heap【堆】掌握
手写上浮、下沉、建堆函数
对一组数进行堆排序
直接使用接口函数heapq
什么是堆???堆是一个二叉树。也就是有两个叉。下面是一个大根堆:
大根堆的每一个根节点比他的子节点都大
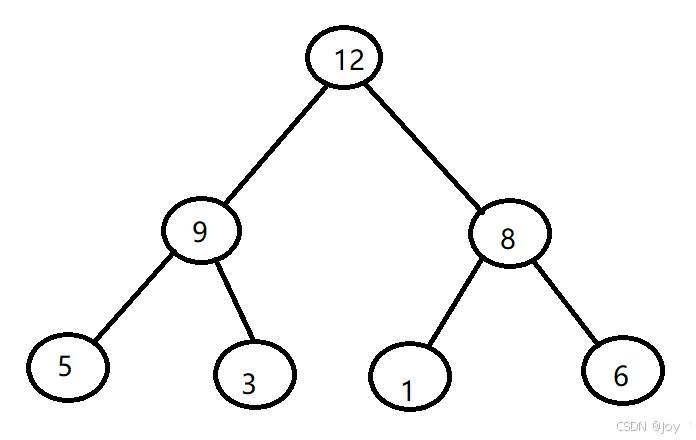
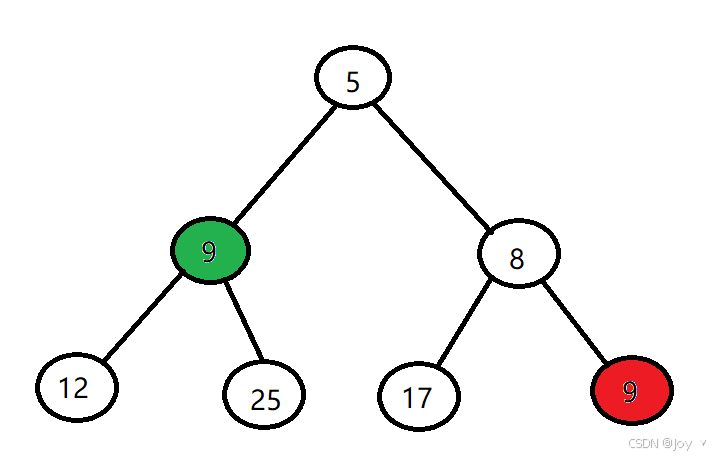
有大根堆就有小根堆:
我们可以看到红9在绿9的下一层,大小堆中我们需要注意,【只有根节点对子节点的大小比较】,没有子节点之间的比较。
一、手写函数
def siftup(heap, pos): endpos = len(heap) startpos = pos newitem = heap[pos] # Bubble up the smaller child until hitting a leaf. childpos = 2*pos + 1 # leftmost child position while childpos < endpos: # Set childpos to index of smaller child. rightpos = childpos + 1 if rightpos < endpos and not heap[childpos] < heap[rightpos]: childpos = rightpos # Move the smaller child up. heap[pos] = heap[childpos] pos = childpos childpos = 2*pos + 1 # The leaf at pos is empty now. Put newitem there, and bubble it up # to its final resting place (by sifting its parents down). heap[pos] = newitem '''up操作只是将孩子提上去,但是没有保证根节点比孩子小,现在比较孩子和父节点, 如果父节点更大,往下覆盖孩子节点,并且往上继续,比较上面的父节点,直至到头start, 将原来的子节点的值覆盖在此时的父节点上。''' siftdown(heap, startpos, pos) '''up与down一起维持小根堆性质''' def siftdown(heap, startpos, pos): newitem = heap[pos] # Follow the path to the root, moving parents down until finding a place # newitem fits. while pos > startpos: parentpos = (pos - 1) >> 1 parent = heap[parentpos] if newitem < parent: heap[pos] = parent pos = parentpos continue break heap[pos] = newitem def heappop(heap): """Pop the smallest item off the heap, maintaining the heap invariant.""" lastelt = heap.pop() # raises appropriate IndexError if heap is empty print('pop:', lastelt) if heap: returnitem = heap[0] heap[0] = lastelt siftup(heap, 0) print('heap:', heap) print('returnitem', returnitem) return returnitem return lastelt def heapify(x): """Transform list into a heap, in-place, in O(len(x)) time.""" n = len(x) for i in reversed(range(n//2)): '''从最后一个根节点开始,将孩子节点最小的覆盖根节点, 并不断往下找,将较小的孩子提上来。直到没有孩子,将根节点的值覆盖到此时的孩子节点上''' siftup(x, i) def heap_sort(arr): # 将数组转换为小根堆 heapify(arr) print(arr) # 弹出堆顶元素直到堆为空 '''每次pop最后一个节点,并输出根节点。 将最后一个节点覆盖在根节点上,并且进行up——down操作位置小根堆性质''' return [heappop(arr) for _ in range(len(arr))] if __name__ == '__main__': # 示例数组 arr = [3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9, 2, 6, 5, 3, 5] # 执行堆排序 sorted_arr = heap_sort(arr) # 打印排序后的数组 print('sorted_arr', sorted_arr)二、调用python接口
import heapq def heap_sort(arr): # 将数组转换为小根堆 heapq.heapify(arr) print(arr) # 弹出堆顶元素直到堆为空 '''每次pop最后一个节点,并输出根节点。 将最后一个节点覆盖在根节点上,并且进行up——down操作位置小根堆性质''' return [heapq.heappop(arr) for _ in range(len(arr))] if __name__ == '__main__': # 示例数组 arr = [3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9, 2, 6, 5, 3, 5] # 执行堆排序 sorted_arr = heap_sort(arr) # 打印排序后的数组 print('sorted_arr', sorted_arr)输出:
[1, 1, 2, 3, 3, 9, 4, 6, 5, 5, 5]
sorted_arr [1, 1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5, 5, 5, 6, 9]
三、时间复杂度
siftup(heap, pos)函数:
- 这个函数将一个元素上浮到它应该在的位置。在最坏的情况下,它可能需要上浮到堆的根节点,时间复杂度是 O(log n),其中 n 是堆中元素的数量。
siftdown(heap, startpos, pos)函数:
- 这个函数将一个元素下沉到它应该在的位置。同样,在最坏的情况下,它可能需要下沉到叶子节点,时间复杂度也是 O(log n)。
heappop(heap)函数:
- 这个函数移除并返回堆顶元素(最小元素),然后通过调用
siftup来修复堆。siftup的时间复杂度是 O(log n),所以heappop的时间复杂度也是 O(log n)。
heapify(x)函数:
- 这个函数将一个数组转换成一个堆。它从最后一个父节点开始,向上调用
siftup。由于堆的最后一个父节点的索引是 n/2 - 1(n 是数组的长度),所以它实际上调用了大约 n/2 次siftup。因此,heapify的时间复杂度是 O(n)。
heap_sort(arr)函数:
- 这个函数首先调用
heapify将数组转换成一个堆,然后通过 n 次调用heappop来移除所有元素。由于heapify的时间复杂度是 O(n),并且heappop的时间复杂度是 O(log n),heap_sort的总时间复杂度是 O(n log n)。总结:
- 时间复杂度:
siftup: O(log n)siftdown: O(log n)heappop: O(log n)heapify: O(n)heap_sort: O(n log n)整体上,对于堆排序算法的时间复杂度分析如下
构建堆(Heapify):
heapify函数将数组转换成一个堆。对于一个长度为 n 的数组,heapify的时间复杂度是 O(n)。这是通过从最后一个父节点开始,向上调用siftup实现的,每个siftup操作的时间复杂度是 O(log n),但由于堆的结构特性,实际上heapify的总体时间复杂度是线性的。堆排序(Heap Sort):在
heap_sort函数中,首先调用heapify将数组转换成一个堆,然后通过 n 次调用heappop来移除所有元素。每次heappop操作的时间复杂度是 O(log n)。因此,n 次heappop的总时间复杂度是 O(n log n)。综合以上两点,堆排序的整体时间复杂度是 O(n + n log n),简化后为 O(n log n)。这是因为在堆排序过程中,构建堆是一次性的,而移除元素需要 n 次操作,每次操作的复杂度是 log n。
- 空间复杂度:O(1),因为所有操作都是原地进行的。
