前言
这次文章将带大家实现一个图书管理系统,界面如下:
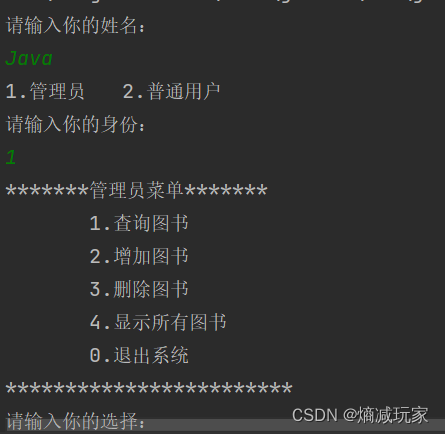
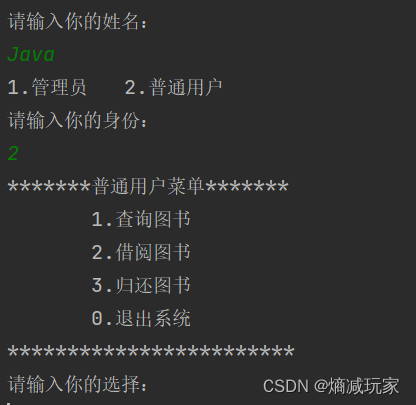
找到对象
我们从上面就可以知道,我们需要创建两个对象,一个是管理员对象,一个是普通用户对象,由于这两个对象都是用户这一范畴,所以我们可以为他们创建一个父类,那我们可以将这三个类放在同一个包上,如下图所示:

然后我们进一步思考我们还需要什么类,由于这是一个图书管理系统,所以我们可以创建书这个类用来创建多本的书,我们还可以创建一个书架用来存放书籍,这两个类我们把他们放在同一个包上:
我们有很多个功能需要实现,例如增加图书,删除图书,查询图书等等…我们可以再创建一个包用来专门存放这些功能:

最后我们需要创建一个Main类用来组装上面的代码,使其成为一个管理系统。
代码实现
book包
Book类
这里的书包括书名,作者,书的类型,价格以及书是否被借出的状态,这样我们可以创建对应的成员变量,为了有封装的体现,我们可以使用private修饰这些创元变量,然后通过Getter and Setter 来实现成员变量的访问就可以了.
由于我们会访问这本书的所有信息,我们就需要打印,这时候我们就要重写toString 方法,尽管IDEA编译器会自动帮我们实现,但是对于书是否被借出的状态打印,我们需要打印字符串(“未借阅” 和 “已借阅”)这两种状态,但是这个成员变量是boolean类型的,所以我们如果不去修改toString 方法的话,我们就会得到false和true这两种打印形式,那么我们就要稍微修改一下代码,这时候我们可以使用三目表达式来进行修改
如果直接使用编译器自动生成 toString 代码:
public Book(String name, String author, String type, double price, boolean is_borrowed) { this.name = name; this.author = author; this.type = type; this.price = price; this.is_borrowed = is_borrowed; } 结合上述的要点,我们可以得到下面的代码:
public class Book { private String name; private String author; private String type; private double price; private boolean is_borrowed; @Override public String toString() { return "Book{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", author='" + author + '\'' + ", type='" + type + '\'' + ", price=" + price + (is_borrowed == false ? " 未借阅": " 已借阅") + '}'; } public Book(String name, String author, String type, double price) { this.name = name; this.author = author; this.type = type; this.price = price; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getAuthor() { return author; } public void setAuthor(String author) { this.author = author; } public String getType() { return type; } public void setType(String type) { this.type = type; } public double getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(double price) { this.price = price; } public boolean isIs_borrowed() { return is_borrowed; } public void setIs_borrowed(boolean is_borrowed) { this.is_borrowed = is_borrowed; } } BookList 类 (书架)
我们可以使用组合来将书放在代码里,我们还可以先将三本书放在书架上,这时候我们可以通过构造方法来初始化书架,我们还需要知道书架上目前有多少本书,容量是多少,成员变量要相应的写上去,并且通过getter和setter方法来来实现成员变量的访问…
public class BookList { private Book[] books; private int curSize; private int count; public BookList(){ books = new Book[10]; books[0] = new Book("三国演义","罗贯中","名著",30.12); books[1] = new Book("西游记","吴承恩","名著",30.14); books[2] = new Book("红楼梦","曹雪芹","名著",50.42); curSize = 3; count = 10; } public int getCurSize() { return curSize; } public void setCurSize(int curSize) { this.curSize = curSize; } public int getCount() { return count; } public void setCount(int count) { this.count = count; } public Book getBooks(int i) { return books[i]; } public void setBooks(int pos,Book newBook) { books[pos] = newBook; } } user包
我们先来创建父类 User,需要姓名这一个成员变量,由于父类本身是要被继承的,所以我们可以将其实现为抽象类,不同的身份有不同的菜单列表,既然都是菜单我们不妨在父类写一个抽象方法,提醒子类要记得写菜单,还有用户会输入不同的数字来实现不同的功能,这里我们可以创建一个功能实现的方法,这样子我们就可以通过父类的引用来实现不同的子类所对应的功能…
public abstract class User { public String name; protected Ioperate[] opertions; public User(String name) { this.name = name; } public abstract int menu(); public void work(int choice, BookList bookList){ opertions[choice].operate(bookList); } } 管理者
public class Manager extends User{ public Manager(String name) { super(name); opertions = new Ioperate[] { new Exit(), new Find(), new Add(), new Delete(), new Show() }; } @Override public int menu() { System.out.println("*******管理员菜单*******"); System.out.println(" 1.查询图书"); System.out.println(" 2.增加图书"); System.out.println(" 3.删除图书"); System.out.println(" 4.显示所有图书"); System.out.println(" 0.退出系统"); System.out.println("************************"); System.out.println("请输入你的选择:"); Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); int choice = scan.nextInt(); return choice; } } 普通用户
public class DomesticConsumer extends User { public DomesticConsumer(String name) { super(name); opertions = new Ioperate[] { new Exit(), new Find(), new Borrow(), new Return() }; } @Override public int menu() { System.out.println("*******普通用户菜单*******"); System.out.println(" 1.查询图书"); System.out.println(" 2.借阅图书"); System.out.println(" 3.归还图书"); System.out.println(" 0.退出系统"); System.out.println("************************"); System.out.println("请输入你的选择:"); Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); int choice = scan.nextInt(); return choice; } } Ioperation包
接口
我们可以通过一个接口来实现功能的有机联系,这样我们就可以通过这个接口类型来实现不同的方法,我们知道这些方法几乎都会操作书架,所以我们将书架作为参数进行传递就可以了。
public interface Ioperate { void operate(BookList bookList); } Add
我们直接采用尾插,我们需要判断一下书架是否还能继续放书,需要将目前的图书数目和书架容量进行比较就可以了,接下来就是创建新书,将新书放到书架即可,这时候我们要注意书架放书的代码是否正确,我们使用IDEA编译器只能实现Book[]类型的getter和setter,但是书的类型是Book,所以我们需要自己写一个放书的代码:
public void setBooks(int pos,Book newBook) { books[pos] = newBook; } 为什么不直接写books[curSize] = newBook呢?
因为我们后面删除图书的代码里也是需要对书架上的书进行移动,会用到setter方法,所以为了代码的通用性高,我们就多加了一个pos参数
public class Add implements Ioperate{ @Override public void operate(BookList bookList) { int count = bookList.getCount(); int curSize = bookList.getCurSize(); if(count == curSize){ System.out.println("书架已满,无法再放入别的图书......."); return; } System.out.println("请输入你要增加的书名:"); Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); String name = scan.nextLine(); System.out.println("请输入作者名字"); String author = scan.nextLine(); System.out.println("请输入图书类型:"); String type = scan.nextLine(); System.out.println("请输入图书价格:"); double price = scan.nextDouble(); Book newBook = new Book(name,author,type,price); bookList.setBooks(curSize,newBook); bookList.setCurSize(curSize + 1); } } 在进行删除图书,查询图书,这里我采用的是通过书名进行遍历访问的方式。
这时候我们就要小心,因为我们是对书架进行操控的,所以我们要先拿到书这个对象,那我们就要看怎么拿出对应的书,由于编译器只能实现Book[]类型的getter,所以我们还是要自己写一个拿书的代码。
由于书名是String类型,所以可以使用equals方法经行字符串的比对。所以我们拿到书后还要访问书的书名再进行比对即可。
public Book getBooks(int i) { return books[i]; } Book book = bookList.getBooks(i); if(book.getName().equals(name)){ //...... } Delete
删除书也很容易,我们需要把待删除的书后面的书进行前移
public class Delete implements Ioperate{ @Override public void operate(BookList bookList) { int curSize = bookList.getCurSize(); if(curSize == 0){ System.out.println("书架已空,无法继续删除......"); } System.out.println("请输入你要删除图书的书名:"); Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); String name = scan.nextLine(); for (int i = 0; i < curSize; i++) { Book book = bookList.getBooks(i); if(book.getName().equals(name)){ System.out.println("删除成功......"); for (int j = i; j < curSize - 1; j++) { bookList.setBooks(j,bookList.getBooks(j+1)); } bookList.setCurSize(curSize - 1); return; } } System.out.println("未查询到该书....."); } } Borrow
public class Borrow implements Ioperate{ @Override public void operate(BookList bookList) { System.out.println("请输入你要借阅图书书名:"); Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); String name = scan.nextLine(); int curSize = bookList.getCurSize(); for (int i = 0; i < curSize; i++) { Book book = bookList.getBooks(i); if(book.getName().equals(name)){ if(book.isIs_borrowed() == false){ System.out.println("该书已被你成功借阅......"); book.setIs_borrowed(true); }else{ System.out.println("该书已被借阅,无法被再次借阅....."); } return; } } System.out.println("未查询到此书......"); } } Find
public class Find implements Ioperate{ @Override public void operate(BookList bookList) { System.out.println("输入你要查询的书名:"); Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); String name = scan.nextLine(); int count = bookList.getCurSize(); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { Book book = bookList.getBooks(i); if(book.getName().equals(name)){ System.out.println(book); return; } } System.out.println("未查询到此书......"); } } Return
public class Return implements Ioperate{ @Override public void operate(BookList bookList) { System.out.println("请输入你要归还书名:"); Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); String name = scan.nextLine(); int count = bookList.getCurSize(); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { Book book = bookList.getBooks(i); if(book.getName().equals(name)){ if(book.isIs_borrowed() == true){ System.out.println("归还成功......"); book.setIs_borrowed(false); }else{ System.out.println("该图书已被归还到书架上,无需重复归还......"); } return; } } System.out.println("未查询到该图书....."); } } Show
public class Show implements Ioperate{ @Override public void operate(BookList bookList) { int count = bookList.getCurSize(); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { System.out.println(bookList.getBooks(i)); } } } Exit
退出程序的代码就是System.exit(数字),数字零表示正常退出的意思。
public class Exit implements Ioperate{ @Override public void operate(BookList bookList) { System.out.println("退出系统......"); System.exit(0); } } 登录
我们再Main类写一个login方法
public static User login(){ Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入你的姓名:"); String name = scan.nextLine(); System.out.println("1.管理员 2.普通用户"); System.out.println("请输入你的身份:"); int identity = scan.nextInt(); if(identity == 1){ return new Manager(name); }else{ return new DomesticConsumer(name); } } 主逻辑实现
我们先登录,然后创建书架,接着打印菜单,用户输入指令,计算机进行对应的操作:
public static void main(String[] args) { //创建书架 BookList bookList = new BookList(); //login User user = login(); while(true){ //功能菜单选择 int choice = user.menu(); //功能实现 user.work(choice,bookList); } } 最终代码
Main类
import book.BookList; import user.DomesticConsumer; import user.Manager; import user.User; import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static User login(){ Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入你的姓名:"); String name = scan.nextLine(); System.out.println("1.管理员 2.普通用户"); System.out.println("请输入你的身份:"); int identity = scan.nextInt(); if(identity == 1){ return new Manager(name); }else{ return new DomesticConsumer(name); } } public static void main(String[] args) { //创建书架 BookList bookList = new BookList(); //login User user = login(); while(true){ //功能菜单选择 int choice = user.menu(); //功能实现 user.work(choice,bookList); } } } user包
User
package user; import Ioperation.Ioperate; import book.BookList; public abstract class User { public String name; protected Ioperate[] opertions; public User(String name) { this.name = name; } public abstract int menu(); public void work(int choice, BookList bookList){ opertions[choice].operate(bookList); } } Manager
package user; import Ioperation.*; import java.util.Scanner; public class Manager extends User{ public Manager(String name) { super(name); opertions = new Ioperate[] { new Exit(), new Find(), new Add(), new Delete(), new Show() }; } @Override public int menu() { System.out.println("*******管理员菜单*******"); System.out.println(" 1.查询图书"); System.out.println(" 2.增加图书"); System.out.println(" 3.删除图书"); System.out.println(" 4.显示所有图书"); System.out.println(" 0.退出系统"); System.out.println("************************"); System.out.println("请输入你的选择:"); Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); int choice = scan.nextInt(); return choice; } } DomesticConsumer
package user; import Ioperation.*; import java.util.Scanner; public class DomesticConsumer extends User { public DomesticConsumer(String name) { super(name); opertions = new Ioperate[] { new Exit(), new Find(), new Borrow(), new Return() }; } @Override public int menu() { System.out.println("*******普通用户菜单*******"); System.out.println(" 1.查询图书"); System.out.println(" 2.借阅图书"); System.out.println(" 3.归还图书"); System.out.println(" 0.退出系统"); System.out.println("************************"); System.out.println("请输入你的选择:"); Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); int choice = scan.nextInt(); return choice; } } book 包
Book
package book; public class Book { private String name; private String author; private String type; private double price; private boolean is_borrowed; @Override public String toString() { return "Book{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", author='" + author + '\'' + ", type='" + type + '\'' + ", price=" + price + (is_borrowed == false ? " 未借阅": " 已借阅") + '}'; } public Book(String name, String author, String type, double price) { this.name = name; this.author = author; this.type = type; this.price = price; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getAuthor() { return author; } public void setAuthor(String author) { this.author = author; } public String getType() { return type; } public void setType(String type) { this.type = type; } public double getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(double price) { this.price = price; } public boolean isIs_borrowed() { return is_borrowed; } public void setIs_borrowed(boolean is_borrowed) { this.is_borrowed = is_borrowed; } } BookList
package book; public class BookList { private Book[] books; private int curSize; private int count; public BookList(){ books = new Book[10]; books[0] = new Book("三国演义","罗贯中","名著",30.12); books[1] = new Book("西游记","吴承恩","名著",30.14); books[2] = new Book("红楼梦","曹雪芹","名著",50.42); curSize = 3; count = 10; } public int getCurSize() { return curSize; } public void setCurSize(int curSize) { this.curSize = curSize; } public int getCount() { return count; } public void setCount(int count) { this.count = count; } public Book getBooks(int i) { return books[i]; } public void setBooks(int pos,Book newBook) { books[pos] = newBook; } } Ioperation包
Ioperate
package Ioperation; import book.BookList; public interface Ioperate { void operate(BookList bookList); } Add
package Ioperation; import book.Book; import book.BookList; import java.util.Scanner; public class Add implements Ioperate{ @Override public void operate(BookList bookList) { int count = bookList.getCount(); int curSize = bookList.getCurSize(); if(count == curSize){ System.out.println("书架已满,无法再放入别的图书......."); return; } System.out.println("请输入你要增加的书名:"); Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); String name = scan.nextLine(); System.out.println("请输入作者名字"); String author = scan.nextLine(); System.out.println("请输入图书类型:"); String type = scan.nextLine(); System.out.println("请输入图书价格:"); double price = scan.nextDouble(); Book newBook = new Book(name,author,type,price); bookList.setBooks(curSize,newBook); bookList.setCurSize(curSize + 1); } } Borrow
package Ioperation; import book.Book; import book.BookList; import java.util.Scanner; public class Borrow implements Ioperate{ @Override public void operate(BookList bookList) { System.out.println("请输入你要借阅图书书名:"); Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); String name = scan.nextLine(); int curSize = bookList.getCurSize(); for (int i = 0; i < curSize; i++) { Book book = bookList.getBooks(i); if(book.getName().equals(name)){ if(book.isIs_borrowed() == false){ System.out.println("该书已被你成功借阅......"); book.setIs_borrowed(true); }else{ System.out.println("该书已被借阅,无法被再次借阅....."); } return; } } System.out.println("未查询到此书......"); } } Delete
package Ioperation; import book.Book; import book.BookList; import java.util.Scanner; public class Delete implements Ioperate{ @Override public void operate(BookList bookList) { int curSize = bookList.getCurSize(); if(curSize == 0){ System.out.println("书架已空,无法继续删除......"); } System.out.println("请输入你要删除图书的书名:"); Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); String name = scan.nextLine(); for (int i = 0; i < curSize; i++) { Book book = bookList.getBooks(i); if(book.getName().equals(name)){ System.out.println("删除成功......"); for (int j = i; j < curSize - 1; j++) { bookList.setBooks(j,bookList.getBooks(j+1)); } bookList.setCurSize(curSize - 1); return; } } System.out.println("未查询到该书....."); } } Exit
package Ioperation; import book.BookList; public class Exit implements Ioperate{ @Override public void operate(BookList bookList) { System.out.println("退出系统......"); System.exit(0); } } Find
package Ioperation; import book.Book; import book.BookList; import java.util.Scanner; public class Find implements Ioperate{ @Override public void operate(BookList bookList) { System.out.println("输入你要查询的书名:"); Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); String name = scan.nextLine(); int count = bookList.getCurSize(); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { Book book = bookList.getBooks(i); if(book.getName().equals(name)){ System.out.println(book); return; } } System.out.println("未查询到此书......"); } } Return
package Ioperation; import book.Book; import book.BookList; import java.util.Scanner; public class Return implements Ioperate{ @Override public void operate(BookList bookList) { System.out.println("请输入你要归还书名:"); Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); String name = scan.nextLine(); int count = bookList.getCurSize(); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { Book book = bookList.getBooks(i); if(book.getName().equals(name)){ if(book.isIs_borrowed() == true){ System.out.println("归还成功......"); book.setIs_borrowed(false); }else{ System.out.println("该图书已被归还到书架上,无需重复归还......"); } return; } } System.out.println("未查询到该图书....."); } } Show
package Ioperation; import book.BookList; public class Show implements Ioperate{ @Override public void operate(BookList bookList) { int count = bookList.getCurSize(); for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { System.out.println(bookList.getBooks(i)); } } } 