,直接使用java8 的流特性,写完了遍历的过程。大家要注意一段代码就是factory.name(),这里使用了一个方法;
default String name() { return NameUtils.normalizeRoutePredicateName(getClass()); } 主要就是把当前类包含工厂名字的部分去掉了,然后用剩下的字符串当key值,所以我们可以使用工厂名字做后坠,也可以不用,但是剩下的字符则是你要写进配置的关键字,不过博主基本都是按照系统自带属性一样,用的是工厂接口的名字做的后缀。
好了,今天就讲解这么多,下次在讲解gateway接到请求后,是如何进行一步一步过滤的,何时进行断言校验的。一次不讲这么多,消化了就好。
