阅读量:1
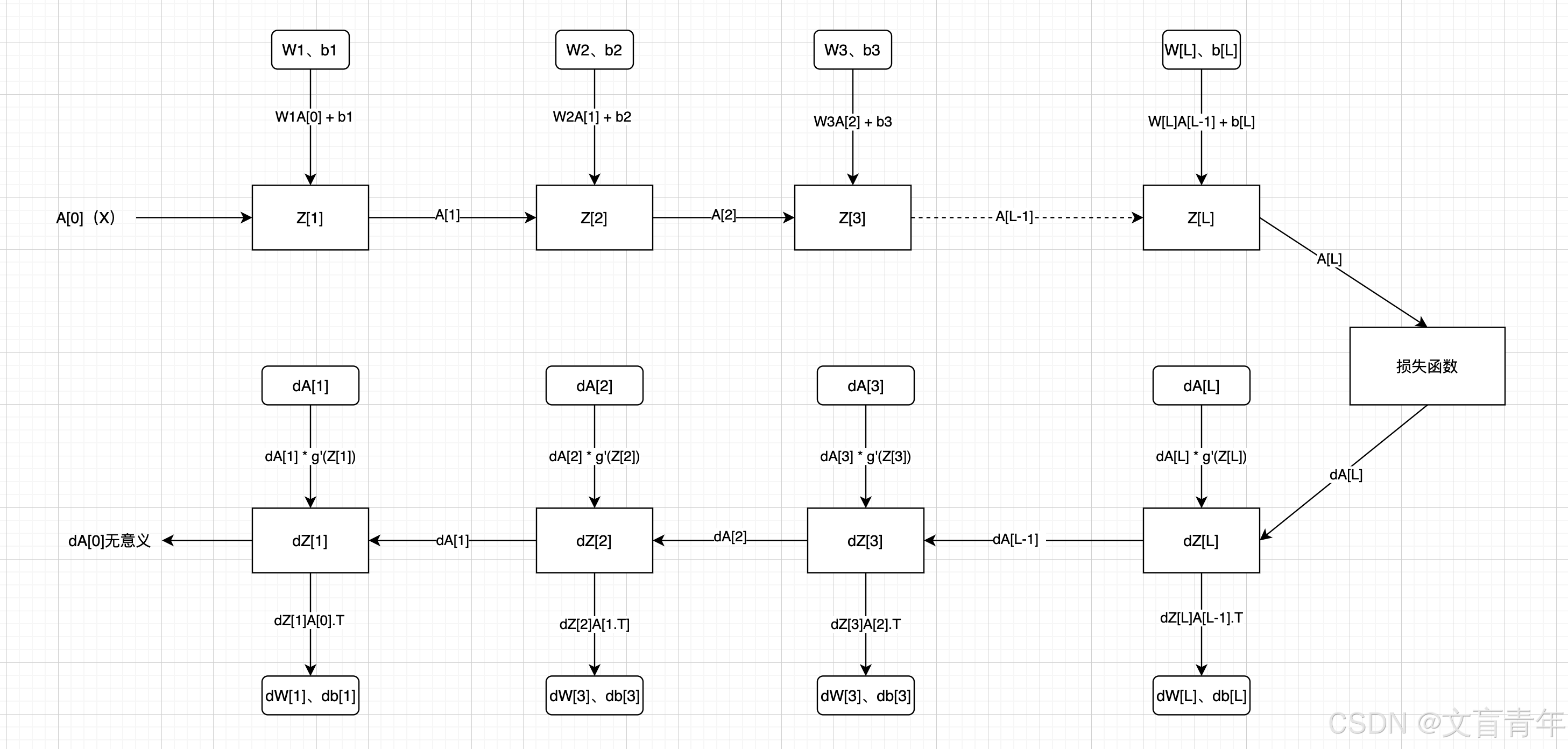
维度说明:
A[L]、Z[L]:(本层神经元个数、样本数)
W[L]:(本层神经元个数、上层神经元个数)
b[L]:(本层神经元个数、1)
dZ[L]:dA[L] * g’A(Z[L])
dZ[L]:(本层神经元个数、样本数)
dw = dL/dz * dz/dw = dz*x(链式法则)
db = dz(链式法则)
dW[L]:(本层神经元个数、上层神经元个数)
dA[L]:(本层神经元个数、样本数)
da = dz * w
dA[L-1] = W[L].T dZ[L],注意这里没有除以神经元个数,得到平均da。比如结果的第一个元素是多个dw1 * dz + dw1 * dz+ …dw1 * dz(神经元个数)的累加和
输出层采用sigmoid,隐藏层采用tanh
import numpy as np # 设置一些画图相关的参数 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (5.0, 4.0) plt.rcParams['image.interpolation'] = 'nearest' plt.rcParams['image.cmap'] = 'gray' from project_03.utils.dnn_utils import * from project_03.utils.testCases import * def load_dataset(): train_dataset = h5py.File('../deep_learn_01/project_01/datasets/train_catvnoncat.h5', 'r') train_set_x_orig = np.array(train_dataset['train_set_x'][:]) train_set_y_orig = np.array(train_dataset["train_set_y"][:]) # 加载训练数据 test_dataset = h5py.File('../deep_learn_01/project_01/datasets/test_catvnoncat.h5', "r") # 加载测试数据 test_set_x_orig = np.array(test_dataset["test_set_x"][:]) test_set_y_orig = np.array(test_dataset["test_set_y"][:]) classes = np.array(test_dataset["list_classes"][:]) # 加载标签类别数据,这里的类别只有两种,1代表有猫,0代表无猫 train_set_y_orig = train_set_y_orig.reshape( (1, train_set_y_orig.shape[0])) # 把数组的维度从(209,)变成(1, 209),这样好方便后面进行计算[1 1 0 1] -> [[1][1][0][1]] test_set_y_orig = test_set_y_orig.reshape((1, test_set_y_orig.shape[0])) # 从(50,)变成(1, 50) return train_set_x_orig, train_set_y_orig, test_set_x_orig, test_set_y_orig, classes def sigmoid(Z): A = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-Z)) return A def relu(Z): A = np.maximum(0, Z) assert (A.shape == Z.shape) return A def initialize_parameters_deep(layers_dims): """ :param layers_dims: list of neuron num example: layer_dims=[5,4,3],表示输入层有5个神经元,第一层有4个,最后二层有3个神经元(还有输出层的1个神经元) :return: parameters: the w,b of each layer """ np.random.seed(1) parameters = {} L = len(layers_dims) for l in range(1, L): parameters[f"W{l}"] = np.random.randn(layers_dims[l], layers_dims[l - 1]) / np.sqrt(layers_dims[l - 1]) parameters[f"b{l}"] = np.zeros((layers_dims[l], 1)) assert (parameters[f"W{l}"].shape == (layers_dims[l], layers_dims[l - 1])) assert (parameters[f"b{l}"].shape == (layers_dims[l], 1)) return parameters # W1,b1,W2,b2 def linear_forward(A, W, b): """ 线性前向传播 """ Z = np.dot(W, A) + b assert (Z.shape == (W.shape[0], A.shape[1])) return Z def linear_activation_forward(A_prev, W, b, activation): """ :param A_prev: 上一层得到的A,输入到本层来计算本层的Z和A,第一层时A_prev就是输入X :param W:本层的w :param b:本层的b :param activation: 激活函数 """ Z = linear_forward(A_prev, W, b) if activation == "sigmoid": A = sigmoid(Z) elif activation == "relu": A = relu(Z) else: assert (1 != 1), "there is no support activation!" assert (A.shape == (W.shape[0], A_prev.shape[1])) linear_cache = (A_prev, W, b) cache = (linear_cache, Z) return A, cache def L_model_forward(X, parameters): """ 前向传播 :param X: 输入特征 :param parameters: 每一层的初始化w,b """ caches = [] A = X L = len(parameters) // 2 # W1,b1,W2,b2, L=2 for l in range(1, L): A_prev = A A, cache = linear_activation_forward(A_prev, parameters[f"W{l}"], parameters[f"b{l}"], 'relu') caches.append(cache) # A1,(X,W1,b1,Z1) AL, cache = linear_activation_forward(A, parameters[f"W{L}"], parameters[f"b{L}"], activation="sigmoid") caches.append(cache) # A2,(A1,W2,b2,Z2) assert (AL.shape == (1, X.shape[1])) return AL, caches def compute_cost(AL, Y): m = Y.shape[1] logprobs = np.multiply(Y, np.log(AL)) + np.multiply((1 - Y), np.log(1 - AL)) cost = (-1 / m) * np.sum(logprobs) assert (cost.shape == ()) return cost def linear_backward(dZ, cache): """ :param dZ: 后面一层的dZ :param cache: 前向传播保存下来的本层的变量 :return 本层的dw、db,前一层da """ A_prew, W, b = cache m = A_prew.shape[1] dW = np.dot(dZ, A_prew.T) / m db = np.sum(dZ, axis=1, keepdims=True) / m dA_prev = np.dot(W.T, dZ) assert (dA_prev.shape == A_prew.shape) assert (dW.shape == W.shape) assert (db.shape == b.shape) return dA_prev, dW, db def linear_activation_backward(dA, cache, activation): """ :param dA: 本层的dA :param cache: 前向传播保存的本层的变量 :param activation: 激活函数:"sigmoid"或"relu" :return 本层的dw、db,前一次的dA """ linear_cache, Z = cache # 首先计算本层的dZ if activation == 'relu': dZ = 1 * dA dZ[Z <= 0] = 0 elif activation == 'sigmoid': A = sigmoid(Z) dZ = dA * A * (1 - A) else: assert (1 != 1), "there is no support activation!" assert (dZ.shape == Z.shape) # 这里我们又顺带根据本层的dZ算出本层的dW和db以及前一层的dA dA_prev, dW, db = linear_backward(dZ, linear_cache) return dA_prev, dW, db def L_model_backward(AL, Y, caches): """ :param AL: 最后一层A :param Y: 真实标签 :param caches: 前向传播的保存的每一层的相关变量 (A_prev, W, b),Z """ grads = {} L = len(caches) # 2 Y = Y.reshape(AL.shape) # 让真实标签与预测标签的维度一致 dAL = -np.divide(Y, AL) + np.divide(1 - Y, 1 - AL) # dA2 # 计算最后一层的dW和db,由成本函数来计算 current_cache = caches[-1] # 1,2 grads[f"dA{L - 1}"], grads[f"dW{L}"], grads[f"db{L}"] = linear_activation_backward(dAL, current_cache, "sigmoid") # dA1, dW2, db2 # 计算前L-1层的dw和db,因为最后一层用的是sigmoid, for c in reversed(range(1, L)): # reversed(range(1,L))的结果是L-1,L-2...1。是不包括L的。第0层是输入层,不必计算。 caches[0,1] L = 2 1,1 # c表示当前层 grads[f"dA{c - 1}"], grads[f"dW{c}"], grads[f"db{c}"] = linear_activation_backward(grads[f"dA{c}"], caches[c - 1], "relu") return grads def update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate): L = len(parameters) // 2 for l in range(1, L + 1): parameters[f"W{l}"] = parameters[f"W{l}"] - grads[f"dW{l}"] * learning_rate parameters[f"b{l}"] = parameters[f"b{l}"] - grads[f"db{l}"] * learning_rate return parameters def dnn_model(X, Y, layers_dim, learning_rate=0.0075, num_iterations=3000, print_cost=False): np.random.seed(1) costs = [] parameters = initialize_parameters_deep(layers_dim) for i in range(0, num_iterations): AL, caches = L_model_forward(X, parameters) cost = compute_cost(AL, Y) grads = L_model_backward(AL, Y, caches) parameters = update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate) if print_cost and i % 100 == 0: print("训练%i次后成本是: %f" % (i, cost)) costs.append(cost) # 画出成本曲线图 plt.plot(np.squeeze(costs)) plt.ylabel('cost') plt.xlabel('iterations (per tens)') plt.title("Learning rate =" + str(learning_rate)) plt.show() return parameters def predict(X, parameters): m = X.shape[1] n = len(parameters) // 2 p = np.zeros((1, m)) probas, caches = L_model_forward(X, parameters) # 将预测结果转化成0和1的形式,即大于0.5的就是1,否则就是0 for i in range(0, probas.shape[1]): if probas[0, i] > 0.5: p[0, i] = 1 else: p[0, i] = 0 return p if __name__ == "__main__": train_set_x_orig, train_set_y, test_set_x_orig, test_set_y, classes = load_dataset() # 我们要清楚变量的维度,否则后面会出很多问题。下面我把他们的维度打印出来。 train_set_x_flatten = train_set_x_orig.reshape(train_set_x_orig.shape[0], -1).T test_set_x_flatten = test_set_x_orig.reshape(test_set_x_orig.shape[0], -1).T print("train_set_x_flatten shape: " + str(train_set_x_flatten.shape)) print("test_set_x_flatten shape: " + str(test_set_x_flatten.shape)) train_set_x = train_set_x_flatten / 255 test_set_x = test_set_x_flatten / 255 layers_dims = [12288, 20, 7, 5, 1] # 根据上面的层次信息来构建一个深度神经网络,并且用之前加载的数据集来训练这个神经网络,得出训练后的参数 parameters = dnn_model(train_set_x, train_set_y, layers_dims, num_iterations=2000, print_cost=True) # 对训练数据集进行预测 pred_train = predict(train_set_x, parameters) print("预测准确率是: " + str(np.sum((pred_train == train_set_y) / train_set_x.shape[1]))) # 对测试数据集进行预测 pred_test = predict(test_set_x, parameters) print("预测准确率是: " + str(np.sum((pred_test == test_set_y) / test_set_x.shape[1]))) 