文章目录
- PyQt界面开发的两种方式:可视化UI + 编程式UI
- 一、PyQt 简介
- 二、PyQt 与 Qt 的蒙娜丽莎
- 三、PyQt 布局管理器(Layout Manager)
- 四、PyQt 常用组件
- 4.1、简介
- 4.2、项目实战
- 【菜单类 - 组件】菜单+菜单栏+工具栏+状态栏 QMenuBar + QMenu + QToolBar + QStatusBar
- 【对话框类 - 组件】输入对话框+颜色对话框+字体对话框+文件选择对话框+进度对话框+消息对话框:QInputDialog + QColorDialog + QFontDialog + QFileDialog + QProgressDialog + QMessageBox
- 4.2.0、设置组件属性:尺度 + 颜色 + 连接到槽
- 4.2.1、显示文本 QLabel:Hello, PyQt!
- 4.2.2、按钮 QPushButton:用户登录界面
- 4.2.3、文本框 QLineEdit + QTextEdit(单行 + 多行)
- 4.2.4、校验器 QRegExpValidator :用于限制用户在 QLineEdit 中输入的文本(英文 / 数字)
- 4.2.5、校验器 QIntValidator + QDoubleValidator(整数 + 浮点数):用于限制用户在 QLineEdit 中输入的文本必须为数字。
- 4.2.6、输入框 QSpinBox + QDoubleSpinBox(整数 + 浮点数):支持上下按钮调节
- 4.2.7、滑动条 QSlider:获取滑动条点击前后的值
- 4.2.8、进度条 QProgressBar:创建一个进度条窗口(0~100%)
- 4.2.9、下拉框 QComboBox:创建一个下拉框并添加选项
- 4.2.10、复选框 QCheckBox:获取勾选状态
- 4.2.11、单选按钮 QRadioButton:获取勾选状态
- 4.2.12、分组框 QGroupBox:将其他小部件放置在其中
- 4.2.12、打印日志 QTextEdit:获取当前时间 + 设置文本颜色
- 4.2.13、消息提示框 QMessageBox:信息 / 询问 / 警告 / 错误
- 4.2.14、选项卡界面 QTabWidget
- 4.2.14.1、在一个窗口中显示多个页面
- 4.2.14.2、在主界面中,显示其他.py界面类文件
- 4.2.14.3、在主界面中,显示其他.py界面类文件,并进行数据交互
- 4.2.15、调用其他.py文件,并数据交互
- 4.2.16、在当前虚拟环境下,调用其他虚拟环境下的.py文件,并数据交互
PyQt界面开发的两种方式:可视化UI + 编程式UI
(1)
可视化UI:基于Qt Designer可视化编辑工具进行组件拖放、属性设置、布局管理等操作创建界面。
- 一是将其保存为.ui文件,然后在PyQt应用程序中加载和使用.ui文件。
- 二是使用pyuic工具将 .ui转为 .py,然后直接对Python代码进行使用。
(2)
编程式UI或手写UI:直接使用Python代码来创建和配置用户界面组件,而无需依赖可视化编辑工具。
编程式UI优点:
灵活性:完全掌握界面的创建和交互过程,可以根据需要随时动态创建、修改或删除组件,以满足特定需求。定制化:可以精确地控制每个组件的属性、样式和行为,而不受可视化编辑器的限制。因此可以创建高度定制的界面,以满足特定的设计需求。动态性:在运行时动态地创建、修改和删除组件,以响应用户交互或应用程序状态的变化。对于需要动态更新界面的应用程序非常有用。版本控制:可以将整个应用程序界面的定义保存在代码文件中,这使得版本控制更容易,能够跟踪和管理界面的变化。跨平台:Python代码来创建界面,可以实现跨平台的GUI应用程序,因为PyQt是跨平台的,可以在不同操作系统上运行。
编程式UI缺点:
可读性差: 对于不熟悉代码的人来说,代码中的界面布局和配置可能不太容易理解,而可视化编辑器可以提供更直观的可视反馈。难以预览:需要运行程序才能看到界面,而可视化编辑器可以实时看到界面。时间消耗:需要编写更多的代码。如:布局、样式以及更复杂的界面。
如果你有一个main.py文件,但想要在Qt Designer中编辑界面。
(1)使用Qt Designer:创建一个.ui文件,然后将main.py文件中与界面相关的代码复制到.ui中。
(2)使用Qt Designer:编辑和保存.ui。
(3)使用pyuic工具:将.ui转为.py文件,然后将main.py文件中与算法逻辑相关的代码复制到.py中。
注意:仅限于保存静态的界面设计,而不包括任何与界面相关的算法逻辑。
- Qt Designer工具通常用于创建和编辑.ui文件
- .ui文件:包含界面设计的代码。
- .py文件:包含界面设计 + 算法逻辑的代码。
一、PyQt 简介
PyQt官网首页:https://www.riverbankcomputing.com/software/pyqt/
通过 pip 安装 PyQt:pip install pyqt5
PyQt定义
(1)是Python编程语言的一个GUI(图形用户界面)工具包,它允许开发人员使用Python语言创建桌面应用程序。PyQt提供了许多用于创建丰富多样的用户界面的类和功能,以及用于处理用户输入和交互的工具。
(2)是基于Qt库的Python封装,Qt是一个流行的C++框架,用于开发跨平台的应用程序。
PyQt版本
提供了与Qt应用程序框架的Python绑定。每个版本的PyQt都是为不同的Qt版本而设计的。 目前PyQt只支持两个版本:
- PyQt6:仅支持Python 3.6及更高版本,仅支持 Qt6 版本。(1)模块名称变更:在PyQt6中,模块名称进行了更改,以更好地与标准Qt模块名称匹配。例如,QtWidgets模块在PyQt6中被称为QtWidgets,而不是PyQt5.QtWidgets。(2)新特性:PyQt6引入了一些新特性,改进了现有功能,以适应Qt6的变化。这包括新的信号和槽语法等。(3)与PyQt5不同,PyQt6不再支持Qt4。
- PyQt5:仅支持Python 2.7和Python 3.x,仅支持 Qt5 版本。但Python 2在2020年已不再得到官方支持。(
广泛使用)PyQt5是最广泛使用的版本,许多应用程序和项目都在使用它。- PyQt4:主要支持Python 2.x,仅支持 Qt4 版本。尽管它也有一个用于Python 3的版本,但相对较少使用。(
已经过时)不再得到官方支持,因此不建议在新项目中使用它。
二、PyQt 与 Qt 的蒙娜丽莎
Qt 和 PyQt 是用于创建图形用户界面(GUI)的工具包,它们提供了丰富的类和功能,可以用于开发跨平台的桌面应用程序。
Qt(跨平台的C++应用程序开发框架):
(1)Qt是由挪威公司Trolltech(现在是Qt公司的一部分)开发。它最初是为了解决C++开发人员在不同平台上编写重复代码的问题而设计的。
(2)支持多种操作系统(跨平台):Windows、macOS、Linux、iOS、Android等,因此可以实现跨平台的开发和部署。
(3) 用户交互和事件:Qt是一个面向对象的框架,使用信号和槽机制来处理用户交互和事件。
PyQt(Qt的Python绑定,使用Python语言调用和使用Qt框架的功能):
(1)PyQt由Riverbank Computing公司开发和维护。
(2)支持多种操作系统(跨平台):因为PyQt是基于Qt的,并且可以在各种操作系统上运行。
(3)用户交互和事件:PyQt使用Qt的信号和槽机制来处理用户交互和事件,同时也支持Python的语法和特性。备注:PyQt同时支持Qt Designer(图形界面设计器),开发者可以通过Qt Designer可视化设计界面,然后将其转换为Python代码。
Qt 和 PyQt 的区别:
- 编程语言:Qt是C++编写,而PyQt是Qt的Python编写。
- 开发体验:PyQt相对于Qt更容易上手,Python代码通常比C++代码更简洁和易读。
- 性能差异:由于Qt是用C++编写的,其性能可能比PyQt稍微好一些。然而,对于大多数应用程序而言,性能差异并不明显,而开发效率更重要。
- 应用领域:由于Qt和PyQt都是用于GUI开发的,因此它们在各种应用领域中都有广泛的应用,包括桌面应用程序、嵌入式系统、游戏开发、数据可视化等。
- 生态系统:Qt拥有广泛的C++社区和生态系统,可以找到更多的第三方库和资源。相比之下,PyQt稍逊一筹。
三、PyQt 布局管理器(Layout Manager)
3.1、简介
3.1.1、布局管理器的定义
布局管理器(Layout Manager):用于在图形用户界面(GUI)中管理窗口中部件(Widget)布局的工具。通过容器的方式来布置和管理部件的位置和大小,而无需手动计算和设置每个部件的位置(但支持)。
自动布局:根据容器的大小和约束,自动排列和调整部件的位置和大小。这样,当窗口大小改变时,部件的布局也会自动调整,无需手动修改。支持多种类型:水平布局、垂直布局、网格布局等。支持容器嵌套:可以将多个布局管理器嵌套在一起,从而实现复杂的布局设计。- 可扩展性:布局管理器通常具有一定的可扩展性,允许开发者编写自定义的布局管理器,以满足特定的布局需求。
- 与部件关联:布局管理器通常与部件相关联,开发者可以将部件添加到布局管理器中,并指定部件在布局中的位置和大小。
- 事件处理:一些布局管理器还可以处理部件的事件,例如调整大小事件、重绘事件等,以便实现更高级的交互功能。
- 跨平台性兼容性:布局管理器通常是跨平台的,可以在不同的操作系统上使用,并且能够保持一致的布局效果。
3.1.2、布局管理器的类型
盒子布局管理器 QBoxLayout:无法单独使用,其是QVBoxLayout和QHBoxLayout的基类,具体用法参考垂直和水平布局管理器。垂直布局管理器 QVBoxLayout:将部件 从上到下(垂直的) 排列在一列中。水平布局管理器 QHBoxLayout:将部件 从左到右(水平的) 排列在一行中。网格布局管理器 QGridLayout:将部件 指定位置(行 + 列) 排列在一个网格中。
- 如:在同一行中,指定多个部件的位置布局:[3 3 3] to [33 3] 表示将111格式变换为112格局。
表单布局管理器 QFormLayout:对齐标签和输入框。常用于创建表单式的用户界面。堆叠布局管理器 QStackedLayout:管理多个窗口部件,但同一时刻只能显示一个布局管理器,可以通过界面切换以显示不同的部件。如:选项卡界面。
3.1.3、布局管理器的使用方法
(1)将部件添加到布局管理器中
(2)将布局管理器设置为窗口或部件(Widget)的主要布局(即可实现自动布局)
"""################################### (1)管理子部件 (2)将子部件给到主部件 (3)窗口显示主部件 ###################################""" layout = QVBoxLayout() # 创建一个垂直布局管理器对象(用于管理垂直排列的子部件) layout.addWidget(container_widget) # 将名为container_widget的部件添加到垂直布局中 central_widget = QWidget() # 创建一个QWidget对象(用作主窗口的中央部件) central_widget.setLayout(layout) # 将布局设置为central_widget的布局管理器,使布局成为central_widget的主要布局 self.setCentralWidget(central_widget) # 将central_widget设置为主窗口(通常是QMainWindow)的中央部件,以便显示在窗口中 3.2、项目实战
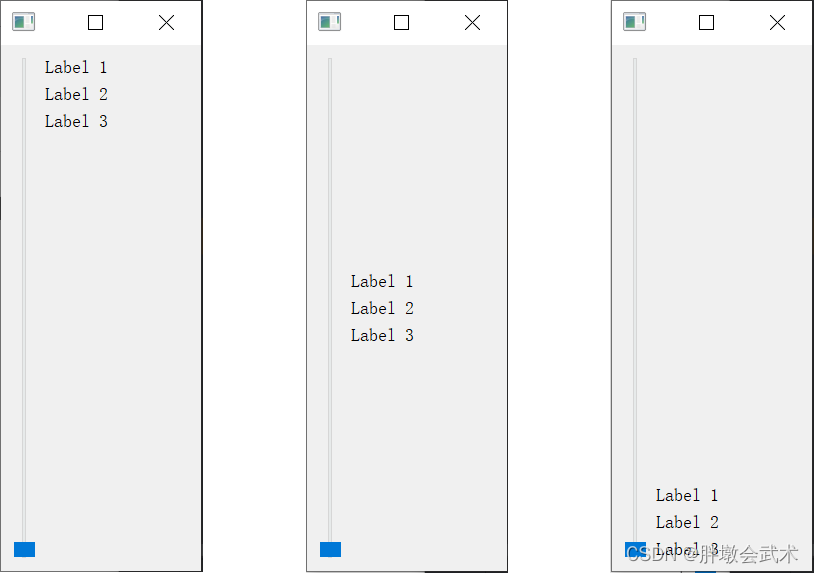
3.2.0、添加伸缩项 layout.addStretch:控制部件之间的间距
import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QVBoxLayout, QHBoxLayout, QPushButton, QLabel, QWidget, QSlider class MainWindow(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() VBox_layout = QVBoxLayout() HBox_Layout = QHBoxLayout() slider = QSlider() slider.setFixedHeight(500) label1 = QLabel("Label 1") label2 = QLabel("Label 2") label3 = QLabel("Label 3") # (1)若在部件之前添加伸缩项,部件跟在伸缩项的后面,从而实现将部件布局到底部 VBox_layout.addStretch(8) HBox_Layout.addWidget(slider) VBox_layout.addWidget(label1) VBox_layout.addWidget(label2) VBox_layout.addWidget(label3) HBox_Layout.addLayout(VBox_layout) VBox_layout.addStretch(1) # (2)若在部件之后添加伸缩项,部件被伸缩项顶在前面,从而实现将部件布局到顶部 # (3)若在部件之前及之后分别添加伸缩项:将部件布局到中间 central_widget = QWidget() central_widget.setLayout(HBox_Layout) self.setCentralWidget(central_widget) if __name__ == "__main__": app = QApplication(sys.argv) window = MainWindow() window.show() sys.exit(app.exec_()) """########################################################################## 函数简介:在布局中创建一个弹性空间,用于调整布局中各个部件的间距,以实现更好的分布和对齐效果。 函数说明:layout.addStretch() 输入参数: 伸缩项的权重为0(默认),这意味着它不会占用任何额外的空间。 伸缩项的权重为1(常用),将会根据权重在布局中占据一部分空间,从而将其他部件推向布局的边缘。 备注:若为其余数字,则权重值越大,伸缩空间越大。 ##########################################################################""" 3.2.1、垂直布局管理器 QVBoxLayout:按照从上到下的顺序排列部件
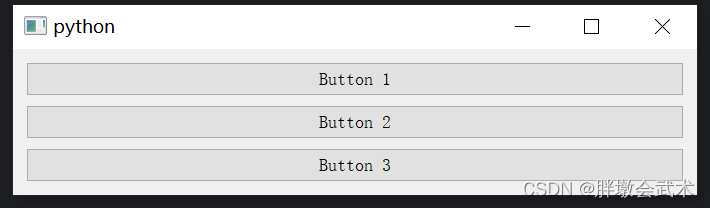
import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QVBoxLayout, QWidget, QPushButton class MainWindow(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() vbox = QVBoxLayout() button1 = QPushButton("Button 1") button2 = QPushButton("Button 2") button3 = QPushButton("Button 3") vbox.addWidget(button1) vbox.addWidget(button2) vbox.addWidget(button3) central_widget = QWidget() central_widget.setLayout(vbox) self.setCentralWidget(central_widget) if __name__ == "__main__": app = QApplication(sys.argv) window = MainWindow() window.show() sys.exit(app.exec_()) 3.2.2、水平布局管理器 QHBoxLayout:按照从左到右的顺序排列部件
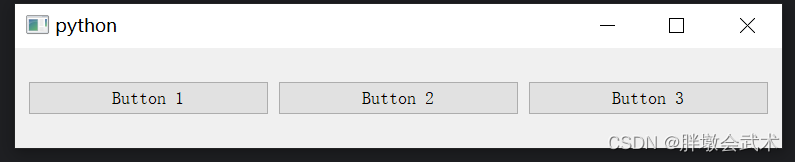
import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QWidget, QHBoxLayout, QPushButton class MainWindow(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() hbox = QHBoxLayout() button1 = QPushButton("Button 1") button2 = QPushButton("Button 2") button3 = QPushButton("Button 3") hbox.addWidget(button1) hbox.addWidget(button2) hbox.addWidget(button3) central_widget = QWidget() central_widget.setLayout(hbox) self.setCentralWidget(central_widget) if __name__ == "__main__": app = QApplication(sys.argv) window = MainWindow() window.show() sys.exit(app.exec_()) 3.2.3、网格布局管理器 QGridLayout:指定每个部件的位置(行 + 列)
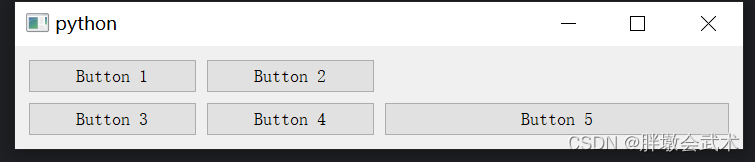
import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QWidget, QGridLayout, QPushButton class MainWindow(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() grid_layout = QGridLayout() button1 = QPushButton("Button 1") button2 = QPushButton("Button 2") button3 = QPushButton("Button 3") button4 = QPushButton("Button 4") button5 = QPushButton("Button 5") grid_layout.addWidget(button1, 0, 0) # 第一行第一列 grid_layout.addWidget(button2, 0, 1) # 第一行第二列 grid_layout.addWidget(button3, 1, 0) # 第二行第一列 grid_layout.addWidget(button4, 1, 1) # 第二行第二列 grid_layout.addWidget(button5, 1, 2, 1, 2) # 第二行的第三和第四列 central_widget = QWidget() central_widget.setLayout(grid_layout) self.setCentralWidget(central_widget) if __name__ == "__main__": app = QApplication(sys.argv) window = MainWindow() window.show() sys.exit(app.exec_()) 3.2.4、表单布局管理器 QFormLayout:对齐标签和输入框
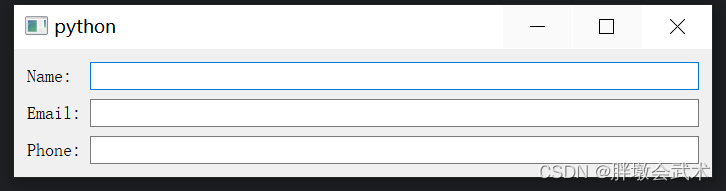
import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QWidget, QFormLayout, QLineEdit, QLabel class MainWindow(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() form_layout = QFormLayout() label1 = QLabel("Name:") name_input = QLineEdit() label2 = QLabel("Email:") email_input = QLineEdit() label3 = QLabel("Phone:") phone_input = QLineEdit() form_layout.addRow(label1, name_input) form_layout.addRow(label2, email_input) form_layout.addRow(label3, phone_input) central_widget = QWidget() central_widget.setLayout(form_layout) self.setCentralWidget(central_widget) if __name__ == "__main__": app = QApplication(sys.argv) window = MainWindow() window.show() sys.exit(app.exec_()) 3.2.5、堆叠布局管理器 QStackedLayout:在一个窗口中,管理多个窗口,但同一时刻只能显示一个窗口(如:选项卡界面)
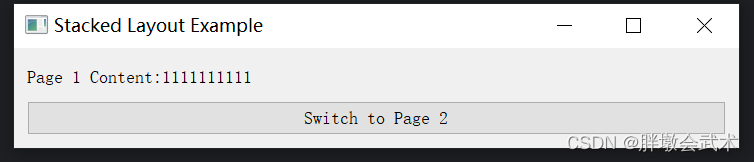
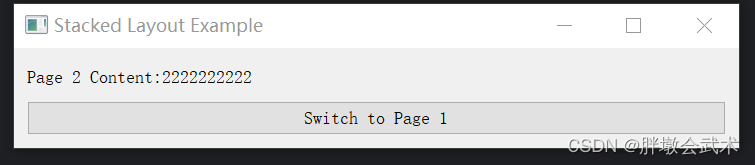
import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QWidget, QPushButton, QLabel, QVBoxLayout, QStackedLayout class MainWindow(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.setWindowTitle("Stacked Layout Example") self.stacked_layout = QStackedLayout() page1 = self.create_page("Page 1 Content", "Switch to Page 2") page2 = self.create_page("Page 2 Content", "Switch to Page 1") self.stacked_layout.addWidget(page1) self.stacked_layout.addWidget(page2) central_widget = QWidget() central_widget.setLayout(self.stacked_layout) self.setCentralWidget(central_widget) def create_page(self, content_text, switch_button_text): layout = QVBoxLayout() content_label = QLabel(content_text) switch_button = QPushButton(switch_button_text) switch_button.clicked.connect(self.switch_page) layout.addWidget(content_label) layout.addWidget(switch_button) page = QWidget() page.setLayout(layout) return page def switch_page(self): # 切换页面 current_index = self.stacked_layout.currentIndex() next_index = (current_index + 1) % 2 # 切换到下一页(循环切换) self.stacked_layout.setCurrentIndex(next_index) if __name__ == "__main__": app = QApplication(sys.argv) window = MainWindow() window.show() sys.exit(app.exec_()) 四、PyQt 常用组件
在 GUI 编程中,术语"组件"、"部件"和"控件"通常用于指代用户界面的基本构建块。术语在不同的 GUI 框架和文档中会略有不同,但可以互换使用。
4.1、简介
PyQt提供了丰富的组件(也称为控件或部件),用于构建图形用户界面。
| 组件(Widget) | 简介 | |
|---|---|---|
| 窗口组件 | QWidget | 所有用户界面对象的基类,用于创建窗口和部件。 |
| QMainWindow | 主窗口的类,通常用作应用程序的主界面。 | |
| 基础组件 | QLabel | 显示文本或图像。 |
| QLineEdit | 输入单行文本。 | |
| QTextEdit | 输入多行文本。 | |
| QSpinBox | (数字)整数输入框。 | |
| QDoubleSpinBox | (数字)浮点数输入框。 | |
| QPushButton | 按钮。 | |
| QRadioButton | 单选按钮。在多个选项中进行单选。 | |
| QCheckBox | 复选框。在多个选项中进行多选 | |
| QGroupBox | 分组框。将其他小部件放置在其中 | |
| QSlider | 滑动条。 | |
| QTabWidget | 选项卡界面。 | |
| QComboBox | 下拉列表框。 | |
| 对话框类 - 组件 | QDialog | 自定义对话框 |
| QInputDialog | 获取用户输入对话框 | |
| QFontDialog | 字体对话框。 | |
| QColorDialog | 颜色对话框。 | |
| QProgressDialog | 进度对话框。 | |
| QFileDialog | 打开文件/文件夹对话框。 | |
| QMessageBox | 消息提示框。 | |
| 菜单类 - 组件 | QMenu | 菜单。 |
| QMenuBar | 菜单栏。 | |
| QToolBar | 工具栏。 | |
| QStatusBar | 状态栏。 | |
| QProgressBar | 进度条。 | |
| 绘图类 - 组件 | QGraphicsScene | 管理2D图形项的场景。 |
| QGraphicsView | 显示二维图形和图像。 | |
| QGraphicsItem | 在QGraphicsScene中显示图形项。 | |
| QTableView | 显示表格数据。 | |
| QTreeWidget | 显示树形数据。 | |
| QListWidget | 显示列表数据。 | |
| QCalendarWidget | 显示日历。 | |
| QDockWidget | 创建可停靠的面板。 | |
| QSplitter | 在界面中创建可调整大小的分割区域。 | |
| QScrollArea | 显示超过容器尺寸的内容,并支持滚动查看。 |
4.2、项目实战
【菜单类 - 组件】菜单+菜单栏+工具栏+状态栏 QMenuBar + QMenu + QToolBar + QStatusBar
QAction:用于表示用户界面上的动作或操作。常与菜单、工具栏和快捷键等用户界面组件连用,以便用户可以执行各种操作。
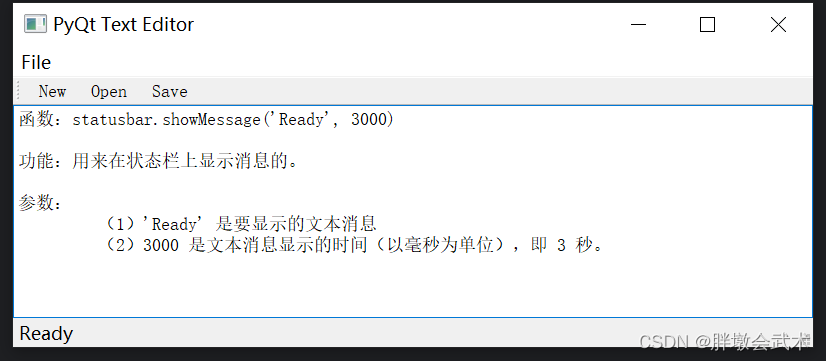
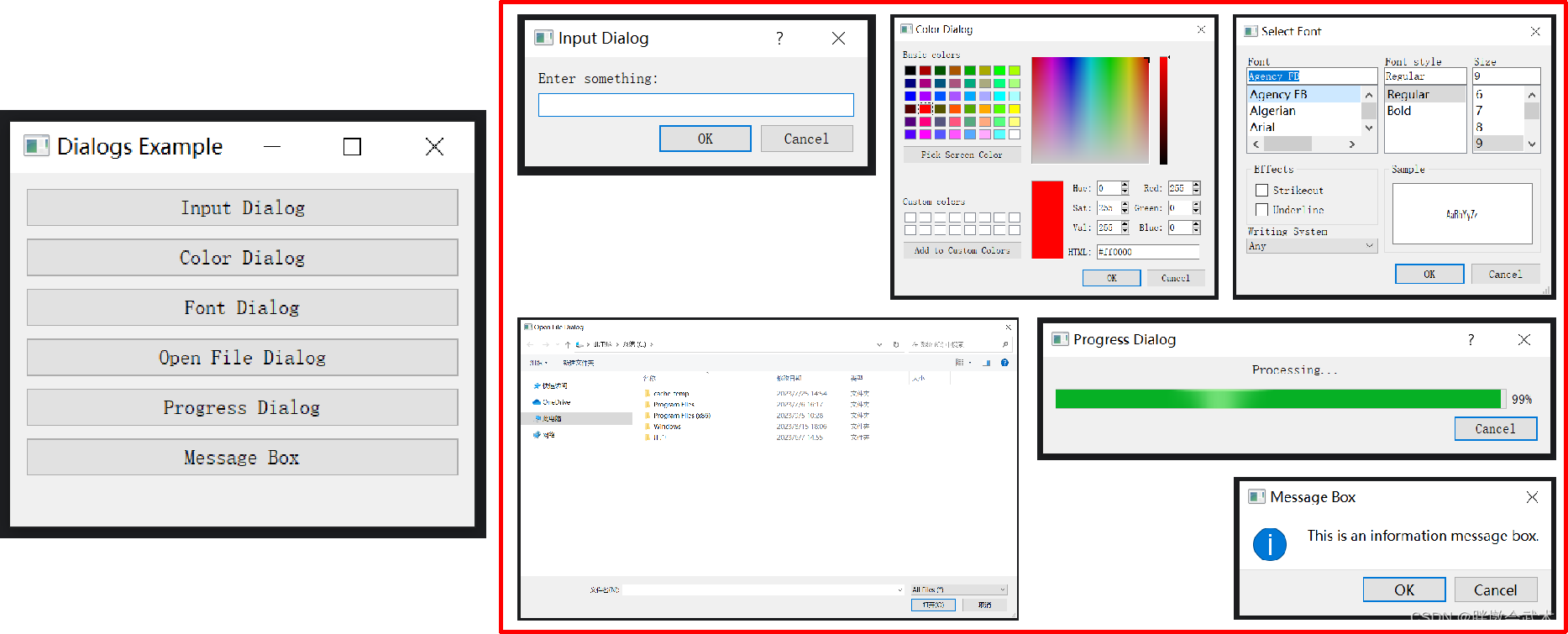
import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QMenu, QMenuBar, QToolBar, QStatusBar, QAction, QTextEdit, QFileDialog class MyWindow(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() ################################################### # 创建菜单栏 menubar = self.menuBar() # 创建文件菜单 file_menu = menubar.addMenu('File') # 创建文件菜单项 new_action = QAction('New', self) open_action = QAction('Open', self) save_action = QAction('Save', self) exit_action = QAction('Exit', self) # 添加文件菜单项到文件菜单 file_menu.addAction(new_action) file_menu.addAction(open_action) file_menu.addAction(save_action) file_menu.addSeparator() # 分隔线 file_menu.addAction(exit_action) # 连接菜单项和工具按钮的槽函数 new_action.triggered.connect(self.newFile) open_action.triggered.connect(self.openFile) save_action.triggered.connect(self.saveFile) exit_action.triggered.connect(self.exitApp) ################################################### # 创建工具栏 toolbar = self.addToolBar('Toolbar') # 在工具栏中添加工具按钮 new_button = toolbar.addAction('New') # 清空(当前)文本编辑框 open_button = toolbar.addAction('Open') # 打开txt文本并添加到文本编辑框 save_button = toolbar.addAction('Save') # 保存文本编辑框到txt文本 # 连接菜单项和工具按钮的槽函数 new_button.triggered.connect(self.newFile) open_button.triggered.connect(self.openFile) save_button.triggered.connect(self.saveFile) ################################################### # 创建状态栏 statusbar = self.statusBar() # 在状态栏中显示消息: 'Ready' 是要显示的文本消息,30000 是消息显示的时间(以毫秒为单位),即30秒。 statusbar.showMessage('Ready', 30000) ################################################### # 创建文本编辑框 self.text_edit = QTextEdit(self) self.setCentralWidget(self.text_edit) # 将文本编辑框设置为主窗口的中心组件 def newFile(self): self.text_edit.clear() # 清空文本编辑框 def openFile(self): try: # 打开文件对话框,选择txt文件并读取内容,然后显示在文本编辑框中 file_dialog = QFileDialog(self) file_path, _ = file_dialog.getOpenFileName() if file_path: with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file: file_contents = file.read() self.text_edit.setPlainText(file_contents) except Exception as e: # 处理异常,例如显示错误消息 print(f"Error opening file: {str(e)}") def saveFile(self): try: # 保存文件对话框,将文本编辑框中的内容保存到txt文件中 file_dialog = QFileDialog(self) file_path, _ = file_dialog.getSaveFileName() if file_path: with open(file_path, 'w') as file: file_contents = self.text_edit.toPlainText() file.write(file_contents) except Exception as e: # 处理异常,例如显示错误消息 print(f"Error saving file: {str(e)}") def exitApp(self): self.close() if __name__ == '__main__': app = QApplication(sys.argv) window = MyWindow() window.setWindowTitle('PyQt Text Editor') window.setGeometry(100, 100, 800, 300) window.show() sys.exit(app.exec_()) 【对话框类 - 组件】输入对话框+颜色对话框+字体对话框+文件选择对话框+进度对话框+消息对话框:QInputDialog + QColorDialog + QFontDialog + QFileDialog + QProgressDialog + QMessageBox
import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QVBoxLayout, QWidget, QPushButton, QLabel, QInputDialog, QColorDialog, QFontDialog, QFileDialog, QProgressDialog, QMessageBox from PyQt5.QtCore import Qt from PyQt5.QtGui import QColor class MainWindow(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.initUI() def initUI(self): self.setWindowTitle("Dialogs Example") self.setGeometry(100, 100, 400, 300) layout = QVBoxLayout() # 显示输入对话框按钮 input_btn = QPushButton("Input Dialog") input_btn.clicked.connect(self.show_input_dialog) layout.addWidget(input_btn) # 颜色对话框按钮 color_btn = QPushButton("Color Dialog") color_btn.clicked.connect(self.show_color_dialog) layout.addWidget(color_btn) # 字体对话框按钮 font_btn = QPushButton("Font Dialog") font_btn.clicked.connect(self.show_font_dialog) layout.addWidget(font_btn) # 打开文件对话框按钮 open_file_btn = QPushButton("Open File Dialog") open_file_btn.clicked.connect(self.show_file_dialog) layout.addWidget(open_file_btn) # 进度对话框按钮 progress_btn = QPushButton("Progress Dialog") progress_btn.clicked.connect(self.show_progress_dialog) layout.addWidget(progress_btn) # 消息框按钮 message_btn = QPushButton("Message Box") message_btn.clicked.connect(self.show_message_box) layout.addWidget(message_btn) # 标签用于显示结果 self.result_label = QLabel() layout.addWidget(self.result_label) central_widget = QWidget() central_widget.setLayout(layout) self.setCentralWidget(central_widget) def show_input_dialog(self): text, ok = QInputDialog.getText(self, "Input Dialog", "Enter something:") if ok and text: self.result_label.setText(f"Input: {text}") else: self.result_label.setText("Input Dialog Canceled") def show_color_dialog(self): color = QColorDialog.getColor(QColor(255, 0, 0), self, "Color Dialog") if color.isValid(): self.result_label.setStyleSheet(f"background-color: {color.name()}") self.result_label.setText(f"Selected Color: {color.name()}") def show_font_dialog(self): font, ok = QFontDialog.getFont(self) if ok: self.result_label.setFont(font) self.result_label.setText(f"Selected Font: {font.family()}, {font.pointSize()}pt") def show_file_dialog(self): file_name, _ = QFileDialog.getOpenFileName(self, "Open File Dialog", "", "All Files (*);;Text Files (*.txt)") if file_name: self.result_label.setText(f"Selected File: {file_name}") def show_progress_dialog(self): progress_dialog = QProgressDialog("Processing...", "Cancel", 0, 100, self) progress_dialog.setWindowModality(Qt.WindowModal) progress_dialog.setWindowTitle("Progress Dialog") for i in range(100): progress_dialog.setValue(i) if progress_dialog.wasCanceled(): break self.result_label.setText("Progress Dialog Completed") def show_message_box(self): msg_box = QMessageBox() msg_box.setIcon(QMessageBox.Information) msg_box.setWindowTitle("Message Box") msg_box.setText("This is an information message box.") msg_box.setStandardButtons(QMessageBox.Ok | QMessageBox.Cancel) result = msg_box.exec_() if result == QMessageBox.Ok: self.result_label.setText("Message Box: Ok button clicked") else: self.result_label.setText("Message Box: Cancel button clicked") if __name__ == "__main__": app = QApplication(sys.argv) window = MainWindow() window.show() sys.exit(app.exec_()) 4.2.0、设置组件属性:尺度 + 颜色 + 连接到槽
# 设置按钮尺度 button.setFixedSize(100, 35) # 设置组件的尺寸 button.setFixedWidth(35) # 设置组件的宽度 button.setFixedHeight(100) # 设置组件的高度 # 设置按钮颜色(背景 + 字体) ———— 可以分别设置 button.setStyleSheet("background-color: green; color: white;") button.setChecked(True) # 设置默认选择 button.setEnabled(True) # 是否启用按钮 checkbox.isChecked() # 判断按钮是否被选中 # 设置连接到槽 self.checkbox.stateChanged.connect(self.function) # 将(复选框)信号连接到槽 self.slider.valueChanged.connect(self.function) # 将(滑动条)信号连接到槽 self.LineEdit.returnPressed.connect(self.function) # 将(输入框)信号连接到槽 self.button.clicked.connect(self.function) # 将(按钮)信号连接到槽 4.2.1、显示文本 QLabel:Hello, PyQt!
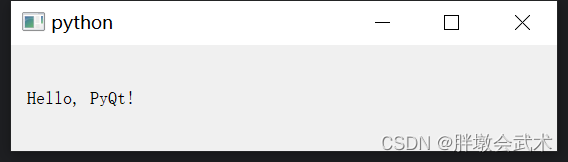
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QLabel, QVBoxLayout class MyApp(QWidget): def __init__(self): super().__init__() # 调用父类的构造函数 # 创建垂直布局管理器 self.layout = QVBoxLayout() # 创建标签对象并添加到布局中 self.label = QLabel('Hello, PyQt!') self.layout.addWidget(self.label) self.setLayout(self.layout) # 设置布局到当前窗口 self.show() # 显示窗口 if __name__ == '__main__': import sys app = QApplication(sys.argv) # 创建应用程序对象 widget = MyApp() # 创建窗口对象 sys.exit(app.exec_()) # 运行应用程序 4.2.2、按钮 QPushButton:用户登录界面
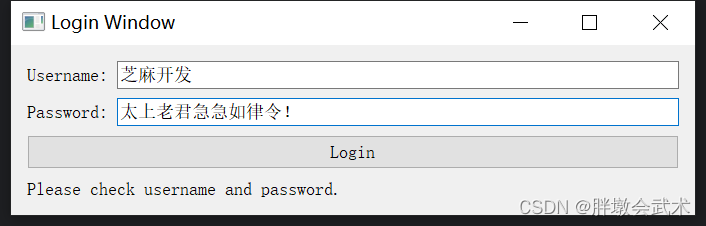
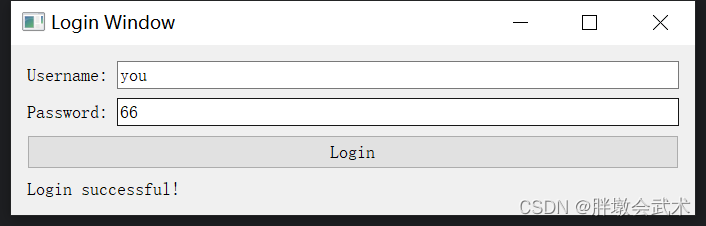
import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QLabel, QLineEdit, QPushButton, QVBoxLayout, QHBoxLayout class LoginWindow(QWidget): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.setWindowTitle("Login Window") # 创建控件 self.username_label = QLabel("Username:") self.username_edit = QLineEdit() self.password_label = QLabel("Password:") self.password_edit = QLineEdit() self.login_button = QPushButton("Login") self.login_button.clicked.connect(self.login) # 连接按钮点击事件到槽函数 self.result_label = QLabel("") # 将容器部件添加到主布局中 layout = QVBoxLayout() # 垂直布局管理器 self.username_layout = QHBoxLayout() # 水平布局管理器 self.username_layout.addWidget(self.username_label) # 将文本框添加到水平布局管理器中 self.username_layout.addWidget(self.username_edit) # 将按钮添加到水平布局管理器中 layout.addLayout(self.username_layout) # layout.addLayout self.password_layout = QHBoxLayout() # 水平布局管理器 self.password_layout.addWidget(self.password_label) # 将文本框添加到水平布局管理器中 self.password_layout.addWidget(self.password_edit) # 将按钮添加到水平布局管理器中 layout.addLayout(self.password_layout) # layout.addLayout # 将登录按钮和结果标签添加到垂直布局中 layout.addWidget(self.login_button) # layout.addWidget layout.addWidget(self.result_label) # layout.addWidget # 设置窗口的主布局 self.setLayout(layout) def login(self): username = self.username_edit.text() password = self.password_edit.text() # 在这里可以编写登录验证逻辑,这里只是简单地判断用户名和密码是否为空 if username == 'you' and password == '66': self.result_label.setText("Login successful!") else: self.result_label.setText("Please check username and password.") if __name__ == "__main__": app = QApplication(sys.argv) window = LoginWindow() window.show() sys.exit(app.exec_()) 4.2.3、文本框 QLineEdit + QTextEdit(单行 + 多行)
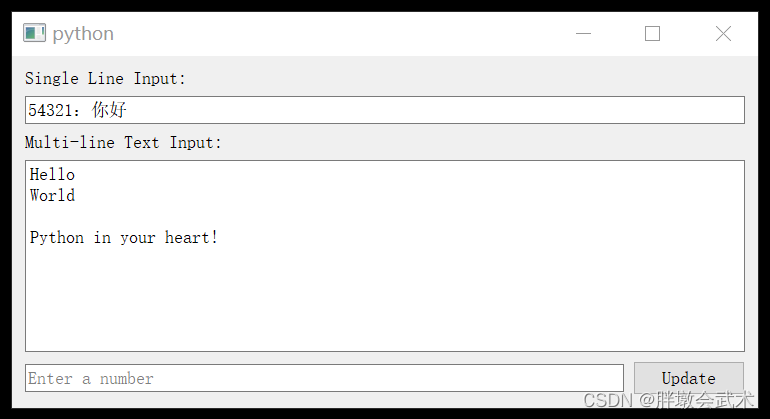
import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QVBoxLayout, QHBoxLayout, QWidget, \ QLabel, QLineEdit, QTextEdit, QPushButton, QMessageBox class MainWindow(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() layout = QVBoxLayout() # QLineEdit 示例 self.line_edit = QLineEdit(self) layout.addWidget(QLabel("Single Line Input:")) layout.addWidget(self.line_edit) self.line_edit.textChanged.connect(self.show_line_edit_text) # QTextEdit 示例 self.text_edit = QTextEdit(self) layout.addWidget(QLabel("Multi-line Text Input:")) layout.addWidget(self.text_edit) self.text_edit.textChanged.connect(self.show_text_edit_text) # QPushButton 示例 self.input_box = QLineEdit(self) self.input_box.setPlaceholderText("Enter a number") self.button = QPushButton("Update", self) self.button.clicked.connect(self.update) H_layout = QHBoxLayout() H_layout.addWidget(self.input_box) H_layout.addWidget(self.button) layout.addLayout(H_layout) central_widget = QWidget() central_widget.setLayout(layout) self.setCentralWidget(central_widget) def show_line_edit_text(self, text): print("Line Edit Text:", text) def show_text_edit_text(self): text = self.text_edit.toPlainText() # 获取 QTextEdit 的文本 print("Text Edit Text:", text) def update(self, a=None): input_text = self.input_box.text() if input_text: try: self.current_value = int(input_text) print(f"current_value: {self.current_value}") except ValueError: QMessageBox.warning(self, "Invalid input", "Please enter a valid number.") else: QMessageBox.warning(self, "Empty input", "Please enter a number.") if __name__ == "__main__": app = QApplication(sys.argv) window = MainWindow() window.show() sys.exit(app.exec_()) 4.2.4、校验器 QRegExpValidator :用于限制用户在 QLineEdit 中输入的文本(英文 / 数字)
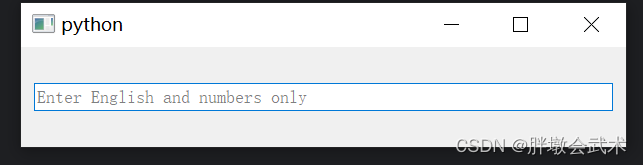
import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QVBoxLayout, QWidget, QLineEdit from PyQt5.QtCore import QRegExp from PyQt5.QtGui import QRegExpValidator class MainWindow(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() layout = QVBoxLayout() self.line_edit = QLineEdit(self) self.line_edit.setPlaceholderText("Enter English and numbers only") # english_only = QRegExp("[a-zA-Z]+") # 创建一个正则表达式,用于匹配只包含英文字符的文本 # numbers_only = QRegExp("[0-9]+") # 创建一个正则表达式,用于匹配只包含数字的文本 regex = QRegExp("[A-Za-z0-9]+") # 创建一个正则表达式,只允许输入英文和数字 validator = QRegExpValidator(regex) self.line_edit.setValidator(validator) layout.addWidget(self.line_edit) central_widget = QWidget() central_widget.setLayout(layout) self.setCentralWidget(central_widget) if __name__ == "__main__": app = QApplication(sys.argv) window = MainWindow() window.show() sys.exit(app.exec_()) """########################################################################## 函数功能:QRegExp 类是 Qt 中用于处理正则表达式的类。 函数说明:QRegExp(pattern: str, caseSensitivity: Qt.CaseSensitivity = Qt.CaseSensitive, syntax: QRegExp.PatternSyntax = QRegExp.RegExp) 输入参数: pattern 构造一个 QRegExp 对象,使用给定的正则表达式 pattern。 caseSensitivity 指定是否区分大小写,默认为区分大小写。 syntax 指定正则表达式的语法,默认为正则表达式语法。 """ """ 函数功能:QRegExpValidator 类是 Qt 中用于输入验证的工具之一。它允许您使用正则表达式来限制用户在 QLineEdit 等控件中输入的文本。 函数说明:QRegExpValidator(regexp: QRegExp, parent: QObject = None) 输入参数: regexp 构造一个 QRegExpValidator 对象,使用给定的正则表达式 regexp 进行验证。 parent 用于设置对象的父级。 ##########################################################################""" 4.2.5、校验器 QIntValidator + QDoubleValidator(整数 + 浮点数):用于限制用户在 QLineEdit 中输入的文本必须为数字。
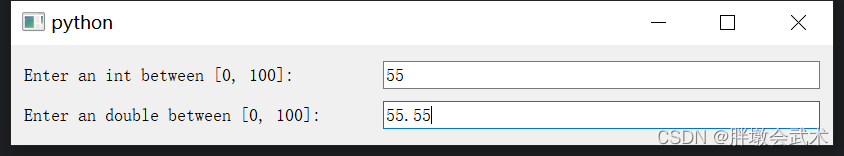
import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QVBoxLayout, QHBoxLayout, QWidget, QLabel, QLineEdit from PyQt5.QtGui import QIntValidator, QDoubleValidator class MainWindow(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() int_label = QLabel("Enter an int between [0, 100]:") int_label.setFixedWidth(350) # 设置固定的宽度 int_validator = QIntValidator(0, 100) # 创建QIntValidator,设置范围:[0, 100] int_lineedit = QLineEdit() # 创建一个 QLineEdit 控件 int_lineedit.setValidator(int_validator) # 设置校验器 # 将校验器应用到QLineEdit控件中,用于限制用户只能输入 0 到 100 之间的整数。 double_label = QLabel("Enter an double between [0.0, 100.0]:") double_label.setFixedWidth(350) # 设置固定的宽度 double_validator = QDoubleValidator(0.0, 100.0, 2) # 创建QDoubleValidator,设置范围:[0.0, 100.0],保留两位小数 double_lineedit = QLineEdit() # 创建一个 QLineEdit 控件 double_lineedit.setValidator(double_validator) # 设置校验器 # 将校验器应用到QDoubleValidator控件中,用于限制用户只能输入 0.0 到 100.0 之间的浮点数。 # 布局管理器 V_layout = QVBoxLayout() H1_layout = QHBoxLayout() H2_layout = QHBoxLayout() H1_layout.addWidget(int_label) H1_layout.addWidget(int_lineedit) H2_layout.addWidget(double_label) H2_layout.addWidget(double_lineedit) V_layout.addLayout(H1_layout) V_layout.addLayout(H2_layout) # 将布局应用于主窗口的中心区域 central_widget = QWidget() central_widget.setLayout(V_layout) self.setCentralWidget(central_widget) if __name__ == "__main__": app = QApplication(sys.argv) window = MainWindow() window.show() sys.exit(app.exec_()) """########################################################################## from PyQt5.QtGui import QIntValidator 函数简介:在输入框中,限制用户输入的内容必须是符合一定范围的整数。 函数说明:QIntValidator(bottom, top, parent=None) 输入参数: bottom: 校验的最小值。 top: 校验的最大值。 parent: 可选,父对象。 属性: bottom(): 获取校验的最小值。 top(): 获取校验的最大值。 方法: setBottom(bottom): 设置校验的最小值。 setTop(top): 设置校验的最大值。 ##########################################################################""" """########################################################################## from PyQt5.QtGui import QDoubleValidator 函数简介:在输入框中,限制用户输入的内容必须是符合一定范围的整数。 函数说明:QDoubleValidator(bottom, top, decimals, parent=None) 输入参数: bottom: 浮点数的最小值,用户输入的浮点数不能小于该值。 top: 浮点数的最大值,用户输入的浮点数不能大于该值。 decimals: 小数位数,表示允许的小数点后的位数。 parent: 可选参数,父级 QObject。 方法: bottom(): 返回校验器设置的最小值。 top(): 返回校验器设置的最大值。 decimals(): 返回校验器设置的小数位数。 setBottom(bottom: float): 设置校验器的最小值。 setTop(top: float): 设置校验器的最大值。 setDecimals(decimals: int): 设置校验器的小数位数。 ##########################################################################""" 4.2.6、输入框 QSpinBox + QDoubleSpinBox(整数 + 浮点数):支持上下按钮调节
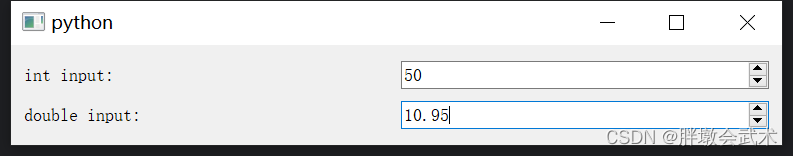
import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QVBoxLayout, QHBoxLayout, QWidget, QSpinBox, QDoubleSpinBox, QLabel class MainWindow(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() # 使用 QSpinBox 限制整数范围 QSpinBox_label = QLabel("int input:") int_spinbox = QSpinBox() int_spinbox.setRange(0, 100) # 限制范围:[0, 100] # 使用 QDoubleSpinBox 限制浮点数范围 QDoubleSpinBox_label = QLabel("double input:") double_spinbox = QDoubleSpinBox() double_spinbox.setRange(0.0, 100.0) # 限制范围:[0.0, 100.0] double_spinbox.setDecimals(2) # 保留2位小数 # 布局管理器 V_layout = QVBoxLayout() # 垂直布局 H1_layout = QHBoxLayout() # 水平布局 H2_layout = QHBoxLayout() # 水平布局 H1_layout.addWidget(QSpinBox_label) H1_layout.addWidget(int_spinbox) V_layout.addLayout(H1_layout) H2_layout.addWidget(QDoubleSpinBox_label) H2_layout.addWidget(double_spinbox) V_layout.addLayout(H2_layout) # 将布局应用于主窗口的中心区域 central_widget = QWidget() central_widget.setLayout(V_layout) self.setCentralWidget(central_widget) if __name__ == "__main__": app = QApplication(sys.argv) window = MainWindow() window.show() sys.exit(app.exec_()) 4.2.7、滑动条 QSlider:获取滑动条点击前后的值
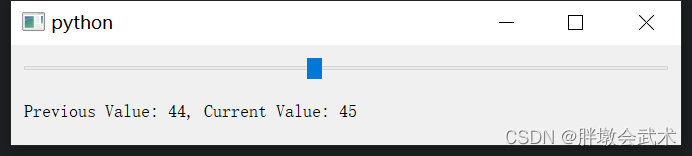
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QVBoxLayout, QWidget, QSlider, QLabel from PyQt5.QtCore import Qt class MainWindow(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() layout = QVBoxLayout() self.slider = QSlider() self.slider.setOrientation(Qt.Horizontal) self.slider.setRange(0, 100) layout.addWidget(self.slider) self.label = QLabel("Previous Value: 0, Current Value: 0") layout.addWidget(self.label) self.previous_value = 0 self.slider.valueChanged.connect(self.slider_value_changed) central_widget = QWidget() central_widget.setLayout(layout) self.setCentralWidget(central_widget) def slider_value_changed(self, new_value): self.label.setText(f"Previous Value: {self.previous_value}, Current Value: {new_value}") self.previous_value = self.slider.value() # self.slider.value():获取的是点击slider之后的值,而不是当前slider显示的值 if __name__ == "__main__": app = QApplication([]) window = MainWindow() window.show() app.exec_() 4.2.8、进度条 QProgressBar:创建一个进度条窗口(0~100%)
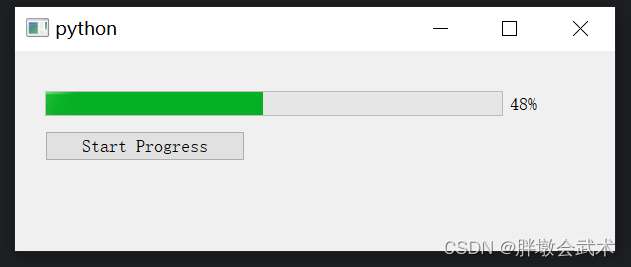
import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QPushButton, QProgressBar from PyQt5.QtCore import QTimer class MainWindow(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() # 设置窗口的几何属性 self.setGeometry(100, 100, 600, 200) # 创建一个进度条并设置其几何属性 self.progress_bar = QProgressBar(self) self.progress_bar.setGeometry(30, 40, 500, 25) # 创建一个 "Start Progress" 按钮 start_button = QPushButton('Start Progress', self) # 连接按钮的点击事件到 startProgress 函数 start_button.clicked.connect(self.startProgress) # 设置按钮的固定宽度和位置 start_button.setFixedWidth(200) start_button.move(30, 80) def startProgress(self): # 初始化进度为0 self.progress = 0 # 创建一个定时器 self.timer = QTimer(self) # 连接定时器的超时事件到 updateProgress 函数 self.timer.timeout.connect(self.updateProgress) # 每0.1秒触发一次定时器 self.timer.start(100) def updateProgress(self): # 增加进度 self.progress += 1 # 设置进度条的值 self.progress_bar.setValue(self.progress) # 当进度达到100%时,停止定时器 if self.progress >= 100: self.timer.stop() if __name__ == '__main__': app = QApplication(sys.argv) window = MainWindow() window.show() sys.exit(app.exec_()) 4.2.9、下拉框 QComboBox:创建一个下拉框并添加选项
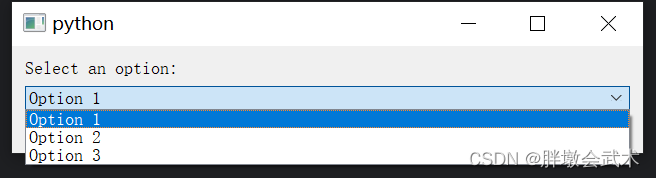
import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QVBoxLayout, QWidget, QLabel, QComboBox class MainWindow(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() label = QLabel("Select an option:") combo_box = QComboBox() combo_box.addItem("Option 1") combo_box.addItem("Option 2") combo_box.addItem("Option 3") combo_box.currentIndexChanged.connect(self.selection_changed) # 连接选项变更事件 self.result_label = QLabel("", self) layout = QVBoxLayout() layout.addWidget(combo_box) layout.addWidget(label) layout.addWidget(self.result_label) central_widget = QWidget() central_widget.setLayout(layout) self.setCentralWidget(central_widget) def selection_changed(self, index): selected_option = self.sender().currentText() self.result_label.setText(f"Selected: {selected_option}") if __name__ == "__main__": app = QApplication(sys.argv) window = MainWindow() window.show() sys.exit(app.exec_()) 4.2.10、复选框 QCheckBox:获取勾选状态
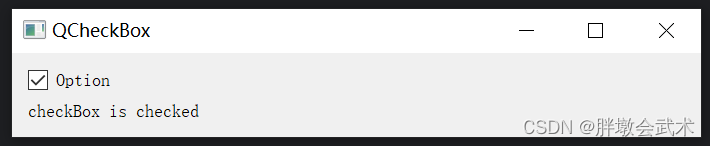
import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QLabel, QCheckBox, QVBoxLayout, QWidget class CheckBoxExample(QWidget): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.initUI() def initUI(self): self.setWindowTitle('QCheckBox') self.label = QLabel("") self.checkBox = QCheckBox("Option") layout = QVBoxLayout() layout.addWidget(self.checkBox) layout.addWidget(self.label) self.setLayout(layout) self.checkBox.clicked.connect(self.on_checkbox_clicked) def on_checkbox_clicked(self): if self.checkBox.isChecked(): self.label.setText("checkBox is checked") else: self.label.setText("checkBox is unchecked") if __name__ == '__main__': app = QApplication(sys.argv) window = CheckBoxExample() window.show() sys.exit(app.exec_()) 4.2.11、单选按钮 QRadioButton:获取勾选状态
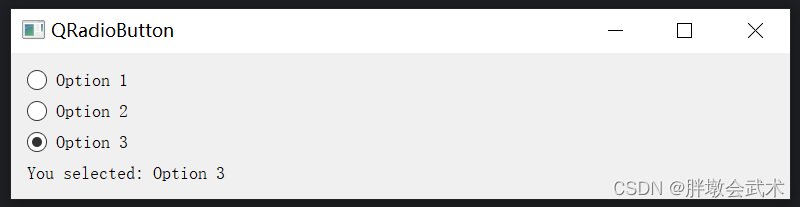
import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QLabel, QRadioButton, QVBoxLayout, QWidget class RadioButtonExample(QWidget): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.initUI() def initUI(self): self.setWindowTitle('QRadioButton') # 创建标签 self.label = QLabel("") # 创建单选按钮 self.radioButton1 = QRadioButton("Option 1") self.radioButton2 = QRadioButton("Option 2") self.radioButton3 = QRadioButton("Option 3") # 将单选按钮和标签添加到布局 layout = QVBoxLayout() layout.addWidget(self.radioButton1) layout.addWidget(self.radioButton2) layout.addWidget(self.radioButton3) layout.addWidget(self.label) # 将布局设置为窗口的主布局 self.setLayout(layout) # 连接单选按钮的点击事件到槽函数 self.radioButton1.clicked.connect(self.on_radio_button_clicked) self.radioButton2.clicked.connect(self.on_radio_button_clicked) self.radioButton3.clicked.connect(self.on_radio_button_clicked) def on_radio_button_clicked(self): sender = self.sender() # 获取点击的单选按钮 self.label.setText("You selected: " + sender.text()) # 更新标签文本 if __name__ == '__main__': app = QApplication(sys.argv) window = RadioButtonExample() window.show() sys.exit(app.exec_()) 4.2.12、分组框 QGroupBox:将其他小部件放置在其中
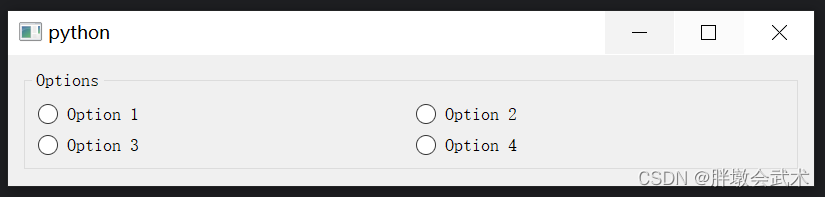
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QGroupBox, QHBoxLayout, QRadioButton, QVBoxLayout, QWidget app = QApplication([]) widget = QWidget() # 创建布局 main_layout = QVBoxLayout() group_box = QGroupBox("Options") group_box_layout = QVBoxLayout() # 创建组件 button1 = QRadioButton("Option 1") button2 = QRadioButton("Option 2") button3 = QRadioButton("Option 3") button4 = QRadioButton("Option 4") # 将组件添加到布局 layout1 = QHBoxLayout() layout1.addWidget(button1) layout1.addWidget(button2) layout2 = QHBoxLayout() layout2.addWidget(button3) layout2.addWidget(button4) group_box_layout.addLayout(layout1) group_box_layout.addLayout(layout2) group_box.setLayout(group_box_layout) # 添加组件到主布局 main_layout.addWidget(group_box) widget.setLayout(main_layout) widget.show() app.exec_() 4.2.12、打印日志 QTextEdit:获取当前时间 + 设置文本颜色
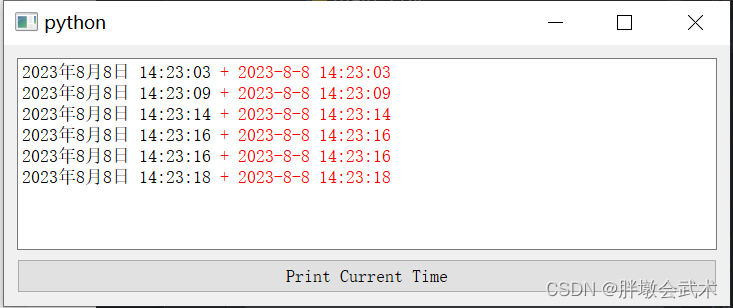
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QTextEdit, QVBoxLayout, QPushButton, QMainWindow, QWidget from PyQt5.QtCore import Qt, QDateTime class MainWindow(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.log_text_edit = QTextEdit() self.button = QPushButton("Print Current Time") self.button.clicked.connect(self.print_current_time) layout = QVBoxLayout() layout.addWidget(self.log_text_edit) layout.addWidget(self.button) widget = QWidget() widget.setLayout(layout) self.setCentralWidget(widget) def print_current_time(self): current_time1 = QDateTime.currentDateTime().toString(Qt.DefaultLocaleLongDate) # 指定默认格式 current_time2 = QDateTime.currentDateTime().toString("yyyy-M-d hh:mm:ss") # 指定日期格式 message = current_time1 + r'<font color="red"> + {}</font>'.format(current_time2) self.log_text_edit.append(message) if __name__ == '__main__': app = QApplication([]) window = MainWindow() window.show() app.exec() from datetime import datetime current_time = datetime.now() # 获取当前时间 formatted_time = current_time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S") print("Time:", formatted_time) # 打印格式化后的时间 # Time: 2023-08-08 14:25:29 4.2.13、消息提示框 QMessageBox:信息 / 询问 / 警告 / 错误
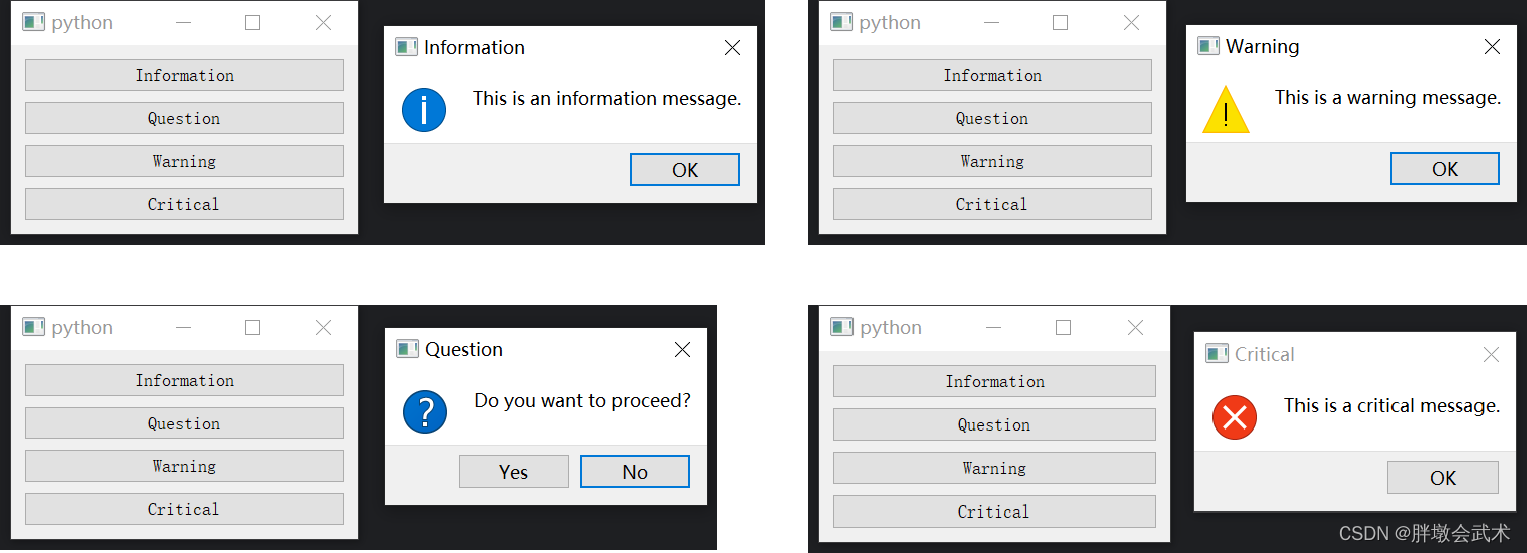
import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QPushButton, QVBoxLayout, QWidget, QMessageBox class MainWindow(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() info_button = QPushButton("Information") question_button = QPushButton("Question") warning_button = QPushButton("Warning") critical_button = QPushButton("Critical") info_button.clicked.connect(self.show_information) question_button.clicked.connect(self.show_question) warning_button.clicked.connect(self.show_warning) critical_button.clicked.connect(self.show_critical) layout = QVBoxLayout() layout.addWidget(info_button) layout.addWidget(question_button) layout.addWidget(warning_button) layout.addWidget(critical_button) widget = QWidget() widget.setLayout(layout) self.setCentralWidget(widget) def show_information(self): QMessageBox.information(self, "Information", "This is an information message.", QMessageBox.Ok, QMessageBox.Ok) def show_question(self): result = QMessageBox.question(self, "Question", "Do you want to proceed?", QMessageBox.Yes | QMessageBox.No, QMessageBox.No) if result == QMessageBox.Yes: print("User clicked Yes") else: print("User clicked No") def show_warning(self): QMessageBox.warning(self, "Warning", "This is a warning message.", QMessageBox.Ok, QMessageBox.Ok) def show_critical(self): QMessageBox.critical(self, "Critical", "This is a critical message.", QMessageBox.Ok, QMessageBox.Ok) if __name__ == "__main__": app = QApplication(sys.argv) window = MainWindow() window.show() sys.exit(app.exec_()) """########################################################################## from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QMessageBox 函数简介:用于显示消息框、询问框、警告框等用户交互提示框的类。 函数说明: 信息消息框 QMessageBox.information(parent, title, message, buttons, defaultButton) 询问消息框 QMessageBox.question(parent, title, message, buttons, defaultButton) 警告消息框 QMessageBox.warning(parent, title, message, buttons, defaultButton) 严重错误消息框 QMessageBox.critical(parent, title, message, buttons, defaultButton) 输入参数: parent: 可选参数,父级窗口。 title: 消息框的标题。 message: 消息框中显示的消息文本。 buttons: 消息框中显示的按钮类型,如 QMessageBox.Yes、QMessageBox.No 等。 defaultButton: 可选参数,指定默认按钮。 ##########################################################################""" 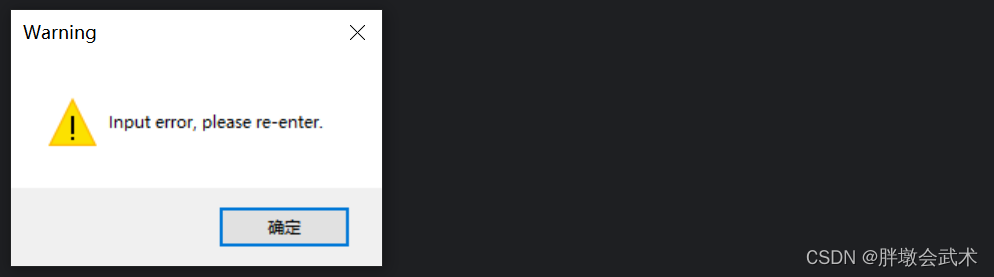
def show_warning(message=None): import tkinter as tk from tkinter import messagebox root = tk.Tk() root.withdraw() # 隐藏主窗口 messagebox.showwarning("Warning", message) root.destroy() # 关闭主窗口 if __name__ == '__main__': show_warning(message="请仔细检查") 4.2.14、选项卡界面 QTabWidget
4.2.14.1、在一个窗口中显示多个页面
Tab控件:可以在一个窗口中显示多个页面,每个页面对应一个选项卡,用户可以通过点击选项卡来切换不同的页面。
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QTabWidget, QWidget, QVBoxLayout, QLabel class MyWindow(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() # 创建Tab控件 self.tab_widget = QTabWidget() self.setCentralWidget(self.tab_widget) # 创建页面并添加到Tab控件中 self.page1 = QWidget() self.page2 = QWidget() self.tab_widget.addTab(self.page1, "Page 1") self.tab_widget.addTab(self.page2, "Page 2") # 设置页面的布局和内容 layout1 = QVBoxLayout() layout1.addWidget(QLabel("This is Page 1")) self.page1.setLayout(layout1) layout2 = QVBoxLayout() layout2.addWidget(QLabel("This is Page 2")) self.page2.setLayout(layout2) if __name__ == "__main__": app = QApplication([]) window = MyWindow() window.show() app.exec_() 4.2.14.2、在主界面中,显示其他.py界面类文件
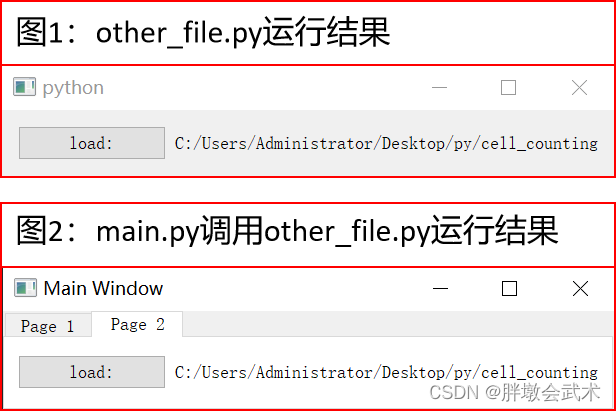
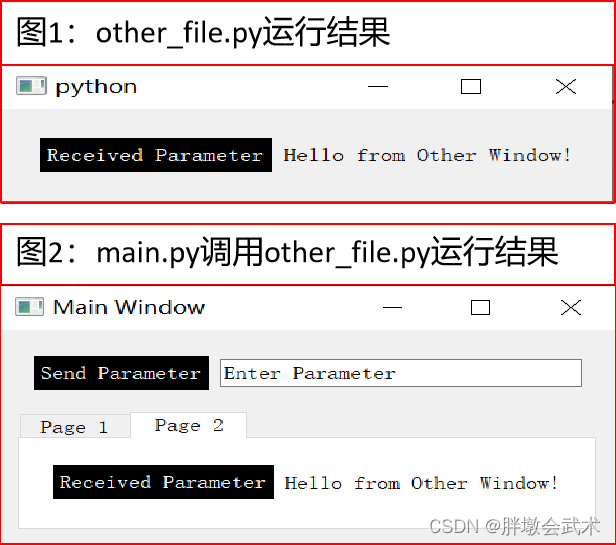
实现选项卡自动显示不同界面,可以在主界面的初始化过程中创建并添加不同的界面类实例,并根据选项卡的切换来显示相应的界面。
# main.py import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QTabWidget, QVBoxLayout, QWidget, QPushButton from other_file import OtherWindow # 导入其他文件中的界面类 class MainWindow(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.setWindowTitle("Main Window") self.setGeometry(200, 200, 300, 200) # 创建一个QTabWidget控件 self.tab_widget = QTabWidget(self) self.setCentralWidget(self.tab_widget) # 创建页面1和页面2 self.page1 = QWidget() self.page2 = OtherWindow() # 调用其他文件中的界面类 # 将页面1和页面2添加到QTabWidget控件中 self.tab_widget.addTab(self.page1, "Page 1") self.tab_widget.addTab(self.page2, "Page 2") if __name__ == "__main__": app = QApplication(sys.argv) main_window = MainWindow() main_window.show() sys.exit(app.exec_()) # other_file.py import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QLabel, QVBoxLayout, QHBoxLayout, QPushButton, QFileDialog class OtherWindow(QWidget): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.button = QPushButton("load:", self) self.button.clicked.connect(self.load_image) self.label = QLabel("") button_layout = QHBoxLayout() button_layout.addWidget(self.button) button_layout.addWidget(self.label) layout = QVBoxLayout() layout.addLayout(button_layout) # 将button_layout布局添加到主布局中 self.setLayout(layout) # 设置窗口的主布局 def load_image(self): self.folder_path = QFileDialog.getExistingDirectory(self, 'Select Folder', './') if self.folder_path: print('Selected Folder:', self.folder_path) self.label.setText(self.folder_path) if __name__ == '__main__': app = QApplication(sys.argv) window = OtherWindow() window.show() sys.exit(app.exec_()) 4.2.14.3、在主界面中,显示其他.py界面类文件,并进行数据交互
# main.py import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QTabWidget, QVBoxLayout, QWidget, QLineEdit, QPushButton, QHBoxLayout from other_file import OtherWindow class MainWindow(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.setWindowTitle("Main Window") self.setGeometry(200, 200, 300, 200) self.send_button = QPushButton("Send Parameter", self) # 新建按钮,并设置初始参数 self.send_button.clicked.connect(self.send_parameter) # 使用connect方法将信号连接到槽 self.send_button.setStyleSheet("background-color: black; color: white;") # 设置按钮的背景和字体颜色 self.input_line_edit = QLineEdit("Enter Parameter", self) # 新建文本框,并设置初始参数 ##################################################################### # 创建一个QTabWidget控件 self.tab_widget = QTabWidget(self) self.setCentralWidget(self.tab_widget) # 创建页面1和页面2 self.page1 = QWidget() self.other_window = OtherWindow() # 调用其他文件中的界面类 # 将页面1和页面2添加到QTabWidget控件中 self.tab_widget.addTab(self.page1, "Page 1") self.tab_widget.addTab(self.other_window, "Page 2") ##################################################################### self.button_layout = QHBoxLayout() self.button_layout.addWidget(self.send_button) self.button_layout.addWidget(self.input_line_edit) layout = QVBoxLayout() layout.addLayout(self.button_layout) layout.addWidget(self.tab_widget) central_widget = QWidget() central_widget.setLayout(layout) self.setCentralWidget(central_widget) def send_parameter(self): parameter = self.input_line_edit.text() self.other_window.receive_parameter(parameter) # 调用其他界面类other_window中的函数receive_parameter if __name__ == "__main__": app = QApplication(sys.argv) window = MainWindow() window.show() sys.exit(app.exec_()) # other_file.py from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QWidget, QVBoxLayout, QHBoxLayout, QPushButton, QLabel import sys class OtherWindow(QWidget): def __init__(self): super().__init__() button_layout = QHBoxLayout() # 水平布局管理器 self.Received_button = QPushButton("Received Parameter", self) # 新建按钮,并设置初始参数 self.Received_button.setStyleSheet("background-color: black; color: white;") # 设置按钮的背景和字体颜色 self.label = QLabel("Hello from Other Window!") button_layout.addWidget(self.Received_button) button_layout.addWidget(self.label) layout = QVBoxLayout() layout.addLayout(button_layout) self.setLayout(layout) def receive_parameter(self, parameter): self.label.setText(f"{parameter}") if __name__ == "__main__": app = QApplication(sys.argv) window = OtherWindow() window.show() sys.exit(app.exec_()) 4.2.15、调用其他.py文件,并数据交互
共有两种方法:
- (1)
QProcess(process.start):需要依赖Qt库。实现与外部应用程序的交互、启动和管理等功能,更加灵活。适用于更复杂的交互和进程管理。- (2)
subprocess(subprocess.run):Python标准库提供的方法,更加简单方便。适用于在Python脚本中执行外部命令或脚本,并获取其结果。
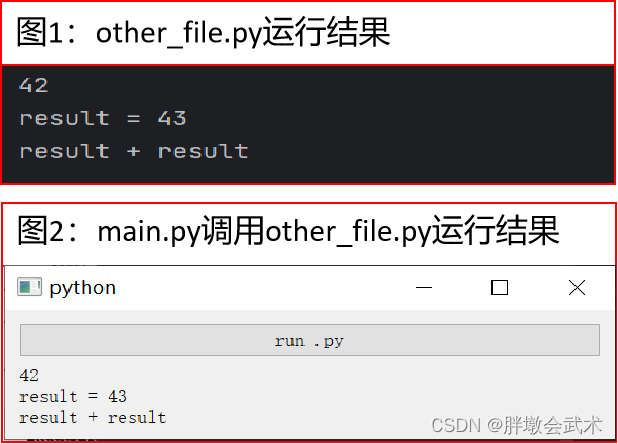
测试文件.py
# other_file.py # 在这里进行运算或其他处理 result = 42 # 将结果打印到控制台 print(result) print("result =", result + 1) print("result" + " + " + "result") 方法一:subprocess(subprocess.run)
# main.py import sys import subprocess from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QVBoxLayout, QWidget, QPushButton, QLabel class MainWindow(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.run_button = QPushButton("run .py") self.run_button.clicked.connect(self.run) self.run_label = QLabel("", self) layout = QVBoxLayout() layout.addWidget(self.run_button) layout.addWidget(self.run_label) central_widget = QWidget() central_widget.setLayout(layout) self.setCentralWidget(central_widget) def run(self): try: ######################################################### # 若不确定other_file.py是否调用成功,可以使用绝对路径。 # 不建议:调用.py文件 # 建议:将py文件封装成一个函数,然后调用函数。 ######################################################### result = subprocess.run(["python", "other_file.py"], capture_output=True, text=True, check=True) output = result.stdout.strip() # 获取输出结果并去除首尾空格 self.run_label.setText(output) except subprocess.CalledProcessError as e: self.run_label.setText(str(e)) if __name__ == "__main__": app = QApplication(sys.argv) window = MainWindow() window.show() sys.exit(app.exec_()) """########################################################################## import subprocess 函数简介:Python标准库subprocess模块中的一个函数,用于运行一个子进程并等待其完成。 可以执行系统命令或其他可执行文件,并可以通过参数来控制进程的行为和交互。 函数说明:subprocess.run(args, *, stdin=None, input=None, stdout=None, stderr=None, shell=False, cwd=None, timeout=None, check=False, encoding=None, errors=None, text=None, env=None, universal_newlines=None, start_new_session=False) 输入参数: args: 要运行的命令或可执行文件,以列表或字符串形式传递。如果shell=True,可以传递一个字符串,使用Shell运行命令。 stdin: 用于传递子进程的标准输入的文件对象。 input: 用于传递子进程的标准输入的字节或字符串数据。 stdout: 用于接收子进程的标准输出的文件对象。 stderr: 用于接收子进程的标准错误输出的文件对象。 shell: 是否在Shell中运行命令。如果为True,可以使用通配符等Shell特性。 cwd: 子进程的当前工作目录。 timeout: 等待子进程完成的超时时间,如果子进程在此时间内未完成,将会被终止。 check: 是否检查返回代码。如果为True,如果子进程返回的代码非零,将会引发CalledProcessError异常。 encoding: 用于解码子进程输出的编码。 errors: 用于处理解码错误的策略。 text: 是否使用文本模式传递数据,相当于同时设置universal_newlines和encoding。 env: 用于指定子进程的环境变量。 universal_newlines: 是否使用通用换行符模式,相当于同时设置stdin、stdout和stderr的text参数。 start_new_session: 是否在新的会话(session)中启动子进程。 输出参数: 返回一个CompletedProcess对象,它包含有关子进程执行的信息,如返回代码、标准输出、标准错误等。 ##########################################################################""" 方法二:QProcess(process.start)
# main.py import sys from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QVBoxLayout, QWidget, QPushButton, QLabel from PyQt5.QtCore import QProcess class MainWindow(QMainWindow): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.run_button = QPushButton("run .py") self.run_button.clicked.connect(self.run) self.run_label = QLabel("", self) layout = QVBoxLayout() layout.addWidget(self.run_button) layout.addWidget(self.run_label) central_widget = QWidget() central_widget.setLayout(layout) self.setCentralWidget(central_widget) def run(self): # 清空结果标签 self.run_label.setText("") ######################################################### # (1)启动进程执行外部脚本 process = QProcess() python_script = r'other_file.py' # 注意:若不确定other_file.py是否调用成功,可以使用绝对路径。 para1 = str(9) # (1)传递参数只能是字符串(2)与外部脚本完成交互。 process.start("python", [python_script, para1]) process.waitForFinished(-1) # 用于等待进程执行完成。传入参数-1表示无限等待 # (2)进程的退出代码:(1)0表示进程成功执行完成;(2)非零值表示出现错误。 exit_code = process.exitCode() if exit_code == 0: self.run_label.setText("调用【成功】,退出代码:{}".format(exit_code)) else: self.run_label.setText("调用【失败】,退出代码:{}".format(exit_code)) if __name__ == "__main__": app = QApplication(sys.argv) window = MainWindow() window.show() sys.exit(app.exec_()) """###################################################################################### # 函数介绍:QProcess 是 Qt 框架中用于创建和管理外部进程的类。它允许你启动外部应用程序,并与其进行通信。 # 常见方法: # (1)启动外部进程: 使用start()方法启动一个外部进程 # (2)与进程通信: 使用write()方法向进程的标准输入写入数据,并使用readAllStandardOutput()和readAllStandardError()方法读取进程的标准输出和标准错误输出。 # (2)等待进程执行完成: 使用waitForFinished()方法来等待进程执行完成 # (3)获取进程退出代码: 使用exitCode()方法可以获取进程的退出代码 # (4)支持信号与槽机制: 使用readyReadStandardOutput()信号在进程有标准输出可读时发出 # (5)中断进程: 使用terminate()方法尝试终止进程的执行。不一定会立即停止进程,具体行为取决于操作系统和进程本身。 # # process = QProcess() # process.start("python", ["script.py", "arg1", "arg2"]) # if process.waitForFinished(): # print("Process finished") # exit_code = process.exitCode() # if exit_code == 0: # print("调用成功") # else: # print("调用失败,退出代码:", exit_code) # # process.write(b"input data") # output = process.readAllStandardOutput() # error_output = process.readAllStandardError() # process.readyReadStandardOutput.connect(handle_output) # process.terminate() ######################################################################################""" """###################################################################################### # 函数介绍:waitForFinished 是 QProcess 类的一个成员函数。用于阻塞当前线程,直到关联的进程完成执行为止。 # 函数说明:bool QProcess.waitForFinished(int msecs = 30000) # 输入参数: msecs:等待的时间(以毫秒为单位)。默认值是 30000 毫秒(30 秒)。如果设置为 -1,表示无限等待。 # 输出参数: 如果进程在给定的时间内完成执行,则返回 True,否则返回 False。 # # (1)主要用于等待 QProcess 执行外部程序的过程完成。程序会阻塞当前线程,阻塞在当前行,直到被调用的进程执行完毕。 # (2)如果进程执行的时间很长,这会导致界面冻结,因为界面线程会被阻塞。 # (3)如果你需要在界面上显示进度或状态,或者想要允许用户继续操作界面,而不阻塞界面线程,可以考虑使用多线程、异步编程等技术,以避免界面的冻结。 ######################################################################################""" 4.2.16、在当前虚拟环境下,调用其他虚拟环境下的.py文件,并数据交互
import subprocess import os virtual_env_name = "tensorflow36" # (1)指定要激活的虚拟环境名称 cmd_activate_env = f"conda activate {virtual_env_name}" # (2)构建激活虚拟环境的命令 script_path = r"deeplearning.py" # (3)指定.py文件路径 path = os.getcwd() + 'image.tif' # (4)指定.py文件参数 cmd_script_file = f"python {script_path} --image_path {path}" # (5)构建调用.py文件的命令,包括传递参数 # (6)使用subprocess执行命令 ################################################################################### # 在Windows上,通过subprocess.run来激活一个Conda环境并不是一种有效的方式。 # 原因分析:因为conda activate命令会在一个新的子进程中执行,该子进程的环境变量变化不会影响到当前Python进程中运行的后续代码。 # 解决方法:将激活环境和执行py文件的命令,同时传递给subprocess.run。 ################################################################################### combined_cmd = f"{cmd_activate_env} && {cmd_script_file}" # 组合两个命令并在子进程中执行 try: subprocess.run(combined_cmd, shell=True, check=True) except subprocess.CalledProcessError as e: print(f"Error: {e}") """###################################################################### import argparse # 导入argparse模块 if __name__ == "__main__": parser = argparse.ArgumentParser() # 创建解析对象 parser.add_argument('--image_path') # 添加命令行参数和选项 args = parser.parse_args() # 解析添加的参数 image_path = args.image_path # 获取添加的参数 ######################################################################"""