阅读量:7
数据来源于这篇博客,直接下载好csv文件。
这篇内容均在VScode的jupyter notebook上完成,操作可以看我的另一篇博客:http://t.csdnimg.cn/69sDJ
一、准备工作
1. 导入数据库
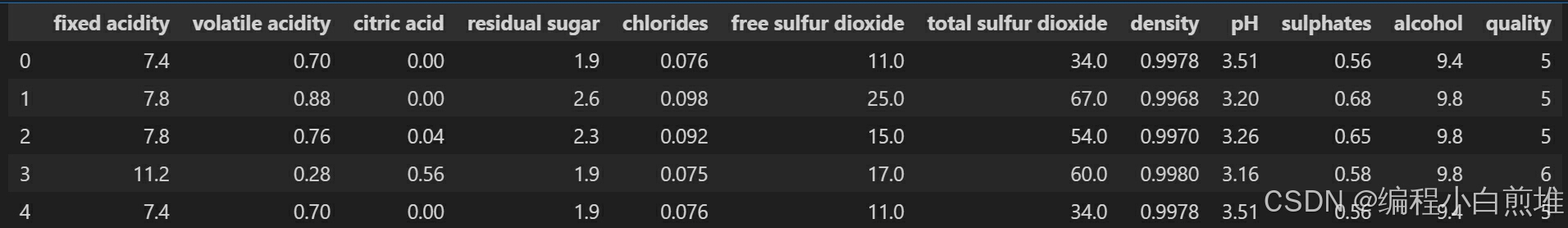
#功能是可以内嵌绘图,并且可以省略掉plt.show()这一步,具体作用是当你调用matplotlib.pyplot的绘图函数plot()进行绘图的时候,或者生成一个figure画布的时候,可以直接在你的python console里面生成图像。 %matplotlib inline import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np import pandas as pd #Seaborn是基于matplotlib的Python可视化库 import seaborn as sns plt.style.use('ggplot')# 创建调色板 color = sns.color_palette() #设置字体等,方便我们在下面使用中文写label plt.rcParams['font.family'] = ['SimHei'] plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False sns.set_style('darkgrid',{'font.sans-serif':['SimHei','Arial']}) import warnings warnings.filterwarnings('ignore') # 读取数据 wine_df = pd.read_csv('winequality-red.csv',sep=';') wine_df.head()得到下图:
2. 查看文本数量
一个较大的样本通常意味着数据更加全面二号具有代表性,可以减少随机误差的影响,提高分析结果的可靠性。并且大样本量可以增强分析结果的推广性,使得分析结果可以更可靠地推广到更大的总体中。
len(wine_df)3. 更换文本文件名称为中文
为了方便看表格,将文本文件名称改为中文。
这里的代码很累赘,但是CV大法好!
#把标题换成中文,方便我们看数据 wine_df.rename(columns={"fixed acidity":"固定酸度"},inplace=True) wine_df.rename(columns={"volatile acidity":"挥发性酸度"},inplace=True) wine_df.rename(columns={"citric acid":"柠檬酸"},inplace=True) wine_df.rename(columns={"residual sugar":"残糖"},inplace=True) wine_df.rename(columns={"chlorides":"氯化物"},inplace=True) wine_df.rename(columns={"free sulfur dioxide":"游离二氧化硫"},inplace=True) wine_df.rename(columns={"total sulfur dioxide":"总二氧化硫"},inplace=True) wine_df.rename(columns={"density":"密度"},inplace=True) wine_df.rename(columns={"sulphates":"硫酸盐"},inplace=True) wine_df.rename(columns={"alcohol":"酒精"},inplace=True) wine_df.rename(columns={"quality":"品质"},inplace=True) wine_df.head() 4. 查看基本信息
初步了解数据的整体情况,检查数据的完整性,看看数据有没有缺失值,然后确认数据的类型,确定分析方法。
wine_df.info()得到下面:

二、数据处理
1. 将品质作为表格的索引
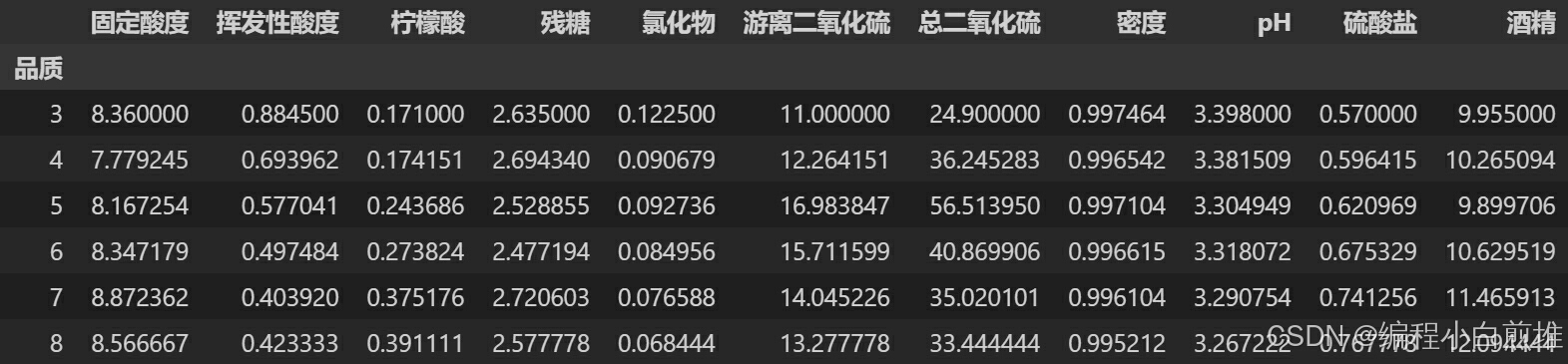
在分析过程中,可以根据品质对数据进行分类和聚合。
#按品质分组,查看每组均值,进一步分析数据 wine_df.groupby('品质').mean()得到如下:
2. 计算相关系数
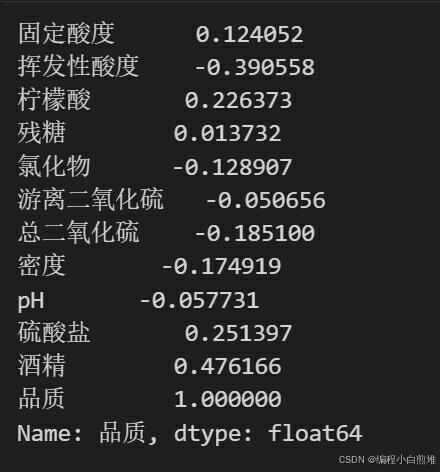
查看各个理化性质与品质的关系是否紧密。
三、 绘制图表
1. 各个品质与理化性质的箱线图
总结得出品质更好的就有更高的柠檬酸、硫酸盐和酒精度数,还具有更低的挥发性酸度、密度。
对于品质优于7或者劣于4的酒,直观上是线性可分的,离群点较少,但是品质5、6的酒很难区分。
下图只展示了品质8,其它的类推:
quality_column = '品质' factors = ['固定酸度','挥发性酸度','柠檬酸','残糖','氯化物','游离二氧化硫','总二氧化硫','密度','pH','硫酸盐','酒精'] # 确保这里包含了所有你想要绘制箱线图的列名 # 创建一个3x4的网格,用于绘制11个子图 fig, axs = plt.subplots(3, 4, figsize=(10, 10)) # 遍历每个因素并绘制箱线图 for i, factor in enumerate(factors): # 计算行和列的索引 row = i // 4 col = i % 4 # 选择具有特定品质等级的行 eight_data = wine_df[wine_df[quality_column] == 8] # 绘制箱线图 axs[row, col].boxplot(eight_data[factor]) # 设置标题和轴标签 axs[row, col].set_title(f'{factor}与品质8的关系', fontsize=12) axs[row, col].set_ylabel(factor) # 关闭最后一个子图 axs[2, 3].axis('off') # 显示图表 plt.tight_layout() plt.show() 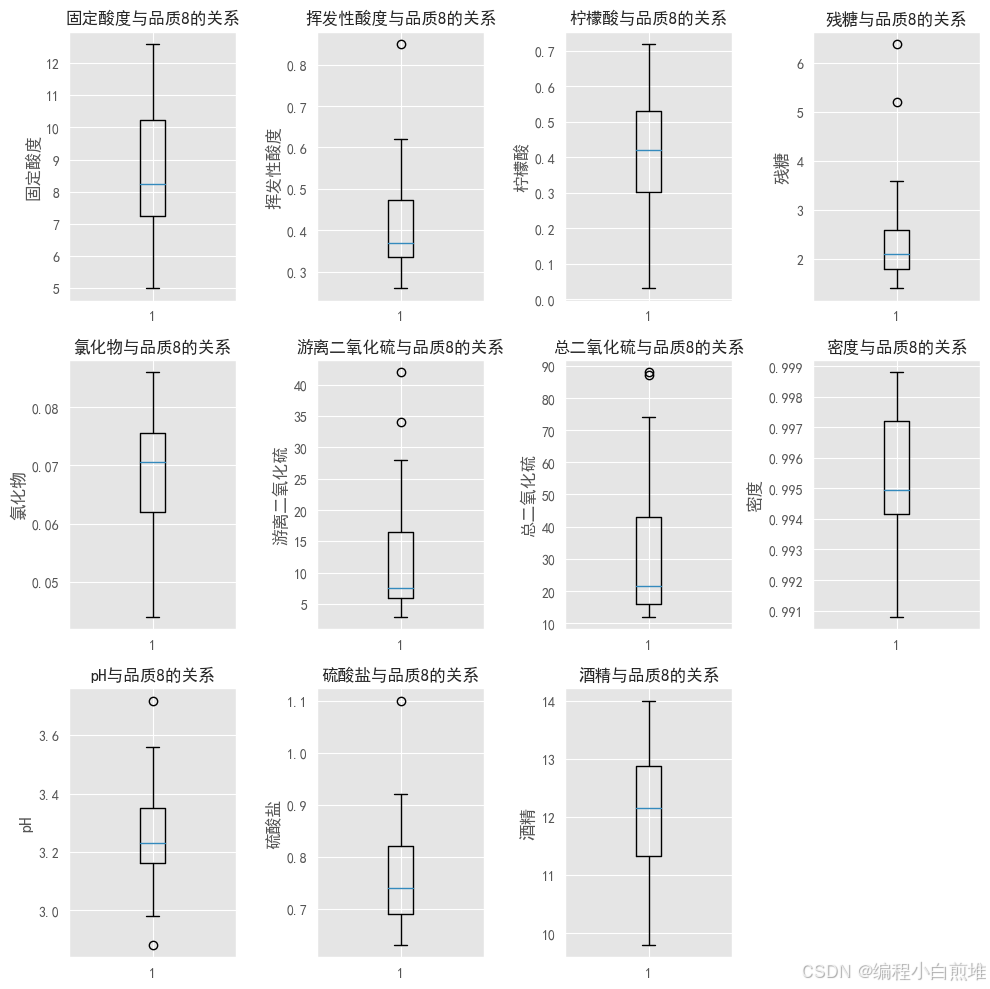
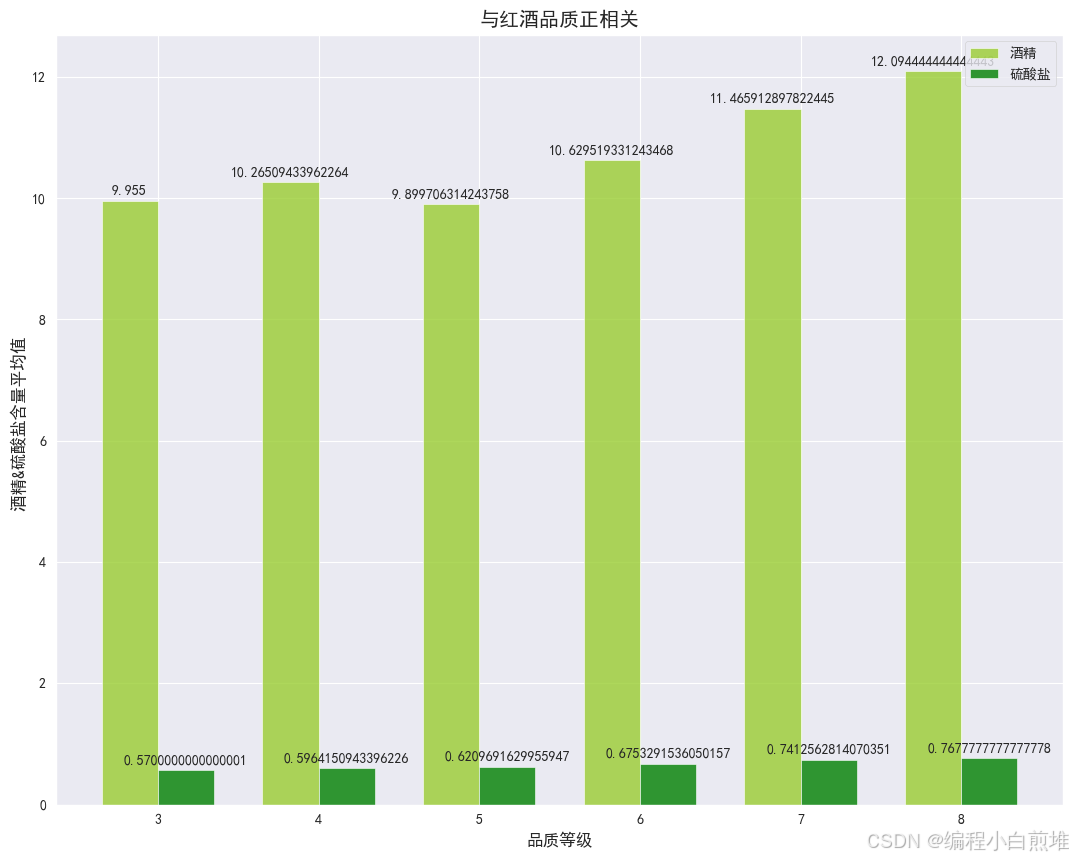
2. 酒精和硫酸盐的数值指标条形图
grouped_df = wine_df.groupby('品质').mean() #然后我们选出来酒精和硫酸盐两个指标 alcohol_content = grouped_df['酒精'] sulfur_content = grouped_df['硫酸盐'] width = 0.35 ind = np.arange(len(grouped_df.index)) plt.figure(figsize=(13,10)) # 使用matplotlib绘制条形图 plt.bar(ind - width/2, alcohol_content, color='yellowgreen',width=0.35, alpha=0.8,label='酒精') plt.bar(ind + width/2, sulfur_content, color='green', width=0.35,alpha=0.8, label='硫酸盐') #添加数据 for i, content in enumerate(alcohol_content): plt.text(i-width/2, content + 0.1, str(content), ha='center') # ha='center' 表示水平对齐方式为居中 for i, content in enumerate(sulfur_content): plt.text(i+width/2, content + 0.1, str(content), ha='center') # ha='center' 表示水平对齐方式为居中 # 设置图表标题和轴标签 plt.title('与红酒品质正相关') plt.xlabel('品质等级') plt.ylabel('酒精&硫酸盐含量平均值 ') plt.xticks(ind,[3,4,5,6,7,8]) #添加图例 plt.legend() # 显示图表 plt.show()得到如下:
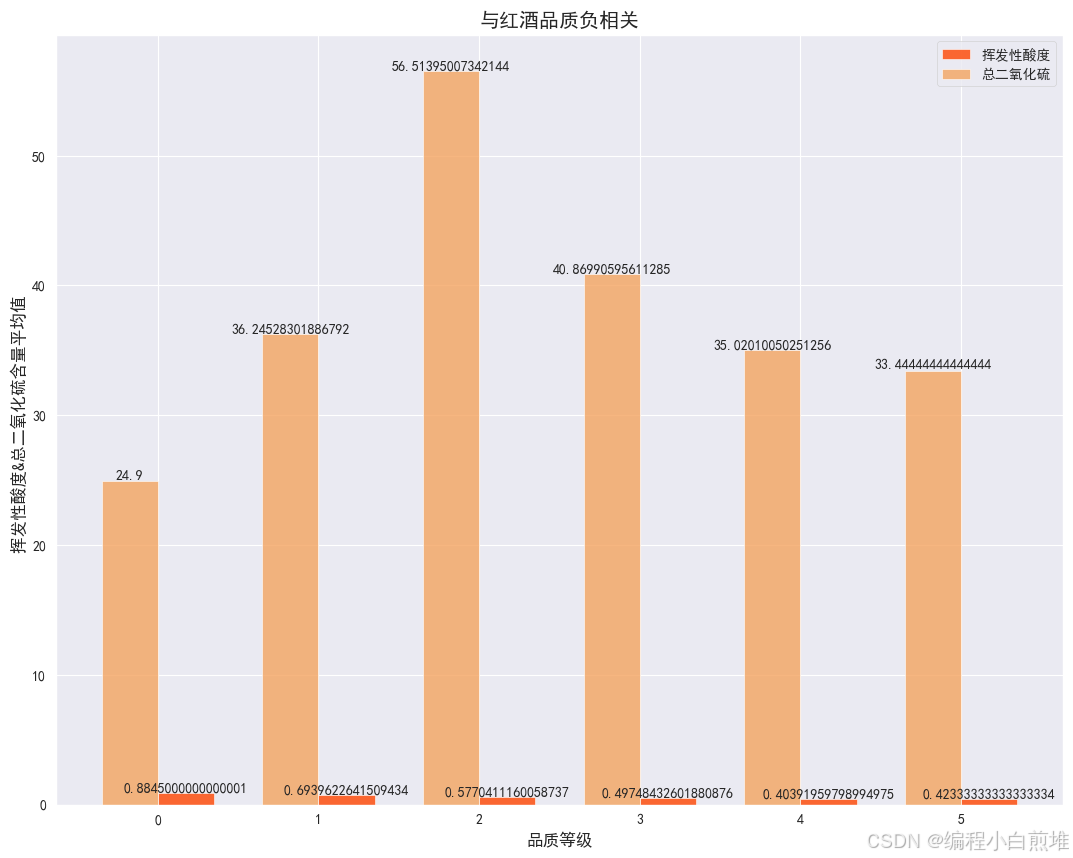
3. 挥发性酸度和总二氧化硫条形图
grouped_df = wine_df.groupby('品质').mean() #我们选出负相关性强的两个指标:挥发性酸度和总二氧化硫 volatile_acidity_content = grouped_df['挥发性酸度'] sulfur_dioxide_content = grouped_df['总二氧化硫'] width = 0.35 ind = np.arange(len(grouped_df.index)) plt.figure(figsize=(13,10)) # 使用matplotlib绘制条形图 plt.bar(ind + width/2, volatile_acidity_content, color='orangered', alpha=0.8, width=0.35, label='挥发性酸度') plt.bar(ind - width/2, sulfur_dioxide_content, color='sandybrown', alpha=0.8, width=0.35, label='总二氧化硫') #添加数据 for i, content in enumerate(sulfur_dioxide_content): plt.text(i-width/2, content + 0.1, str(content), ha='center') # ha='center' 表示水平对齐方式为居中 for i, content in enumerate(volatile_acidity_content): plt.text(i+width/2, content + 0.1, str(content), ha='center') # ha='center' 表示水平对齐方式为居中 # 设置图表标题和轴标签 plt.title('与红酒品质负相关') plt.xlabel('品质等级') plt.ylabel('挥发性酸度&总二氧化硫含量平均值 ') #添加图例 plt.legend() # 显示图表 plt.show()得到如下:
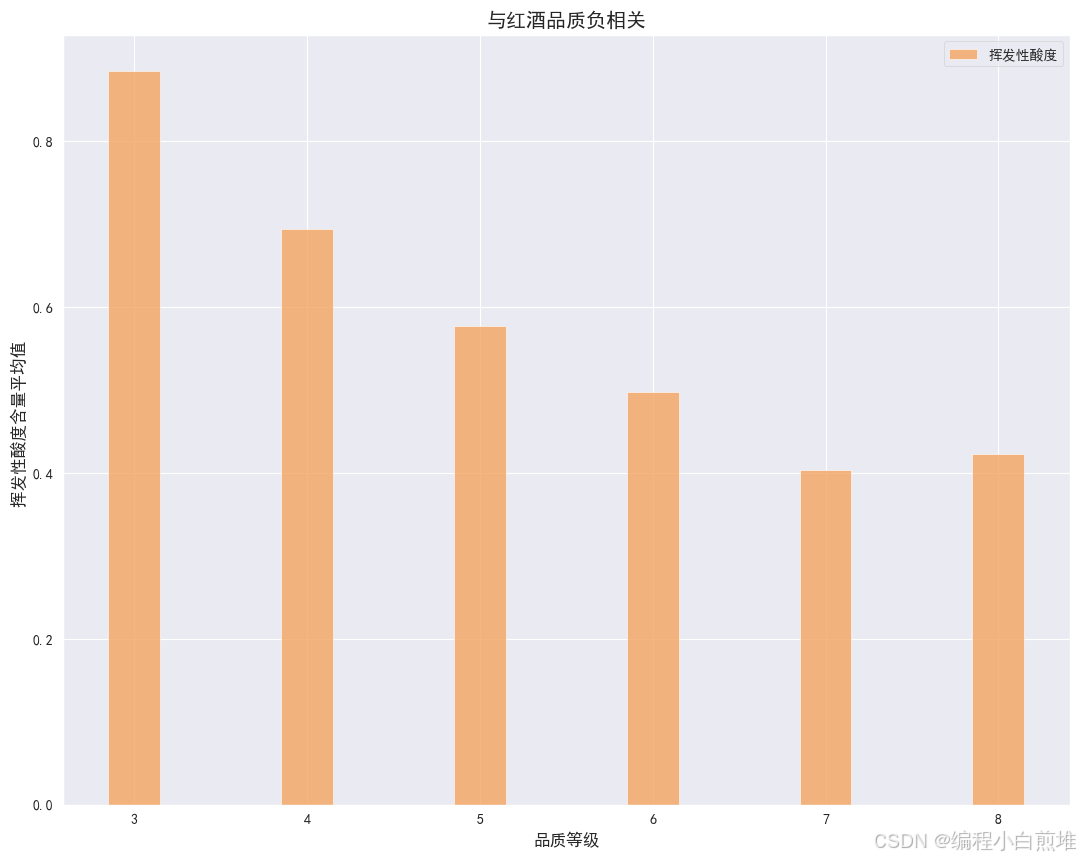
4. 挥发性酸度条形图
#总二氧化硫的数据不够理想,现在只保留挥发性酸度的数据 volatile_acidity_content = grouped_df['挥发性酸度'] #sulfur_dioxide_content = grouped_df['总二氧化硫'] width = 0.35 ind = np.arange(len(grouped_df.index)) plt.figure(figsize=(13,10)) # 使用matplotlib绘制条形图 plt.bar(grouped_df.index, volatile_acidity_content, color='sandybrown', alpha=0.8, width=0.3, label='挥发性酸度') #plt.bar(grouped_df.index, sulfur_dioxide_content, color='sandybrown', alpha=0.8, width=0.3, label='总二氧化硫') # 设置图表标题和轴标签 plt.title('与红酒品质负相关') plt.xlabel('品质等级') plt.ylabel('挥发性酸度含量平均值 ') #添加图例 plt.legend() # 显示图表 plt.show()得到如下:
5. 多变量分析
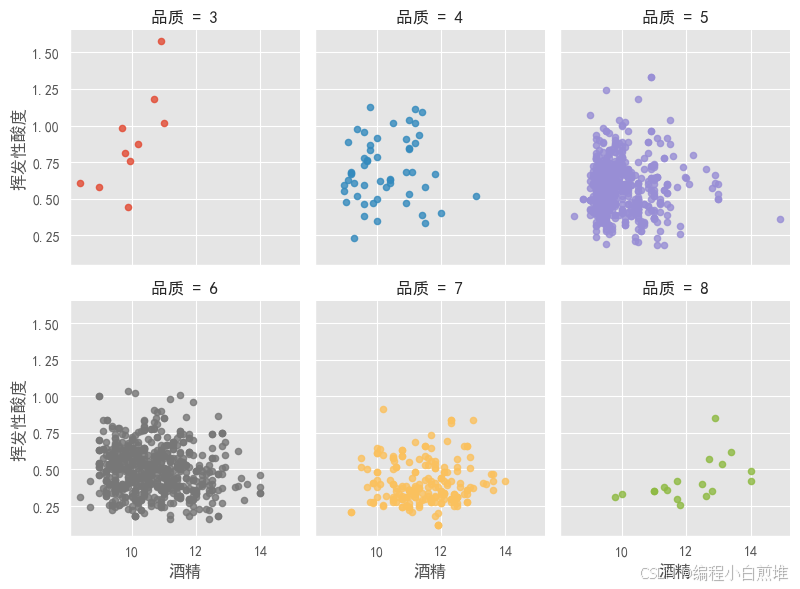
与品质相关性最高的两个特征是酒精浓度、挥发性酸度。下面图中显示酒精浓度、挥发性酸度的关系。
plt.style.use('ggplot') sns.lmplot(x='酒精', y='挥发性酸度', hue='品质', data=wine_df, fit_reg=False, scatter_kws={'s': 10}, height=5, aspect=1) print("Figure 11-1: Scatter Plots of Alcohol, Volatile Acid and Quality") 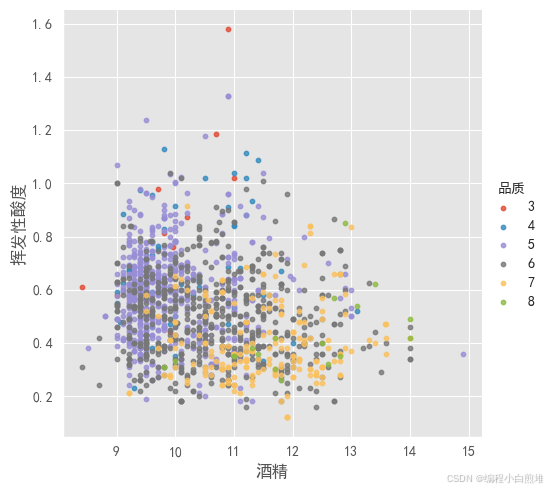
sns.lmplot(x = '酒精', y = '挥发性酸度', col='品质', hue = '品质', data = wine_df,fit_reg = False, height = 3, aspect = 0.9, col_wrap=3,scatter_kws={'s':20}) print("Figure 11-2: Scatter Plots of Alcohol, Volatile Acid and Quality")