一、简单表格制作
Latex表格需要用到 table 和 tabular 环境。其中 table 环境里写表格的标题(caption)、表格的位置之类的。 tabular 环境则是绘制表格的内容。一个简单的表格绘制代码如下所示:
\documentclass{article} \begin{document} \begin{table}[h!] \begin{center} \caption{Your first table.} \begin{tabular}{l|c|r} % <-- Alignments: 1st column left, 2nd middle and 3rd right, with vertical lines in between \textbf{Value 1} & \textbf{Value 2} & \textbf{Value 3}\\ $\alpha$ & $\beta$ & $\gamma$ \\ \hline 1 & 1110.1 & a\\ 2 & 10.1 & b\\ 3 & 23.113231 & c\\ \end{tabular} \end{center} \end{table} \end{document} 结果如下: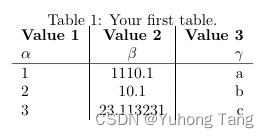
首先是 table 环境部分,\begin{center}让表格居中,\caption{Your first table.}写表格的标题。
然后是 tabular 环境部分,\begin{tabular}{l|c|r}这里面的{l|c|r},包含了三个字母,代表了表格总共有三列,第一列靠左偏移,第二列居中,第三列靠右偏移。竖线代表列之间用线分隔开来,如果想要左右两边都用线包围起来,应该改成{|l|c|r|}。接下来就是正式的表格绘制部分。
Latex里的表格是一行行来绘制的,每一行里面用&来分隔各个元素,用\\来结束当前这一行的绘制。代码中\textbf{Value 1} & \textbf{Value 2} & \textbf{Value 3}\\绘制表格的第一行,是三个加粗的字符串。第二行$\alpha$ & $\beta$ & $\gamma$ \\则是三个希腊字符。
接着是\hline,它的作用是画一整条横线,注意如果想画一条只经过部分列的横线,则可以用cline{a-b},代表的是画一条从第a列到第b列的横线。
二、表格单元占据多个行或者列
表格单元占据多个行或者列需要用到multirow和multicolumn,首先要引入相关的包:
%... \usepackage{multirow} % Required for multirows \begin{document} %... multirow和multicolumn的格式如下:
\multirow{NUMBER_OF_ROWS}{WIDTH}{CONTENT} NUMBER_OF_ROWS代表该表格单元占据的行数,WIDTH代表表格的宽度,一般填 * 代表自动宽度,CONTENT则是表格单元里的内容。
\multicolumn{NUMBER_OF_COLUMNS}{ALIGNMENT}{CONTENT} NUMBER_OF_COLUMNS代表该表格单元占据的列数,ALIGNMENT代表表格内容的偏移(填l,c或者r),CONTENT则是表格单元里的内容。
2. 1 一个multirow的例子
\begin{table}[h!] \begin{center} \caption{Multirow table.} \label{tab:table1} \begin{tabular}{l|S|r} \textbf{Value 1} & \textbf{Value 2} & \textbf{Value 3}\\ $\alpha$ & $\beta$ & $\gamma$ \\ \hline \multirow{2}{*}{12} & 1110.1 & a\\ % <-- Combining 2 rows with arbitrary with (*) and content 12 & 10.1 & b\\ % <-- Content of first column omitted. \hline 3 & 23.113231 & c\\ 4 & 25.113231 & d\\ \end{tabular} \end{center} \end{table} 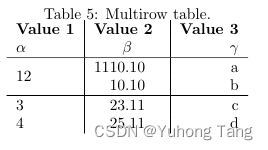
主要是这一句代码\multirow{2}{*}{12} & 1110.1 & a\\,使得内容为 12 的这一个表格单元占据了两行。注意的是,下一行的第一个位置,由于已经被 12 这个单元给占据了,因此第二行的代码是& 10.1 & b\\,这里第一个位置没有写东西,如果写了东西会使得这一行超过3列,表格错位。
2.2 一个multicolumn的例子
\begin{table}[h!] \begin{center} \caption{Multicolumn table.} \label{tab:table1} \begin{tabular}{l|S|r} \textbf{Value 1} & \textbf{Value 2} & \textbf{Value 3}\\ $\alpha$ & $\beta$ & $\gamma$ \\ \hline \multicolumn{2}{c|}{12} & a\\ % <-- Combining two cells with alignment c| and content 12. \hline 2 & 10.1 & b\\ 3 & 23.113231 & c\\ 4 & 25.113231 & d\\ \end{tabular} \end{center} \end{table} 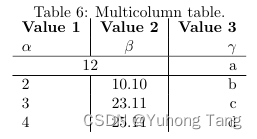
这里主要是这一句代码\multicolumn{2}{c|}{12} & a\\,使得内容为 12 的这一个表格单元占据了两列。所以这一行接下来只能填一个元素a。注意这里的ALIGNMENT写的是c|代表表格内容居中,表格右侧有竖线而左侧没有。
2.3 结合multirow与multicolumn
单元格需要同时占据两行和两列,其实只需要把\multirow{NUMBER_OF_ROWS}{WIDTH}{CONTENT}的CONTENT写成multicolumn就可以了。
\begin{table}[h!] \begin{center} \caption{Multirow and -column table.} \label{tab:table1} \begin{tabular}{l|S|r} \textbf{Value 1} & \textbf{Value 2} & \textbf{Value 3}\\ $\alpha$ & $\beta$ & $\gamma$ \\ \hline \multicolumn{2}{c|}{\multirow{2}{*}{1234}} & a\\ % <-- Multicolumn spanning 2 columns, content multirow spanning two rows \multicolumn{2}{c|}{} & b\\ % <-- Multicolumn spanning 2 columns with empty content as placeholder \hline 3 & 23.113231 & c\\ 4 & 25.113231 & d\\ \end{tabular} \end{center} \end{table} 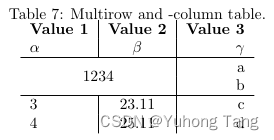 最主要的语句
最主要的语句\multicolumn{2}{c|}{\multirow{2}{*}{1234}} & a\\使得内容为1234的表格单元占据了2行两列,所以当前这一行右边只能再写一个元素a了,然后注意的是下一行是\multicolumn{2}{c|}{} & b\\用一个空的multicolumn来代表前两个位置空置,然后填剩下的一个元素b。
三、复杂表格实例
\begin{table*}[t] \centering \caption{MAP scores of teacher model, different student models with 4 widths and three baseline models with different length of binary codes on CIFAR-10 and SUN datasets.} \label{table1} \begin{tabular}{|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|} \hline \multicolumn{2}{|c|}{\multirow{2}{*}{Model}} &\multirow{2}{*}{FLOPs}&\multirow{2}{*}{Params} & \multicolumn{4}{c|}{CIFAR-10}&\multicolumn{4}{c|}{SUN}\\ \cline{5-12} \multicolumn{2}{|c|}{} & & & 12bits & 24bits & 32bits & 48bits & 12bits & 24bits & 32bits & 48bits \\ \hline \multicolumn{2}{|c|}{Teacher} &4.12G &25.56M &0.87841 &0.89512 &0.9014 &0.90601 &0.83587 &0.85736 &0.86297 &0.87103\\ \hline %0.25x----------------- \multirow{4}{*}{$0.25\times$} & Stu-1 & 0.15G & 1.03M & 0.70746 & 0.73458 & 0.74909 & 0.75833 & 0.69618 & 0.76631 & 0.78075 & 0.78787 \\ \cline{2-12} \multirow{4}{*}{} & Stu-2 &0.19G &1.08M &0.7629 &0.79111 &0.80039 &0.80519 &0.73539 &0.79714 &0.80753 &0.81195\\ \cline{2-12} \multirow{4}{*}{} & Stu-3 &0.26G &1.43M &0.84684 &0.86443 &0.87384 &0.88268 &0.79284 &0.83442 &0.84350 &0.84353\\ \cline{2-12} \multirow{4}{*}{} & Stu-4 & 0.29G &1.99M &0.85901 &0.87269 &0.8836 &0.88728 &0.81997 &0.84620 &0.85041 &0.85036\\ \hline \end{tabular} \label{table_MAP} \end{table*} 输出结果为
这里使用\begin{table*}[t]有一个星号,是为了让表格宽度与页面等宽而不是二分之一宽。
