提示:使用环境为 MAC(M2)
其实 VSCode 很早就下载好了,但是因为在配置过程中总是遇到很多坑,搁置了很久,回头捡起遇到报 Error 还是两眼抓瞎,到处翻 blog。为了减少以后的遇坑可能性,整理了这份笔记(支持编译多cpp文件,支持C++11以上的新特性),希望能够帮助小白同学避坑。
分两个版本,本文是详细版本。
版本区别如下:
详细版本
前提
- 安装 Visual Studio Code
- VSCode 中安装 C/C++扩展
- 确保 Clang 已经安装(在终端中输入命令:
clang --version来确认是否安装)
创建你的第一个 HelloWorld 程序
创建工作区(WorkSpace)
打开 VSCode, 创建一个 project 文件夹。
现在,project 就是我们的工作区(WorkSpace)了。当我们继续做完本教程的配置,这个工作区中将出现一个子文件夹.vscode,包含三个文件。
● tasks.json(编译选项设置)
● launch.json(调试选项设置)
● c_cpp_properties.json(编译器路径以及IntelliSense 设置)
创建 HelloWorld 的源代码文件
在 project 文件夹下创建一个 hello.cpp 文件
在 hello.cpp中粘贴以下内容
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main(){ cout << "Hello World" << endl; } Command+S(⌘S)保存该文件,建议在 File > Auto Save 中打开该选项,自动保存。
添加 IntelliSense 配置
IntelliSense 是 VS Code 中提供的工具,可实现代码补全等,帮助快速开发。
Shift+Command+P(⇧⌘P)打开命令面板,输入Select IntelliSense Configuration,选择 Use clang++
可以看到工作区中新增了一个.vscode 的文件夹,并包含了一个叫做 settings.json 的文件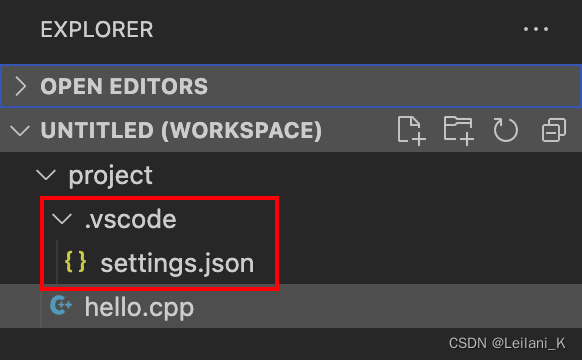
运行 HelloWorld(compile and run)
注意:C++扩展是使用机器上已安装的 C++编译器来生成程序,所以在运行/调试 hello.cpp 前,请确保你已经符合了文章开头的前提,安装好了 C++编译器。
- 打开 hello.cpp,这将它将成为 active file,可以被用于生成和调试
- 点击图中右上角的按钮,选择
Run C/C++ File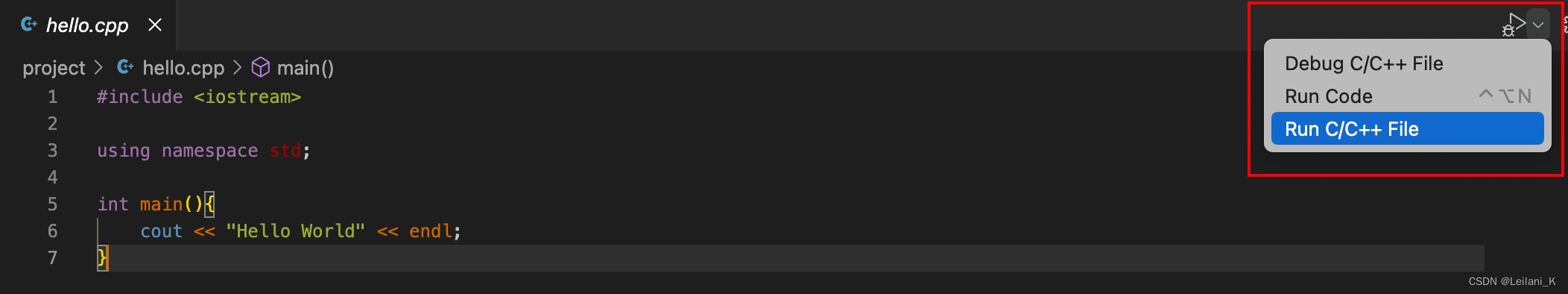
- 在跳出的选项中,选择
C/C++: clang++ build and debug active file。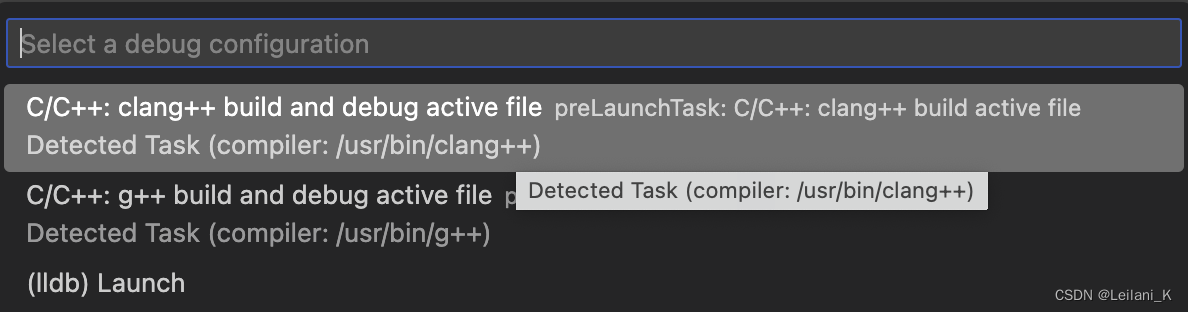
只有在第一次运行 hello.cpp 时才需要做这个选择。选择后,.vscode 文件夹中出现了一个新文件tasks.json,我们选择的编译器配置将作为默认设置。 - 编译成功后,程序的输出将显示在下方的 DEBUG CONSOLE
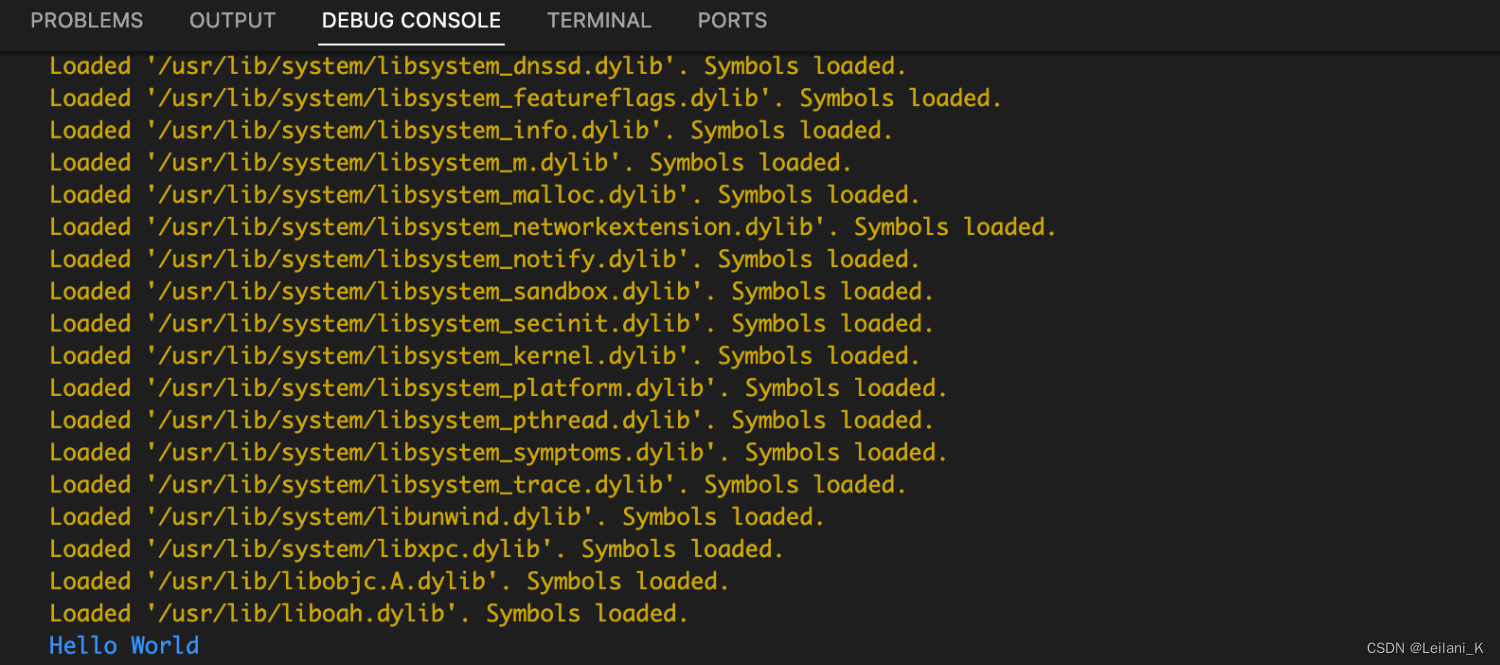
至此,我们已经成功地运行了 VS Code 上的第一个 C++程序!
改造代码目录(include、src、target) 以适应工程需要
在实际的开发中,我们往往需要分类不同的文件至不同的文件夹中。一个简单的形式是在其中创建三个子文件夹 include、src、target 分别用来分类头文件、源文件、以及目标程序。
在 project 文件夹中,清理之前生成出来的其他文件(除了 hello.cpp 和.vscode),增加三个子文件夹 include、src、target,并把 hello.cpp 移动到 src 目录下。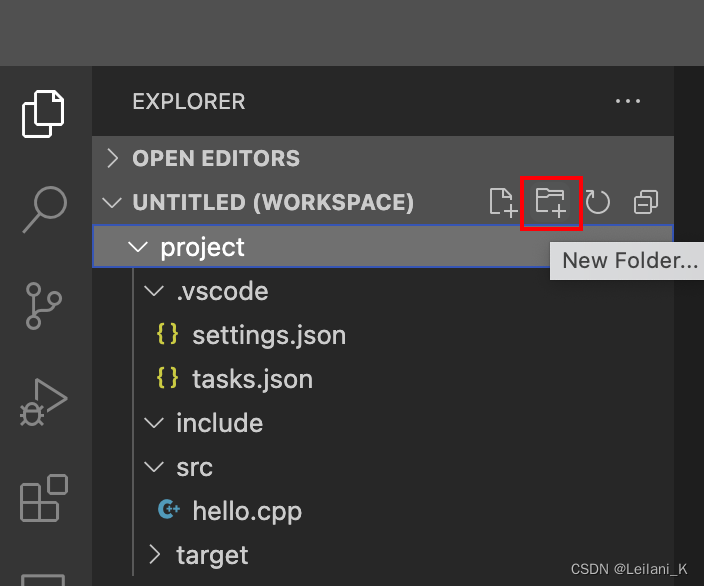
修改 tasks.json
修改了文件组织形式后,存储了编译配置的 tasks.json 也需要做对应修改。
第一次编译运行 hello.cpp 时,我的机器上生成的 tasks.json 如下:
{ "tasks": [ { "type": "cppbuild", "label": "C/C++: clang++ build active file", "command": "/usr/bin/clang++", "args": [ "-fcolor-diagnostics", "-fansi-escape-codes", "-g", "${file}", "-o", "${fileDirname}/${fileBasenameNoExtension}" ], "options": { "cwd": "${fileDirname}" }, "problemMatcher": [ "$gcc" ], "group": { "kind": "build", "isDefault": true }, "detail": "Task generated by Debugger." } ], "version": "2.0.0" } 我们做如下两个修改:
- 工程中往往需要一次性编译选定路径下的所有 cpp 文件。对应的,把
"args"中的:"${file}"改为"${fileDirname}/*.cpp" - 我们希望把编译出的文件统一放置在 target 文件夹下。对应的,把
"args"中的"${fileDirname}/${fileBasenameNoExtension}"改为"${workspaceFolder}/target/${fileBasenameNoExtension}"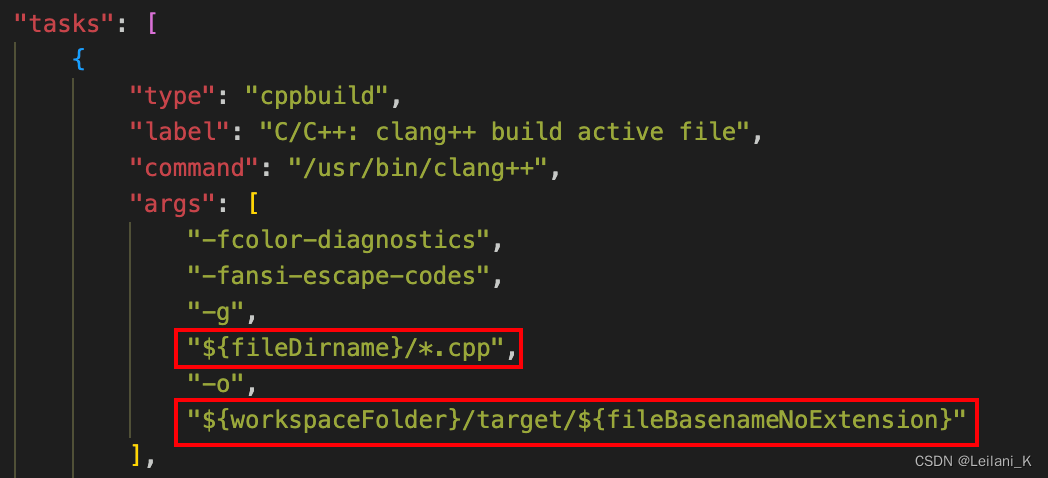
然后我们做下测试,看看修改后的工作区可否正常编译运行 hello.cpp
在 include 中创建 print.h,粘贴如下内容:
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <string> using namespace std; void printMessage(vector<string>& msg); 在 src 中创建 print.cpp,粘贴如下内容:
#include "../include/print.h" void printMessage(vector<string> &msg) { for (int i = 0; i < msg.size(); i ++){ cout << msg[i] << " "; } } 修改 src 下的 hello.cpp,粘贴如下内容:
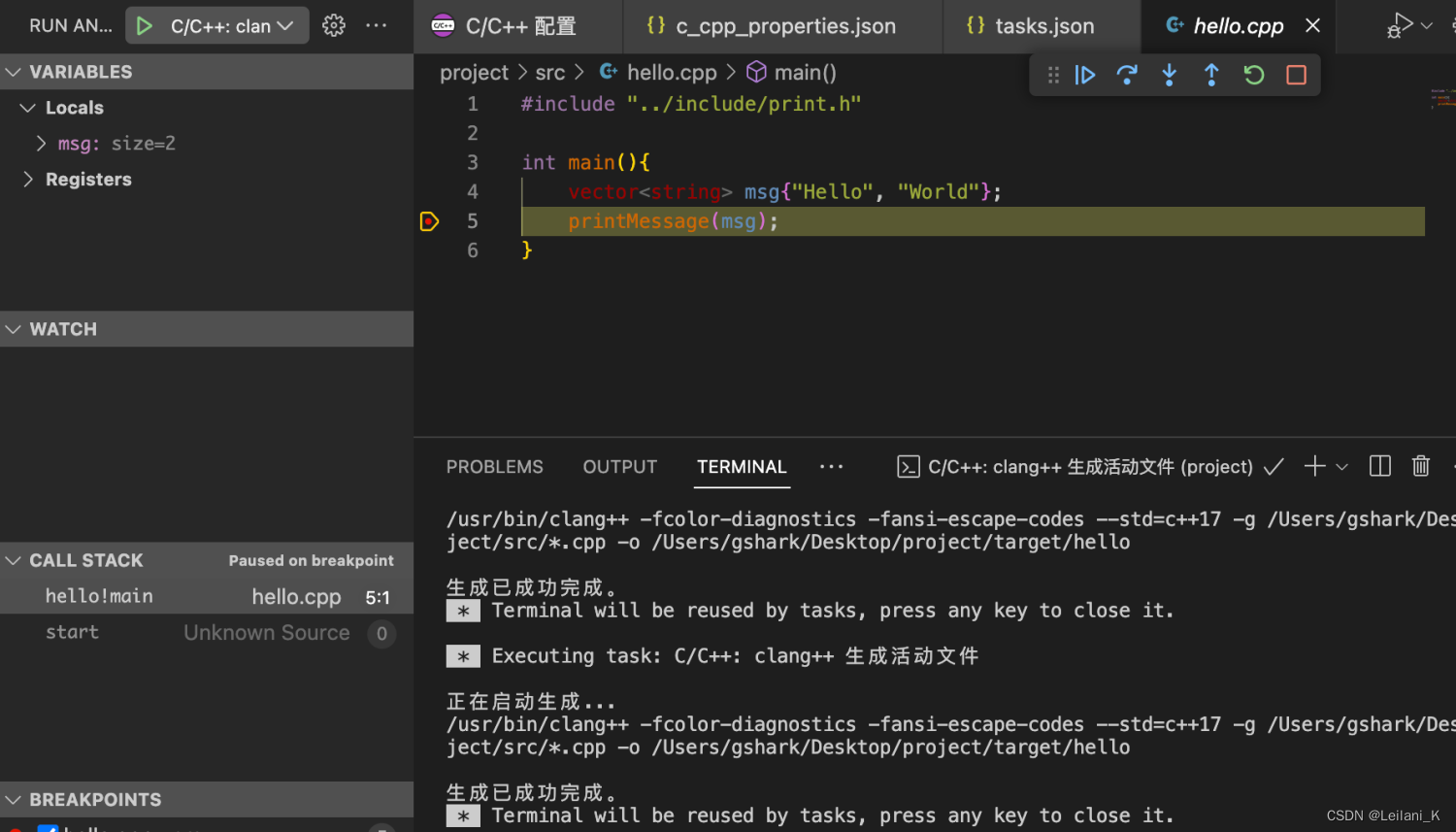
#include "../include/print.h" int main(){ vector<string> msg; msg.push_back("Hello"); msg.push_back("World"); printMessage(msg); } 在 hello.cpp 中点击右上角的 run 按钮,可以看到也成功运行了(这说明我们实现了一次性编译多个 cpp 文件),而且目标文件生成到了 target 下。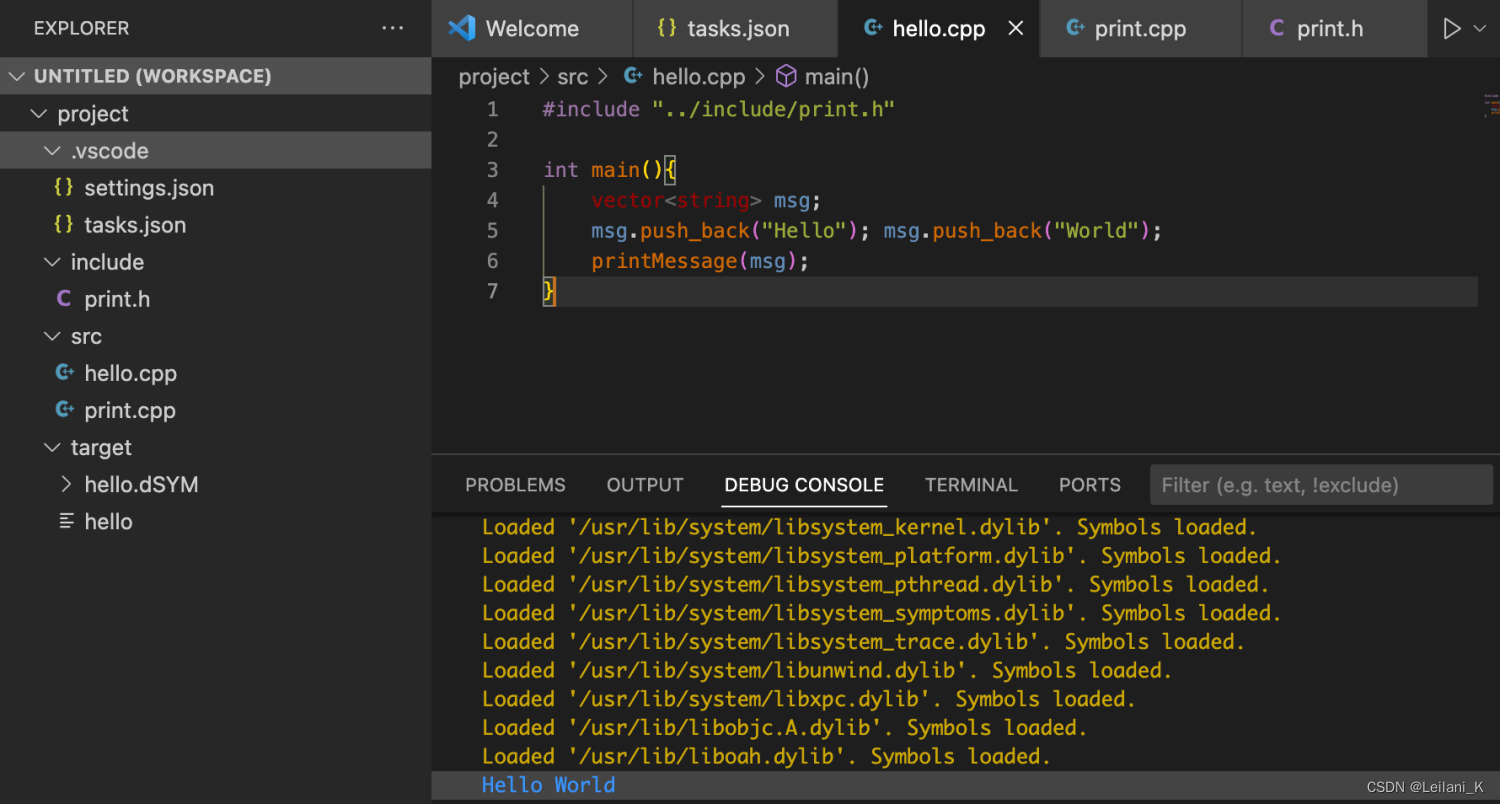
拓展:关于 tasks.json 的设置含义
tasks.json 中存储了编译的设置,更深刻地理解它有助于解决后续可能遇到的编译错误。
以上面贴出的 task.json 内容为例,对 tasks.json 中的参数解析如下:
label
*第一次点击 Run C/C++ File 时指定的选项值。在本例中,是"C/C++: clang++ build active file"command
指定要运行的程序(编译器) 在本例中,是 clang++args
指定传递给编译器的命令行参数,这些参数应当按照一定的顺序排列在最开始生成的 tasks.json 中,args 相关参数设置如下:
"args": ["-g", "${file}", "-o", "${fileDirname}/${fileBasenameNoExtension}"]
他的含义是告知 C++编译器编译 active file(即${file}),生成目标文件(-o)到当前的目录下
(${fileDirname}) ,目标文件的名称和不带后缀的 active file 的名称一致(${fileBasenameNoExtension})。
因此我们第一次运行时,在 hello.cpp 中 run,在 同级目录下编译出了 hello 目标文件。
至此,应该也能理解将原先的"-g", "${file}"改为"-g", "${fileDirname}/*.cpp"带来的影响了吧,就是将编译当前 active file 变成编译同级目录下的所有 cpp 文件
而将"-o", "${fileDirname}/${fileBasenameNoExtension}"
改为"-o", "${workspaceFolder}/target/${fileBasenameNoExtension}"则是改变目标文件的路径到工作区下的 target 目录下。problemMatcher:
在编译器输出中查找错误和警告的输出解析器。对于 clang++,gcc 是最佳的 problemMatchergroup:
里面的 isDefault 选项可以用来指定哪个 task 被作为默认的生成选项。生成了 tasks.json 后,点击 run 按钮就会按照默认选定的 task 配置进行编译运行,tasks 中可以有多个 task,不需要作为默认项的移除
“group"中的"isDefault”: truedetail:
task 的描述。tasks 中可以用多个 task,detail 可用于做区分
调试 HelloWorld(debug)
- 首先,回到 hello.cpp,使得其变为 active file
- 在如图所示处设置一个断点(在该行的前面点击小圆点)
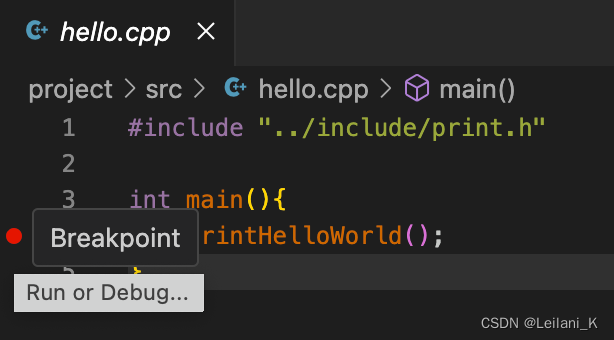
- 选择 Debug C/C++ File
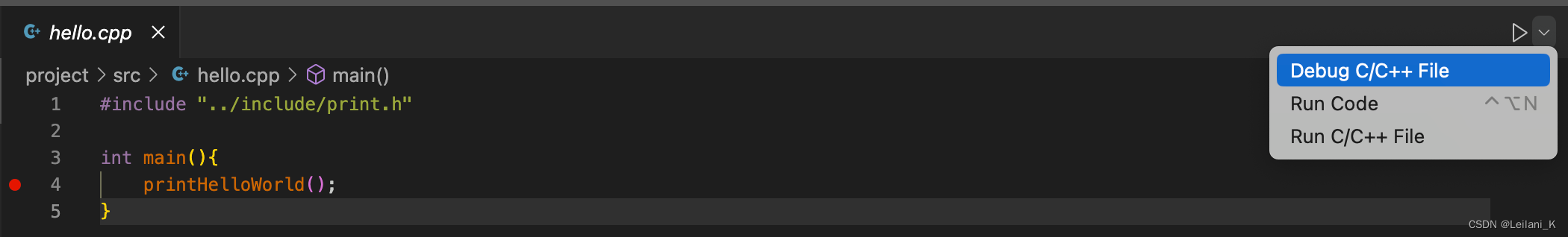
因为之前我们已经在 hello.cpp 上选择过 Run C/C++ File 编译运行过了,当时选择了C/C++: clang++ build and debug active file,此时就不必再选择了。如果此前没有运行过就选择了 debug,那么在跳出的选项中选择C/C++: clang++ build and debug active file。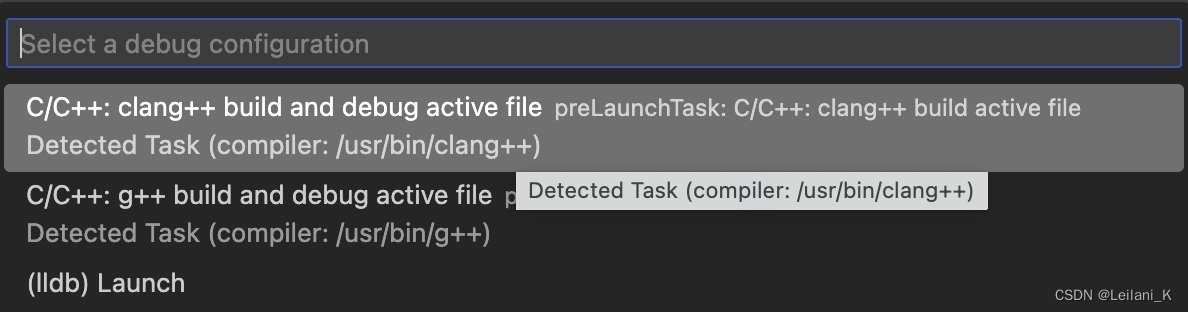
- 可以看到程序执行到端点处,执行位置有高亮表示。出现了调试的工具栏,可以分别选择执行到下一个断点、执行单步、步入、跳出、重新开始、停止。这说明可以正常调试了。

配置调试设置 launch.json
当我们点击调试按钮(Debug C/C++ File)时,其实内部是为我们创建了一个动态调试配置,但往往我们需要去对调试配置做一些修改,可以创建一个 launch.json 文件来存储我们的调试设置。
- 点击右上角的 Add Debug Configuration 按钮
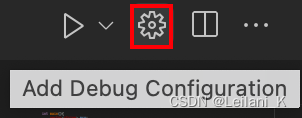
- 在跳出的选项里选择C/C++: clang++ build and debug active file.
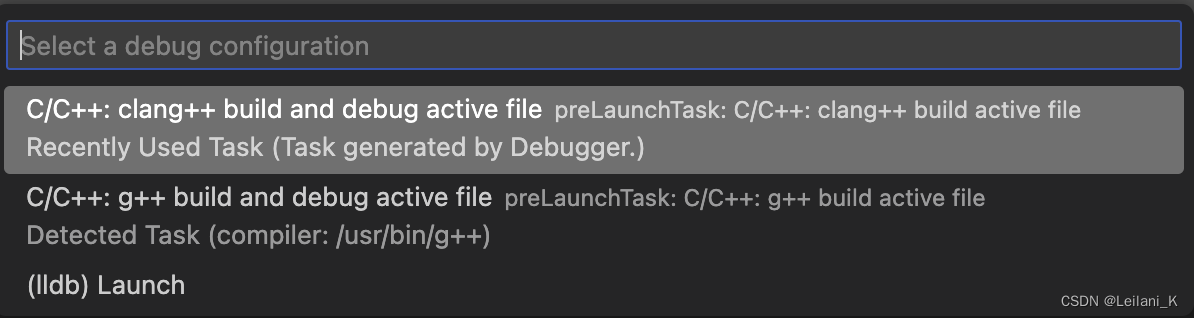
- .vscode 中会自动创建一个 launch.json 文件
{ "configurations": [ { "name": "C/C++: clang++ build and debug active file", "type": "cppdbg", "request": "launch", "program": "${workspaceFolder}/target/${fileBasenameNoExtension}", "args": [], "stopAtEntry": false, "cwd": "${fileDirname}", "environment": [], "externalConsole": false, "MIMode": "lldb", "preLaunchTask": "C/C++: clang++ build active file" } ], "version": "2.0.0" } 其中,重要的几个参数释义如下:
program:需要调试的程序。如果我们是在 hello.cpp 文件中开启调试,则对应调试的程序是project/target/helloargs:运行时传递给程序的参数数组stopAtEntry:为 true 时,程序将在main 方法入口处添加断点preLaunchTask:此处的值应当和tasks.json 中的 label 值保持一致
当我们创建了 launch.json,以后在这个程序上的调试都将按照 launch.json 中的调试配置开展。
配置c_cpp_properties.json
可以通过创建c_cpp_properties.json 文件来实现对 C/C++扩展 的更多设置,这里的正确配置可以帮助扩展找到正确的标准库路径,提供补全或跳转能力,如果程序包含不在工作区或标准库路径中的头文件,需修改其中的“includePath”设置。
Shift+Command+P(⇧⌘P) 打开命令面板,输入C/C++: Edit Configurations (UI),打开。这将在.vscode 中创建一个c_cpp_properties.json 文件。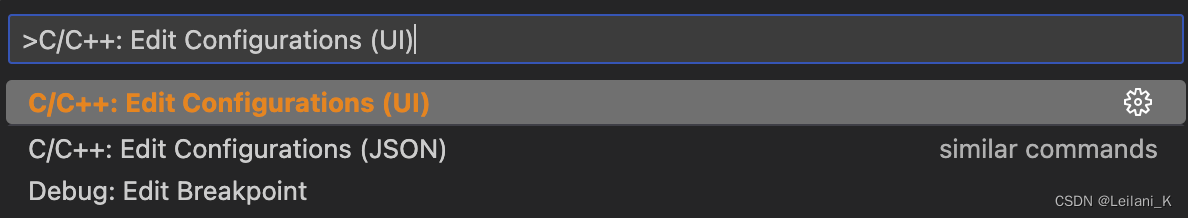
在界面中做如下修改: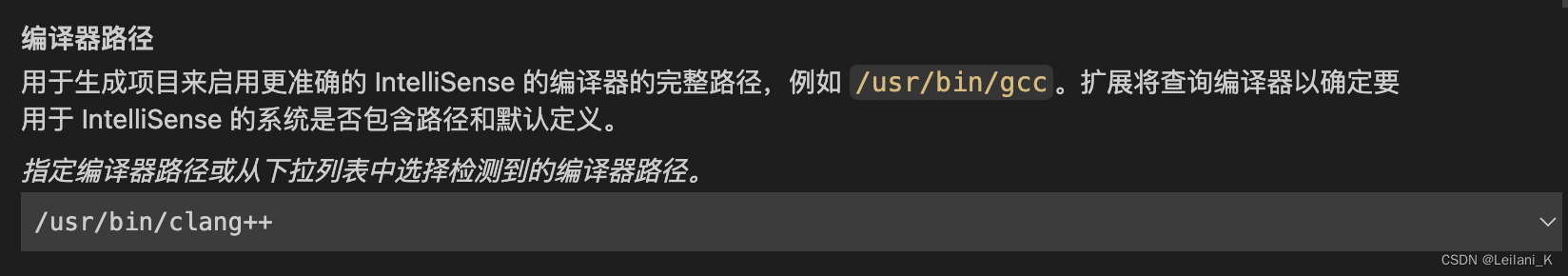
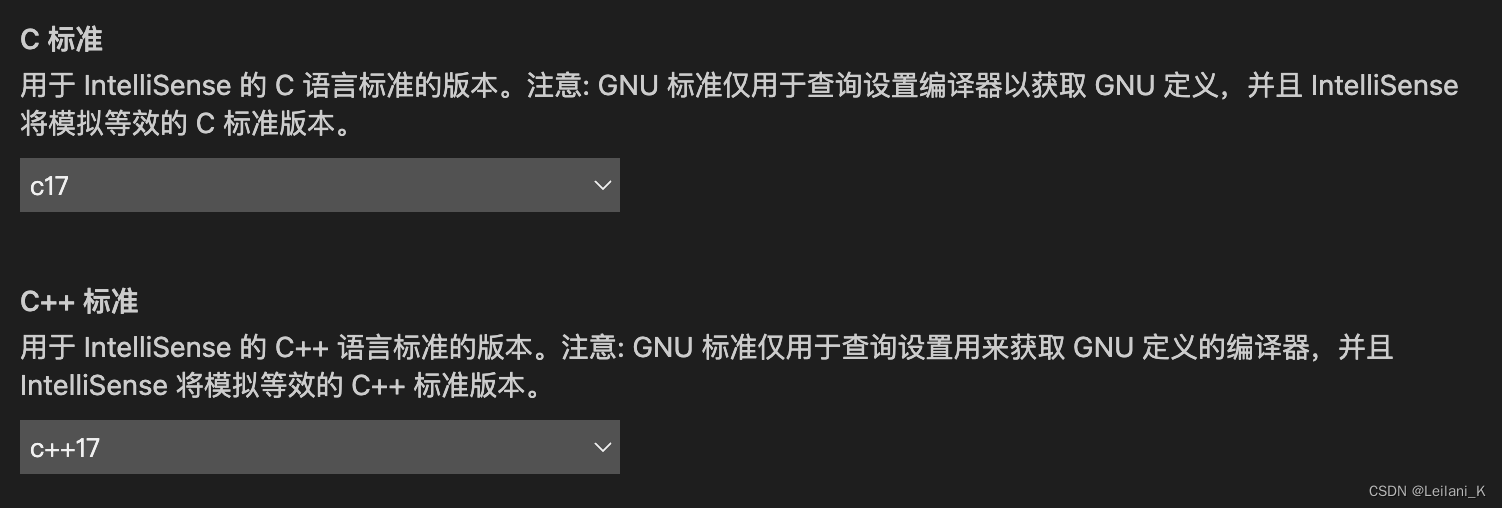
也可以在c_cpp_properties.json 中直接修改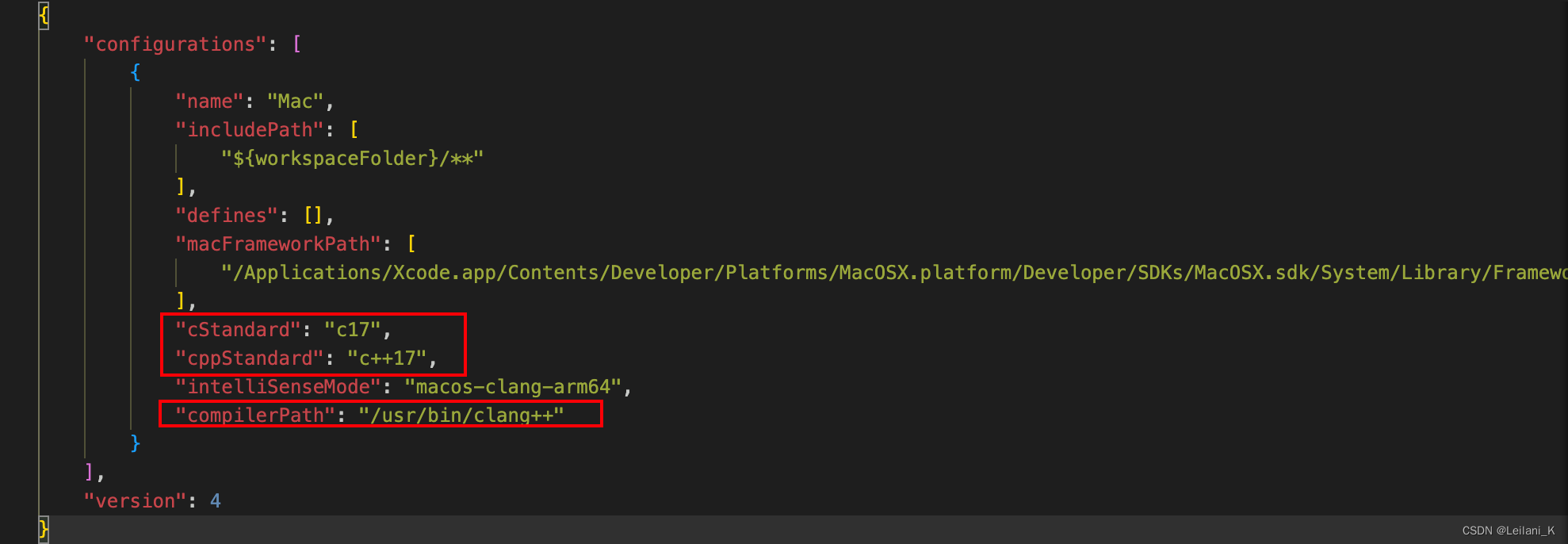
我的c_cpp_properties.json 如下,可以直接复制修改:"cStandard": "c17", "cppStandard": "c++17","compilerPath": "/usr/bin/clang++"这三处。
{ "configurations": [ { "name": "Mac", "includePath": [ "${workspaceFolder}/**" ], "defines": [], "macFrameworkPath": [ "/Applications/Xcode.app/Contents/Developer/Platforms/MacOSX.platform/Developer/SDKs/MacOSX.sdk/System/Library/Frameworks" ], "cStandard": "c17", "cppStandard": "c++17", "intelliSenseMode": "macos-clang-arm64", "compilerPath": "/usr/bin/clang++" } ], "version": 4 } 解决关于 C++新特性支持的问题
在前面的示例中,我有意地在代码里避开了 C++的新特性。
如果我们将代码修改成这样
print.cpp:
#include "../include/print.h" void printMessage(vector<string> &msg) { for (const auto& word: msg){ cout << word << " "; } } hello.cpp:
#include "../include/print.h" int main(){ vector<string> msg{"Hello", "World"}; printMessage(msg); } 运行会发现,将报告如下的错误,不难看出是 C++11 的新特性没有被支持。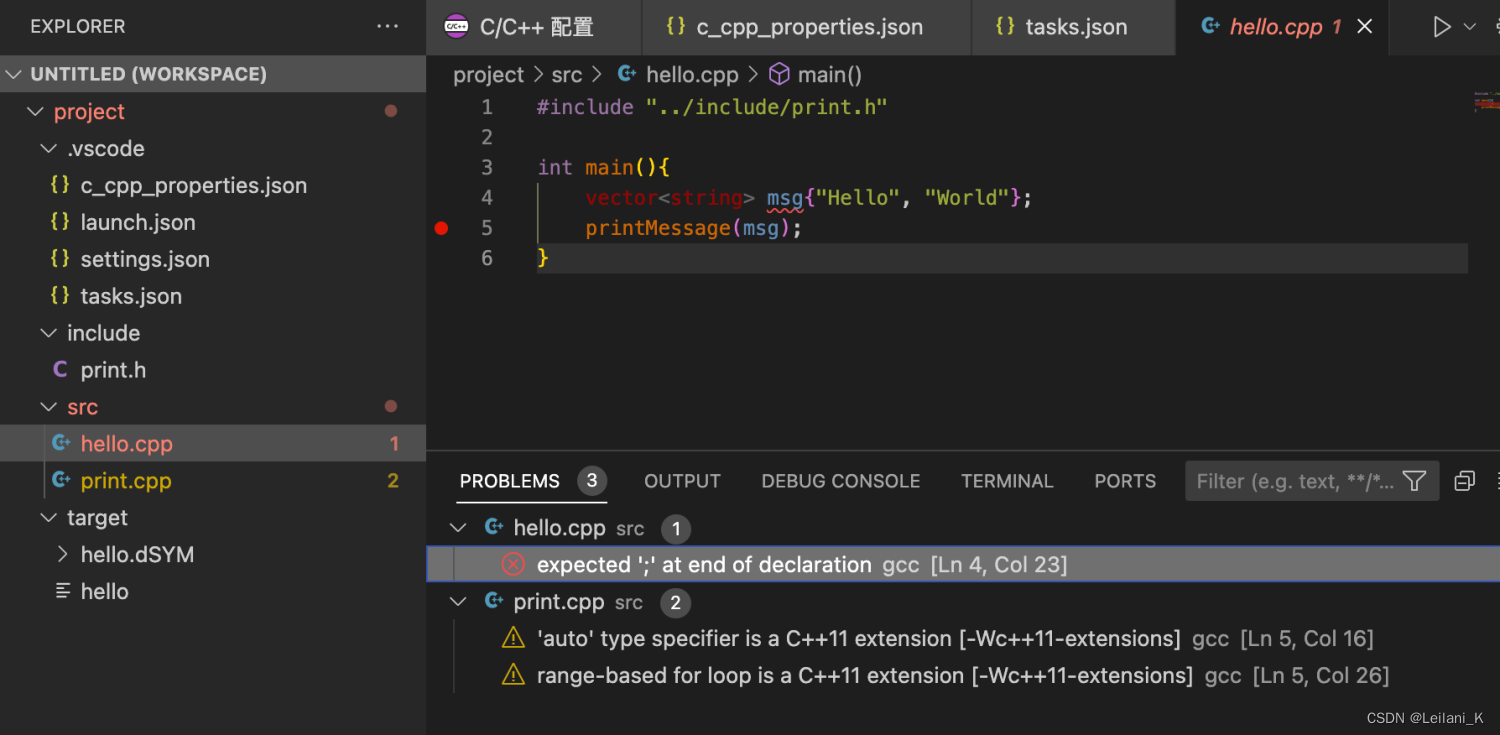
这种编译报错怎么处理?
还记得我们前面说到的编译选项在哪里设置吗?yes,tasks.json!
在 tasks.json 文件的 args 中添加"–std=c++17"选项,使编译支持 C++新特性
"args": [ "-fcolor-diagnostics", "-fansi-escape-codes", "--std=c++17", "-g", "${fileDirname}/*.cpp", "-o", "${workspaceFolder}/target/${fileBasenameNoExtension}" ], 成功运行。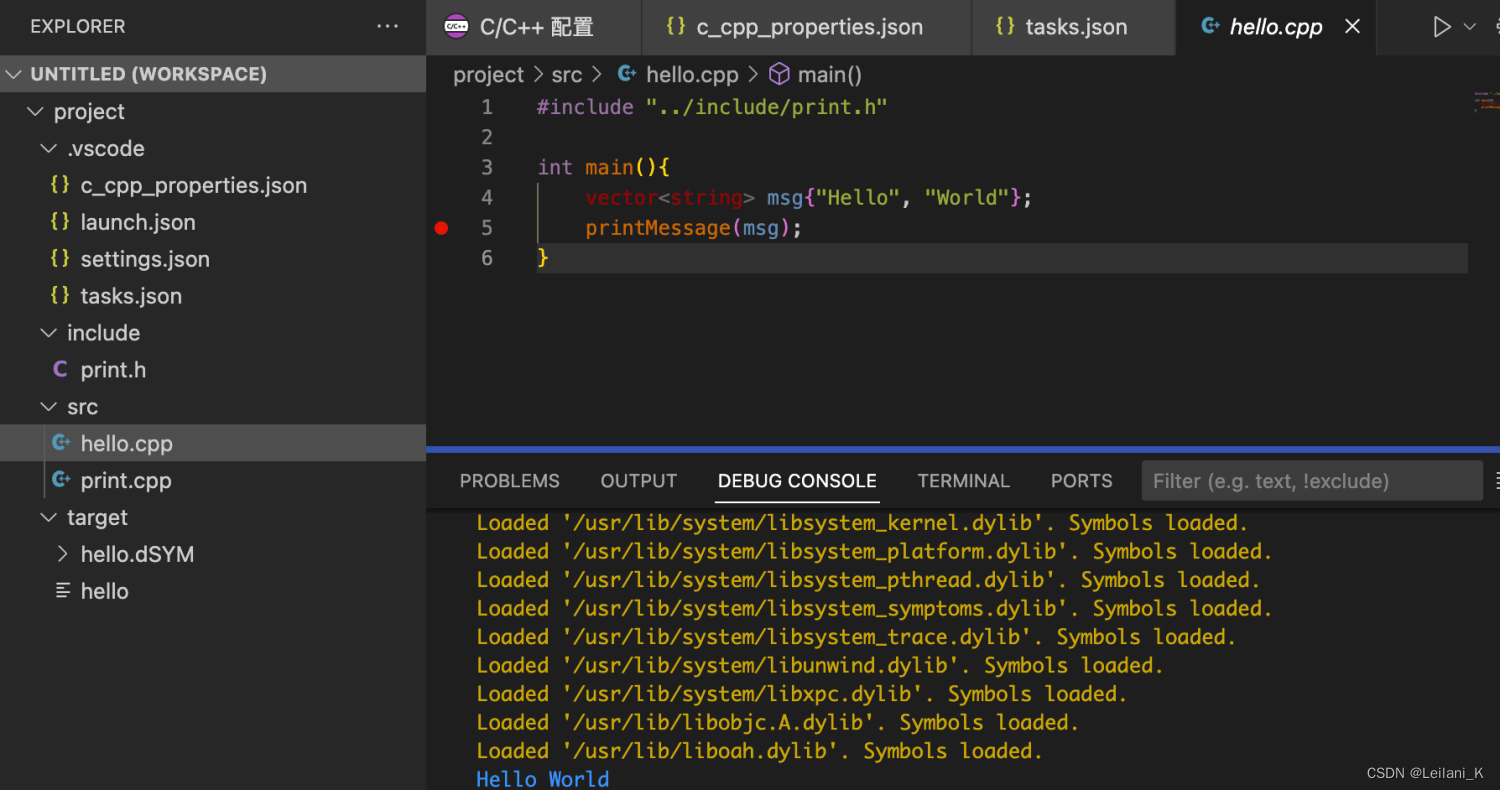
成功调试。