概述
- Spring AOP 是基于动态代理来实现AOP的, 此处主要介绍代理模式和Spring AOP的源码剖析
一.代理模式
代理模式是一种常用的设计模式,它允许为其他对象提供代理,以控制对这个对象的访问。这种结构在不改变原始类的基础上,通过引入代理类来扩展功能,广泛应用于各种编程场景和框架中。
使用代理前:
使用代理后:
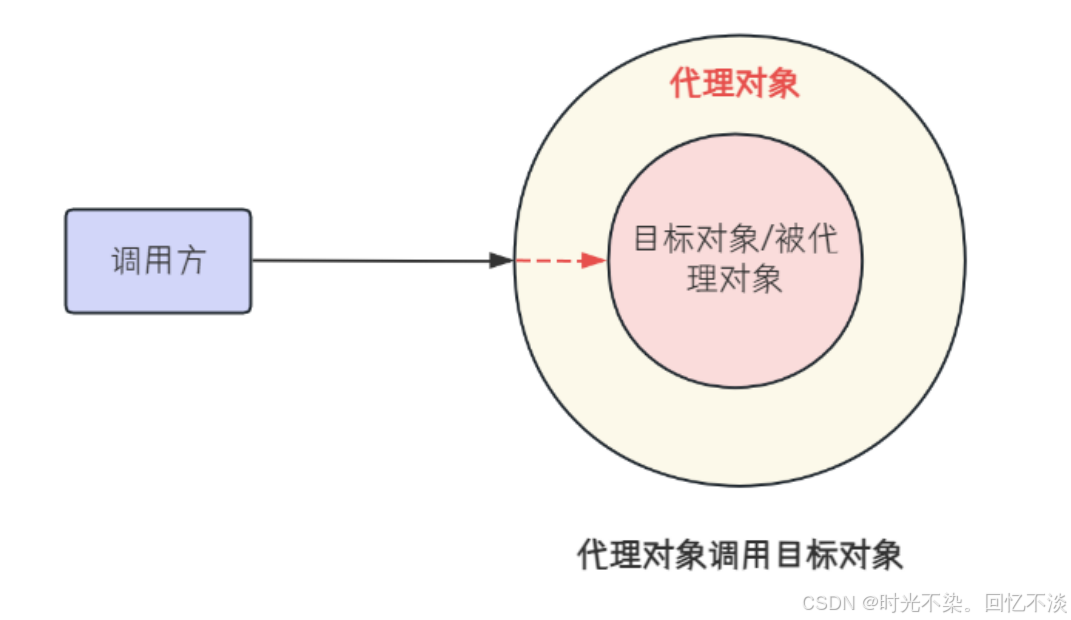
在生活当中也有很多代理模式的例子:
- 艺人经纪人: 广告商找艺人拍广告, 需要经过经纪人,由经纪人来和艺人进行沟通.
- 房屋中介: 房屋进行租赁时, 卖方会把房屋授权给中介, 由中介来代理看房, 房屋咨询等服务.
- 经销商: 厂商不直接对外销售产品, 由经销商负责代理销售.
- 秘书/助理: 合作伙伴找老板谈合作, 需要先经过秘书/助理预约.
代理模式的主要角色
- Subject: 业务接口类. 可以是抽象类或者接口(不⼀定有)
- RealSubject: 业务实现类. 具体的业务执行, 也就是被代理对象.
- Proxy: 代理类. RealSubject的代理.
比如房屋租赁
Subject 就是提前定义了房东做的事情, 交给中介代理, 也是中介要做的事情
RealSubject: 房东
Proxy: 中介根据代理的创建时期, 代理模式分为静态代理和动态代理.
- 静态代理: 由程序员创建代理类或特定工具自动生成源代码再对其编译, 在程序运行前代理类的.class 文件就已经存在了.
- 动态代理: 在程序运行时, 运用反射机制动态创建而成
- 更形象的描述就是就是好比你去买房, 静态代理没买房前就已经分配好销售了(可以是根据一些因素进行划分), 动态代理就是买房的时候随机给你发分配销售
二. 静态代理
- 静态代理是指在程序运行前就已经存在代理类的字节码文件,由程序员手动编写或特定工具自动生成源代码实现的代理方式。
代码实现
我们通过代码来加深对静态代理的理解. 以房租租赁为例:
- 定义接口(定义房东要做的事情, 也是中介需要做的事情)
public interface houseSubject { void rentHouse(); void saleHouse(); } - 实现接口(房东出租房子)
public class RealHouseSubject implements houseSubject{ @Override public void rentHouse() { System.out.println("我是房东,我出租房子"); } @Override public void saleHouse() { System.out.println("我是房东,我出售房子"); } } - 代理(中介, 帮房东出租房子)
public class HouseProxy implements houseSubject{ private RealHouseSubject target; public HouseProxy(RealHouseSubject realHouseSubject) { this.target = realHouseSubject; } @Override public void rentHouse() { //出租前 System.out.println("我是中介,我开始代理"); //出租房子 target.rentHouse(); //出租后 System.out.println("我是中介,结束代理"); } @Override public void saleHouse() { //出售前 System.out.println("我是中介,我开始代理"); //出售房子 target.saleHouse(); //出售后 System.out.println("我是中介,结束代理"); } } - 使用静态代理
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建代理类 HouseProxy houseProxy = new HouseProxy(new RealHouseSubject()); //通过代理类访问目标方法 houseProxy.rentHouse(); } } - 运行结果:

上面这个代理实现方式就是静态代理(仿佛啥也没干). 从上述程序可以看出, 虽然静态代理也完成了对目标对象的代理, 但是由于代码都写死了, 对目标对象的每个方法的增强都是手动完成的,非常不灵活. 所以日常开发几乎看不到静态代理的场景
接下来新增需求: 中介又新增了其他业务, 我们修改接口(Subject)和业务实现类(RealSubject)时, 还需要修改代理类(Proxy). 同样的, 如果有新增接口(Subject)和业务实现类(RealSubject), 也需要对每一个业务实现类新增代理类(Proxy).
三.动态代理.
动态代理是指我们不需要针对每个目标对象都单独创建一个代理对象, 而是把这个创建代理对象的工作推迟到程序运行时由JVM来实现. 也就是说动态代理在程序运行时, 根据需要动态创建生成.
在Java中实现动态代理的方式主要有两种,一种是JDK动态代理,一种是CGLib. 接下来就主要介绍这两种方式.
3.1 JDK动态代理.
- JDK动态代理的实现步骤:
- 定义一个接口及其实现类(静态代理中的 HouseSubject 和 RealHouseSubject )
- 自定义 InvocationHandler 并重写 invoke 方法,在 invoke 方法中我们会调用目标方法(被代理类的方法)并自定义一些处理逻辑.
- 通过 Proxy.newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,Class<?>[]
interfaces,InvocationHandler h) 方法创建代理对象
- 通过 Proxy.newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,Class<?>[]
JDK动态代理的代码实现
1. 实现 InvocationHandler 接口
public class JDKInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler { private Object target; //目标对象 public JDKInvocationHandler(Object target) { this.target = target; } @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { System.out.println("我是代理,开始代理"); //通过反射调用目标函数 Object result = method.invoke(target, args); System.out.println("我是代理,结束代理"); return result; } } 2. 创建一个代理对象并使用
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { /** *public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader, * Class<?>[] interfaces, * InvocationHandler h) { * 加载代理类的classloader * 要实现的接口, * 代理要做的事情,InvocationHandler这个接口 */ //真实的目标对象 RealHouseSubject targer = new RealHouseSubject(); //动态生成代理对象 houseSubject proxy = (houseSubject)Proxy.newProxyInstance(targer.getClass().getClassLoader(), new Class[]{houseSubject.class}, new JDKInvocationHandler(targer)); proxy.rentHouse(); proxy.saleHouse(); JDK动态代理过程中涉及方法的参数讲解
- InvocationHandler接口
InvocationHandler 接口是Java动态代理的关键接口之一, 它定义了一个单一方法 invoke() , 用于处理被代理对象的方法调用.
public interface InvocationHandler { /** * 参数说明 * proxy:代理对象 * method:代理对象需要实现的⽅法,即其中需要重写的⽅法 * args:method所对应⽅法的参数 */ public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable; } 通过实现 InvocationHandler 接口, 可以对被代理对象的方法进行功能增强.
- Proxy
Proxy 类中使用频率最高的方法是: newProxyInstance() , 这个方法主要用来生成一个代理对象.
public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader, Class<?>[] interfaces, InvocationHandler h) throws IllegalArgumentException{ //...代码省略 } - 这个方法一共有 3 个参数:
- Loader: 类加载器, 用于加载代理对象.
- interfaces : 被代理类实现的一些接口(这个参数的定义, 也决定了JDK动态代理只能代理实现了接口的一些类)
- h : 实现了 InvocationHandler 接口的对象.
3.2 CGLib动态代理
- CGLib动态代理的实现步骤:
- 定义一个类(被代理类).
- 自定义 MethodInterceptor 并重写 intercept 方法, intercept 用于增强目标
方法,和 JDK 动态代理中的 invoke 方法类似. - 通过 Enhancer 类的 create()创建代理类.
CGLib动态代理的代码实现
1. 自定义 MethodInterceptor(方法拦截器)实现MethodInterceptor接口.
public class CGLibMethodInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor { private Object target; public CGLibMethodInterceptor(Object target) { this.target = target; } /** * 调用代理对象的方法 */ @Override public Object intercept(Object obj, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy proxy) throws Throwable { System.out.println("我是中介开始代理~~"); Object result = method.invoke(target, args); //proxy.invokeSuper(obj, args); System.out.println("我是中介,结束代理~~"); return result; } } 2.创建代理类, 并使用
- 目标对象,用来代理接口
// 目标对象 代理接口 HouseSubject targer = new RealHouseSubject(); houseSubject houseSubject = (houseSubject) Enhancer.create(targer.getClass(), new CGLibMethodInterceptor(targer)); houseSubject.rentHouse(); houseSubject.saleHouse(); - 目标对象,用来代理类.
HouseSubject targer = new RealHouseSubject(); //目标对象 代理类 RealHouseSubject realHouseSubject = (RealHouseSubject) Enhancer.create(targer.getClass(), new CGLibMethodInterceptor(targer)); realHouseSubject.rentHouse(); realHouseSubject.saleHouse(); CGLib动态代理过程中涉及方法的参数讲解.
- MethodInterceptor
MethodInterceptor 和 JDK动态代理中的 InvocationHandler 类似, 它只定义了一个方法 intercept() , 用于增强目标方法.
public interface MethodInterceptor extends Callback { /** * 参数说明: * o: 被代理的对象 * method: ⽬标⽅法(被拦截的⽅法, 也就是需要增强的⽅法) * objects: ⽅法⼊参 * methodProxy: ⽤于调⽤原始⽅法 */ Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable; } - Enhancer.create()
Enhancer.create() 用来生成一个代理对象
public static Object create(Class type, Callback callback) { //...代码省略 } - 参数说明:
- type: 被代理类的类型(类或接口)
- callback: 自定义方法拦截器 MethodInterceptor
四.Spring AOP源码剖析
- Spring AOP 主要基于两种方式实现的: JDK 及 CGLIB 的方式
- Spring 源码过于复杂, 此处只摘出一些主要内容, 以了解为主.
Spring对于AOP的实现,基本上都是靠 AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator 去完成. 生成代理对象的逻辑在父类 AbstractAutoProxyCreator 中
protected Object createProxy(Class<?> beanClass, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) { return buildProxy(beanClass, beanName, specificInterceptors, targetSource, false); } private Object buildProxy(Class<?> beanClass, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource, boolean classOnly) { if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory clbf) { AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass(clbf, beanName, beanClass); } //创建代理对象 ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory(); proxyFactory.copyFrom(this); /** * 检查proxyTargetClass属性值,spring默认为false * proxyTargetClass 检查接⼝是否对类代理, ⽽不是对接⼝代理 * 如果代理对象为类, 设置为true, 使⽤cglib代理 */ if (proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) { //是否有设置cglib代理 if (Proxy.isProxyClass(beanClass) || ClassUtils.isLambdaClass(beanClass)) { //设置proxyTargetClass为true,使⽤cglib代理 for (Class<?> ifc : beanClass.getInterfaces()) { proxyFactory.addInterface(ifc); } } } else { /** * 如果beanClass实现了接⼝,且接⼝⾄少有⼀个⾃定义⽅法,则使⽤JDK代理 * 否则CGLIB代理(设置ProxyTargetClass为true ) * 即使我们配置了proxyTargetClass=false, 经过这⾥的⼀些判断还是可能会将其 设为true */ if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) { proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true); } else { evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory); } } Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors); proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors); proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource); customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory); proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy); if (advisorsPreFiltered()) { proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true); } // Use original ClassLoader if bean class not locally loaded in overriding class loader ClassLoader classLoader = getProxyClassLoader(); if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader smartClassLoader && classLoader != beanClass.getClassLoader()) { classLoader = smartClassLoader.getOriginalClassLoader(); } return (classOnly ? proxyFactory.getProxyClass(classLoader) : proxyFactory.getProxy(classLoader)); } - 代理工厂有一个重要的属性: proxyTargetClass, 默认值为false. 也可以通过程序设置
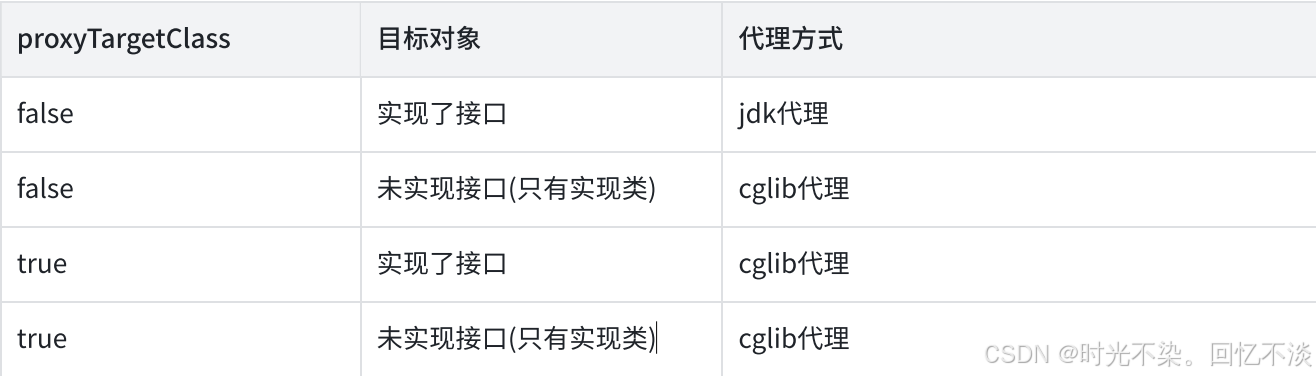
- 可以通过 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true) 来设置
注意:
Spring Boot 2.X开始, 默认使用CGLIB代理. 可以通过配置项 spring.aop.proxy-target-class=false 来进行修改,设置默认为jdk代理. SpringBoot设置 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy 无效, 因为Spring Boot 默认使用AopAutoConfiguration进行装配
@SpringBootApplication public class DemoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args); /** * HouseProxy houseProxy = context.getBean(HouseProxy.class); * 设置spring.aop.proxy-target-class=true cglib代理, 运⾏成功 * 设置spring.aop.proxy-target-class=false jdk代理, 运⾏失败, 不能代理类 * 因为 HouseProxy 是⼀个类, ⽽不是接⼝, 需要修改为 * HouseSubject houseProxy = (HouseSubject) context.getBean("realHouseSubject") * */ HouseProxy houseProxy = context.getBean(HouseProxy.class); //HouseSubject houseProxy = (HouseSubject) context.getBean("realHouseSubject");//正确运⾏ System.out.println(houseProxy.getClass().toString()); } } 使用context.getBean() 需要添加注解,使HouseProxy,RealHouseSubject被Spring管理测试AOP代理, 需要把这些类交给AOP管理(自定义注解或使用@Aspect)
我看点进去看代理工厂的代码
public class ProxyFactory extends ProxyCreatorSupport { //...代码省略 //获取代理 public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { //分两步 先createAopProxy,后getProxy return createAopProxy().getProxy(classLoader); } protected final synchronized AopProxy createAopProxy() { if (!this.active) { activate(); } return getAopProxyFactory().createAopProxy(this); } //...代码省略 } createAopProxy的实现在 DefaultAopProxyFactory中
public class DefaultAopProxyFactory implements AopProxyFactory, Serializable { //...代码省略 @Override public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException { /** * 根据proxyTargetClass判断 * 如果⽬标类是接⼝, 使⽤JDK动态代理 * 否则使⽤cglib动态代理 */ if (!NativeDetector.inNativeImage() && (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config))) { Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass(); if (targetClass == null) { throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " + "Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation."); } if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass) || ClassUtils.isLambdaClass(targetClass)) { return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config); } return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config); } else { return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config); } } //...代码省略 } 接下来就是创建代理了
JDK动态代理
final class JdkDynamicAopProxy implements AopProxy, InvocationHandler, Serializable { //...代码省略 @Override public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Creating JDK dynamic proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource()); } return Proxy.newProxyInstance(determineClassLoader(classLoader), this.proxiedInterfaces, this); } //...代码省略 } CGLIB动态代理
class CglibAopProxy implements AopProxy, Serializable { //...代码省略 @Override public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { //...代码省略 // Configure CGLIB Enhancer... Enhancer enhancer = createEnhancer(); // Generate the proxy class and create a proxy instance. return createProxyClassAndInstance(enhancer, callbacks); } //...代码省略 } 五.总结
- 什么是AOP?
- Spring AOP的实现方式有哪些?
- 基于注解
- 基于XML
- 基于代理
- Spring AOP的实现原理.?
- Spring 使用哪种代理方式?
- JDK和CGLib的区别?
