1. Spring MVC 中 HttpMessageConverter 转换器
文章目录
- 1. Spring MVC 中 HttpMessageConverter 转换器
- 2. 补充:什么是 HTTP 消息
- 3. 转换器
- 4. Spring MVC中的 AJAX 请求
- 5. @ResponseBody 将服务器端的 return 返回值转化为“字符串(JSON格式的字符串)”再返回给客户端
- 6. 补充:@RestController = (@Controller + @ResponseBody )
- 7. @RequestBody 将前端的请求体的信息转换Java程序中的 POJO对象
- 8. RequestEntity 类
- 9. ResponseEntity 类
- 10. 总结:
- 11. 最后:
2. 补充:什么是 HTTP 消息
HTTP 消息其实就是 HTTP 协议。HTTP 协议包括 请求协议 和 响应协议。
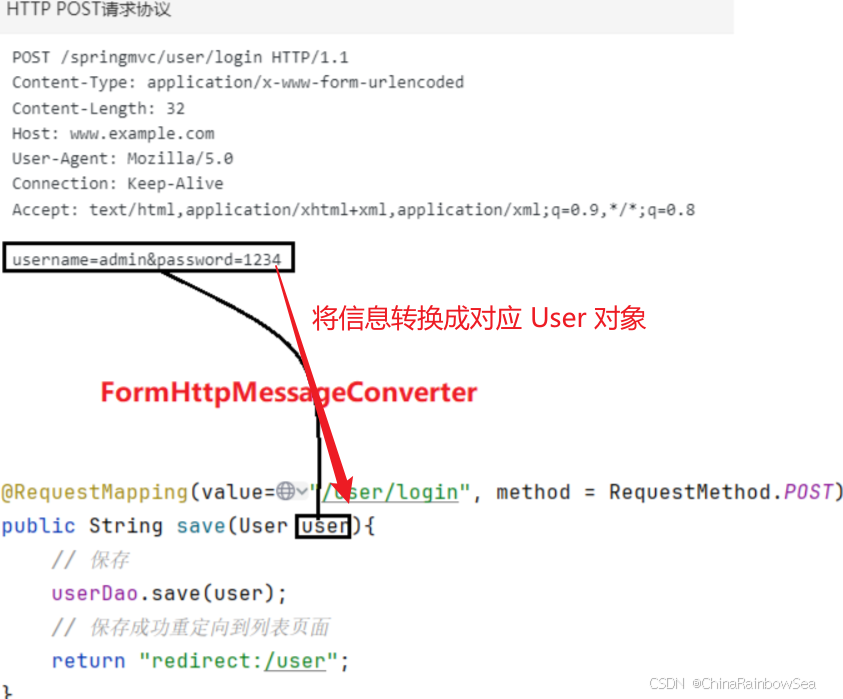
以下是一份HTTP POST请求协议:
POST /springmvc/user/login HTTP/1.1 --请求行 Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded --请求头 Content-Length: 32 Host: www.example.com User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 Connection: Keep-Alive Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8 --空白行 username=admin&password=1234 --请求体 以下是一份HTTP GET请求协议:
GET /springmvc/user/del?id=1&name=zhangsan HTTP/1.1 --请求行 Host: www.example.com --请求头 User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 Connection: Keep-Alive Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,*/*;q=0.8 以下是一份HTTP响应协议:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK --状态行 Date: Thu, 01 Jul 2021 06:35:45 GMT --响应头 Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8 Content-Length: 12 Connection: keep-alive Server: Apache/2.4.43 (Win64) OpenSSL/1.1.1g --空白行 <!DOCTYPE html> --响应体 <html> <head> <title>hello</title> </head> <body> <h1>Hello World!</h1> </body> </html> 3. 转换器
HttpMessageConverter 是 Spring MVC 中非常重要的一个接口。翻译为:HTTP消息转换器。
该接口下提供了很多实现类,不同的实现类有不同的转换方式。
3.1 转换器转换的是什么
转换的是
HTTP协议与Java程序中的对象之间的互相转换。请看下图:
上图是我们之前经常写的代码。请求体中的数据是如何转换成 user 对象的,底层实际上使用了
HttpMessageConverter接口的其中的一个实现类FormHttpMessageConverter。通过上图可以看出
FormHttpMessageConverter是负责将请求协议转换为Java对象的。
上图的代码也是之前我们经常写的,Controller 返回值看做逻辑视图名称,视图解析器将其转换成物理视图名称,生成视图对象,
StringHttpMessageConverter负责将视图对象中的 HTML 字符串写入到 HTTP协议的响应体中。最终完成响应。通过上图可以看出
StringHttpMessageConverter是负责将Java对象转换为响应协议的。
通过以上内容的学习,大家应该能够了解到 HttpMessageConverter接口是用来做什么的了:

如上图所示:HttpMessageConverter 接口的可以将请求协议转换成 Java对象;也可以把 Java对象转换为响应协议。
HttpMessageConverter 是接口,Spring MVC 帮我们提供了非常多而丰富的实现类。每个实现类都有自己不同的转换风格。
对于我们程序员来说,Spring MVC 已经帮助我们写好了,我们只需要在不同的业务场景下,选择合适的HTTP消息转换器即可。
怎么选择呢?当然是通过 Spring MVC 为我们提供的注解,我们通过使用不同的注解来启用不同的消息转换器。
我们重点牢牢把握住下面的这两个注解,两个类 ;
- 两个注解:
@ResponseBody
@RequestBody
- 两个类:
ResponseEntity
RequestEntity
4. Spring MVC中的 AJAX 请求
SpringMVC+Vue3+Thymeleaf+Axios发送一个简单的AJAX请求。
引入 Vue 和 Axios的js文件:
导入相关的 jar 依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>com.rainbowsea</groupId> <artifactId>springmvc-008</artifactId> <version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>war</packaging> <properties> <maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target> </properties> <dependencies> <!--springmvc依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> <version>6.1.4</version> </dependency> <!--logback依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId> <artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId> <version>1.5.3</version> </dependency> <!--servlet依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>jakarta.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>jakarta.servlet-api</artifactId> <version>6.0.0</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> <!--thymeleaf和spring6整合的依赖--> <dependency> <groupId>org.thymeleaf</groupId> <artifactId>thymeleaf-spring6</artifactId> <version>3.1.2.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <!-- 引入jackson依赖,可以将java对象转换为json格式字符串--> <!-- 专门负责将Java对象转换成JSON格式字符串的组件, 当然,它也可以将JSON格式的字符串转换成Java对象--> <dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId> <version>2.17.0</version> </dependency> </dependencies> </project> web.xml 文件的相关配置信息内容:
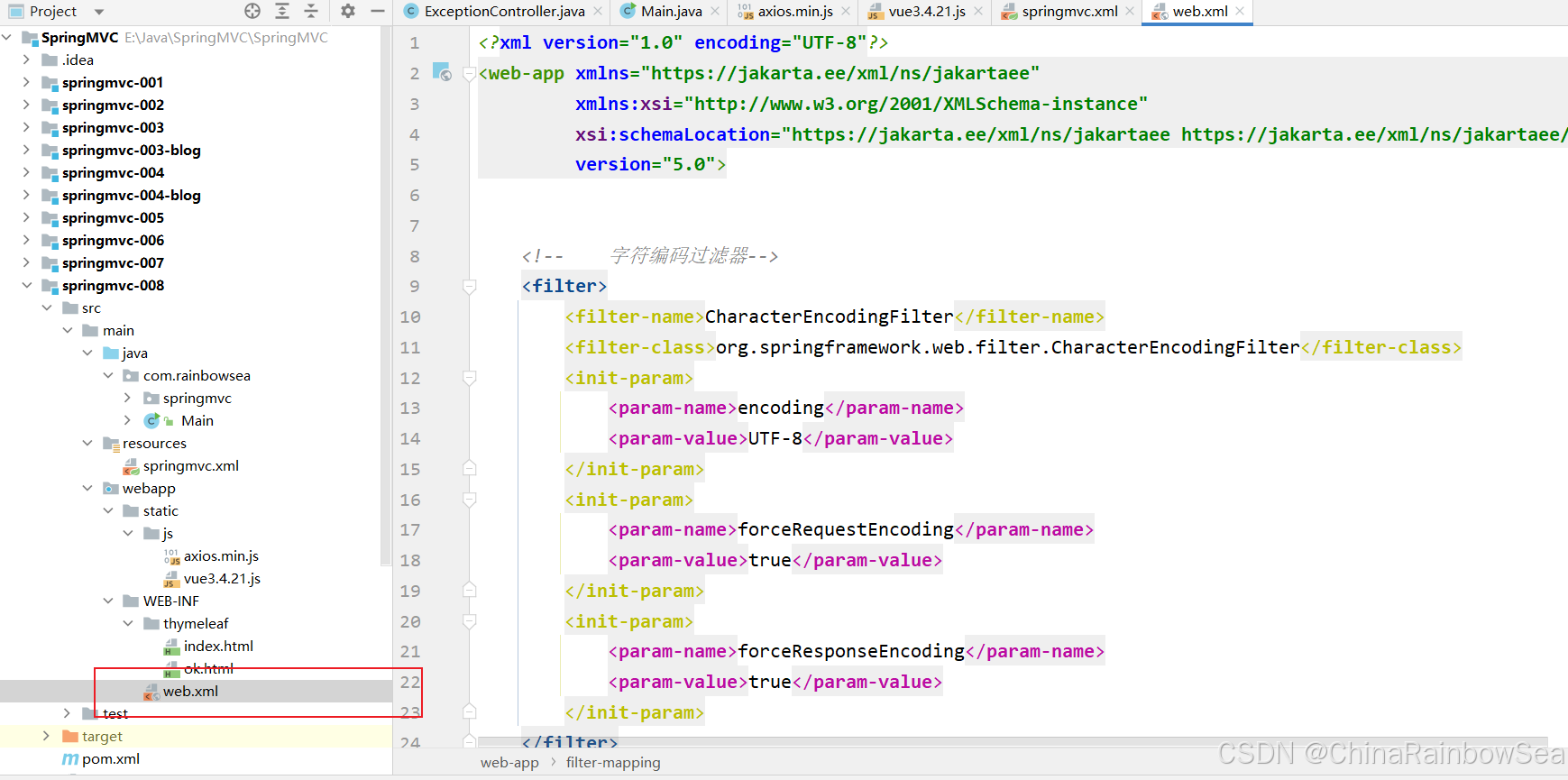
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns="https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee https://jakarta.ee/xml/ns/jakartaee/web-app_5_0.xsd" version="5.0"> <!-- 字符编码过滤器--> <filter> <filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class> <init-param> <param-name>encoding</param-name> <param-value>UTF-8</param-value> </init-param> <init-param> <param-name>forceRequestEncoding</param-name> <param-value>true</param-value> </init-param> <init-param> <param-name>forceResponseEncoding</param-name> <param-value>true</param-value> </init-param> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping> <!-- 前端控制器--> <servlet> <servlet-name>DispatcherServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value> </init-param> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>DispatcherServlet</servlet-name> <!-- 除了 jsp 页面其他的都走这个--> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <!-- 添加一个过滤器,这个过滤器是springmvc提前写好的,直接用就行了,这个过滤器可以帮助你将请求 POST转换成PUT请求/DELETE请求--> <!-- 同时注意:该过滤器一定要在字符编码过滤器后面配置,不然,先设置的话,可能会出现获取到的请求数据是乱码--> <filter> <filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name> <!-- 表示任意的 请求--> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping> </web-app> 相关 springmvc.xml 文件配置信息的编写:
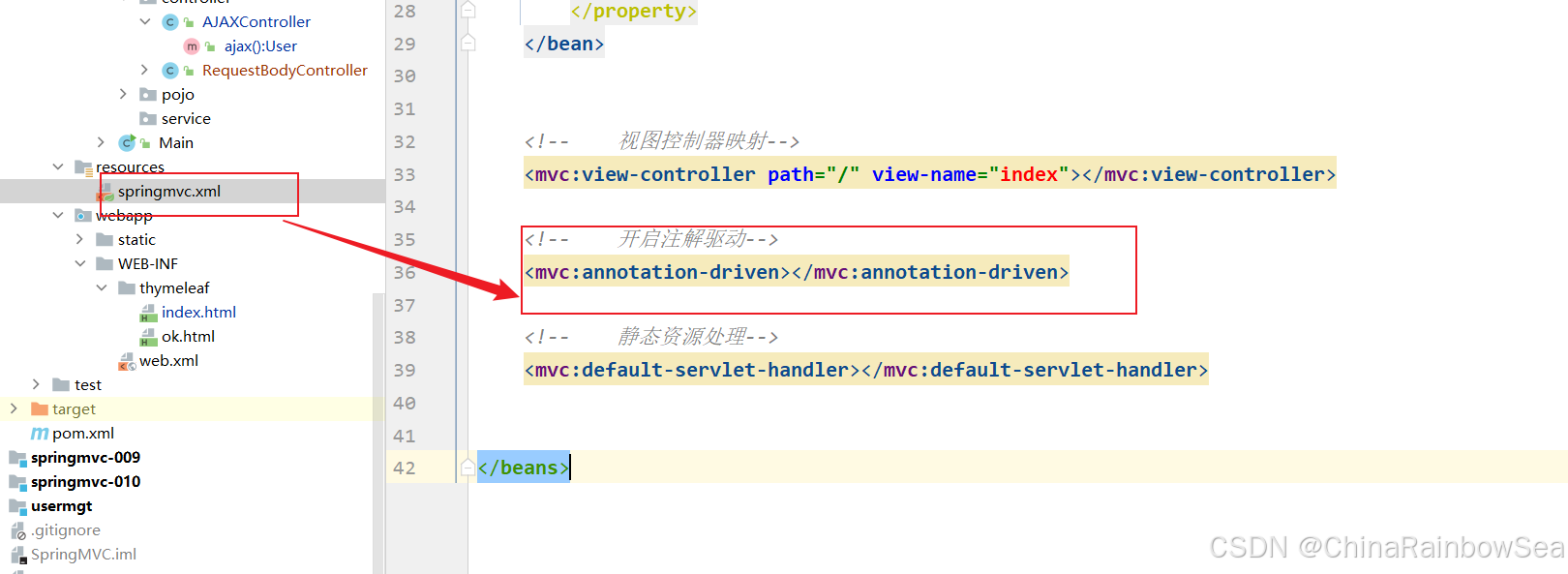
其中重点是:静态资源处理、开启注解驱动、视图控制器映射等相关配置。
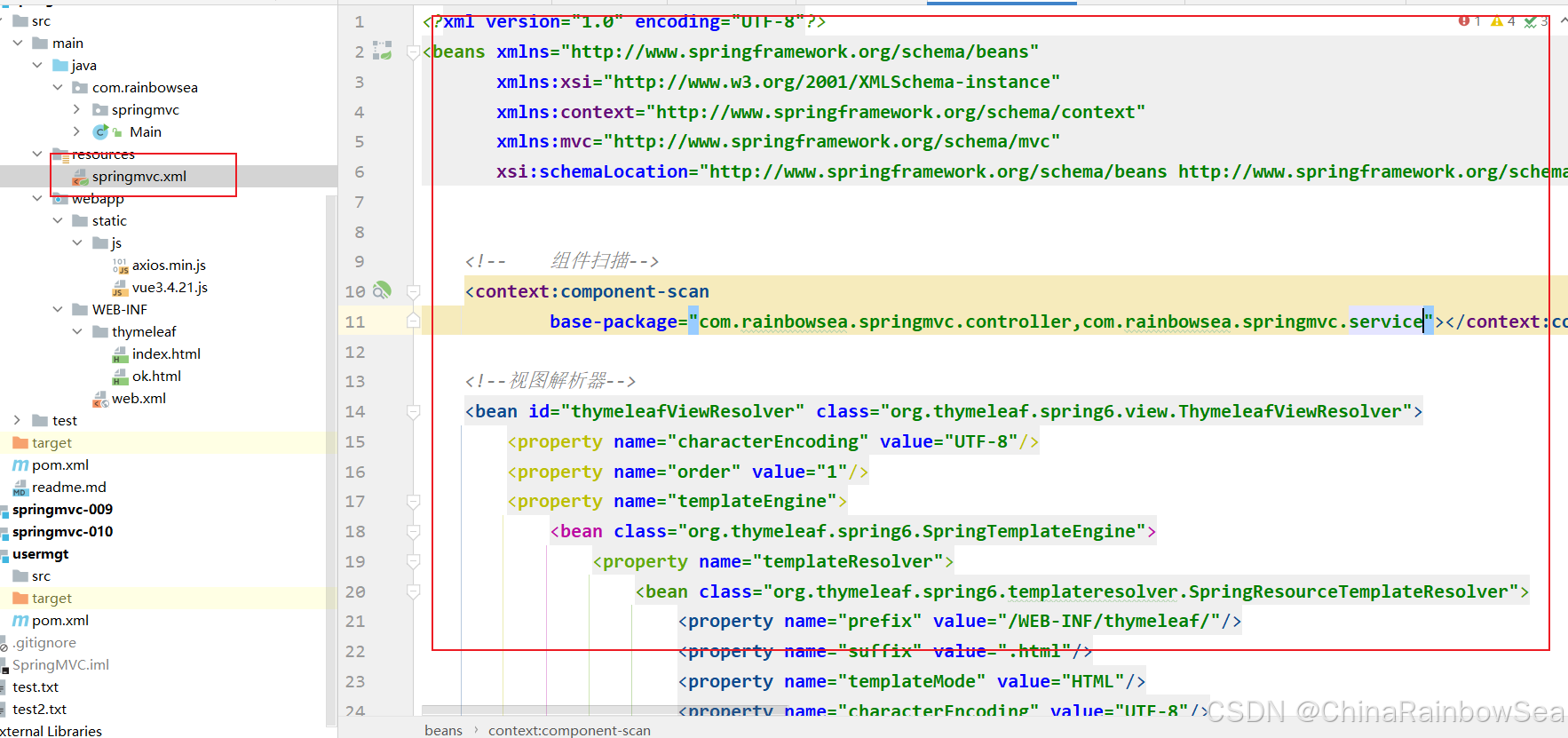
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc https://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd"> <!-- 组件扫描--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.rainbowsea.springmvc.controller,com.rainbowsea.springmvc.service"></context:component-scan> <!--视图解析器--> <bean id="thymeleafViewResolver" class="org.thymeleaf.spring6.view.ThymeleafViewResolver"> <property name="characterEncoding" value="UTF-8"/> <property name="order" value="1"/> <property name="templateEngine"> <bean class="org.thymeleaf.spring6.SpringTemplateEngine"> <property name="templateResolver"> <bean class="org.thymeleaf.spring6.templateresolver.SpringResourceTemplateResolver"> <property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/thymeleaf/"/> <property name="suffix" value=".html"/> <property name="templateMode" value="HTML"/> <property name="characterEncoding" value="UTF-8"/> </bean> </property> </bean> </property> </bean> <!-- 视图控制器映射--> <mvc:view-controller path="/" view-name="index"></mvc:view-controller> <!-- 开启注解驱动--> <mvc:annotation-driven></mvc:annotation-driven> <!-- 静态资源处理--> <mvc:default-servlet-handler></mvc:default-servlet-handler> </beans> Vue3 + Thymeleaf + Axios 发送 AJAX 请求:
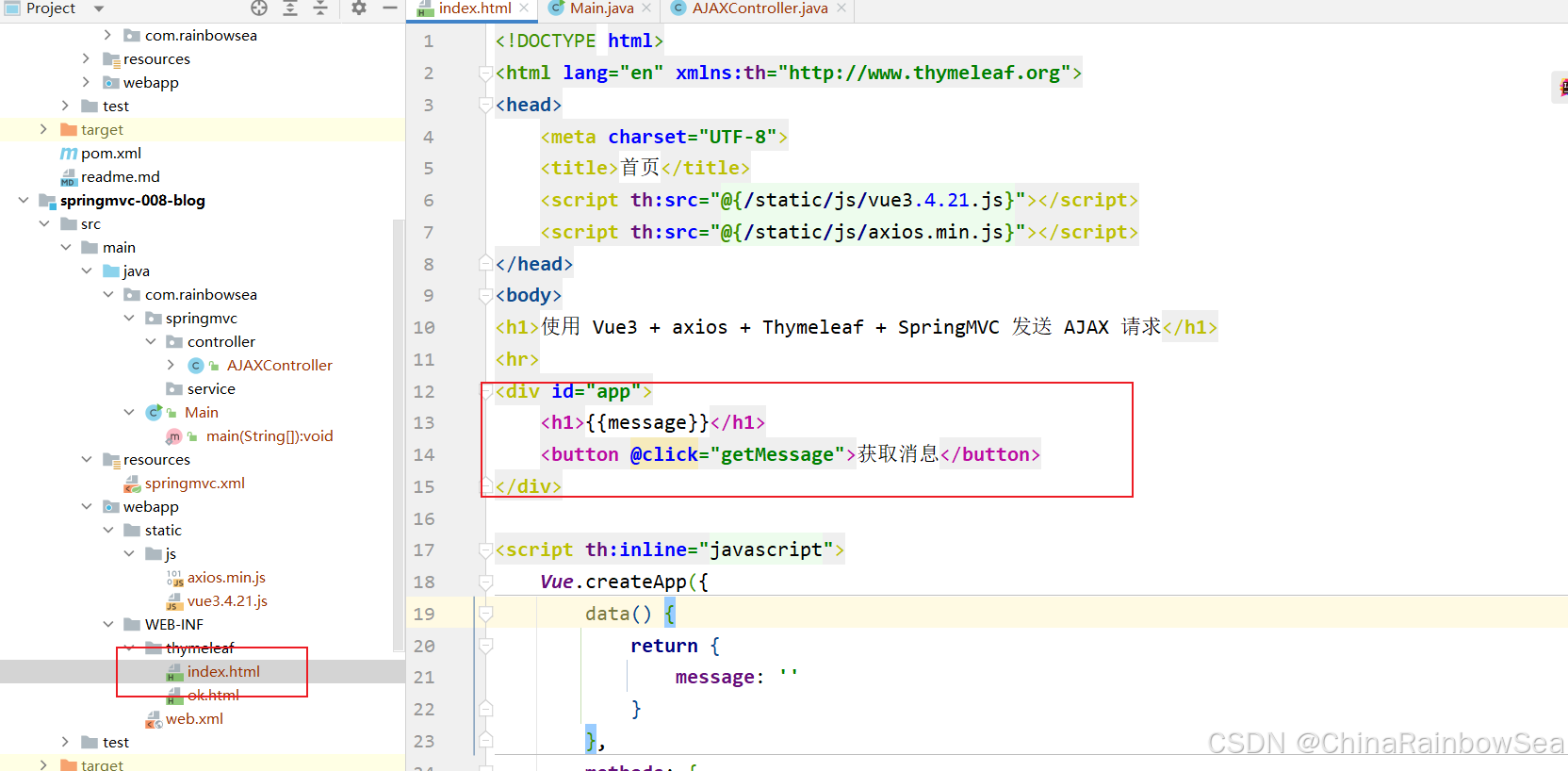
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>首页</title> <script th:src="@{/static/js/vue3.4.21.js}"></script> <script th:src="@{/static/js/axios.min.js}"></script> </head> <body> <h1>使用 Vue3 + axios + Thymeleaf + SpringMVC 发送 AJAX 请求</h1> <hr> <div id="app"> <h1>{{message}}</h1> <button @click="getMessage">获取消息</button> </div> <script th:inline="javascript"> Vue.createApp({ data() { return { message: '' } }, methods: { //异步方法(ajax请求多数情况下都是异步请求) async getMessage() { try { // 发送 ajax请求 // await axios.get('/springmvc/ajax') //动态获取 应用的根/springmvc/ const response = await axios.get([[@{/}]] + 'ajax') // 将返回的数据交给 message this.message = response.data }catch (e) { console.error(e) } } } }).mount("#app") </script> </body> </html> 重点来了,Controller 怎么写呢?
之前我们都是传统的请求,Controller 返回一个 逻辑视图名 。然后交给 视图解析器 —>进行解析,最后跳转页面。而 AJAX 请求是不需要跳转页面的,因为 AJAX 是页面局部刷新,以前我们在 Servlet 中使用
response.getWriter( ).print("message")的方式响应。在 Spring MVC 中怎么办呢?当然,我们在 Spring MVC 中也可以使用 Servelt 原生API 来完成整个功能,代码如下:
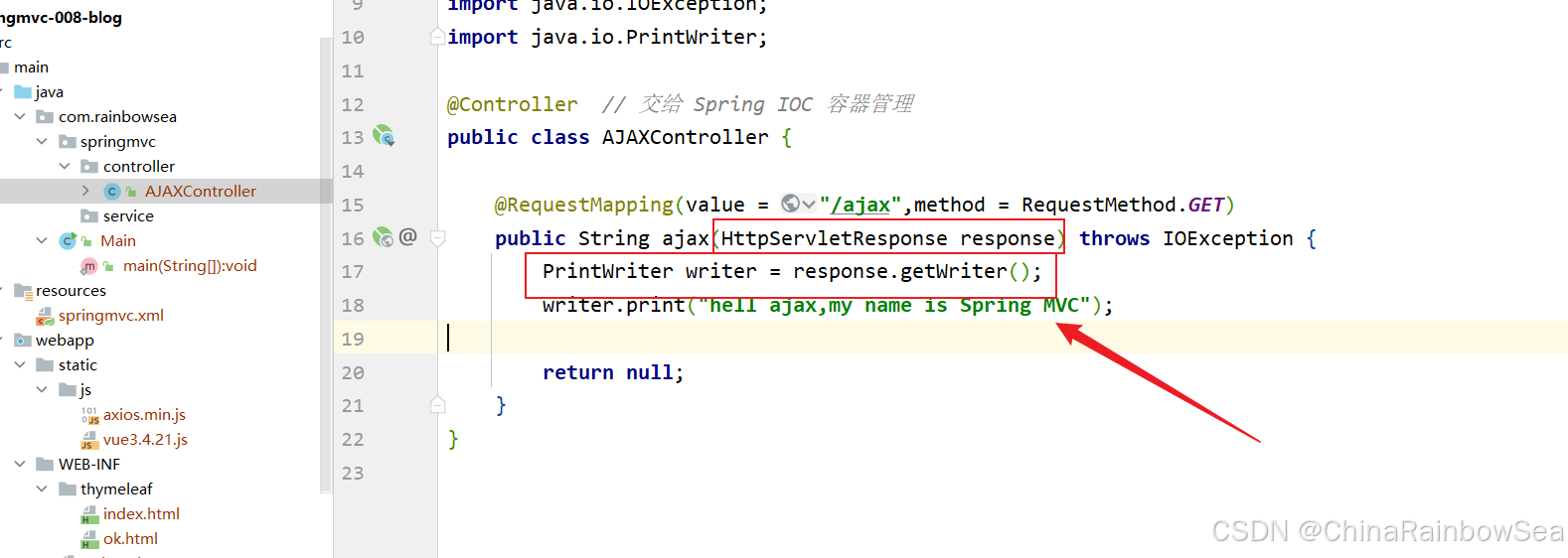
或者这样也行:不需要有返回值
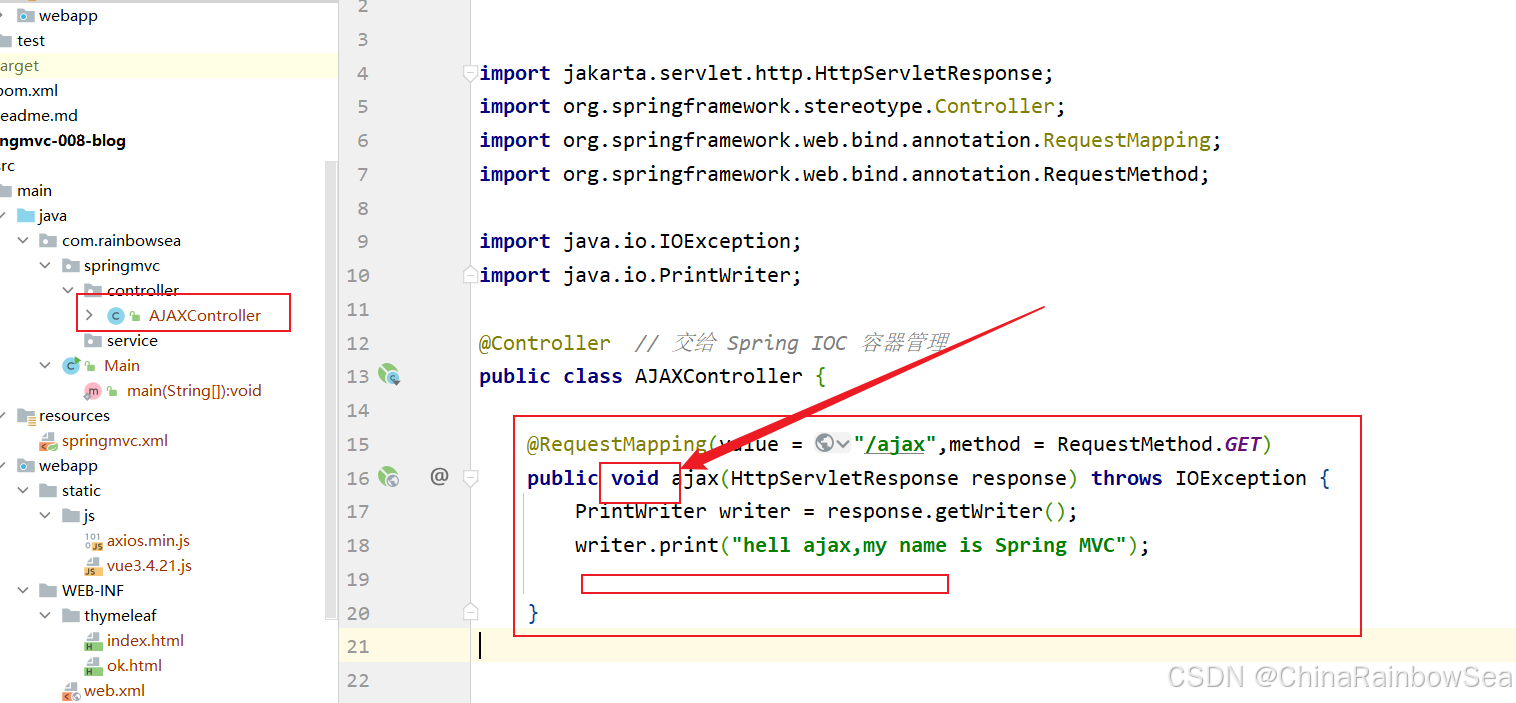
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PrintWriter; @Controller // 交给 Spring IOC 容器管理 public class AJAXController { @RequestMapping(value = "/ajax",method = RequestMethod.GET) public void ajax(HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException { PrintWriter writer = response.getWriter(); writer.print("hell ajax,my name is Spring MVC"); } } 启动服务器测试:http://localhost:8080/springmvc/
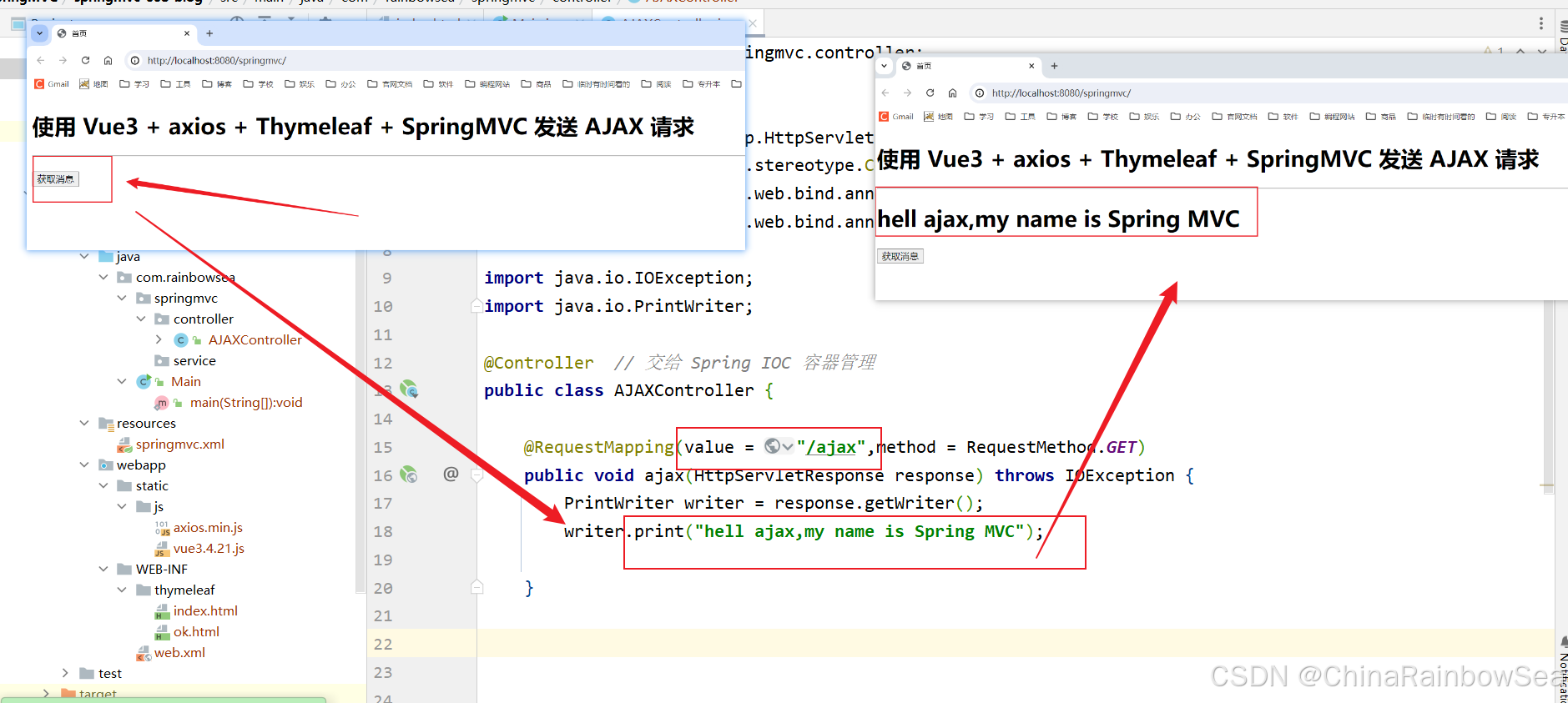
注意:如果采用这种方式响应,则和 springmvc.xml 文件中配置的视图解析器没有关系,不走视图解析器了。
难道我们以后 AJAX 请求 要使用上面这种原生Servlet API吗?
不需要,我们可以使用 SpringMVC 中提供的 HttpMessageConverter 消息转换器。
我们要向前端响应一个字符串 “hell ajax,my name is Spring MVC” ,这个 “hell ajax,my name is Spring MVC” 就是响应协议中的响应体。
我们可以使用 @ResponseBody注解 来启用对应的消息转换器。而这种消息转换器只负责将Controller返回的信息以响应体的形式写入响应协议。
5. @ResponseBody 将服务器端的 return 返回值转化为“字符串(JSON格式的字符串)”再返回给客户端
上面的 AJAX 案例,Controller的代码可以修改为:
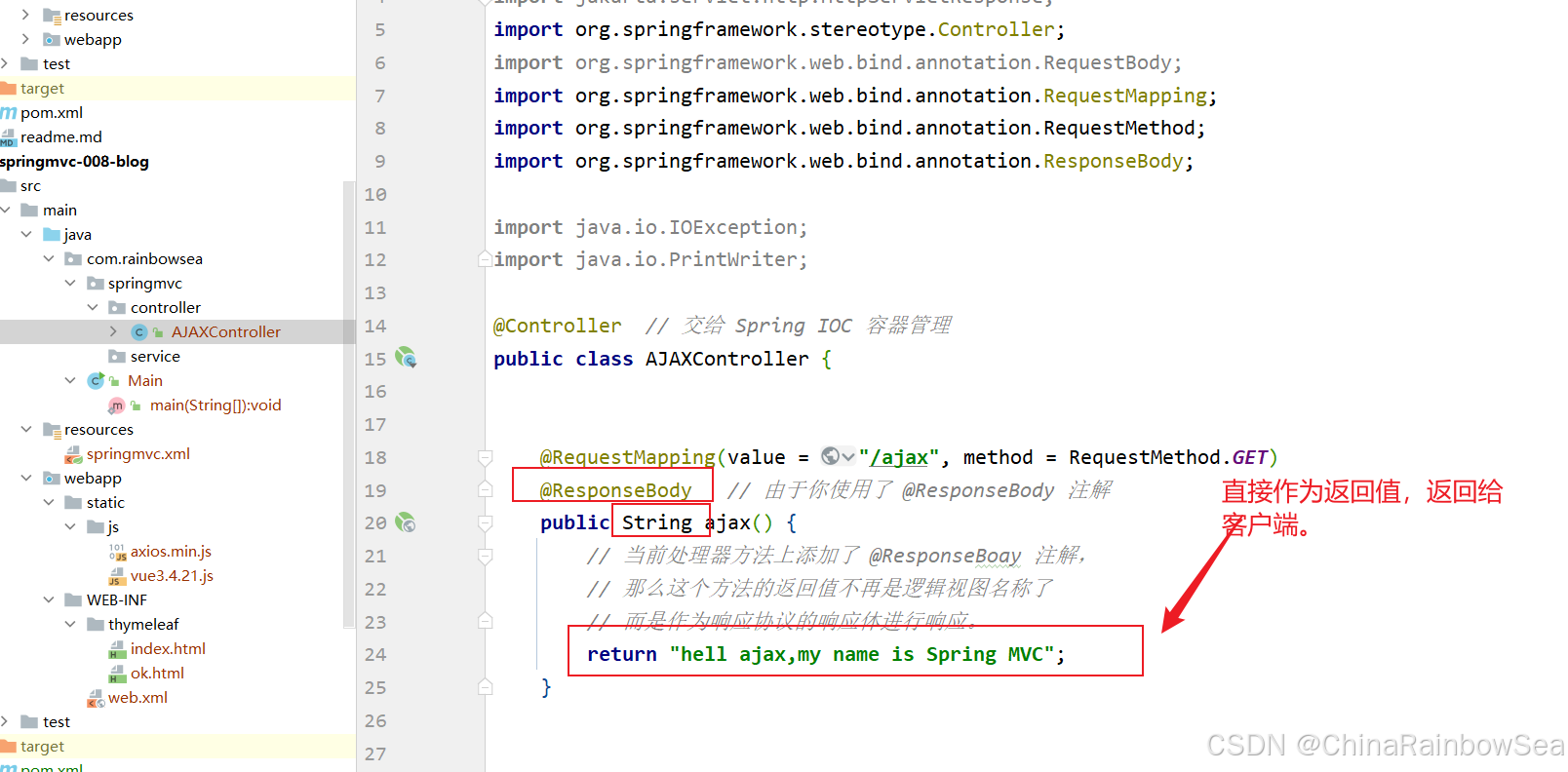
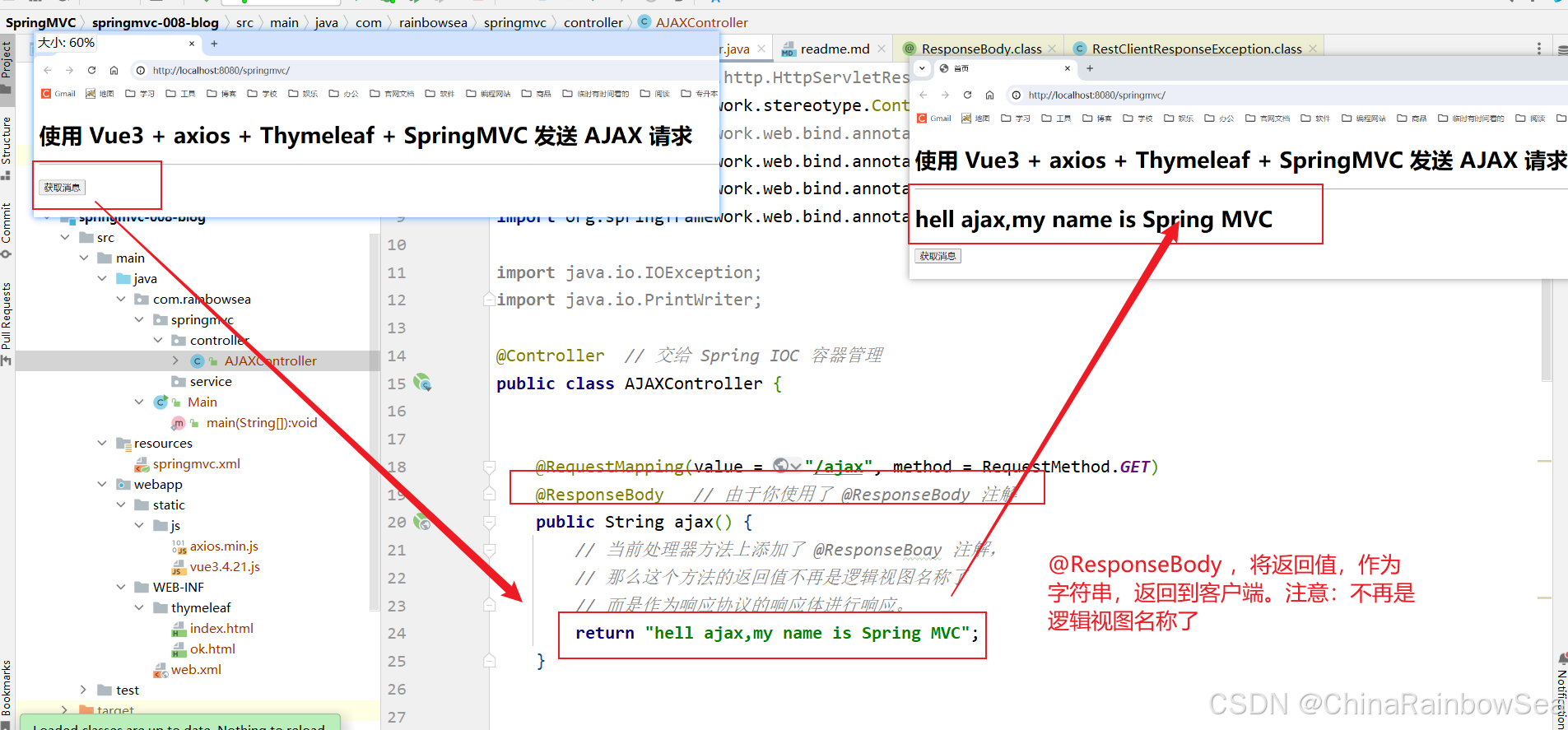
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PrintWriter; @Controller // 交给 Spring IOC 容器管理 public class AJAXController { @RequestMapping(value = "/ajax", method = RequestMethod.GET) @ResponseBody // 由于你使用了 @ResponseBody 注解 public String ajax() { // 当前处理器方法上添加了 @ResponseBoay 注解, // 那么这个方法的返回值不再是逻辑视图名称了 // 而是作为响应协议的响应体进行响应。 return "hell ajax,my name is Spring MVC"; } 最核心需要理解的位置是:
return "hell ajax,my name is Spring MVC";这里的 “hell ajax,my name is Spring MVC” 不是逻辑视图名称了,而是作为响应体的内容进行响应。直接输出到浏览器客户端。
以上程序中使用的消息转换器是:
StringHttpMessageConverter,为什么会启用这个消息转换器呢?因为你添加了@ResponseBody这个注解了。
启动服务器测试:http://localhost:8080/springmvc/
通常 AJAX 请求需要服务器给返回一段JSON格式的字符串,可以返回JSON格式的字符串吗?
这是完全可以的,此时底层使用的消息转换器还是:StringHttpMessageConverter
当然可以,代码如下:
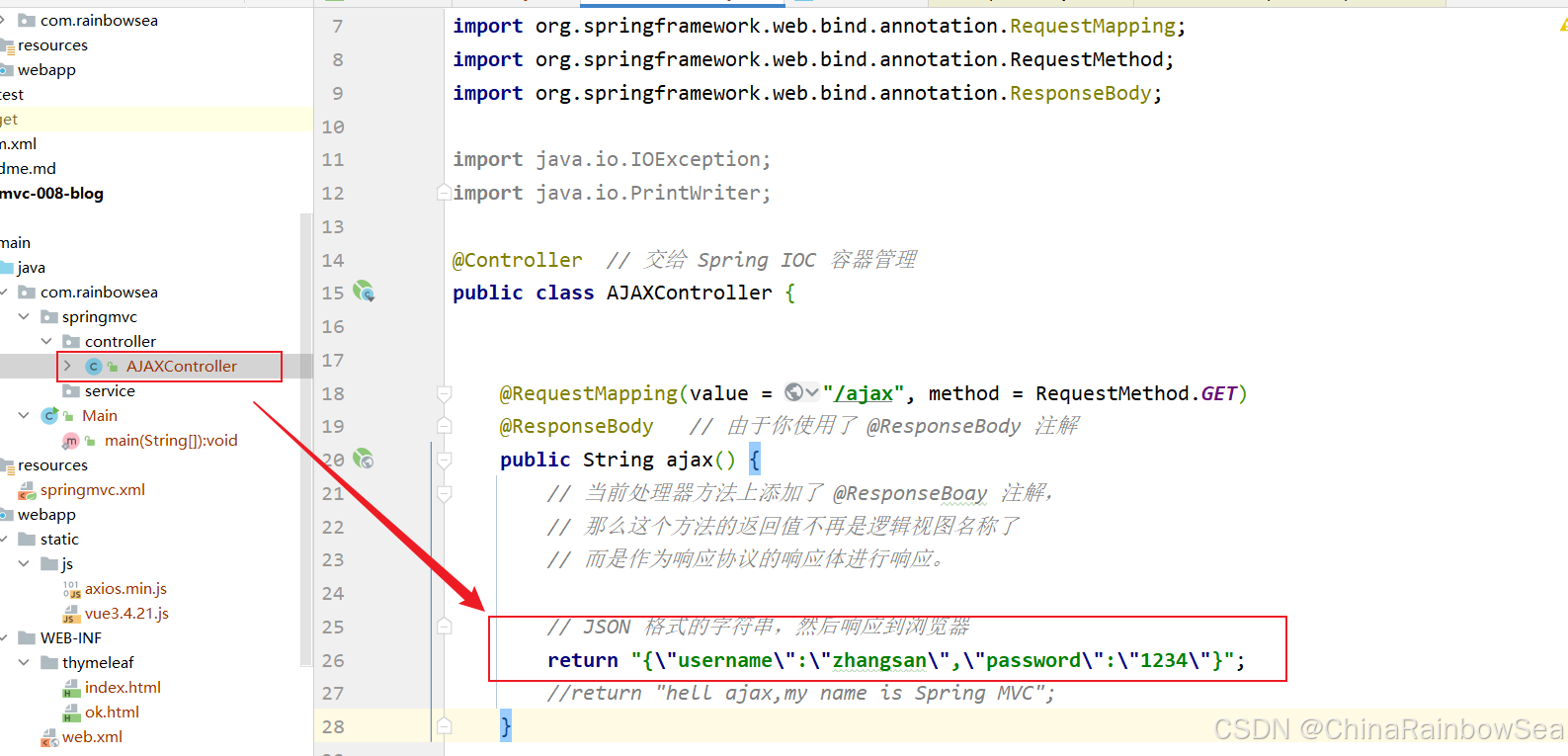
import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PrintWriter; @Controller // 交给 Spring IOC 容器管理 public class AJAXController { @RequestMapping(value = "/ajax", method = RequestMethod.GET) @ResponseBody // 由于你使用了 @ResponseBody 注解 public String ajax() { // 当前处理器方法上添加了 @ResponseBoay 注解, // 那么这个方法的返回值不再是逻辑视图名称了 // 而是作为响应协议的响应体进行响应。 // JSON 格式的字符串,然后响应到浏览器 return "{\"username\":\"zhangsan\",\"password\":\"1234\"}"; //return "hell ajax,my name is Spring MVC"; } } 启动服务器测试:http://localhost:8080/springmvc/
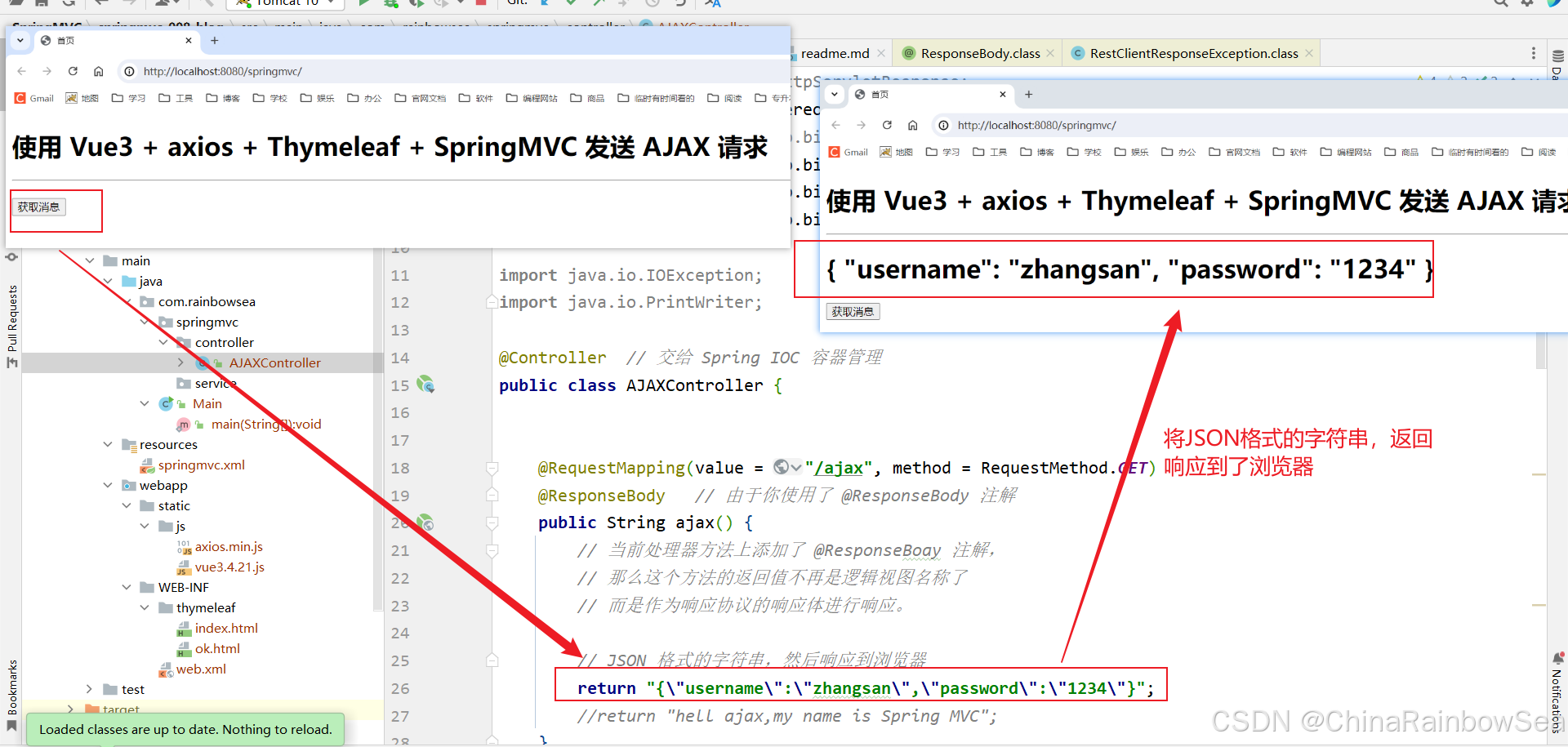
这是完全可以的,此时底层使用的消息转换器还是:StringHttpMessageConverter
那如果在程序中是一个POJO对象,怎么将POJO对象 以 JSON格式 的字符串响应给浏览器呢 ?两种方式:
第一种方式:自己写代码 将POJO对象 转换成JSON格式的字符串(如上面所示 return “{“username”:“zhangsan”,“password”:“1234”}”; ),用上面的方式直接 return即可。
第二种方式:启用
MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter消息转换器。
第二种方式:启用MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter消息转换器。
启用 MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter 消息转换器的步骤如下:
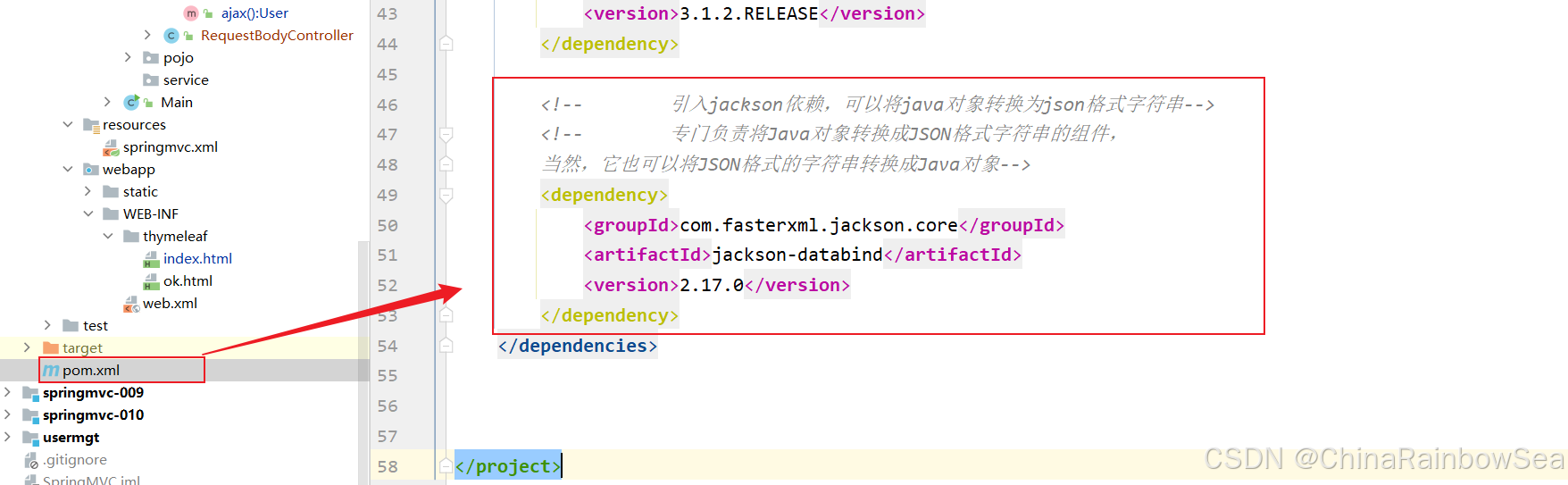
第一步: 引入 jackson依赖,可以将 java对象 转换为 json格式字符串
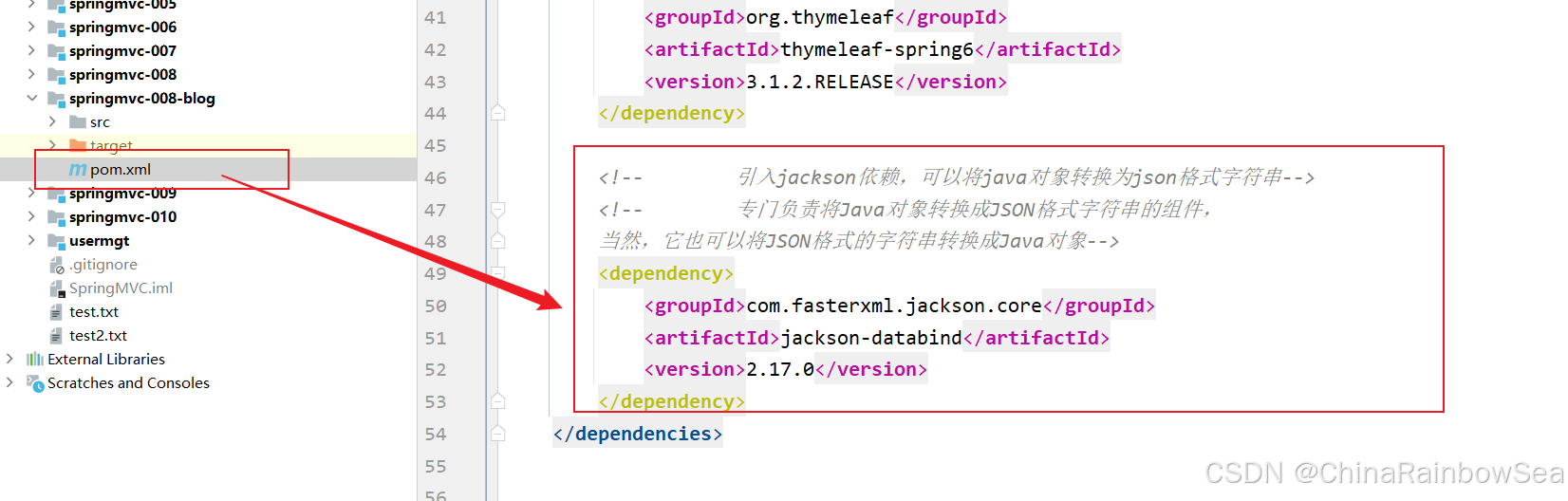
<!-- 引入jackson依赖,可以将java对象转换为json格式字符串--> <!-- 专门负责将Java对象转换成JSON格式字符串的组件, 当然,它也可以将JSON格式的字符串转换成Java对象--> <dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId> <version>2.17.0</version> </dependency> 第二步: 开启注解驱动
这一步非常关键,开启注解驱动后,在 HandlerAdapter 中会自动装配一个消息转换器:MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter
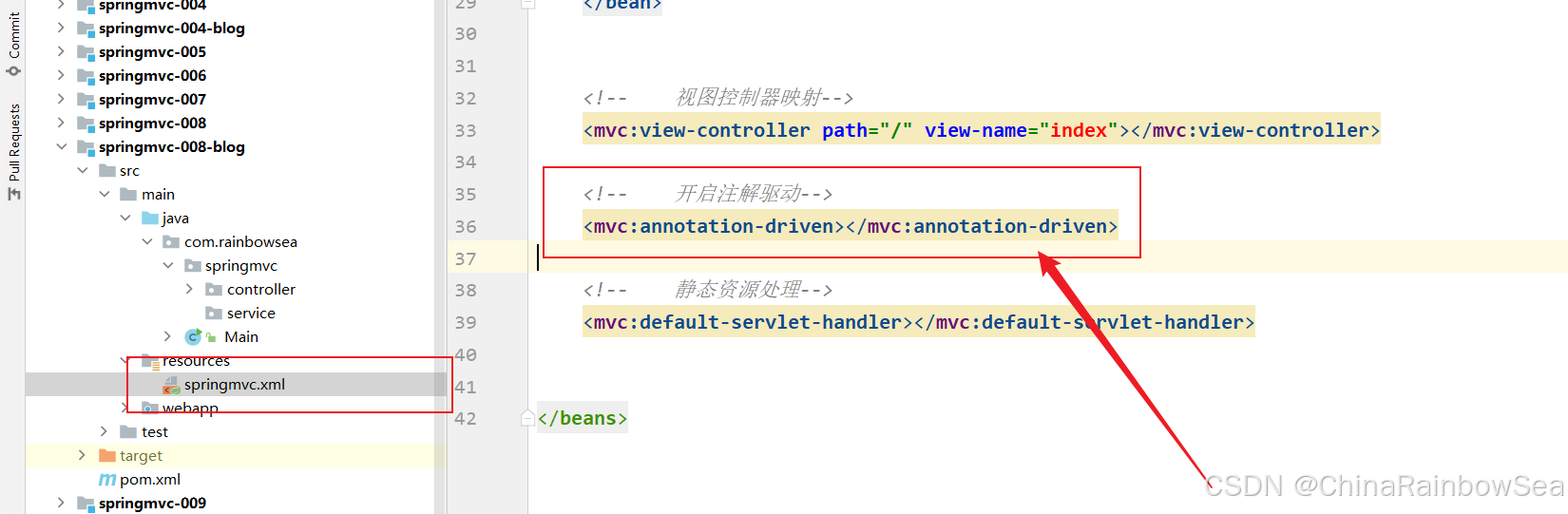
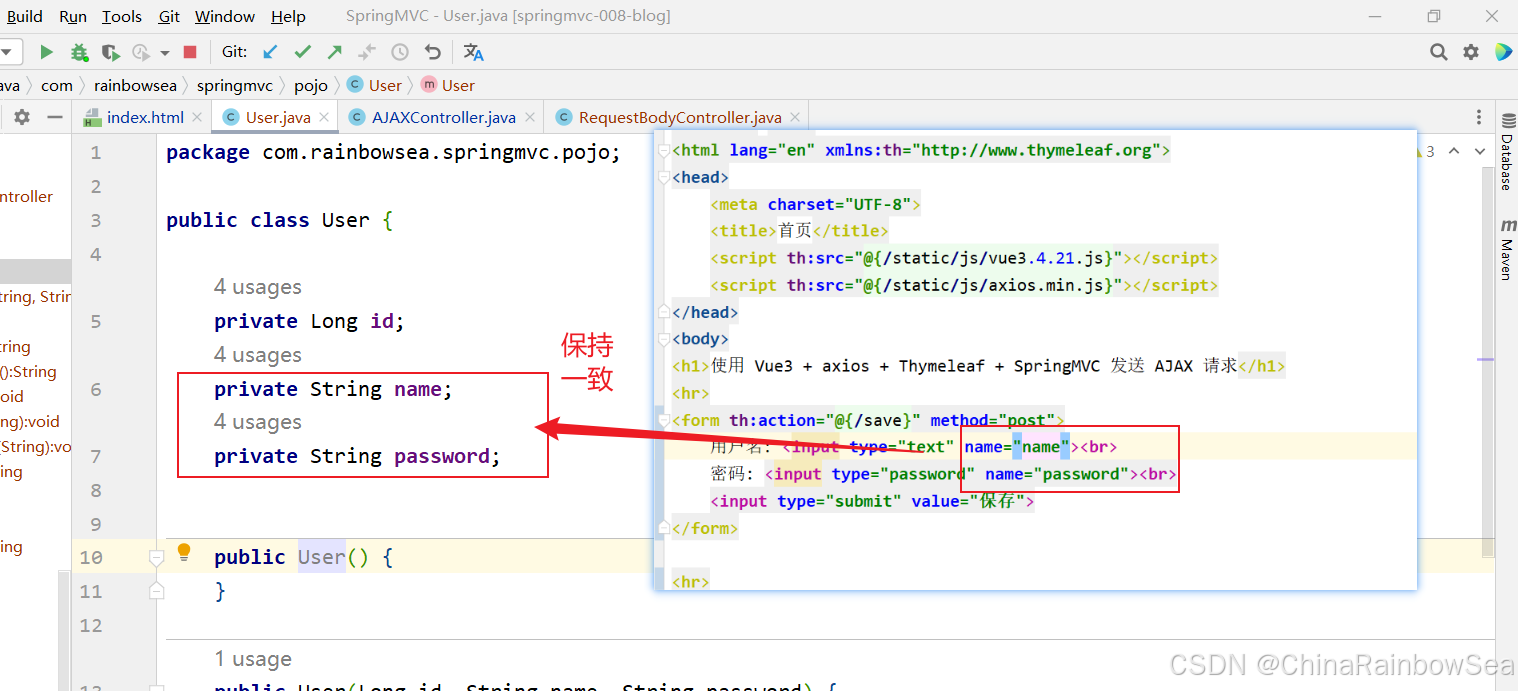
<mvc:annotation-driven/> 第三步: 我们想将以 POJO对象转换为 JOSN 格式的字符串,返回给客户端,我们需要创建一个 POJO对象。
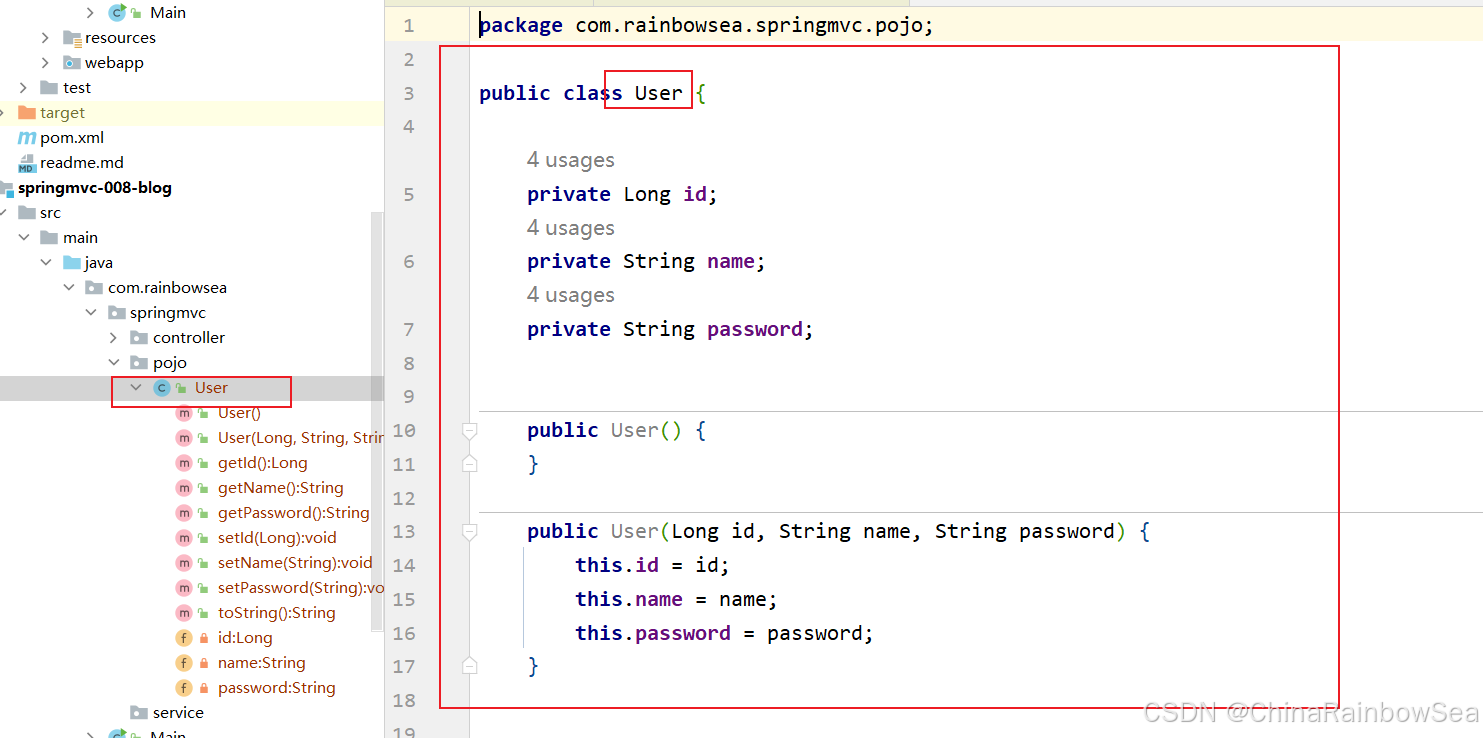
package com.rainbowsea.springmvc.pojo; public class User { private Long id; private String name; private String password; public User() { } public User(Long id, String name, String password) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.password = password; } @Override public String toString() { return "User{" + "id=" + id + ", name='" + name + '\'' + ", password='" + password + '\'' + '}'; } public Long getId() { return id; } public void setId(Long id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } } 第四步: 控制器方法使用 @ResponseBody 注解标注(非常重要),控制器方法返回这个POJO对象
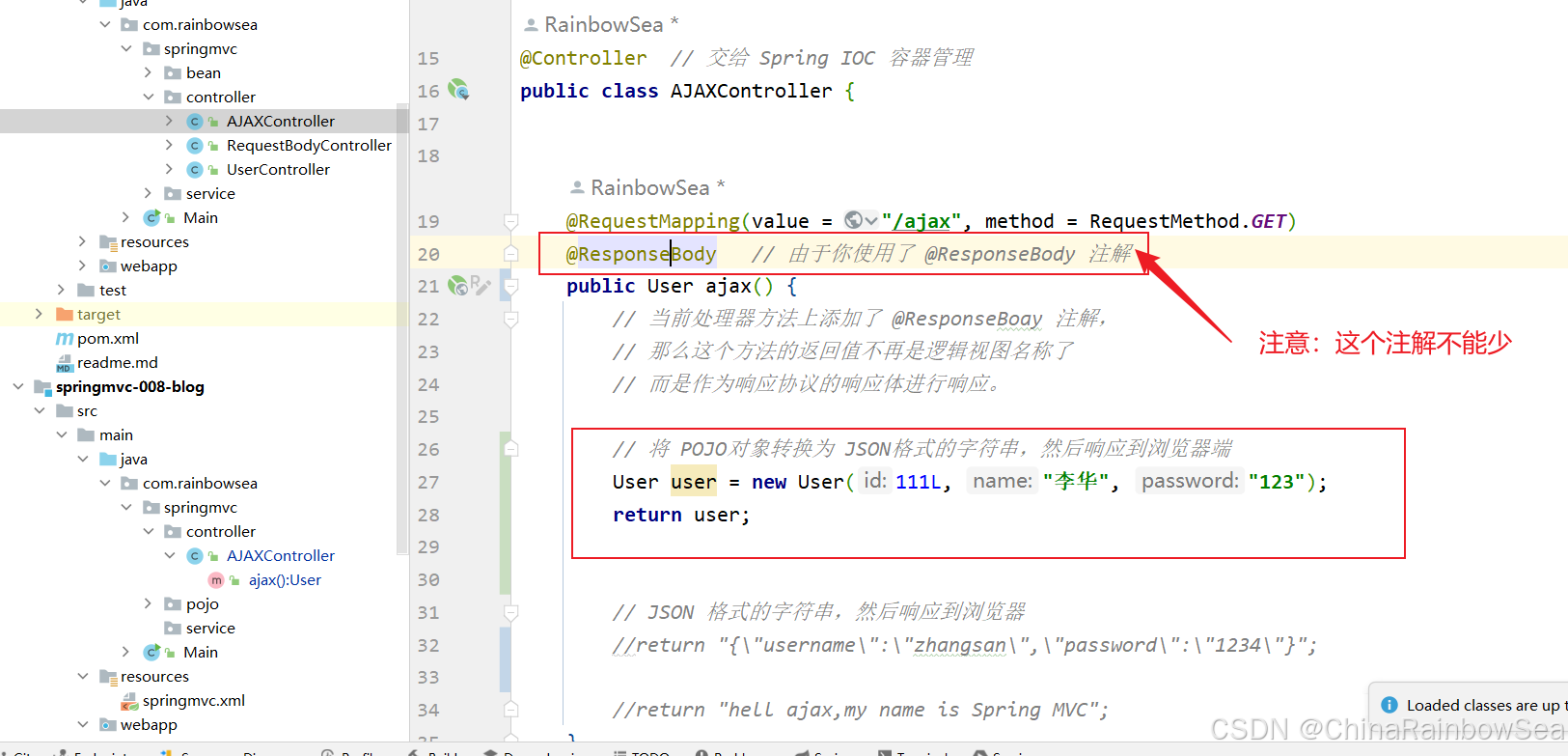
import com.rainbowsea.springmvc.pojo.User; import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PrintWriter; @Controller // 交给 Spring IOC 容器管理 public class AJAXController { @RequestMapping(value = "/ajax", method = RequestMethod.GET) @ResponseBody // 由于你使用了 @ResponseBody 注解 public User ajax() { // 当前处理器方法上添加了 @ResponseBoay 注解, // 那么这个方法的返回值不再是逻辑视图名称了 // 而是作为响应协议的响应体进行响应。 // 将 POJO对象转换为 JSON格式的字符串,然后响应到浏览器端 User user = new User(111L, "李华", "123"); return user; // JSON 格式的字符串,然后响应到浏览器 //return "{\"username\":\"zhangsan\",\"password\":\"1234\"}"; //return "hell ajax,my name is Spring MVC"; } } 启动服务器测试:http://localhost:8080/springmvc/
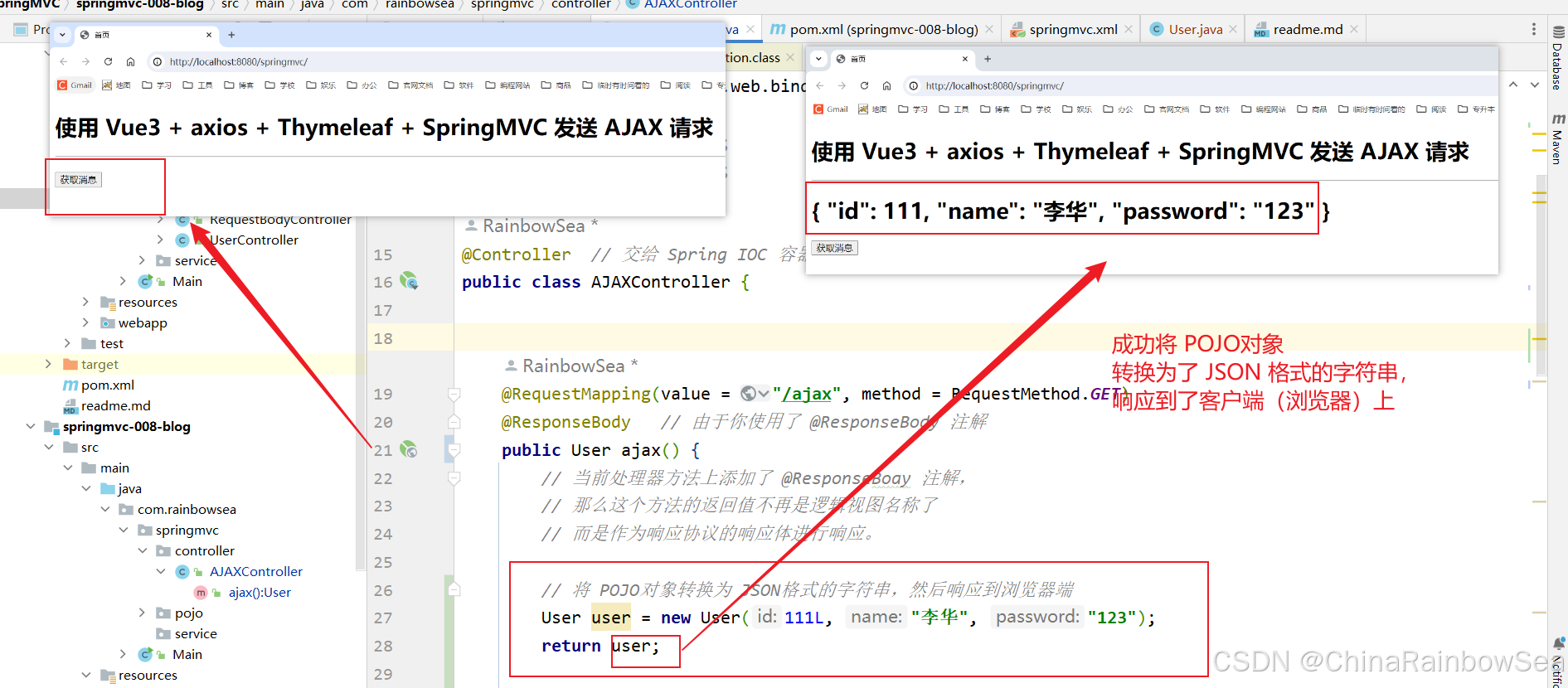
以上代码底层启动的就是:
MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter 消息转换器。它的功能很强大,可以将 POJO对象转换成 JSON格式的字符串,响应给前端。
其实这个消息转换器
MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter本质上只是比:StringHttpMessageConverter稍微多了一个 JSON 字符串的转换,其他的还是一样的。
6. 补充:@RestController = (@Controller + @ResponseBody )
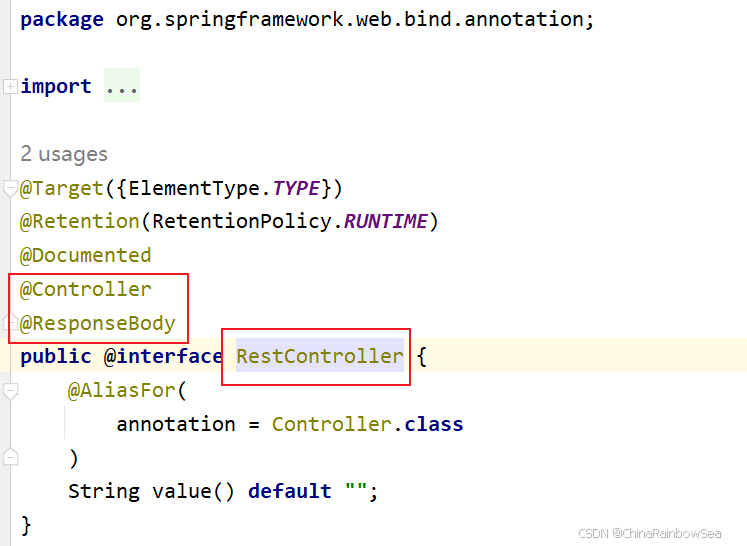
因为我们现代的开发方式都是基于 AJAX 方式的,因此 @ResponseBody注解非常重要,很常用。 为了方便,Spring MVC中提供了一个注解 @RestController。这一个注解代表了:@Controller + @ResponseBody。 @RestController标注在类上即可。
被它标注的@RestController中所有的方法上都会自动标注 @ResponseBody
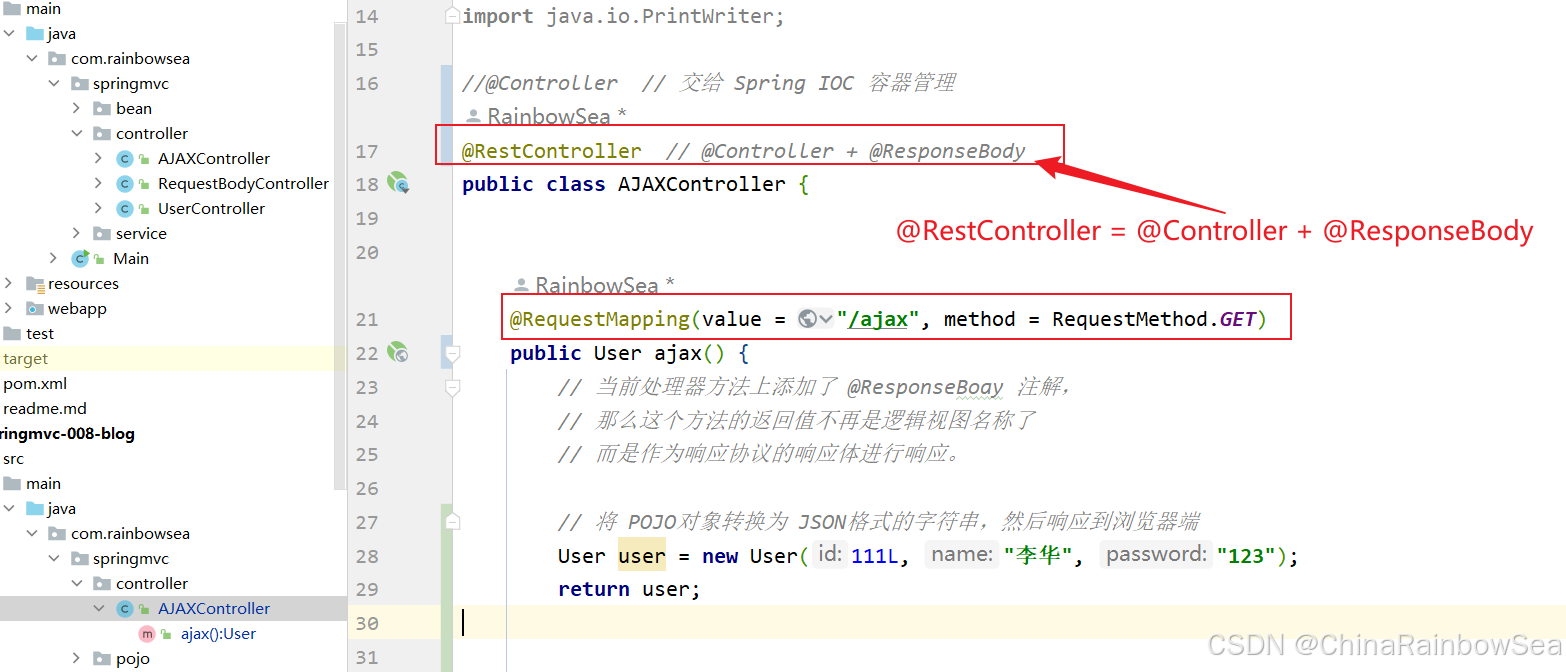
import com.rainbowsea.springmvc.pojo.User; import jakarta.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.PrintWriter; @RestController // @Controller + @ResponseBody public class AJAXController { @RequestMapping(value = "/ajax", method = RequestMethod.GET) public User ajax() { // 当前处理器方法上添加了 @ResponseBoay 注解, // 那么这个方法的返回值不再是逻辑视图名称了 // 而是作为响应协议的响应体进行响应。 // 将 POJO对象转换为 JSON格式的字符串,然后响应到浏览器端 User user = new User(111L, "李华", "123"); return user; } } 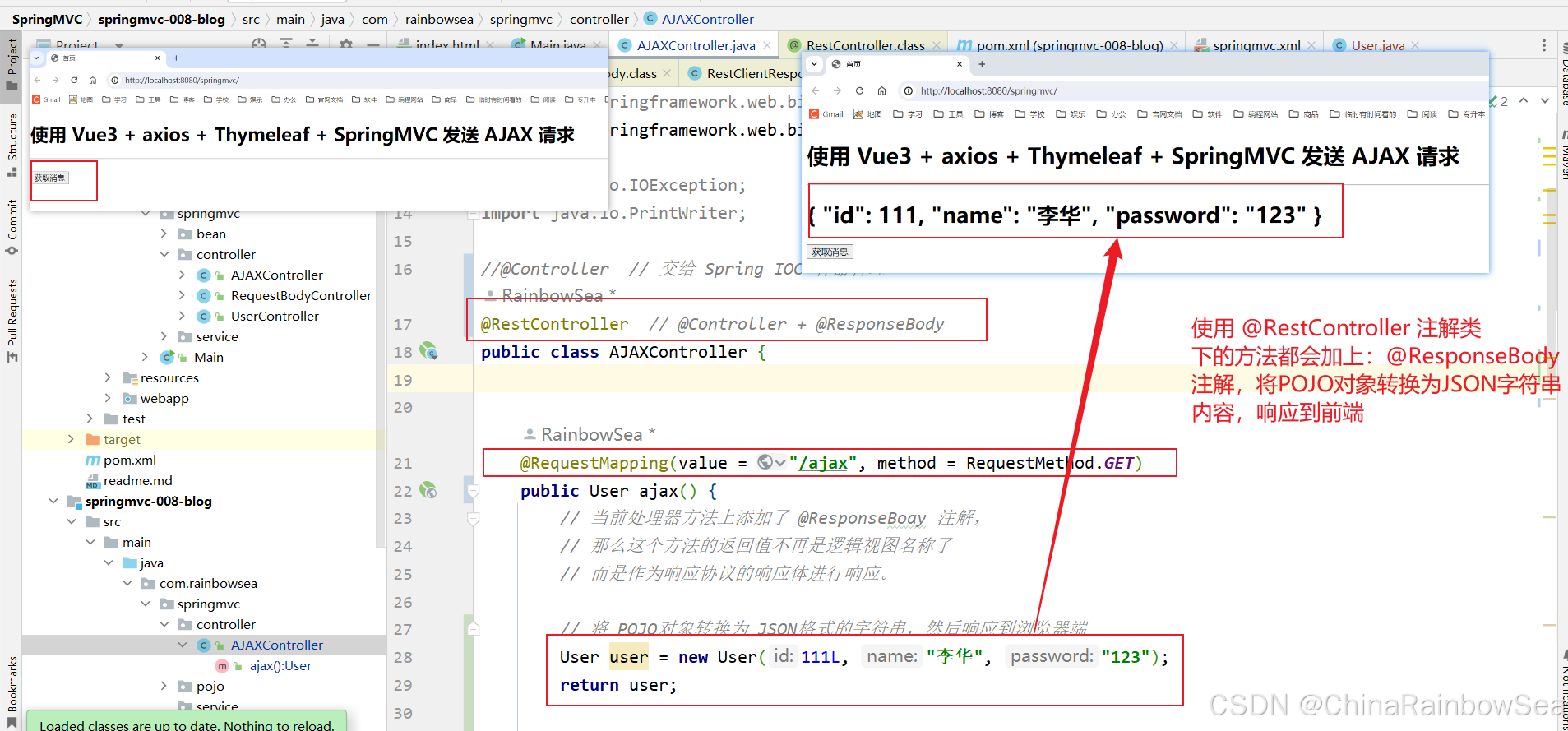
7. @RequestBody 将前端的请求体的信息转换Java程序中的 POJO对象
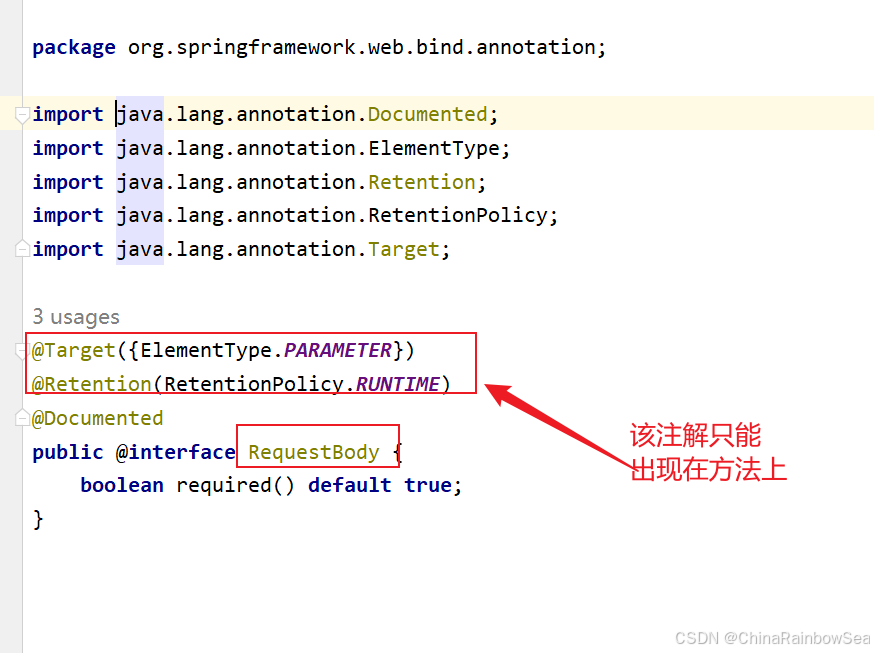
该注解只能使用在处理器方法的形参上,
这个注解的作用是直接将请求体传递给Java程序,在Java程序中可以直接使用一个String 类型的变量接收这个请求体的内容。
底层使用的HTTP消息转换器是:FormHttpMessageConvertor
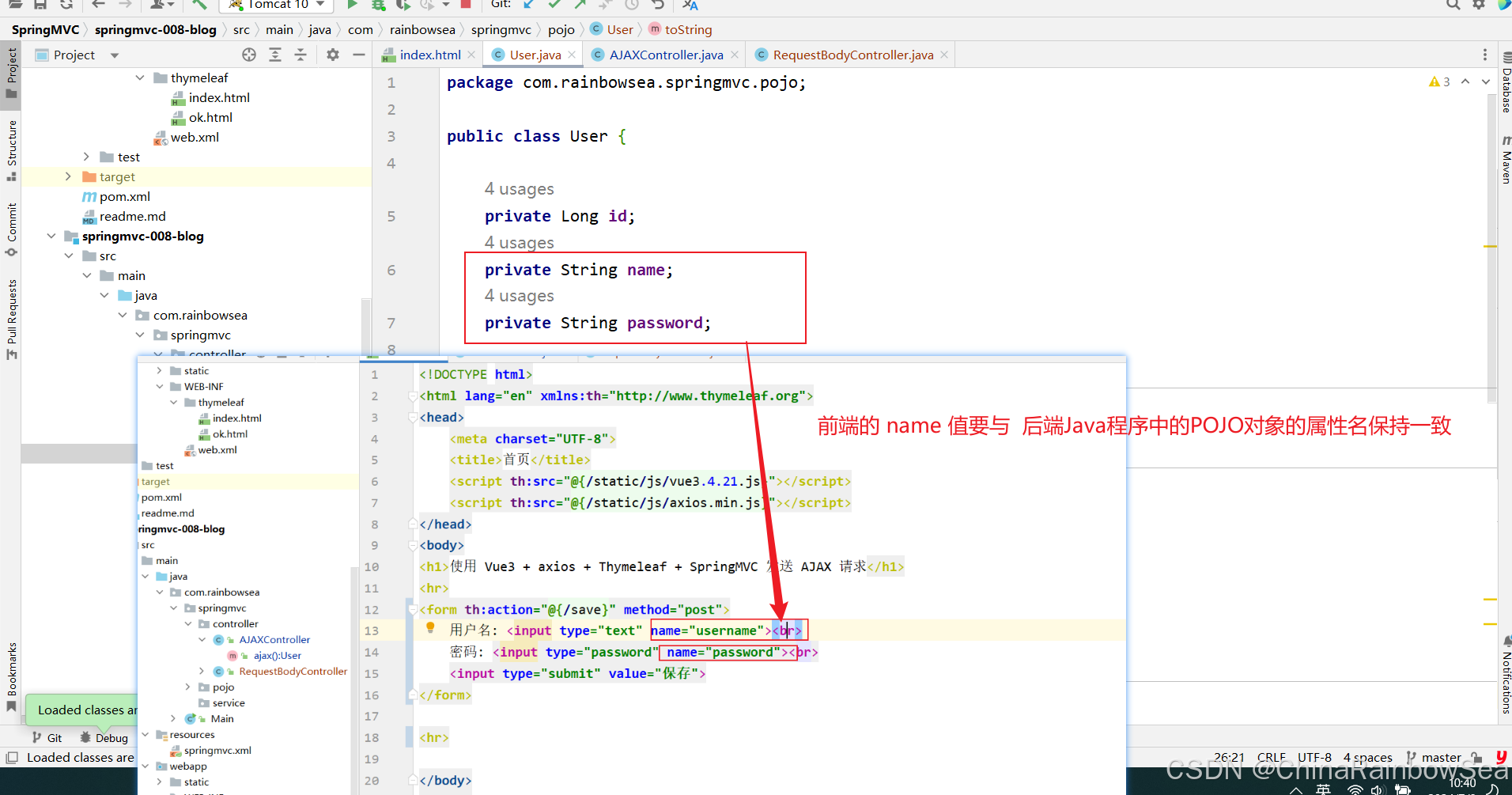
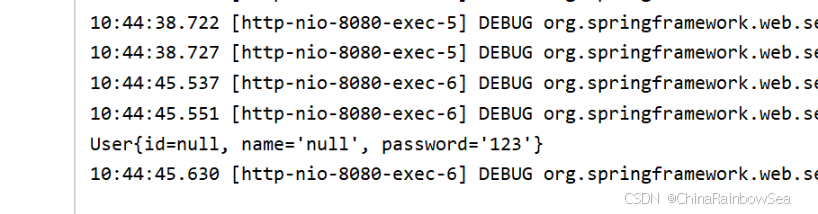
没有保持一致的话,会赋值失败。
在没有使用 @RequestBody 这个注解的时候:
当请求体提交的数据是:
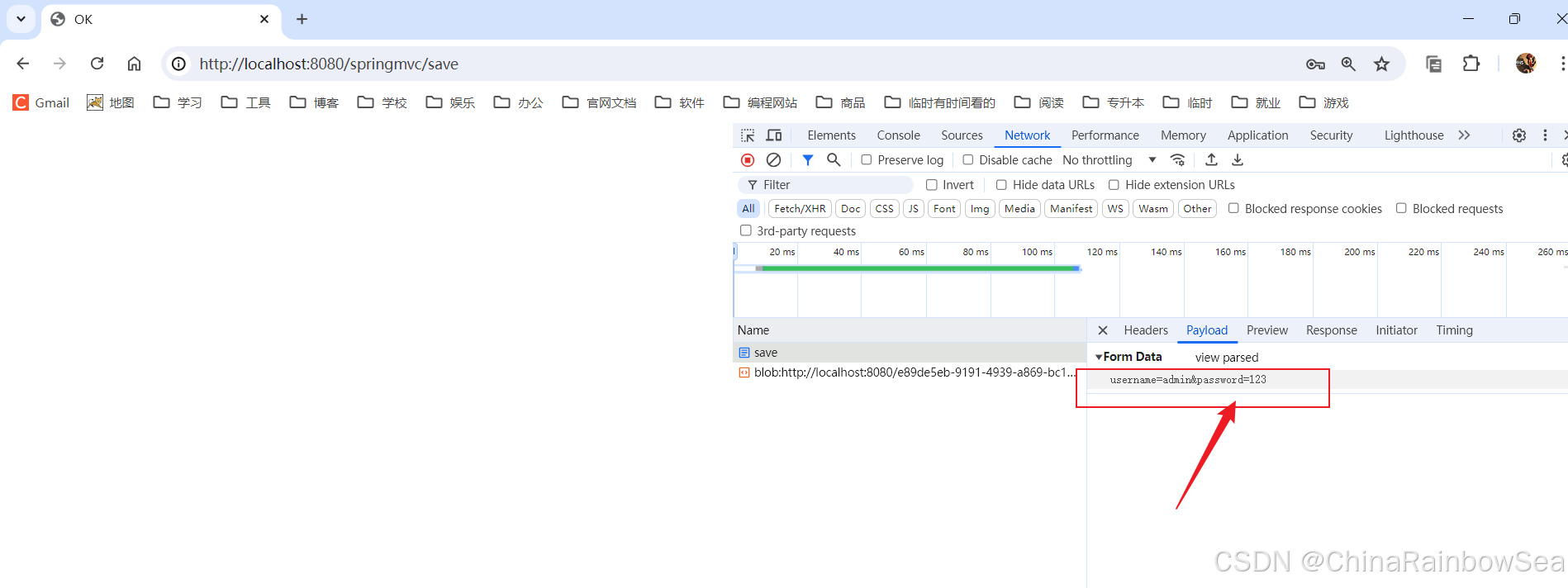
username=admin&password=123 那么 Spring MVC会自动使用 FormHttpMessageConverter消息转换器,将请求体转换成 对应的 POJO对象,这里是 user对象。
package com.rainbowsea.springmvc.controller; import com.rainbowsea.springmvc.pojo.User; import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders; import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod; import org.springframework.http.MediaType; import org.springframework.http.RequestEntity; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; import java.net.URI; @Controller // 交给 Spring IOC 容器管理 public class RequestBodyController { @RequestMapping(value = "/save", method = RequestMethod.POST) public String saveUser( User user) { // @RequestBody 将 将请求体转换成user对象。在方法上使用 System.out.println(user); // 不是逻辑视图,是普通字符串,因为前端发送的请求是 AJAX 请求 return "ok"; } } 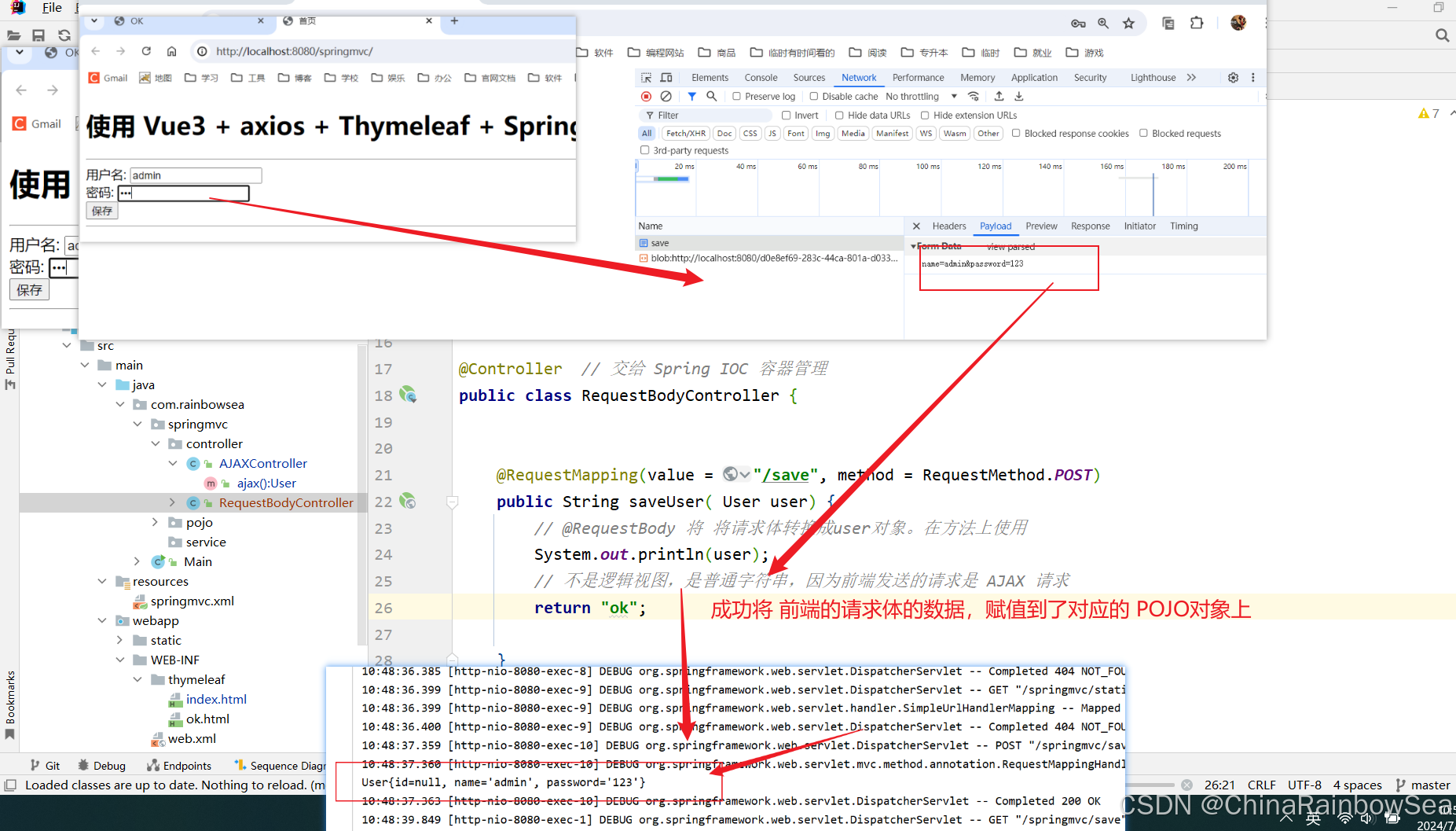
当使用这个注解的时候:这个注解只能出现在方法的参数上。
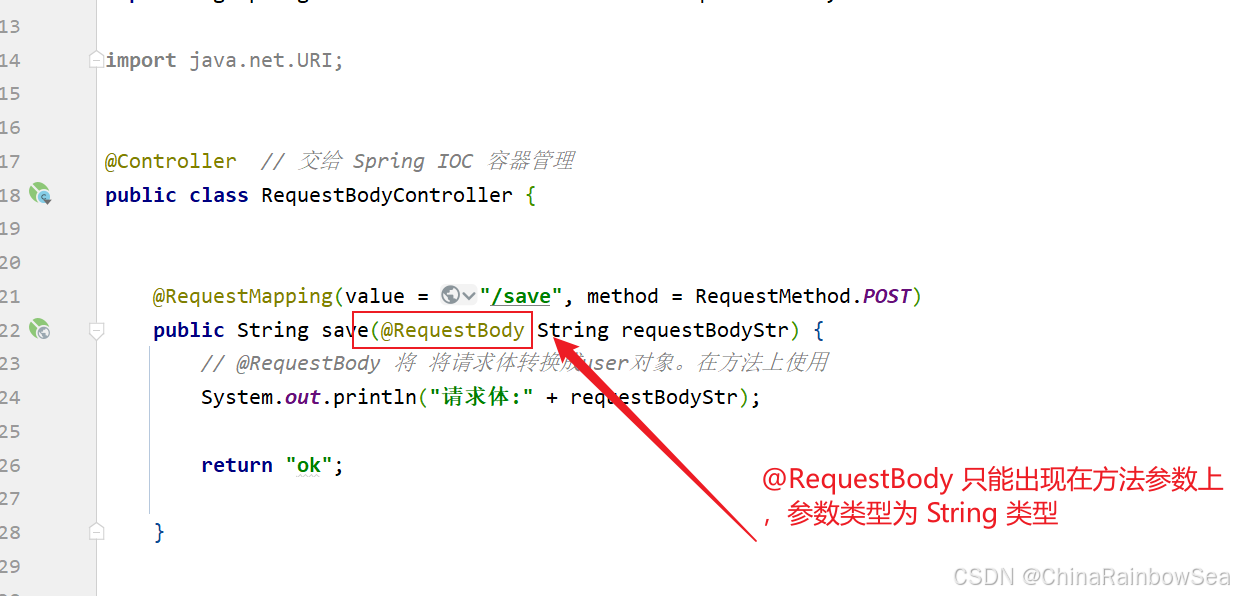
import com.rainbowsea.springmvc.bean.User; import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders; import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod; import org.springframework.http.MediaType; import org.springframework.http.RequestEntity; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; import java.net.URI; @Controller // 交给 Spring IOC 容器管理 public class RequestBodyController { @RequestMapping(value = "/save", method = RequestMethod.POST) public String save(@RequestBody String requestBodyStr) { // @RequestBody 将 将请求体转换成user对象。在方法上使用 System.out.println("请求体:" + requestBodyStr); return "ok"; } } 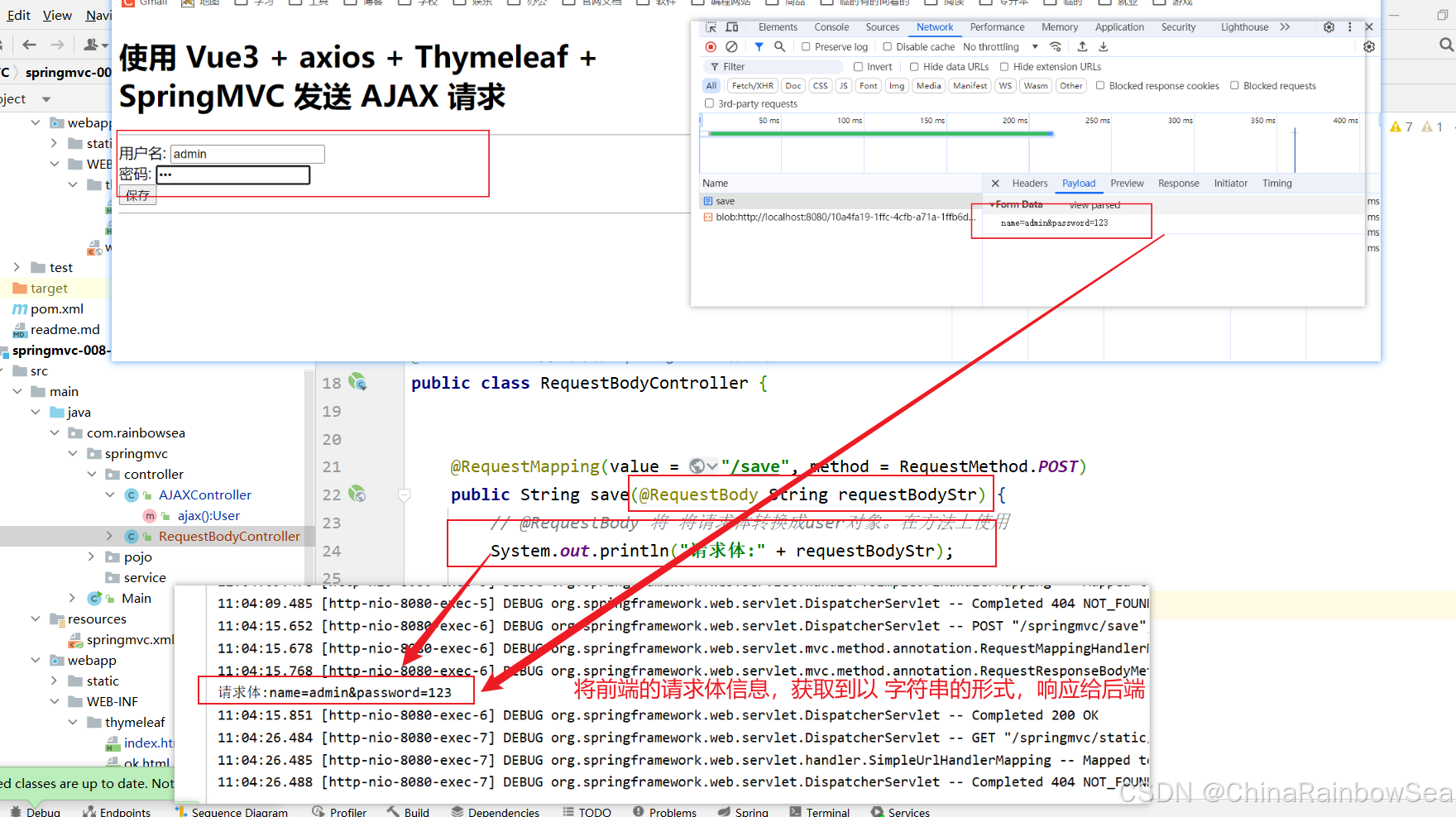
Spring MVC仍然会使用 FormHttpMessageConverter消息转换器,将请求体直接以字符串形式传递给 requestBodyStr 变量。
7.1 MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter 将前端提交的 JSON 格式的字符串,转换为 Java程序中的POJO对象
如果在请求体中提交的是一个 JSON 格式的字符串,这个 JSON 字符串传递给 Spring MVC 之后,能不能将 JSON 字符串转换成 POJO 对象呢?
答案是:可以的
此时必须使用
@RequetBody注解来完成,并且底层使用的消息转换器是:MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter。实现步骤如下:
- 第一步:引入 jackson 依赖
- 第二步:开启注解驱动
- 第三步:创建POJO类,将POJO类作为控制器方法的参数,并使用 @RequestBody 注解标注该参数。
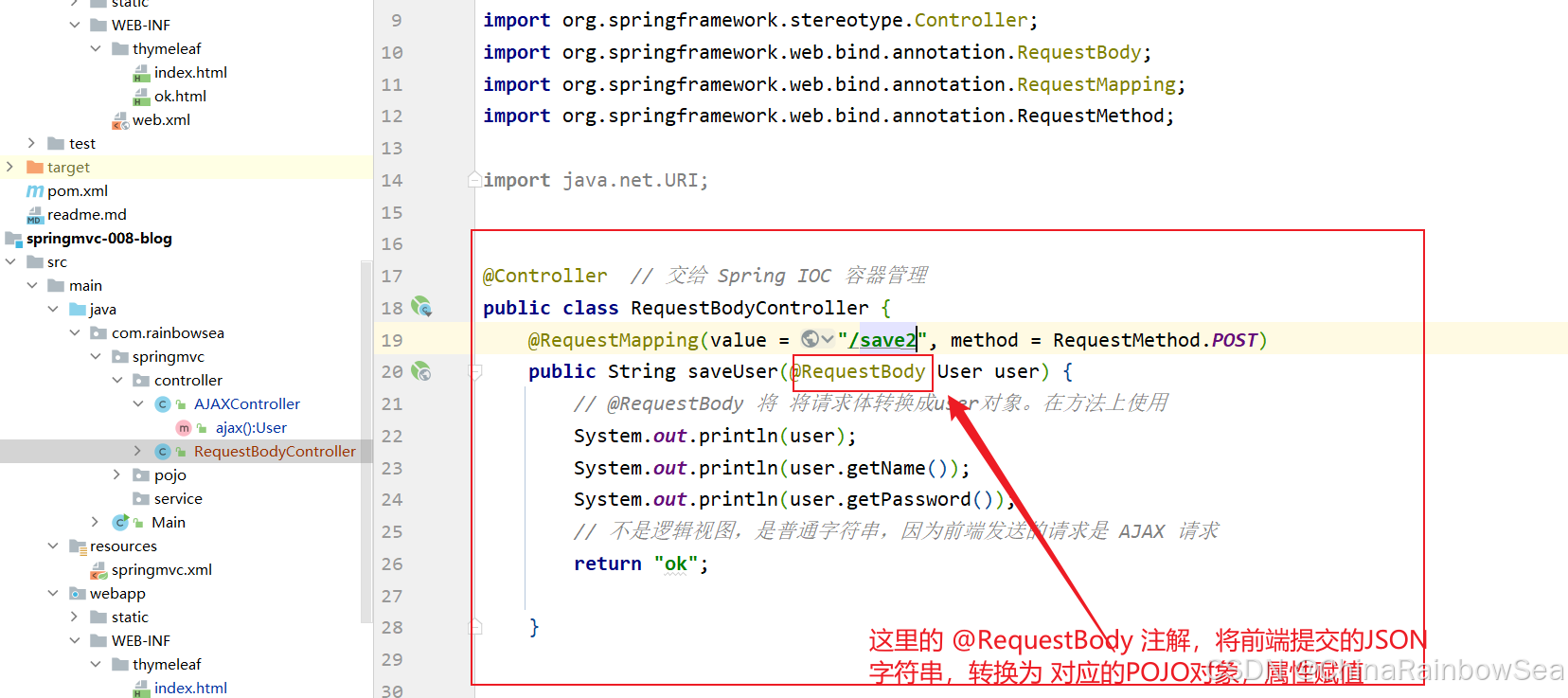
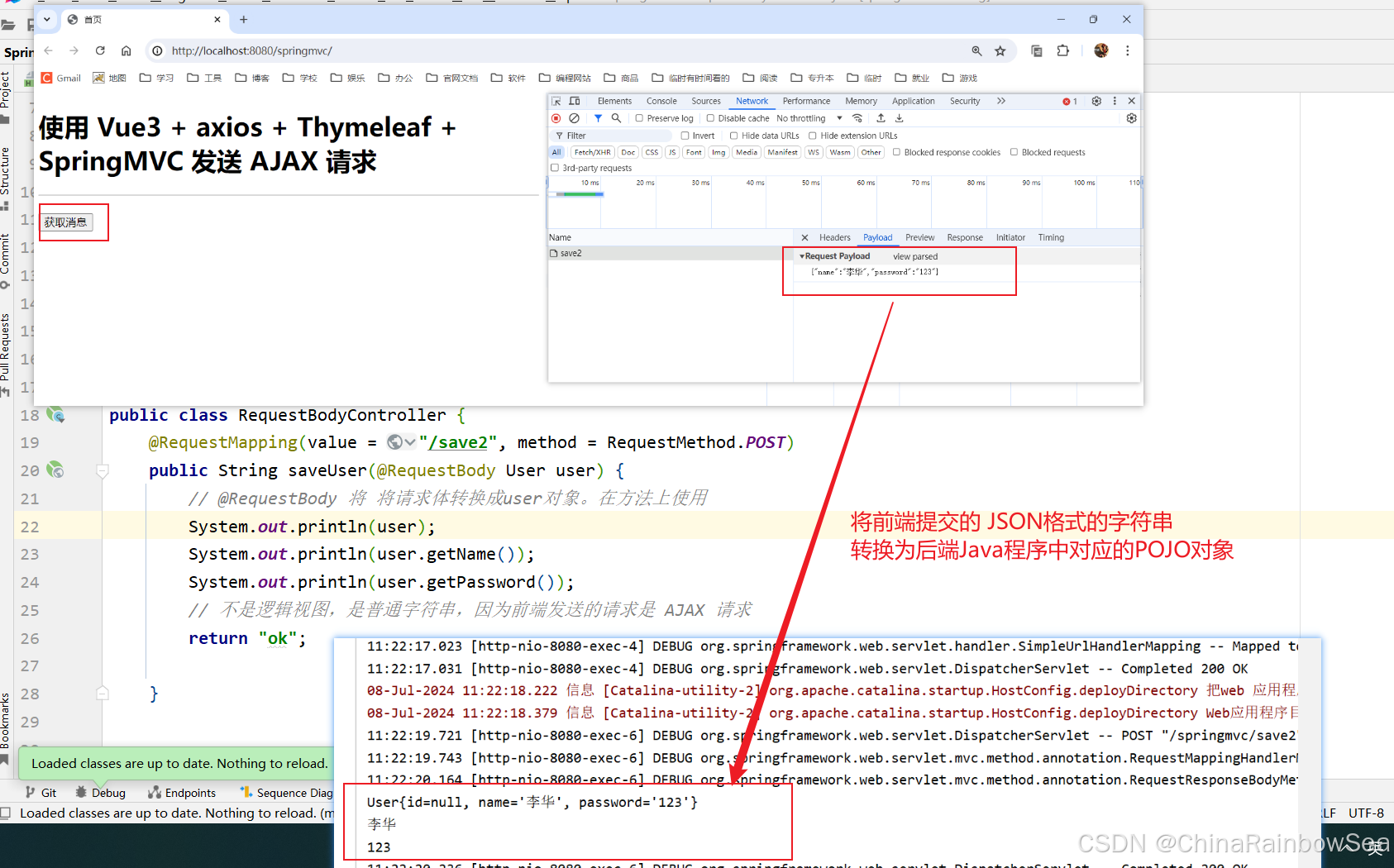
import com.rainbowsea.springmvc.pojo.User; import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders; import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod; import org.springframework.http.MediaType; import org.springframework.http.RequestEntity; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; import java.net.URI; @Controller // 交给 Spring IOC 容器管理 public class RequestBodyController { @RequestMapping(value = "/save2", method = RequestMethod.POST) public String saveUser(@RequestBody User user) { // @RequestBody 将 将请求体转换成user对象。在方法上使用 System.out.println(user); System.out.println(user.getName()); System.out.println(user.getPassword()); // 不是逻辑视图,是普通字符串,因为前端发送的请求是 AJAX 请求 return "ok"; } } 第四步:在前端 请求体中提交 json格式 的数据。
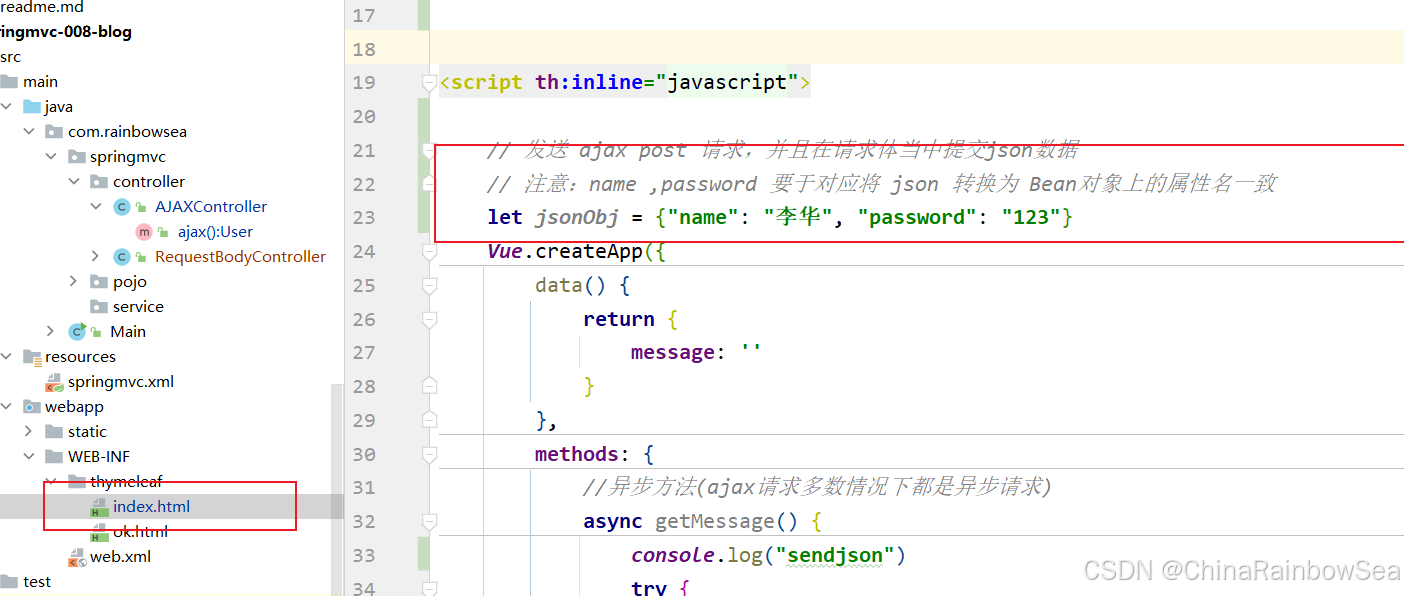
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>首页</title> <script th:src="@{/static/js/vue3.4.21.js}"></script> <script th:src="@{/static/js/axios.min.js}"></script> </head> <body> <h1>使用 Vue3 + axios + Thymeleaf + SpringMVC 发送 AJAX 请求</h1> <hr> <div id="app"> <h1>{{message}}</h1> <button @click="getMessage">获取消息</button> </div> <script th:inline="javascript"> // 发送 ajax post 请求,并且在请求体当中提交json数据 // 注意:name ,password 要于对应将 json 转换为 Bean对象上的属性名一致 let jsonObj = {"name": "李华", "password": "123"} Vue.createApp({ data() { return { message: '' } }, methods: { //异步方法(ajax请求多数情况下都是异步请求) async getMessage() { console.log("sendjson") try { // 发送 ajax请求 // await axios.get('/springmvc/ajax') //动态获取 应用的根/springmvc/ const response = await axios.post([[@{/}]] + 'save2',JSON.stringify(jsonObj),{ headers : { // 请求体的状态信息 "Content-Type" : "application/json" } }) // 将返回的数据交给 message this.message = response.data } catch (e) { console.error(e) } } } }).mount("#app") </script> </body> </html> 测试结果:
8. RequestEntity 类
RequestEntity 不是一个注解,是一个普通的类,这个类的实例封装了整个请求协议:包括请求行,请求头,请求体所有信息。
该 RequestEntity 类出现在控制器方法的参数上。
使用测试:如下是对应的 html 页面
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>首页</title> <script th:src="@{/static/js/vue3.4.21.js}"></script> <script th:src="@{/static/js/axios.min.js}"></script> </head> <body> <h1>使用 Vue3 + axios + Thymeleaf + SpringMVC 发送 AJAX 请求</h1> <hr> <div id="app"> <h1>{{message}}</h1> <button @click="getMessage">获取消息</button> </div> <script th:inline="javascript"> // 发送 ajax post 请求,并且在请求体当中提交json数据 // 注意:name ,password 要于对应将 json 转换为 Bean对象上的属性名一致 let jsonObj = {"name": "李华", "password": "123"} Vue.createApp({ data() { return { message: '' } }, methods: { //异步方法(ajax请求多数情况下都是异步请求) async getMessage() { console.log("sendjson") try { // 发送 ajax请求 // await axios.get('/springmvc/ajax') //动态获取 应用的根/springmvc/ const response = await axios.post([[@{/}]] + 'save2',JSON.stringify(jsonObj),{ headers : { // 请求体的状态信息 "Content-Type" : "application/json" } }) // 将返回的数据交给 message this.message = response.data } catch (e) { console.error(e) } } } }).mount("#app") </script> </body> </html> 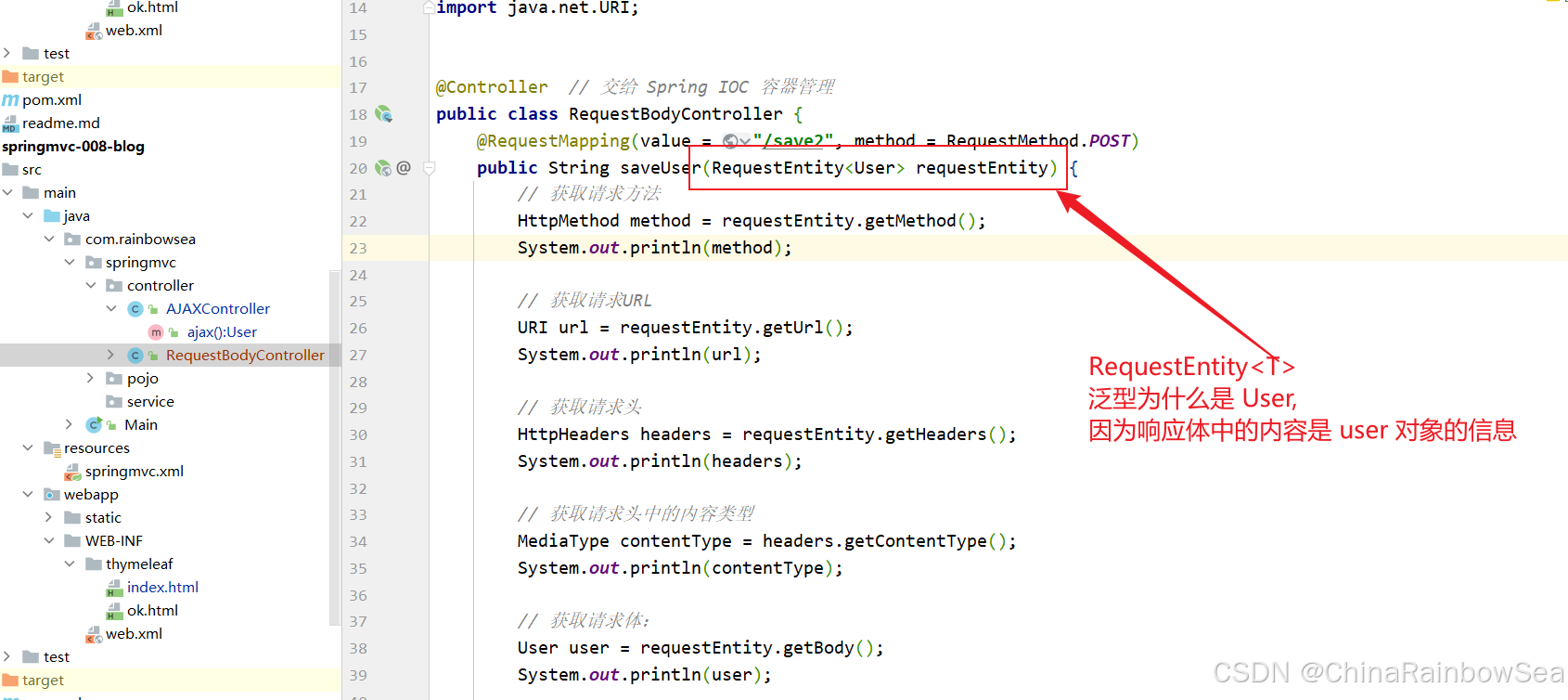
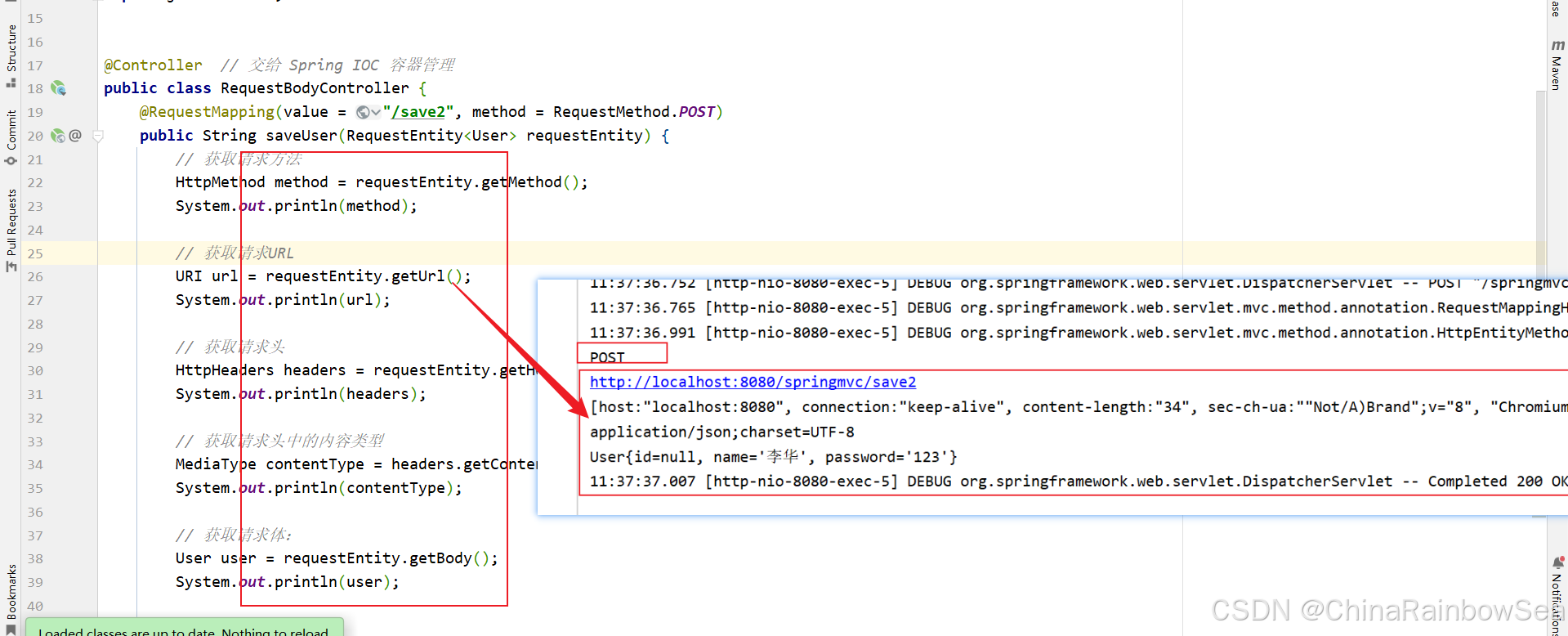
package com.rainbowsea.springmvc.controller; import com.rainbowsea.springmvc.pojo.User; import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders; import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod; import org.springframework.http.MediaType; import org.springframework.http.RequestEntity; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; import java.net.URI; @Controller // 交给 Spring IOC 容器管理 public class RequestBodyController { @RequestMapping(value = "/save2", method = RequestMethod.POST) public String saveUser(RequestEntity<User> requestEntity) { // 获取请求方法 HttpMethod method = requestEntity.getMethod(); System.out.println(method); // 获取请求URL URI url = requestEntity.getUrl(); System.out.println(url); // 获取请求头 HttpHeaders headers = requestEntity.getHeaders(); System.out.println(headers); // 获取请求头中的内容类型 MediaType contentType = headers.getContentType(); System.out.println(contentType); // 获取请求体: User user = requestEntity.getBody(); System.out.println(user); return "ok"; } } 测试结果:
9. ResponseEntity 类
ResponseEntity 不是注解,而是一个类。使用该类的实例可以封装响应协议,包括:状态行,响应头,响应体。 也就是说:如果你想定制属于自己的响应协议,可以使用该类。
举例:这里假如我们有这么一个需求:
前端提交一个 id,后端根据 id 进行查询,如果返回 null,请在前端显示 404 错误,如果返回不是 null,则输出返回 User 对象。
前端页面设置:
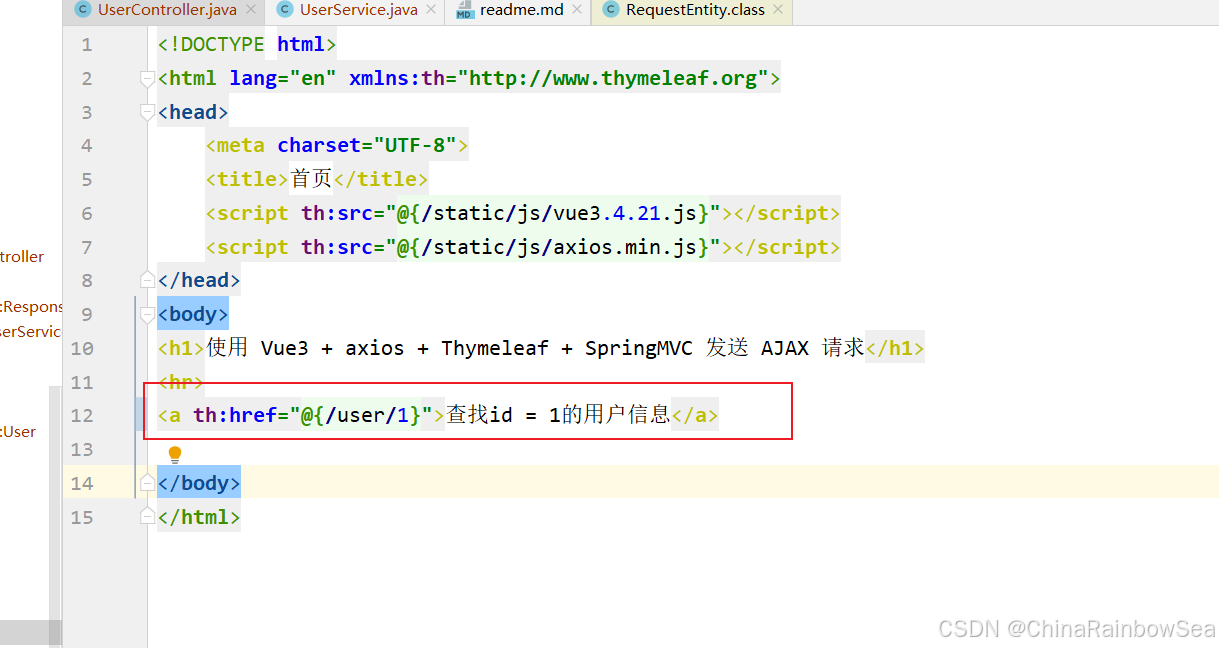
后端处理:
首先编写一个 Service 进行一个查询处理,这里我们就简单判断一下,就不连接数据库了。
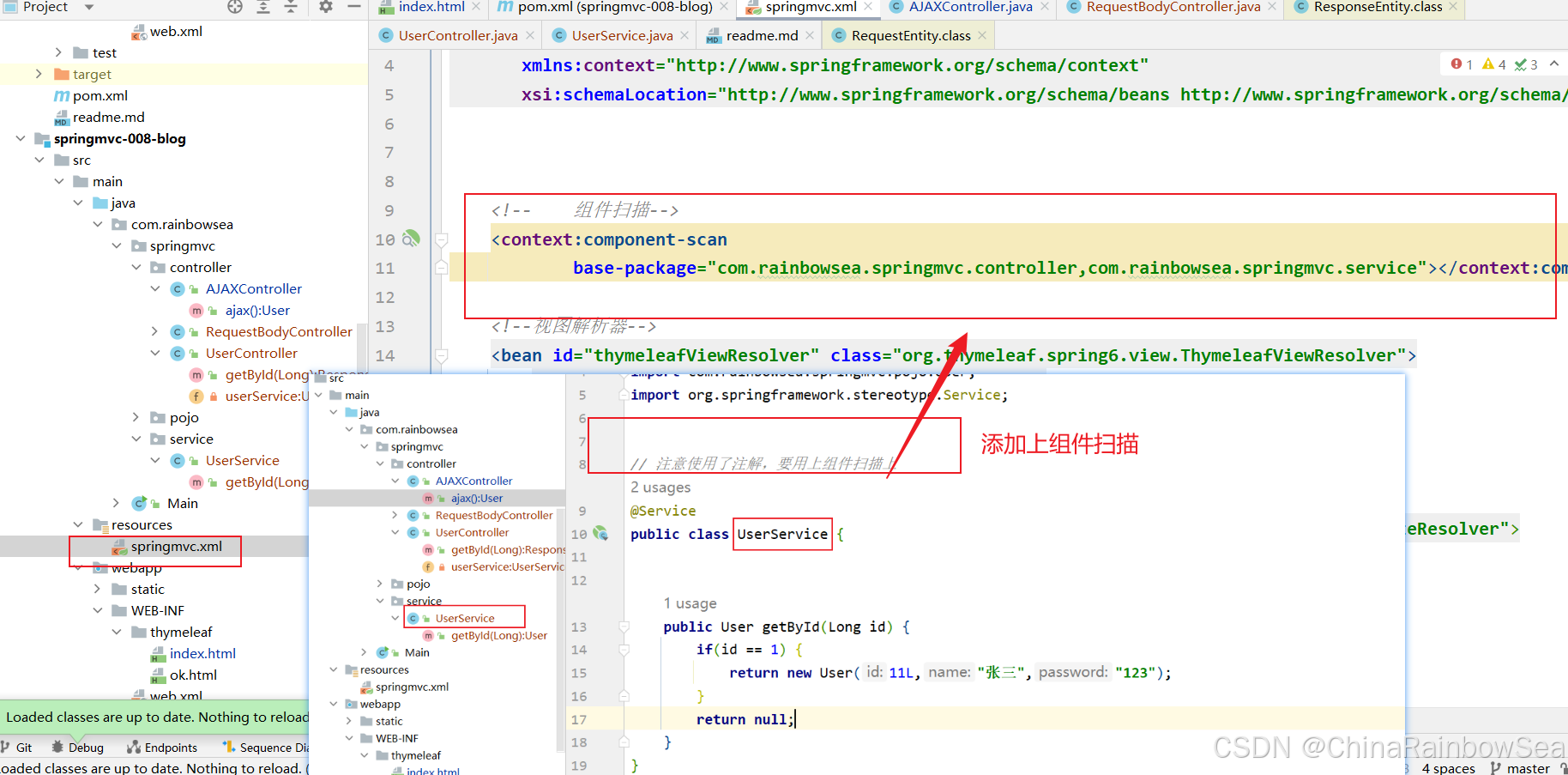
package com.rainbowsea.springmvc.service; import com.rainbowsea.springmvc.pojo.User; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; // 注意使用了注解,要用上组件扫描上 @Service public class UserService { public User getById(Long id) { if(id == 1) { return new User(11L,"张三","123"); } return null; } } 最后是对应 Controller 控制器的编写
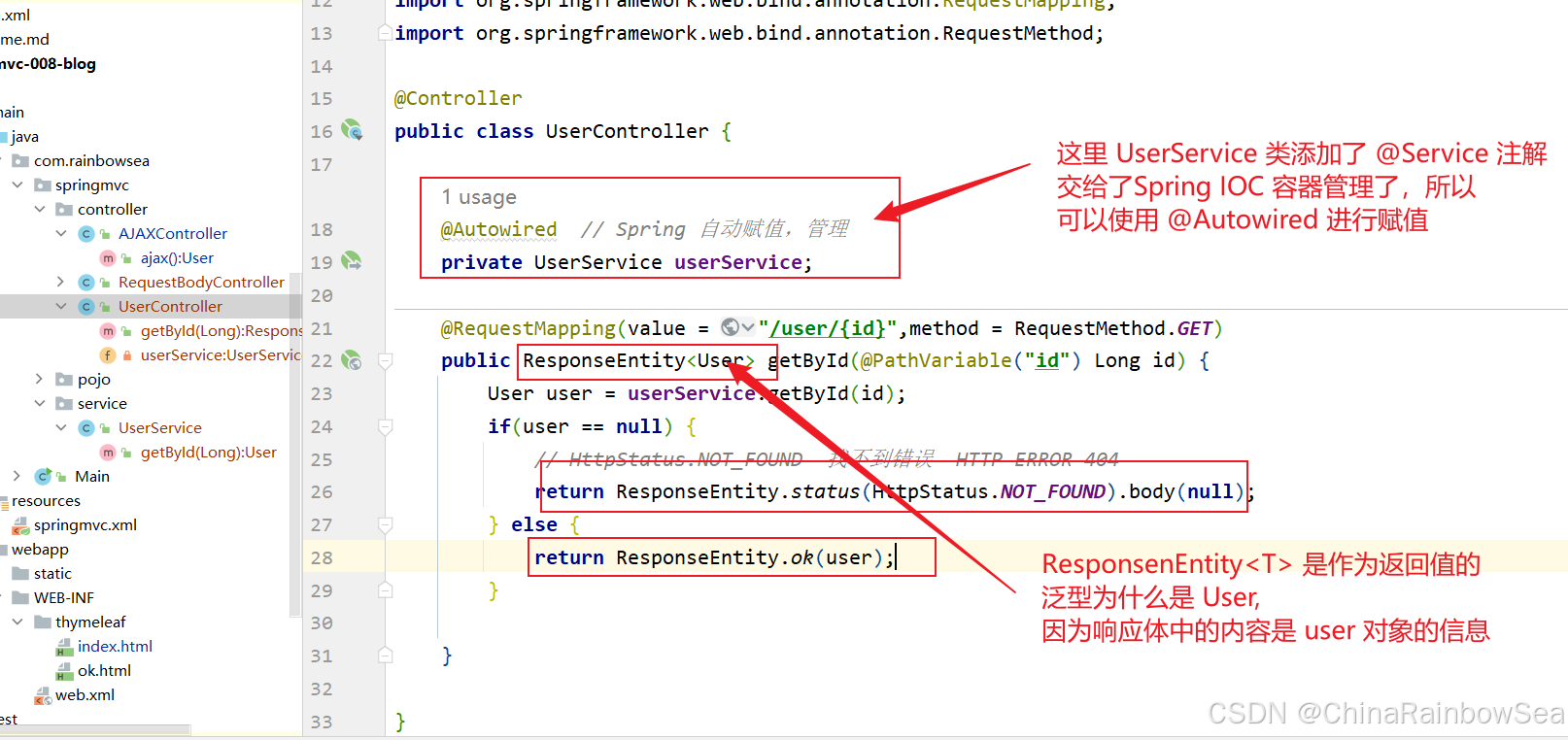
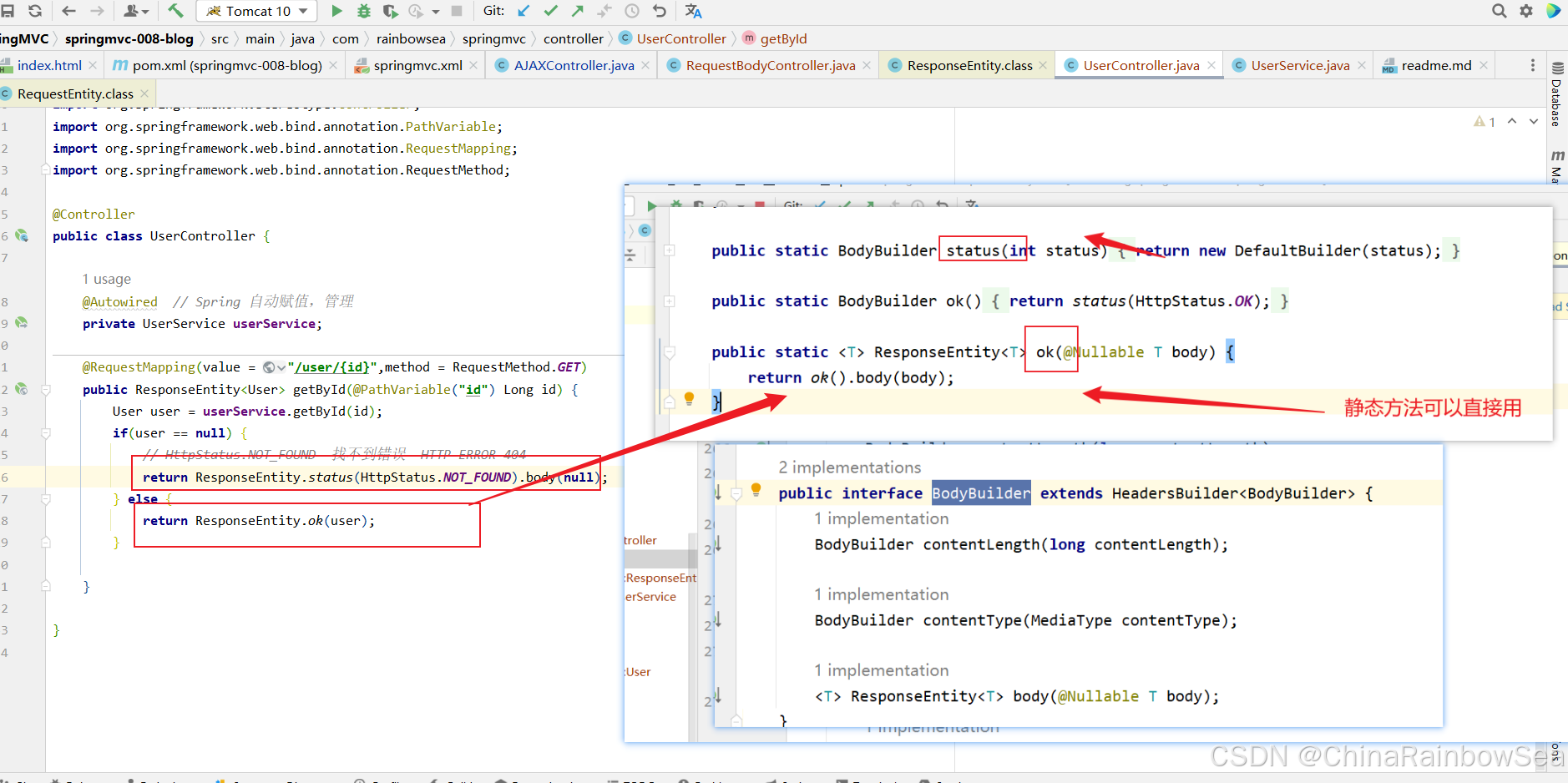
package com.rainbowsea.springmvc.controller; import com.rainbowsea.springmvc.pojo.User; import com.rainbowsea.springmvc.service.UserService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus; import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod; @Controller public class UserController { @Autowired // Spring 自动赋值,管理 private UserService userService; @RequestMapping(value = "/user/{id}",method = RequestMethod.GET) public ResponseEntity<User> getById(@PathVariable("id") Long id) { User user = userService.getById(id); if(user == null) { // HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND 找不到错误 HTTP ERROR 404 return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND).body(null); } else { return ResponseEntity.ok(user); } } } 测试:当用户存在时
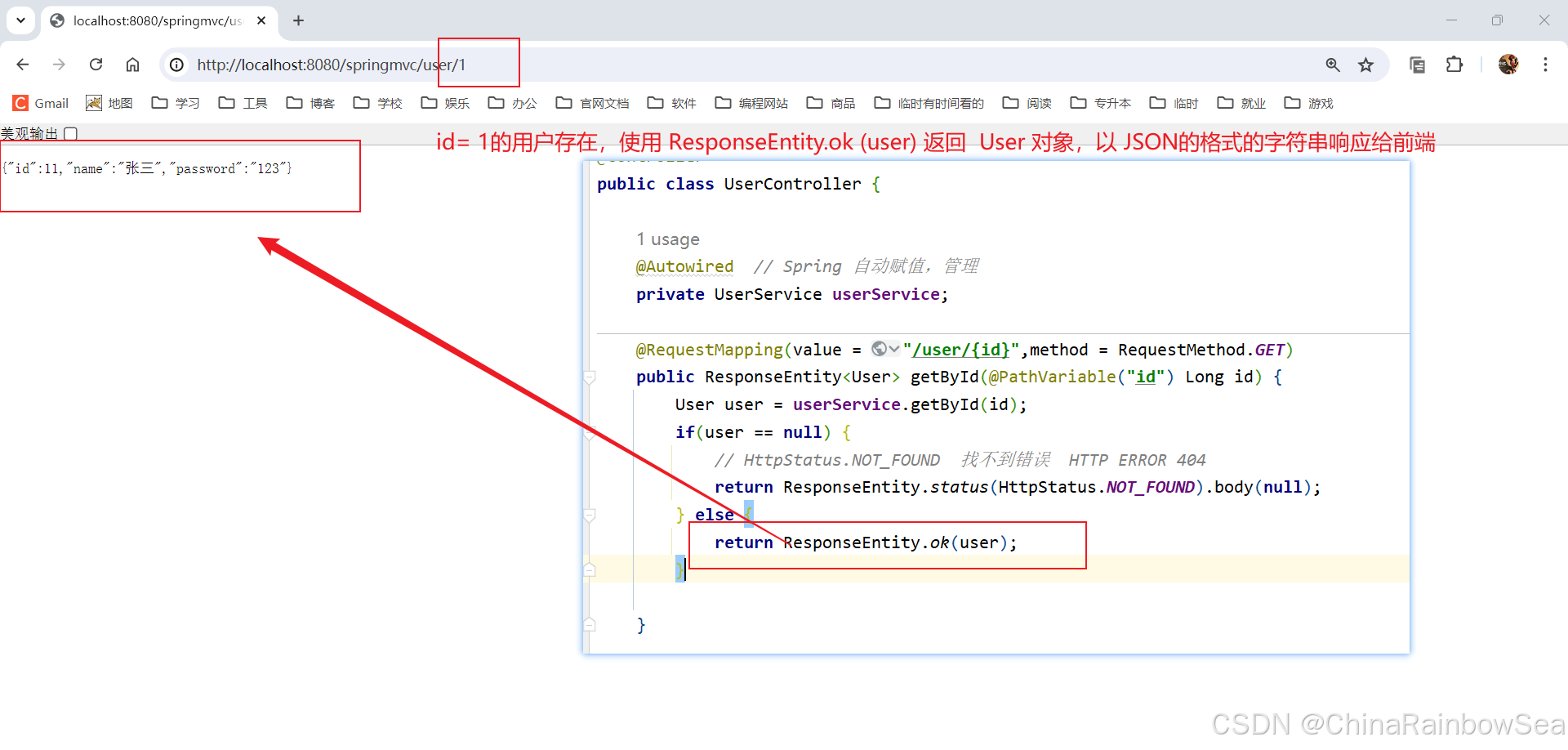
测试:当用户不存在时
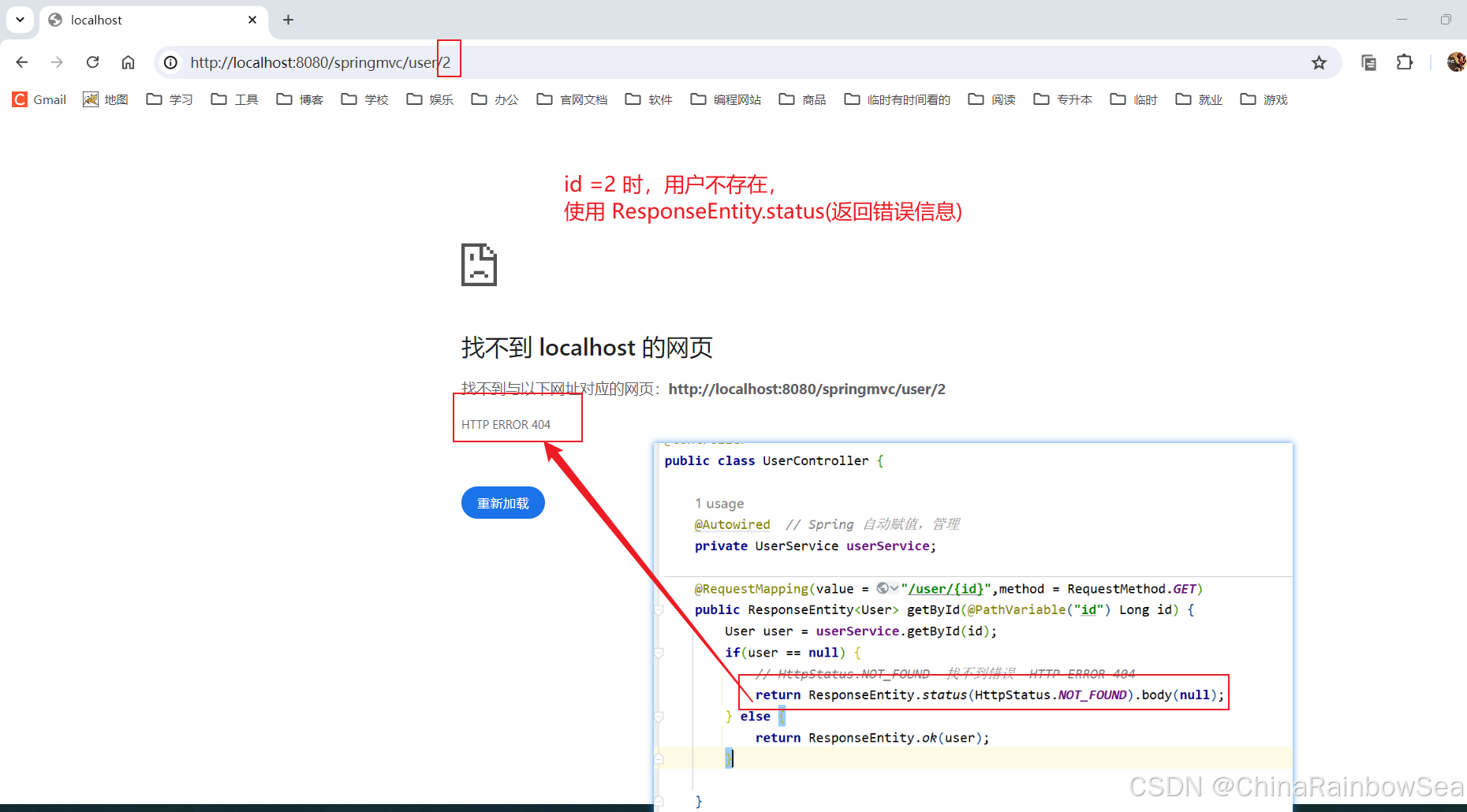
10. 总结:
- HTTP 协议包括
请求协议和响应协议。- @ResponseBody 将服务器端的 return 返回值转化为“字符串(JSON格式的字符串)”再返回给客户端。
- @ResponseBody 将POJO对象 以 JSON格式 的字符串响应给浏览器
- 第一种方式:自己写代码 将POJO对象 转换成JSON格式的字符串(如上面所示 return “{“username”:“zhangsan”,“password”:“1234”}”; ),用上面的方式直接 return即可。
- 第二种方式:启用
MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter消息转换器。- 需要注意的时需要添加:涉及到 JSON格式的转换,都需要导入相关的jar包,以及开启注解驱动。
- @RestController = (@Controller + @ResponseBody ), 被它标注的@RestController中所有的方法上都会自动标注 @ResponseBody
- @RequestBody 将前端的请求体的信息转换Java程序中的 POJO对象,该注解只能使用在处理器方法的形参上,还可以将 前端的请求体直接以字符串形式传递给 requestBodyStr 变量。
@RequetBody注解将前端提交的 JSON 格式的字符串,转换为 Java程序中的POJO对象,涉及到 JSON格式的转换,都需要导入相关的jar包,以及开启注解驱动。- RequestEntity 类是一个普通的类,这个类的实例封装了整个请求协议:包括请求行,请求头,请求体所有信息。 该 RequestEntity 类出现在控制器方法的参数上。
- ResponseEntity 是一个类。使用该类的实例可以封装响应协议,包括:状态行,响应头,响应体。 也就是说:如果你想定制属于自己的响应协议,可以使用该类。
- 无论是那个,只要涉及到 JSON格式的转换,都需要导入相关的jar包,以及开启注解驱动。
11. 最后:
“在这个最后的篇章中,我要表达我对每一位读者的感激之情。你们的关注和回复是我创作的动力源泉,我从你们身上吸取了无尽的灵感与勇气。我会将你们的鼓励留在心底,继续在其他的领域奋斗。感谢你们,我们总会在某个时刻再次相遇。”