
概览
在只有方寸之间大小的手持设备上要想体面的向用户展示海量信息,滚动视图(ScrollView)无疑是绝佳的“东牀之选”。

在 SwiftUI 历史的长河中,总觉得苹果对于 ScrollView 视图功能的升级是在“挤牙膏”。这不,在本届最新 WWDC24 重磅打造的 SwiftUI 6.0 中就让我们来看看 ScrollView 又能挤出怎样的新花样吧?
在本篇博文中,您将学到如下精彩的内容:
- 概览
- 1. SwiftUI 6.0 之前的滚动世界
- 2. SwiftUI 6.0(iOS 18)中全新的 ScrollPosition 类型
- 3. “新老搭配,干活不累”
- 4. 如何判断当前滚动是由用户指尖触发的?
- 5. 实时监听滚动视图的内容偏移(ContentOffset)
- 总结
在 WWDC24 里,苹果对 SwiftUI 6.0 中滚动视图的全新升级无疑解了一众秃头码农们的额燃眉之急。
那还等什么呢?让我们马上开始滚动大冒险吧!
Let‘s rolling!!!😉
1. SwiftUI 6.0 之前的滚动世界
苹果从 SwiftUI 2.0 开始陆续“发力”向 ScrollView 增加了许多新特性,其中包括秃头码农们翘首跂踵的滚动位置读取与设置、滚动模式等高级功能。
在 SwiftUI 6.0 之前,我们是通过单一状态来读取和设置滚动位置的:
struct ContentView: View { @State private var position: Int? var body: some View { ScrollView { LazyVStack { ForEach(0..<100) { index in Text(verbatim: index.formatted()) .id(index) } } .scrollTargetLayout() } .scrollTargetBehavior(.viewAligned) .scrollPosition(id: $position) } } 如上代码所示:滚动视图中滚动位置其实是由其子视图的 id 值来确定的,我们通过读取和更改 position 状态的值达到了把控滚动位置之目的。
2. SwiftUI 6.0(iOS 18)中全新的 ScrollPosition 类型
而从 SwiftUI 6.0 开始,苹果推出了全新的 ScrollPosition 类型专门由于描述 ScrollView 的滚动位置:
有了 ScrollPosition 坐镇,除了通过视图 id 以外我们还能够以多种方式来表示滚动位置了。比如,以滚动边缘(Edge)来描述和设置滚动视图的位置:
struct ContentView: View { @State private var position = ScrollPosition(edge: .top) var body: some View { ScrollView { Button("Scroll to bottom") { position.scrollTo(edge: .bottom) } ForEach(1..<100) { index in Text(verbatim: index.formatted()) .id(index) } Button("Scroll to top") { position.scrollTo(edge: .top) } } .scrollPosition($position) } } 除了使用 position.scrollTo(edge:) 方法滚动到特定的顶部和底部边缘以外,我们还可以一如既往的恣意滚动到任意 id 对应的子视图中去:
struct ContentView: View { @State private var position = ScrollPosition(edge: .top) var body: some View { ScrollView { Button("Random Scroll") { let id = (1..<100).randomElement() ?? 0 position.scrollTo(id: id, anchor: .center) } ForEach(1..<100) { index in Text(verbatim: index.formatted()) .id(index) } } .scrollPosition($position) .animation(.default, value: position) } } 如上代码所示,当用户按下按钮时我们通过 position.scrollTo(id:, anchor:) 方法将视图滚动到了一个随机的位置上。
在 SwiftUI 6.0 中除了按照子视图的 id 滚动以外,我们还可以按照指定的偏移来滚动视图:
struct ContentView: View { @State private var position = ScrollPosition(edge: .top) var body: some View { ScrollView { Button("Scroll to offset") { position.scrollTo(point: CGPoint(x: 0, y: 100)) } ForEach(1..<100) { index in Text(verbatim: index.formatted()) .id(index) } } .scrollPosition($position) .animation(.default, value: position) } } 注意,我们可以分别沿 x 和 y 轴来滚动视图:
Button("Scroll to offset") { position.scrollTo(y: 100) position.scrollTo(x: 200) } 3. “新老搭配,干活不累”
不过从目前(iOS 18)看来,使用新的 scrollPosition(_: anchor:) 视图修改器方法是无法监控到实时滚动位置的。
从下面的示意图中可以验证这一点 —— 只有通过代码设置的滚动位置才能被 scrollPosition(_: anchor:) 方法所捕获到: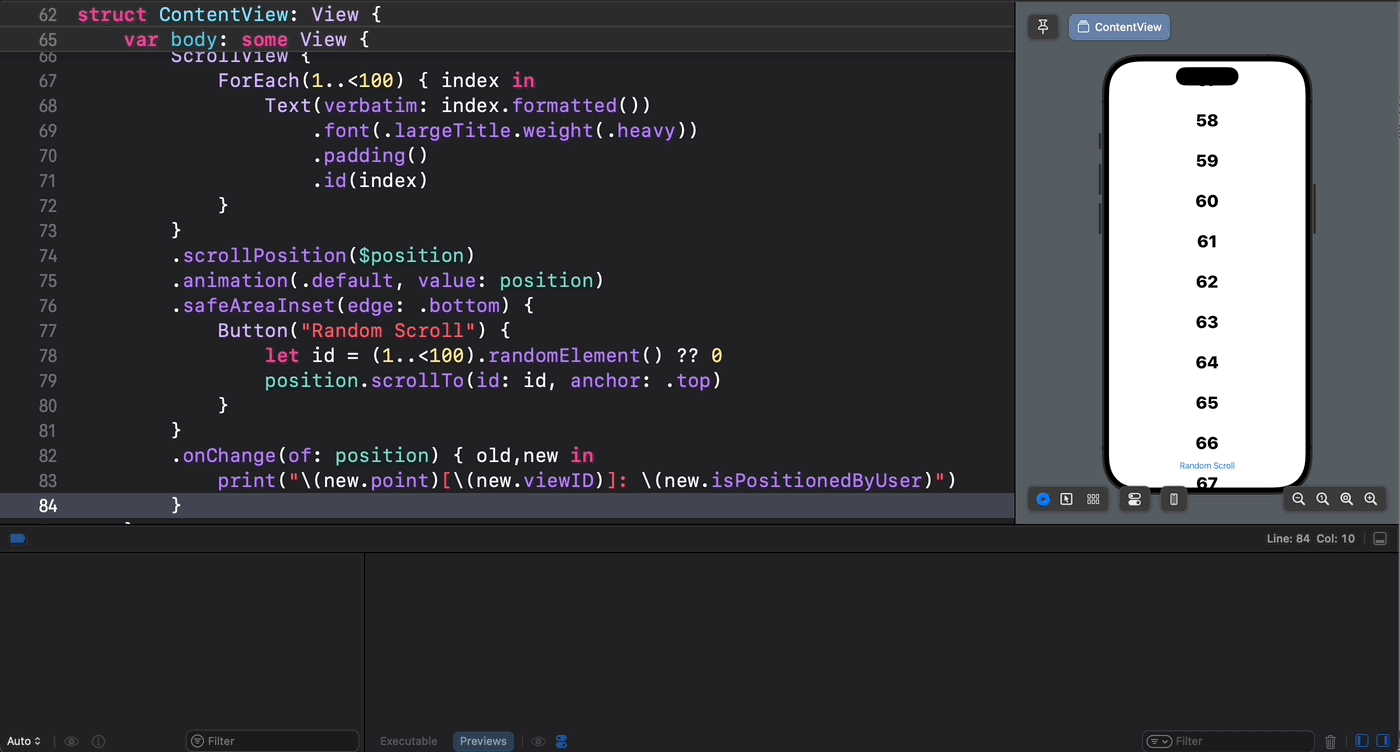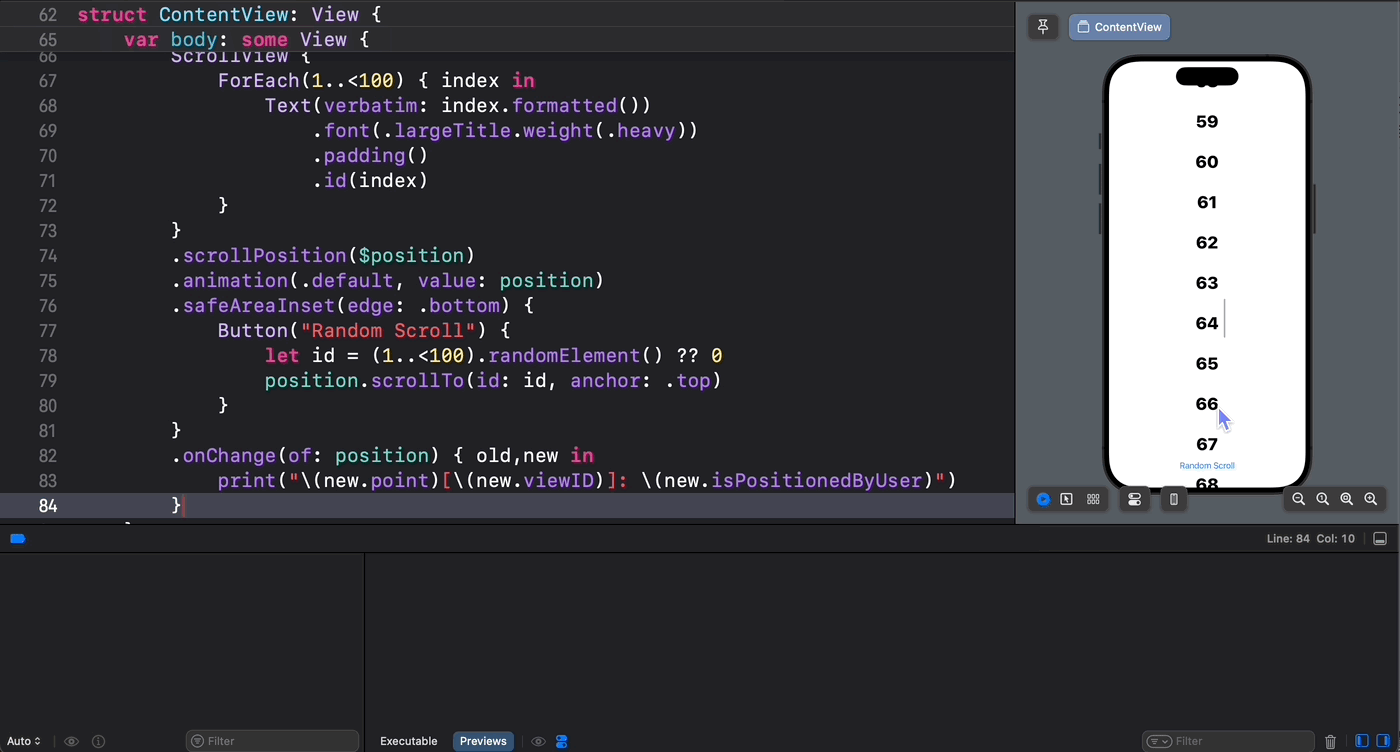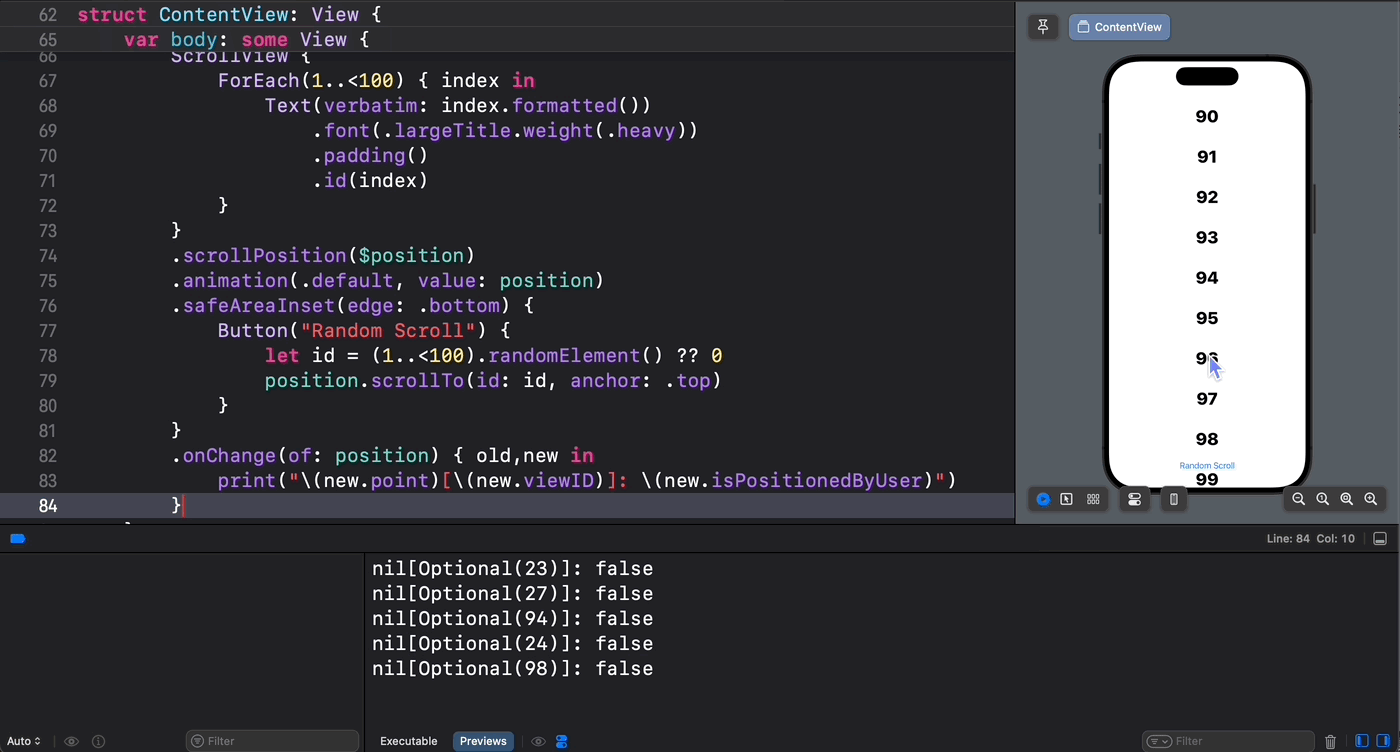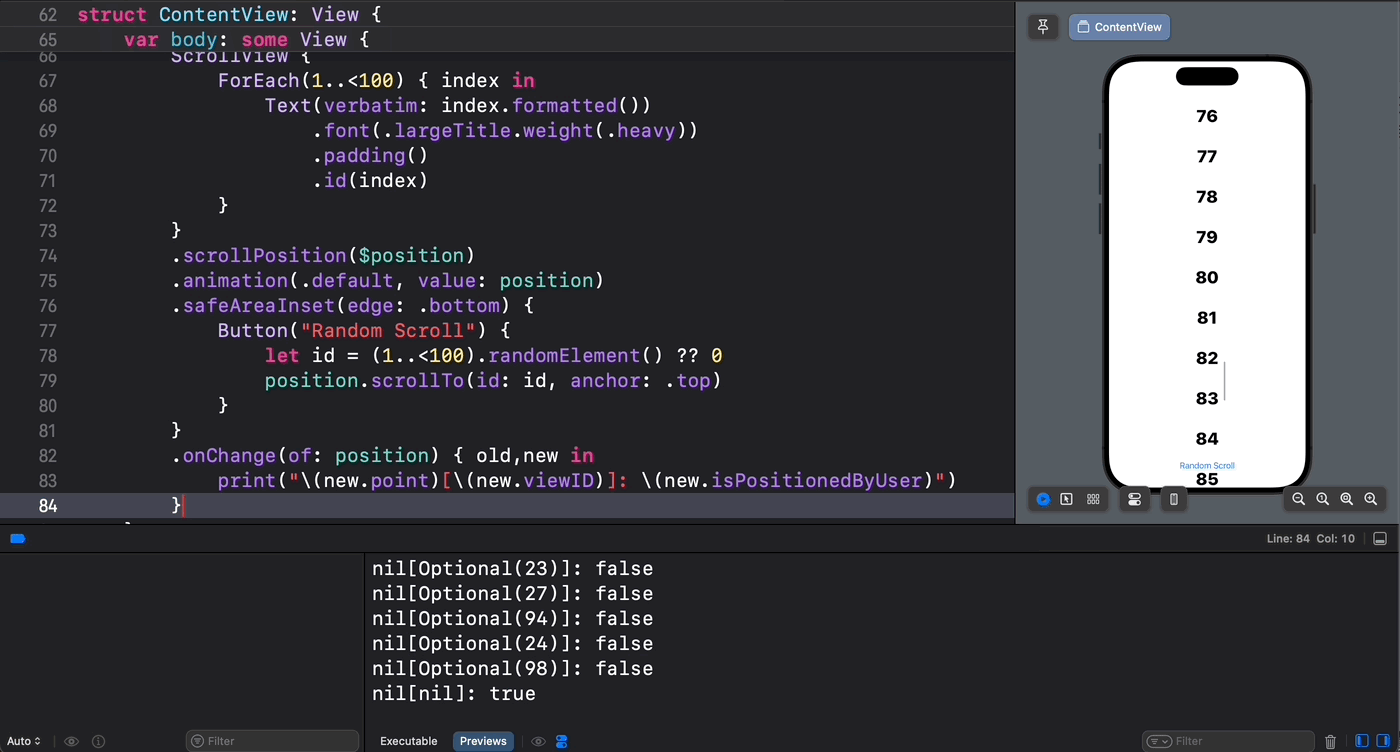
那么,如果大家希望实时监听滚动的位置又该如何是好呢?
别急,我们可以让新旧两种滚动机制珠联璧合从而达到“双剑合璧,秃头治愈”之神奇功效:
struct ContentView: View { @State private var position = ScrollPosition(edge: .top) @State var curPosID: Int? @State var offsetY: CGFloat? var body: some View { ScrollView { ForEach(1..<100) { index in Text(verbatim: index.formatted()) .font(.largeTitle.weight(.heavy)) .padding() .id(index) } .scrollTargetLayout() } .scrollPosition(id: $curPosID) .scrollPosition($position) .animation(.default, value: position) .safeAreaInset(edge: .bottom) { Button("Random Scroll") { let id = (1..<100).randomElement() ?? 0 position.scrollTo(id: id, anchor: .top) } } .onChange(of: position) { old,new in print("用代码滚动视图的ID: \(new.viewID)") curPosID = new.viewID as? Int } .onChange(of: curPosID) { _,new in print("实时滚动视图的 ID: \(new)") } } } 代码执行效果如下所示:
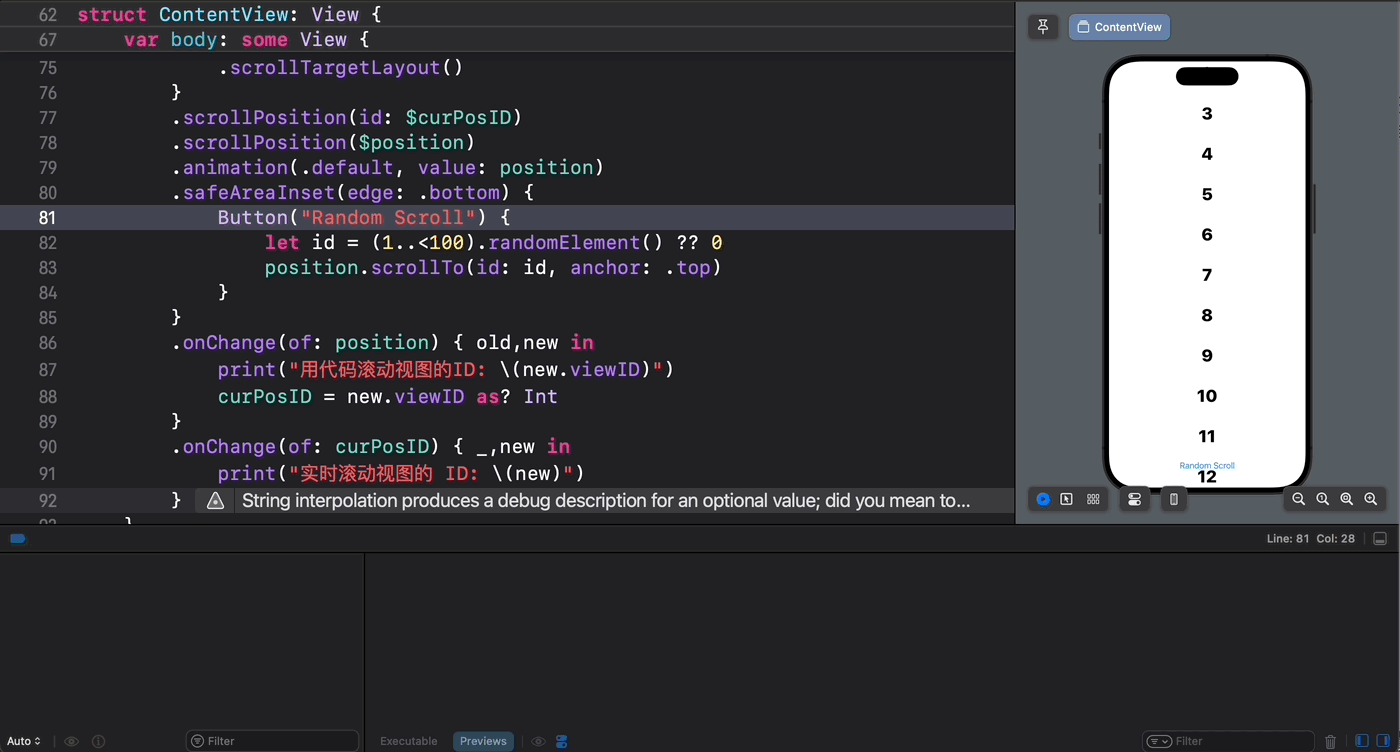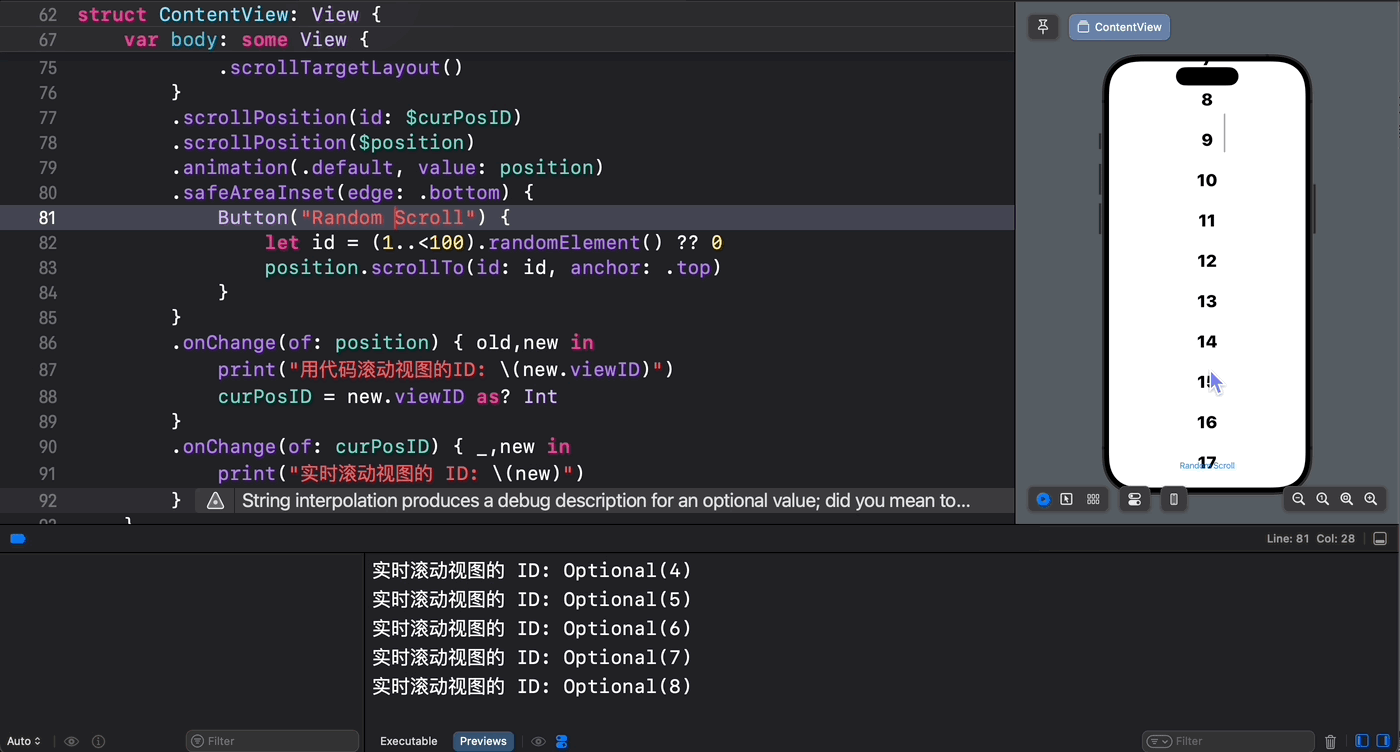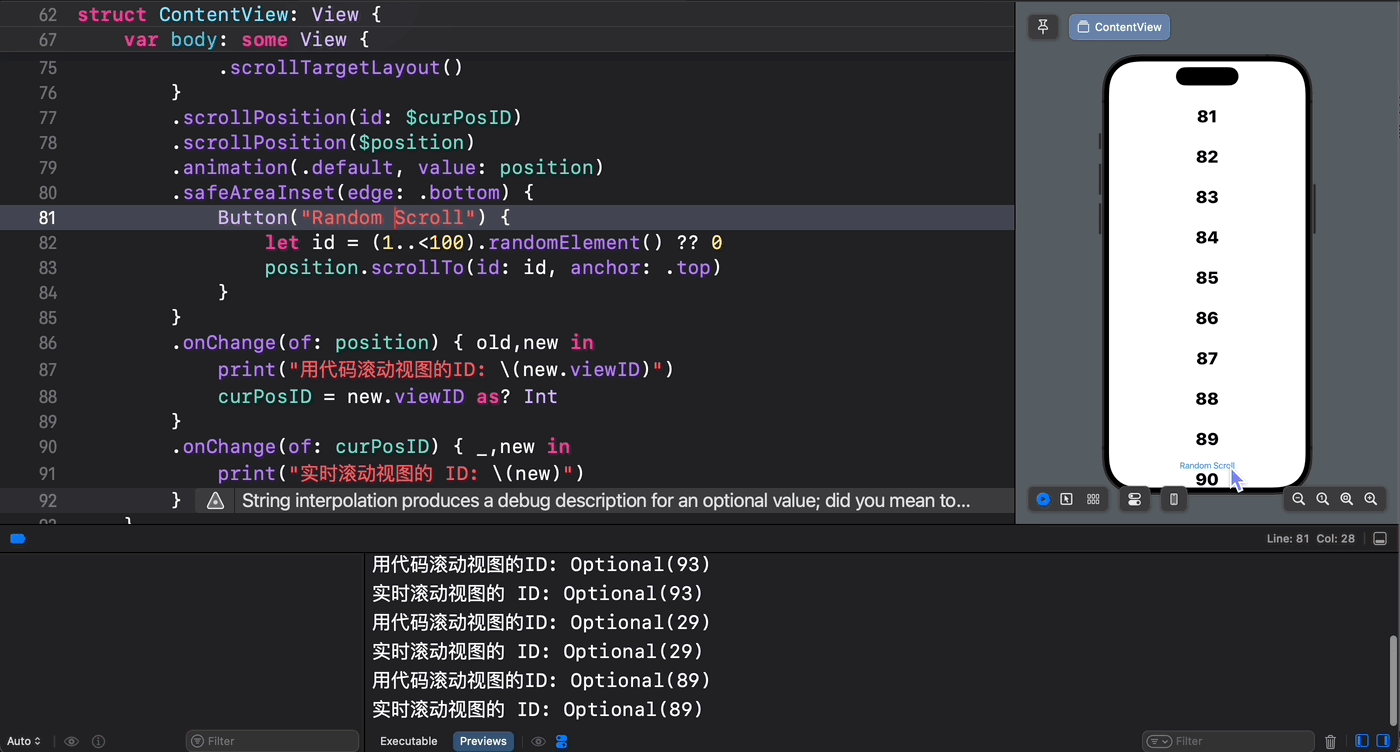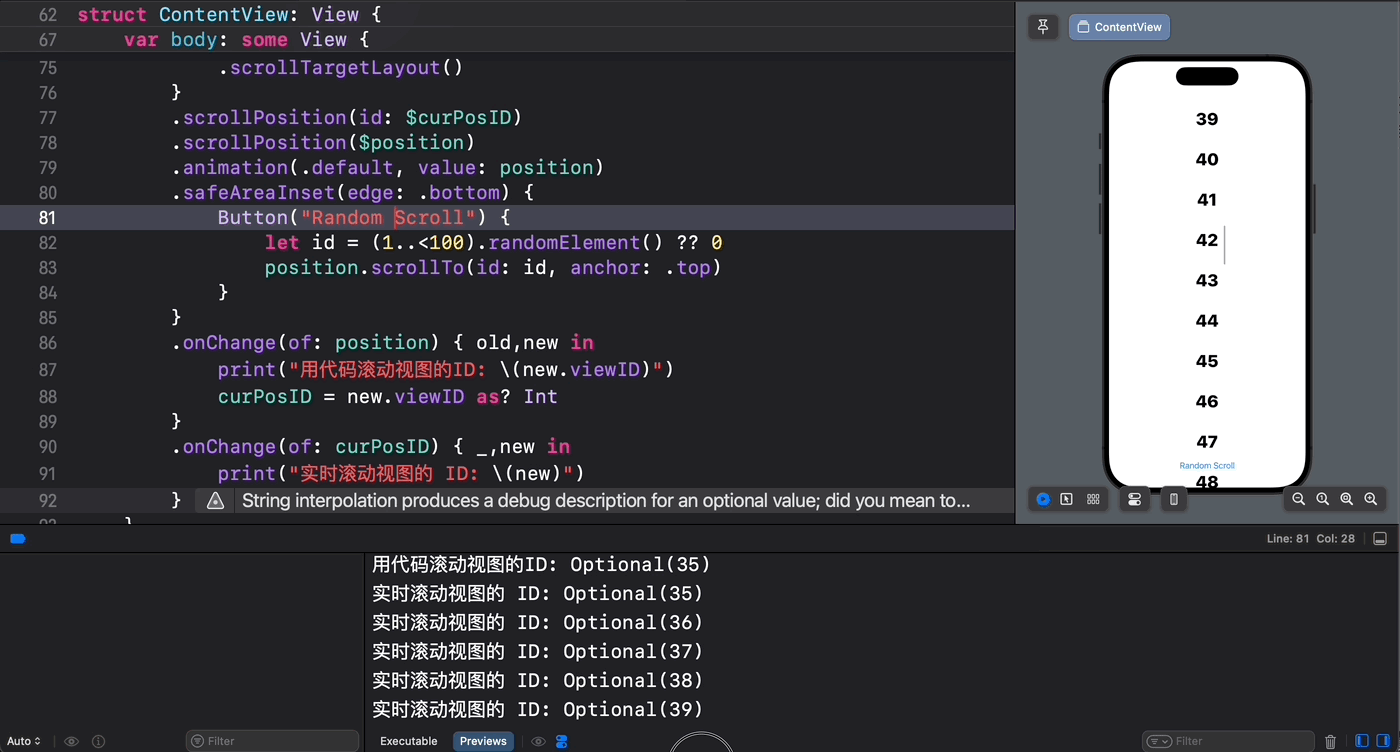
4. 如何判断当前滚动是由用户指尖触发的?
有时候我们需要了解:到底是用户实际滑动还是我们的代码引发了滚动。这在 SwiftUI 6.0 之前几乎是不可能的任务。
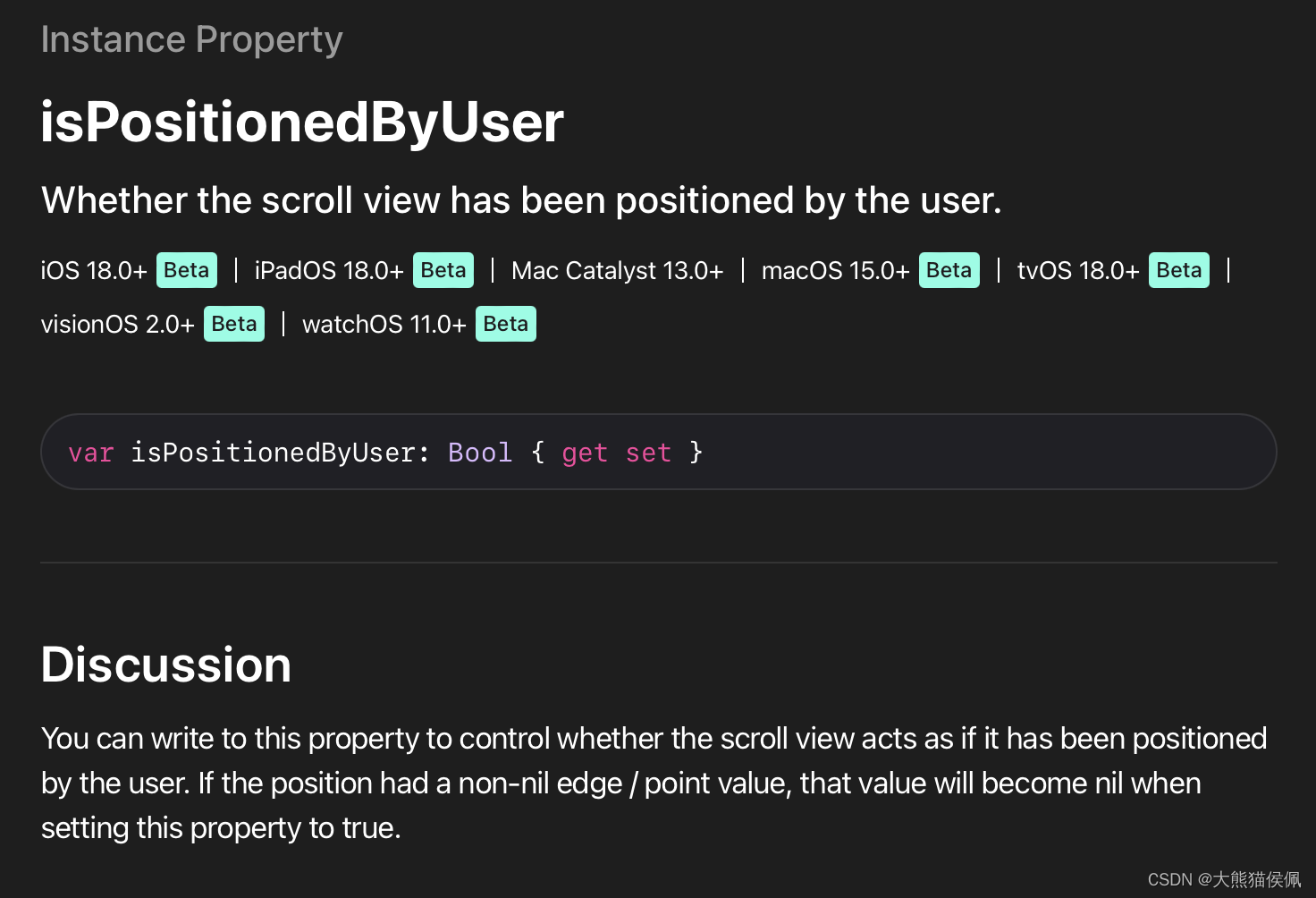
幸运的是,在 SwiftUI 6.0 中新降临 ScrollPosition 类型就包含一个 isPositionedByUser 属性,我们可以用它来明确滚动视图滚动的原因:
struct ContentView: View { @State private var position = ScrollPosition(edge: .top) var body: some View { ScrollView { ForEach(1..<100) { index in Text(verbatim: index.formatted()) .font(.largeTitle.weight(.heavy)) .padding() .id(index) } } .scrollPosition($position) .animation(.default, value: position) .safeAreaInset(edge: .bottom) { Button("Random Scroll") { let id = (1..<100).randomElement() ?? 0 position.scrollTo(id: id, anchor: .top) } } .onChange(of: position) { old,new in print("是否由用户拖动引起的滚动:\(new.isPositionedByUser ? "是" : "否")") } } } 从运行结果可以看到,只有当我们轻盈的指尖引起滚动时 isPositionedByUser 的值才会为真!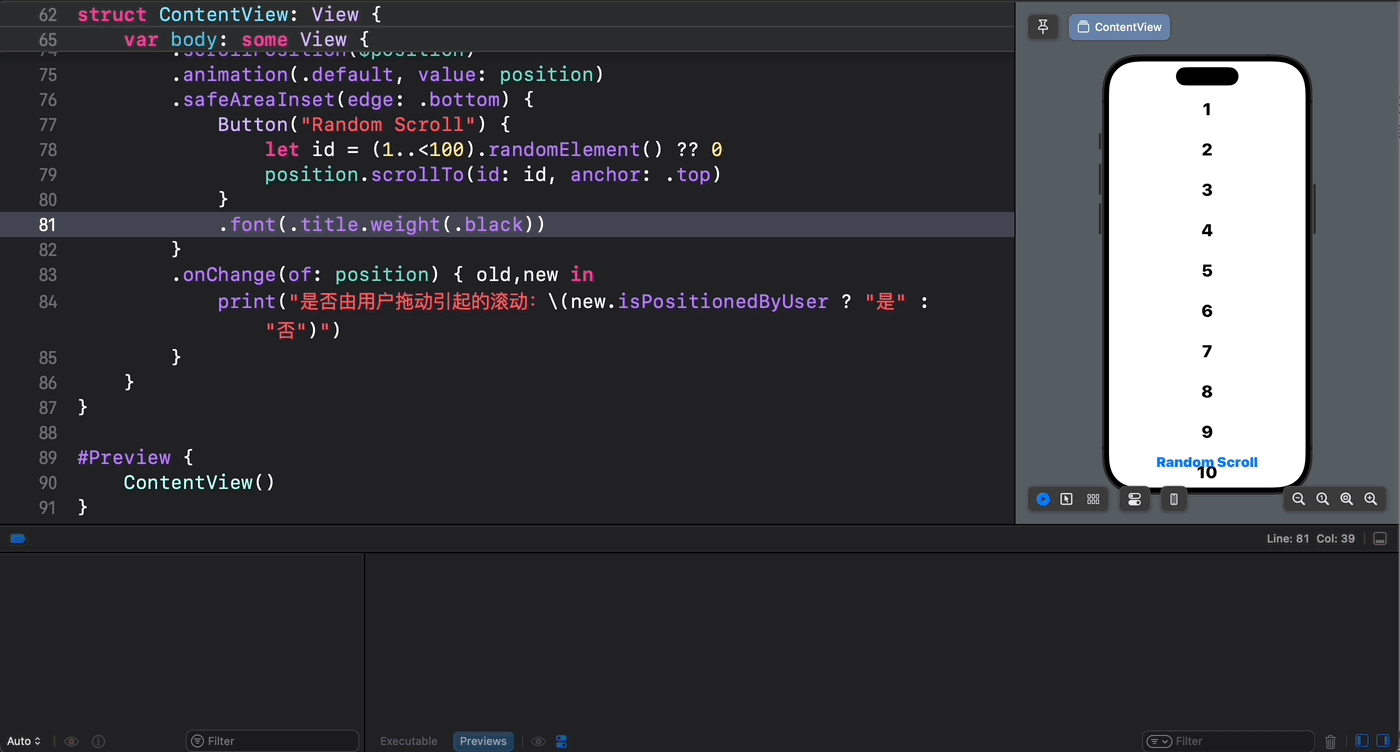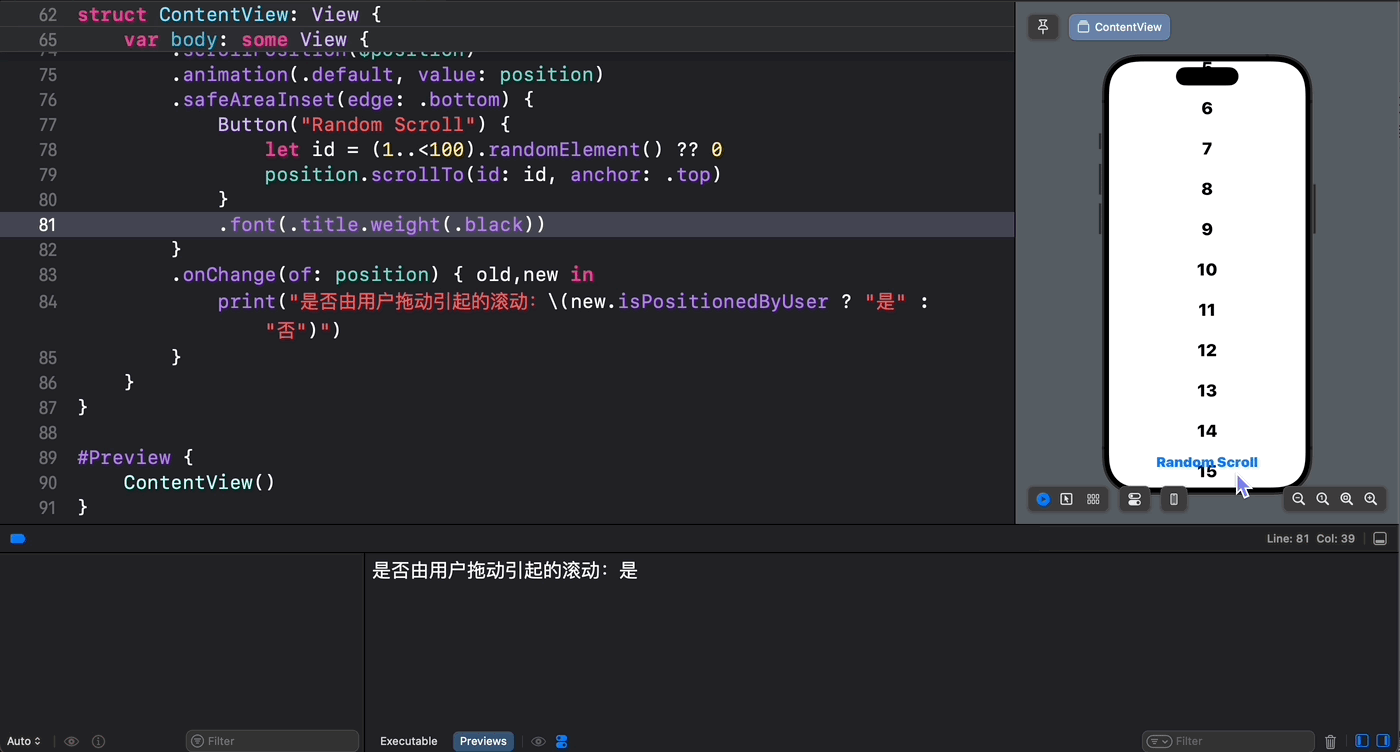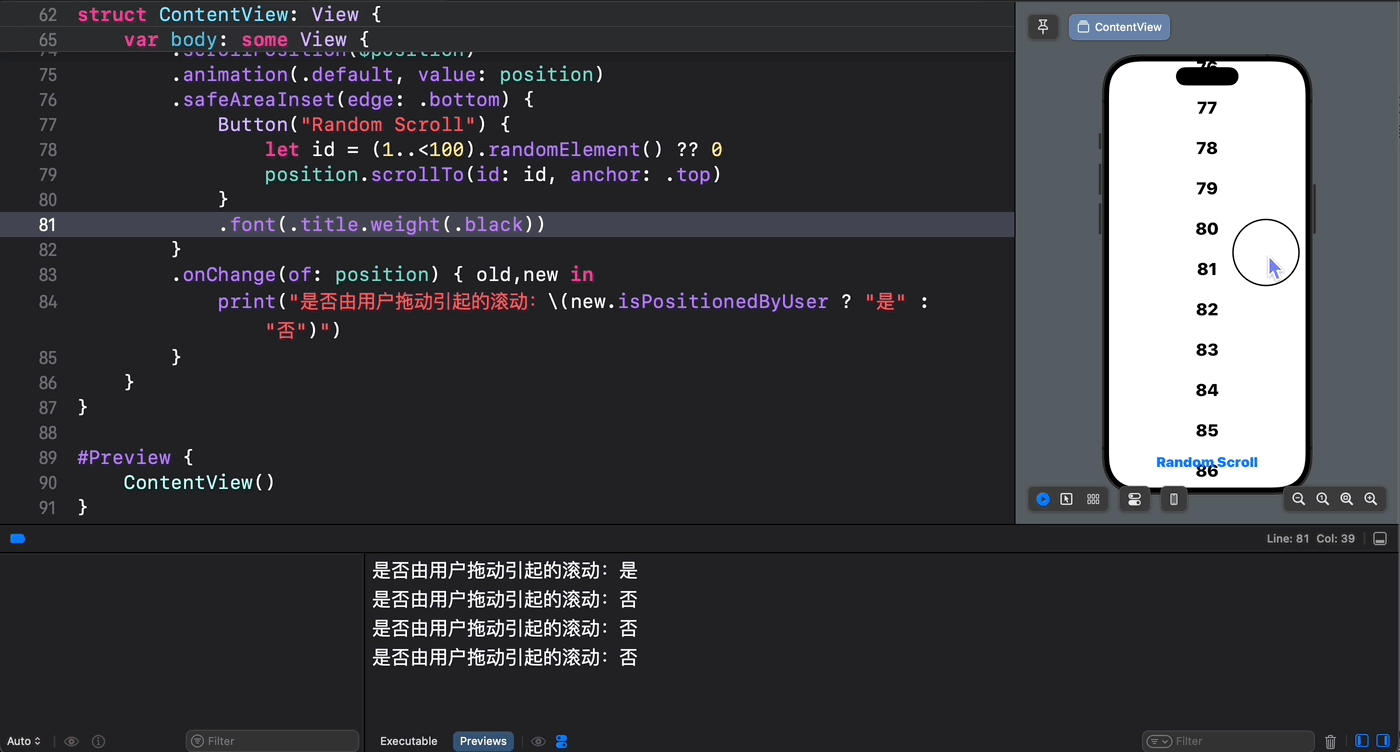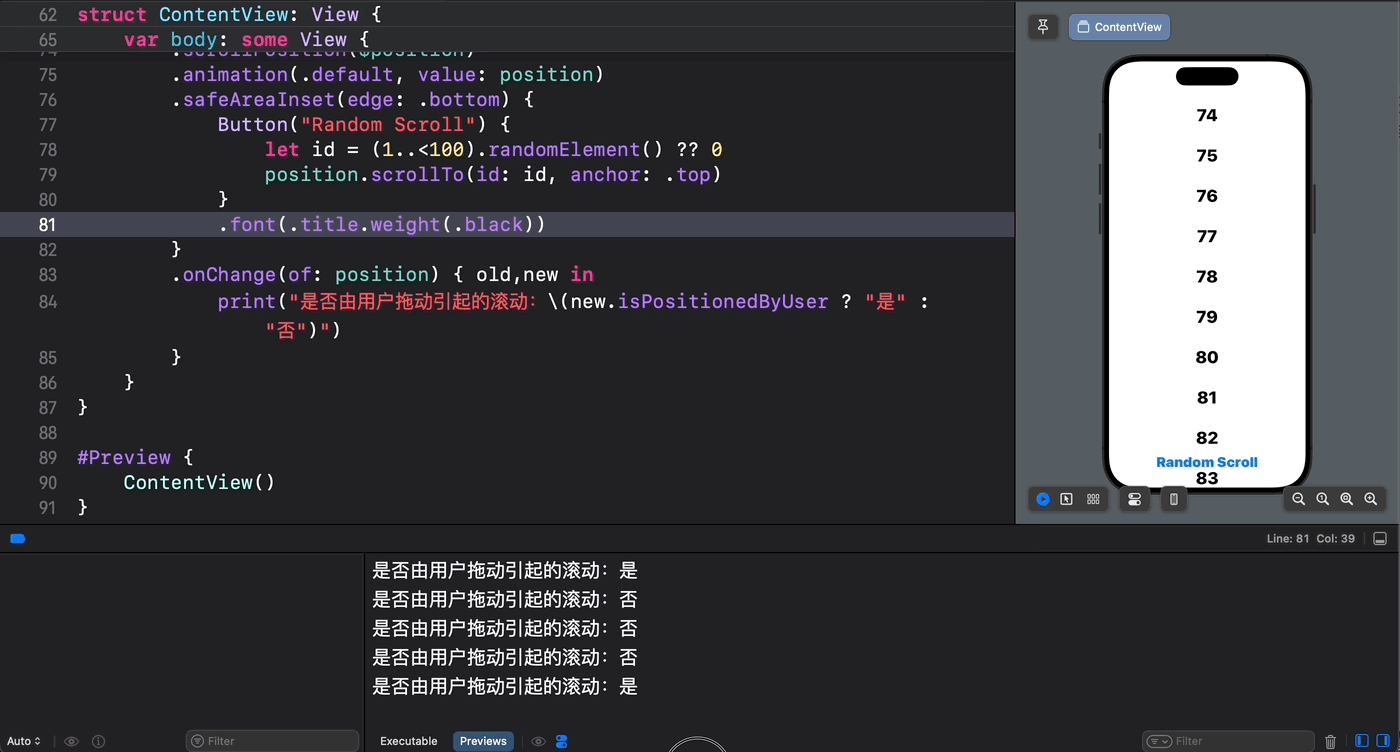
5. 实时监听滚动视图的内容偏移(ContentOffset)
从上面的讨论可知新的滚动机制能够让我们如虎添翼。不过虽然我们可以从 ScrollPosition 对象中获取到很多与滚动相关的信息,可是有一个滚动中至关重要的数据我们却对它束手无策:那就是滚动中内容视图实时的偏移值(ContentOffset)。
在正常情况下,通过直接访问 ScrollPosition 中的 point 属性将会一无所获:
.onChange(of: position) { old,new in print("当前内容滚动偏移:\(new.point)") } 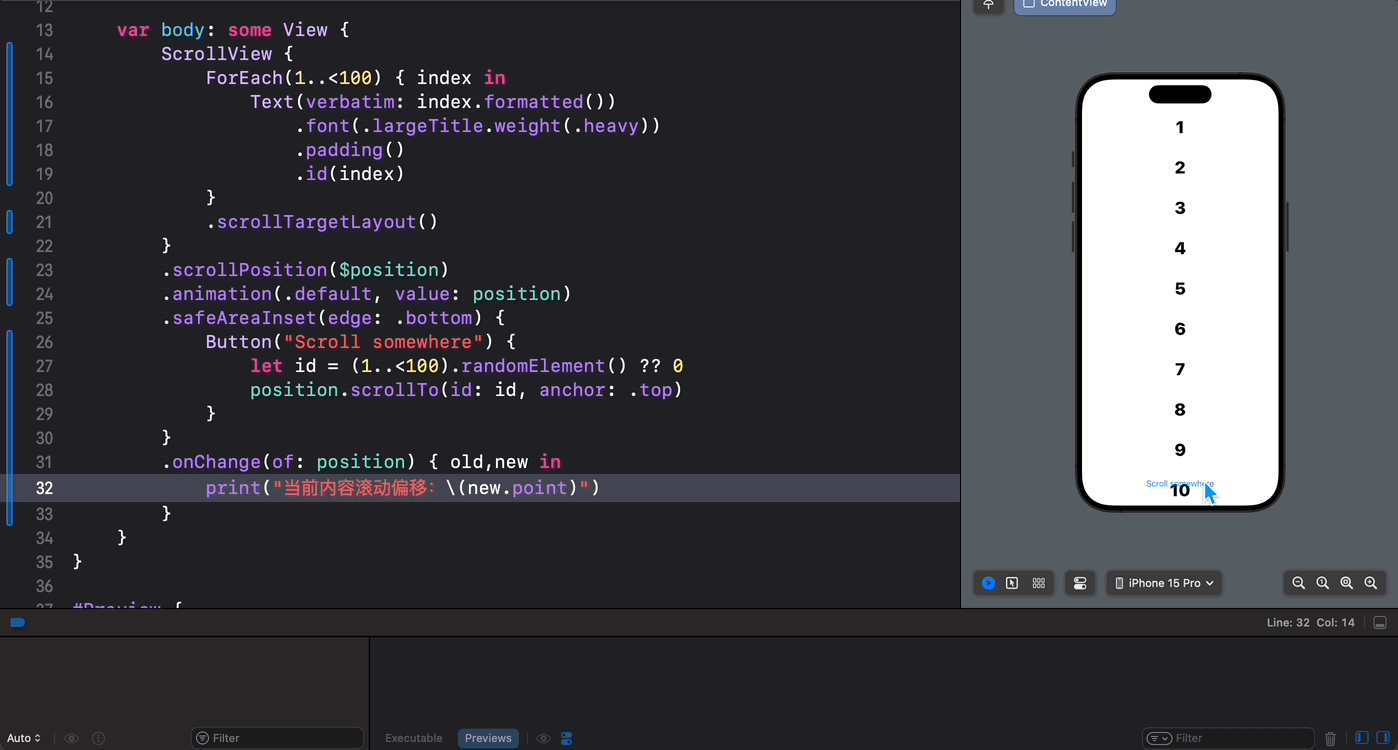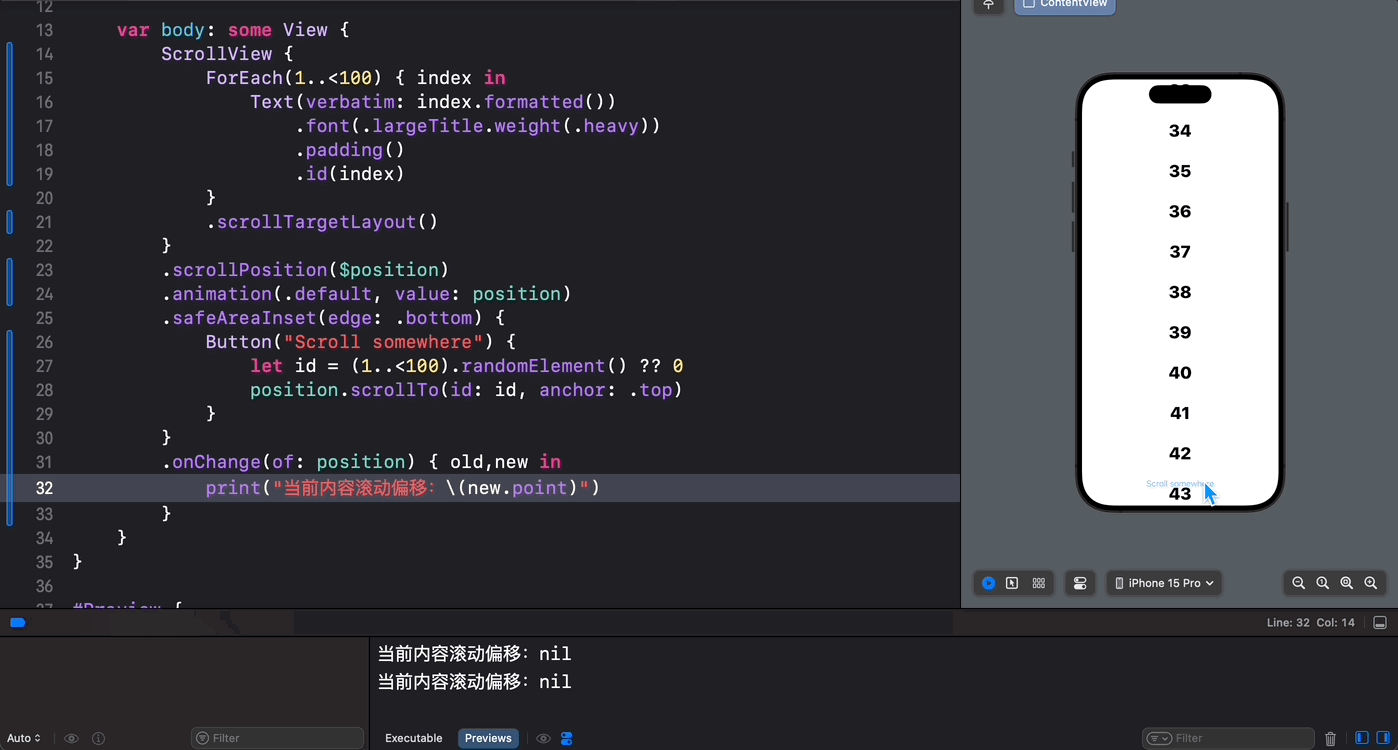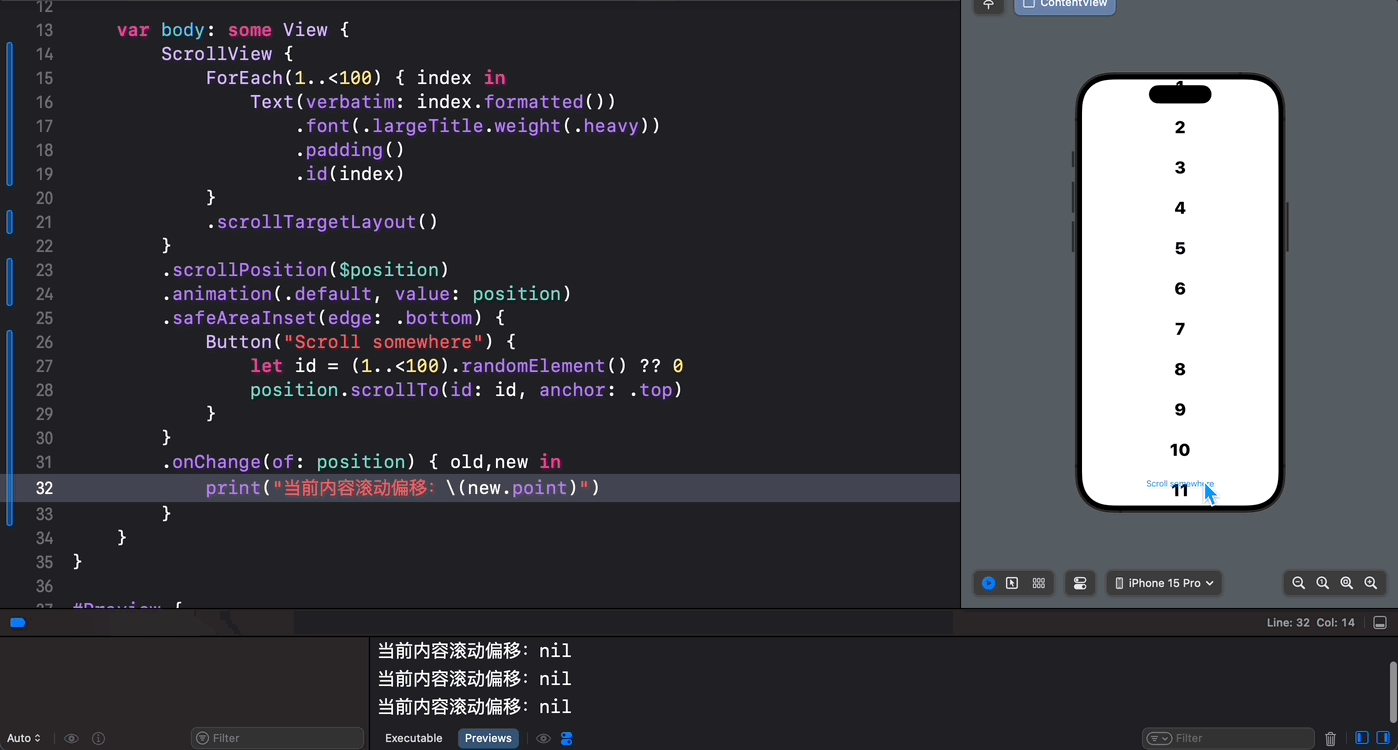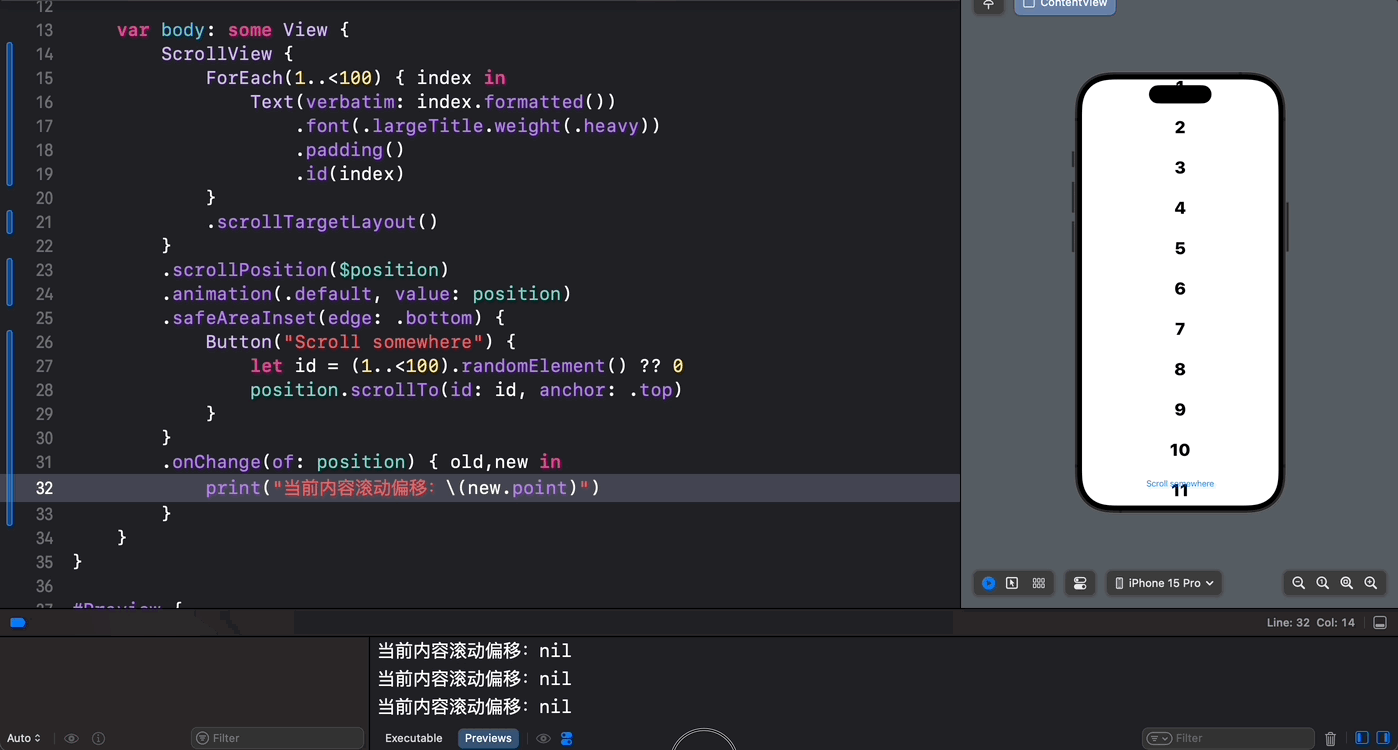
不过别担心,苹果在 SwiftUI 6.0 中又新增了一个 onScrollGeometryChange 修改器方法来专门解决此事:
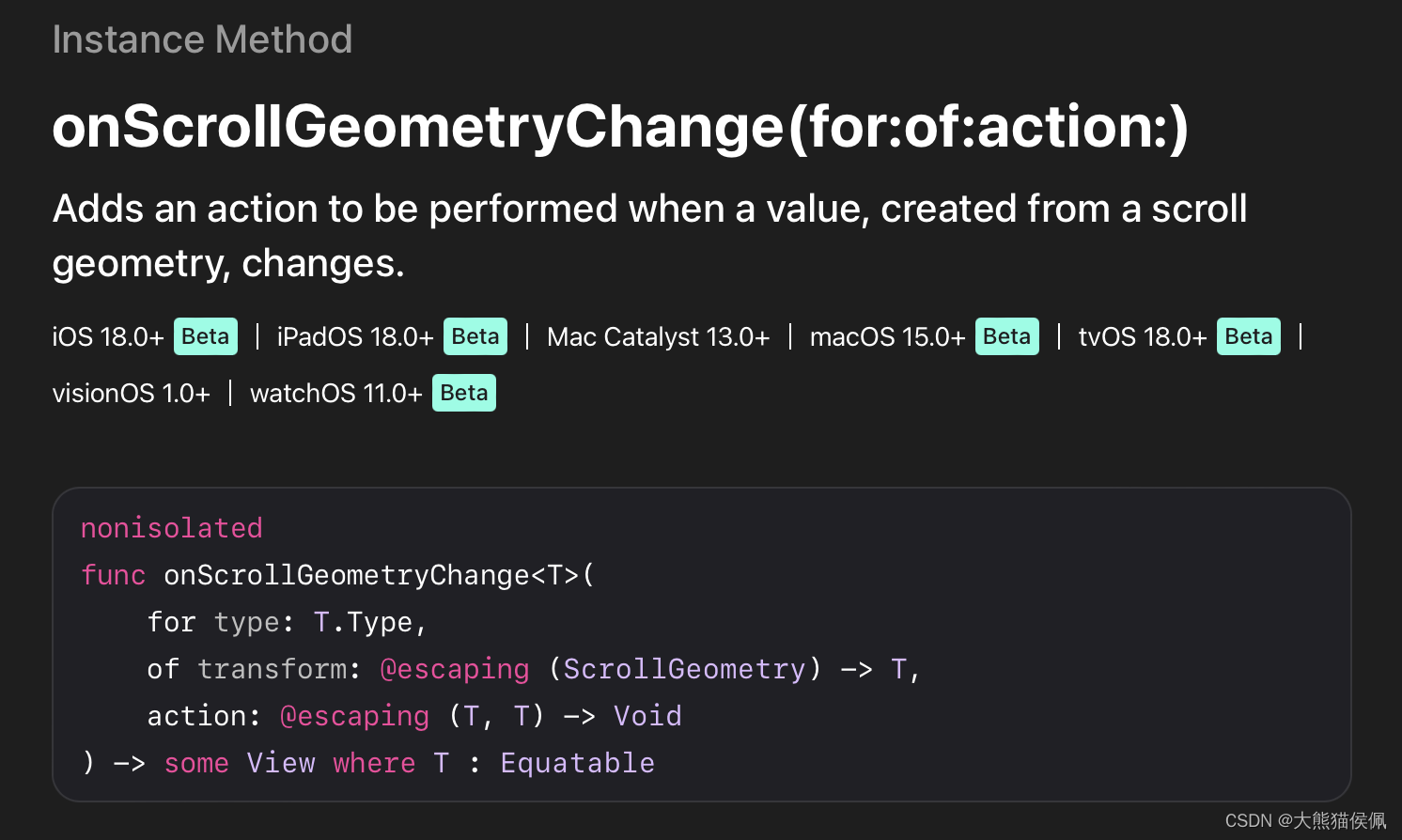
该方法可以在滚动几何构造发生变化时,执行我们想要的动作。注意它的 transform 闭包会传入一个 ScrollGeometry 类型的参数,我们可以用它来获取任何与滚动几何(Geometry)相关的信息:
现在,使用 onScrollGeometryChange() 修改器方法我们可以游刃有余的在滚动中实时获取滚动的偏移啦:
struct ContentView: View { @State private var position = ScrollPosition(edge: .top) @State var curPosID: Int? @State var offsetY: CGFloat? var body: some View { ScrollView { ForEach(1..<100) { index in Text(verbatim: index.formatted()) .font(.largeTitle.weight(.heavy)) .padding() .id(index) } .scrollTargetLayout() } .scrollPosition(id: $curPosID) .scrollPosition($position) .animation(.default, value: position) .safeAreaInset(edge: .bottom) { Button("Random Scroll") { let id = (1..<100).randomElement() ?? 0 position.scrollTo(id: id, anchor: .top) } } .onChange(of: position) { old,new in print("用代码滚动视图的ID: \(new.viewID)") curPosID = new.viewID as? Int } .onChange(of: curPosID) { _,new in print("实时滚动视图的 ID: \(new)") } .onScrollGeometryChange(for: CGFloat.self, of: { geo in geo.contentOffset.y }, action: { old, new in offsetY = new }) .onChange(of: offsetY) { _, new in guard let new else { return } print("当前 y 轴滚动偏移:\(new.formatted())") } } } 最后,我们来看一下执行效果:
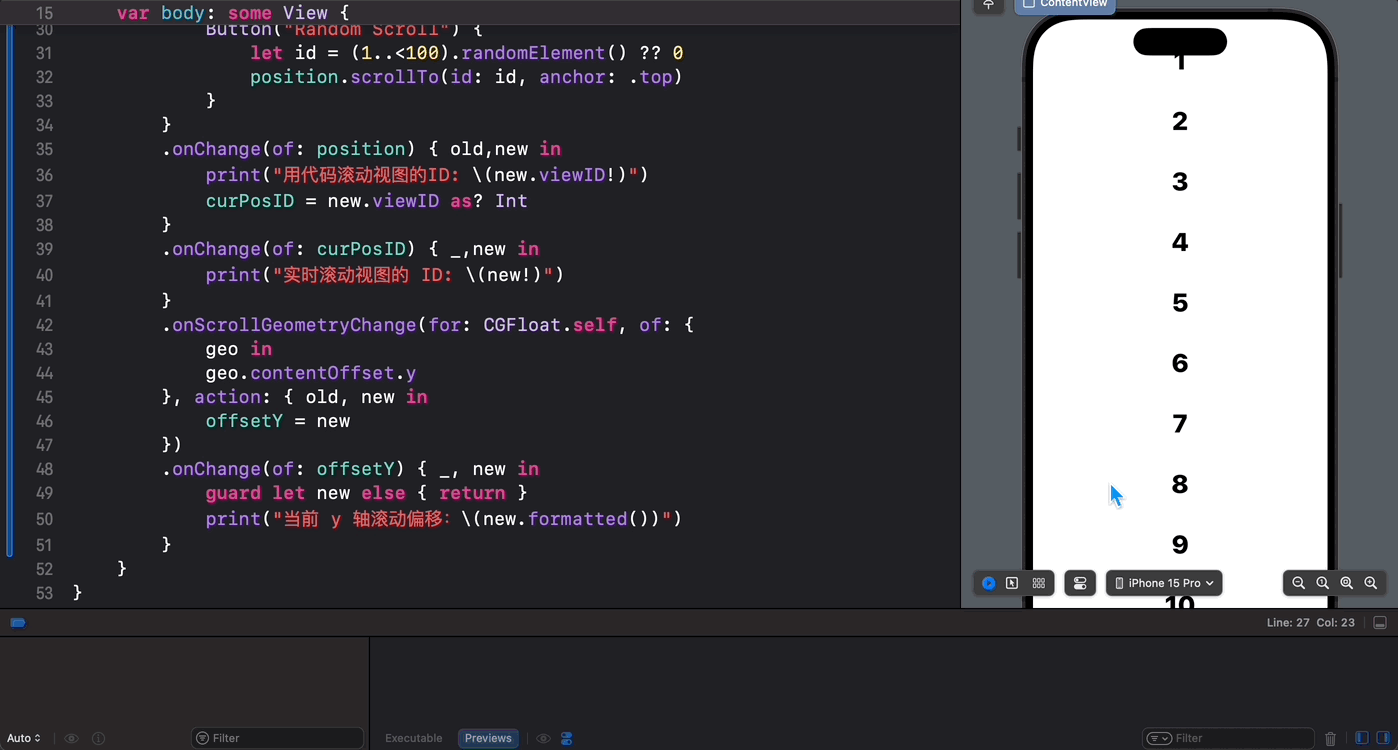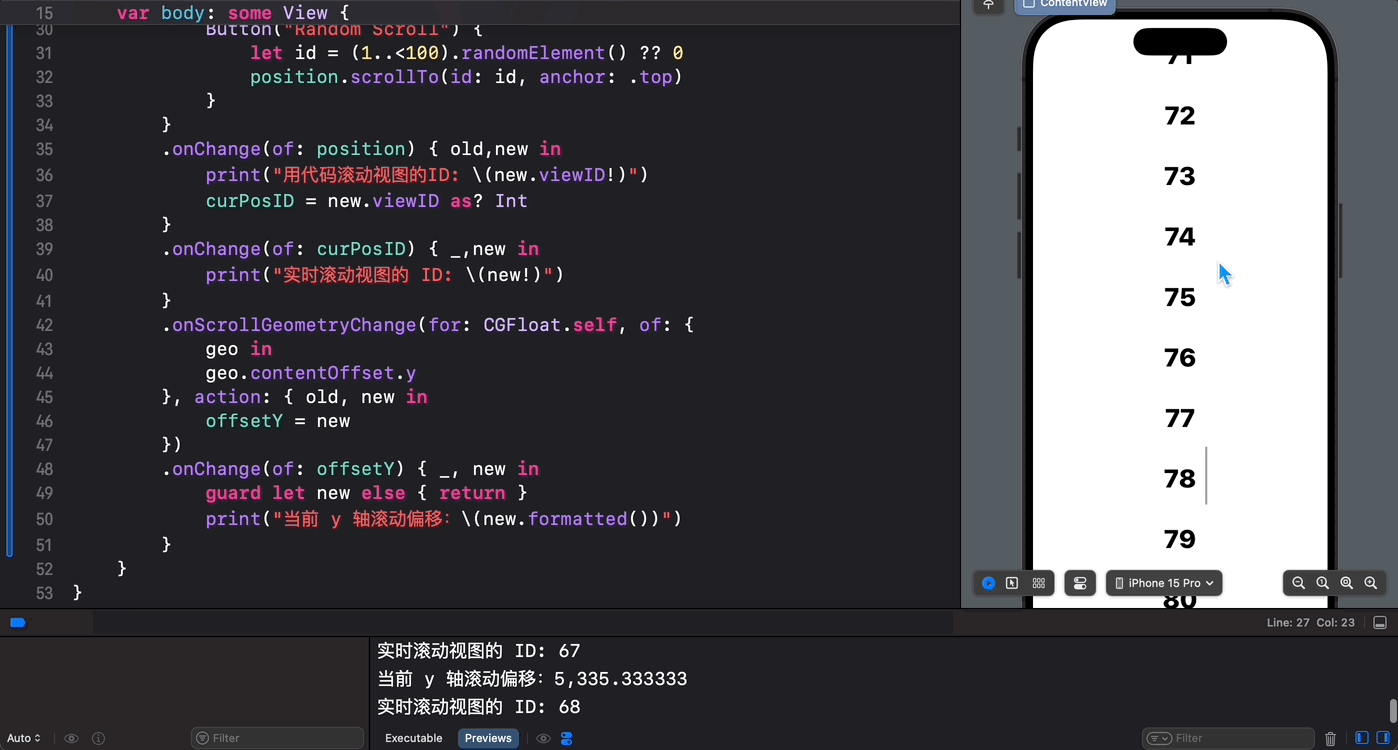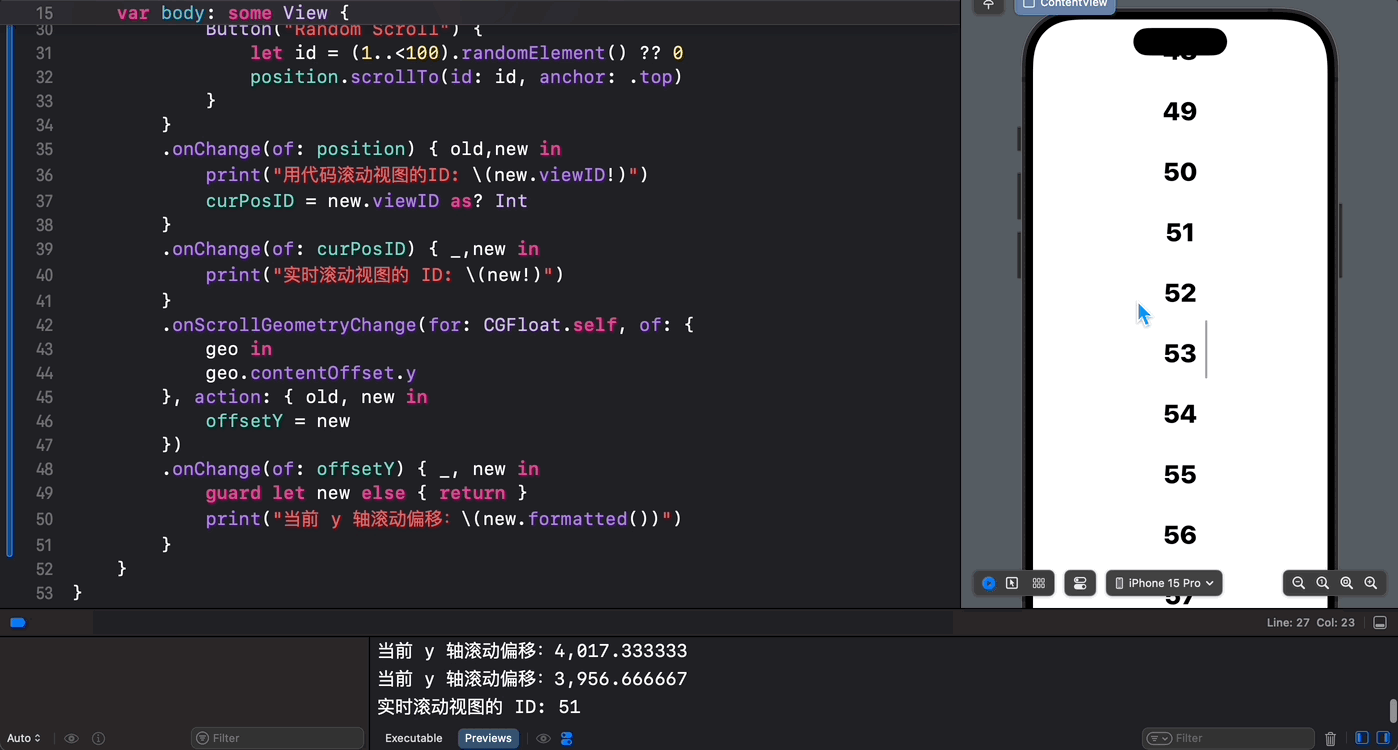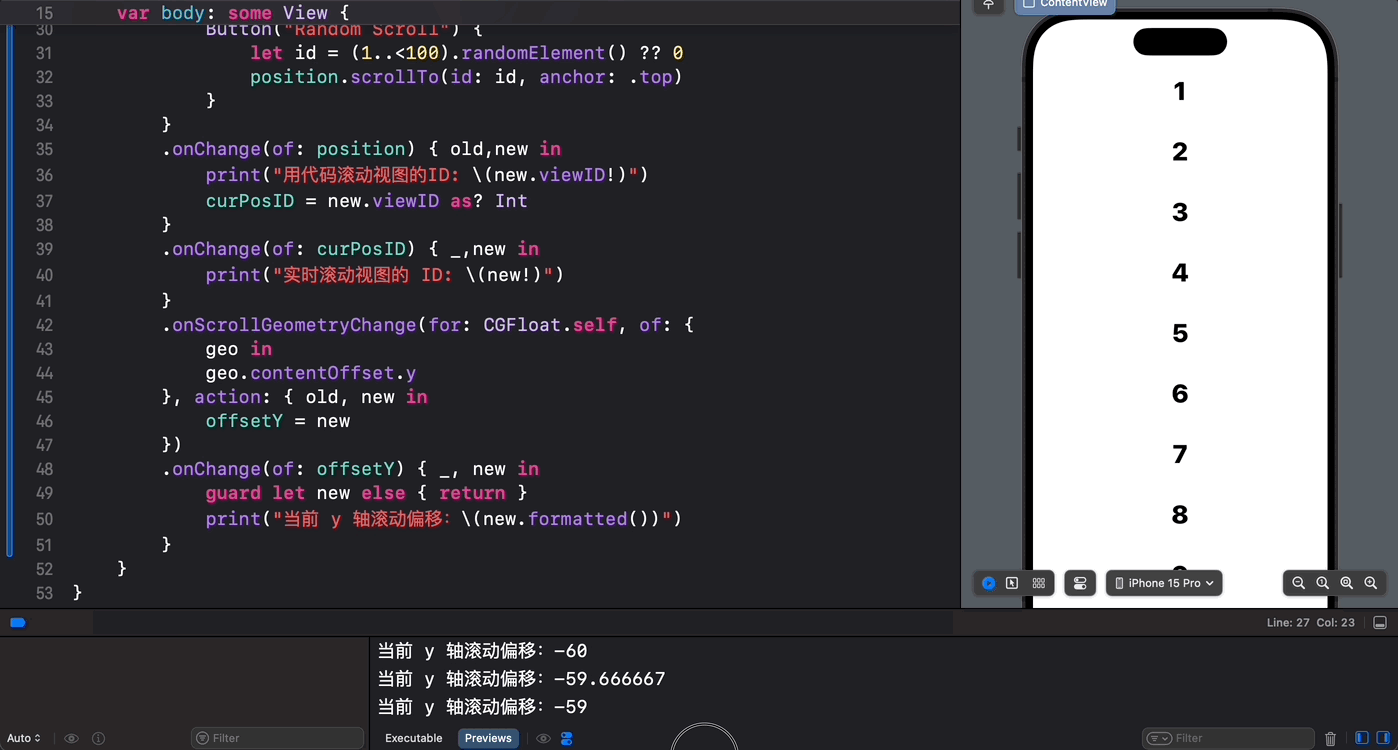
可以看到,有了 SwiftUI 6.0 对 iOS 18 和 iPadOS 18 中滚动视图的“重磅升级”,秃头码农们现在终于可以心无旁骛、怡然自得的和 ScrollView 心照神交啦!棒棒哒!
总结
在本篇博文中,我们介绍了 SwiftUI 6.0(iOS/iPadOS 18)中滚动视图(ScrollView)的全新升级,其中包括 ScrollPosition 以及动态获取滚动实时偏移(Content Offset)等精彩内容。
感谢观赏,再会!😎
